|
Hermann Aron
Hermann Aron (; 1 October 1845 – 29 August 1913) was a German researcher of electrical engineering. Background Aron was born in Kempen (Kępno), in modern-day Poland, at the time a shtetl in the Province of Posen. His father was a chazzan and merchant. The family wanted him to train as a Jewish scholar or scrivener, however wealthy relatives made it possible for him to attend from 1862 the high school at Kölln, Berlin and after graduating in 1867, to study at the University of Berlin. Aron began by studying medicine, but changed in the 3rd term to mathematics and natural sciences. From 1870 he studied at the University of Heidelberg, with such notable physics lecturers as Helmholtz and Kirchhoff. He obtained his doctorate from Berlin in 1873 and became an assistant at the physical laboratory of the trade academy (Gewerbeakademie). He taught at the University of Berlin where he became professor of physics, and at the Prussian Army's school for artillery and engineers. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
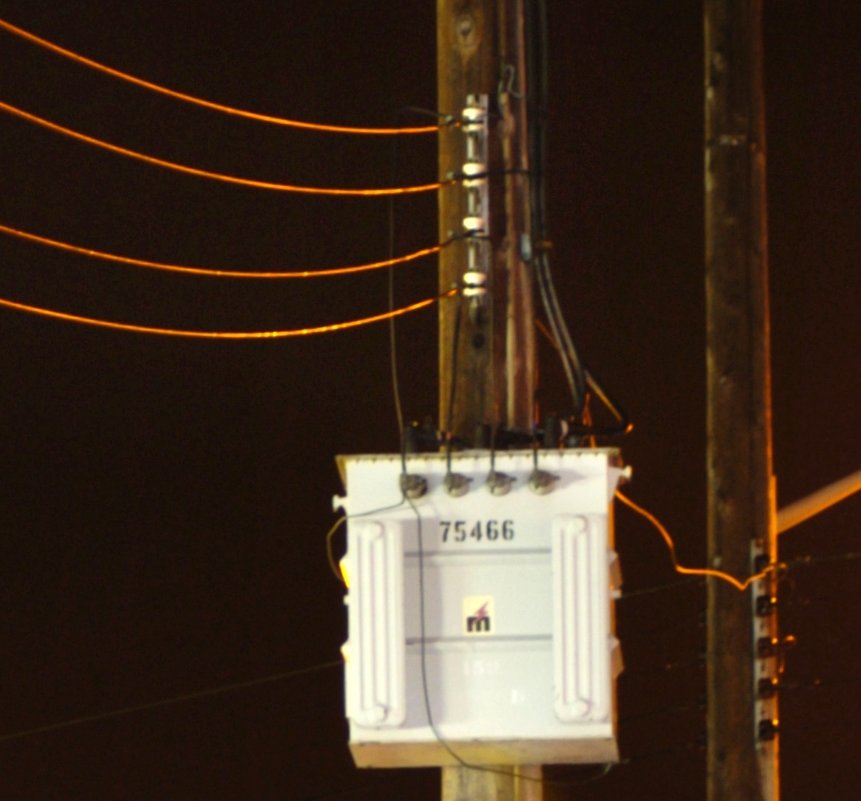
Electricity Meter
North American domestic analog electricity meter. Electricity meter with transparent plastic case (Israel) North American domestic electronic electricity meter An electricity meter, electric meter, electrical meter, energy meter, or kilowatt-hour meter is a device that measures the amount of electric energy consumed by a residence, a business, or an electrically powered device. Electric meter or energy meter measures the total power consumed over a time interval. Electric utilities use electric meters installed at customers' premises for billing and monitoring purposes. They are typically calibrated in billing units, the most common one being the kilowatt hour (''kWh''). They are usually read once each billing period. When energy savings during certain periods are desired, some meters may measure demand, the maximum use of power in some interval. "Time of day" metering allows electric rates to be changed during a day, to record usage during peak high-cost periods and of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split into two main subregions, Lower Silesia in the west and Upper Silesia in the east. Silesia has a diverse culture, including architecture, costumes, cuisine, traditions, and the Silesian language (minority in Upper Silesia). Silesia is along the Oder River, with the Sudeten Mountains extending across the southern border. The region contains many historical landmarks and UNESCO World Heritage Sites. It is also rich in mineral and natural resources, and includes several important industrial areas. The largest city and Lower Silesia's capital is Wrocław; the historic capital of Upper Silesia is Opole. The biggest metropolitan area is the Upper Silesian metropolitan area, the centre of which is Katowice. Parts of the Czech city of Ostrav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternating Current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current which periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time in contrast to direct current (DC) which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences, and it is the form of electrical energy that consumers typically use when they plug kitchen appliances, televisions, fans and electric lamps into a wall socket. A common source of DC power is a battery cell in a flashlight. The abbreviations ''AC'' and ''DC'' are often used to mean simply ''alternating'' and ''direct'', as when they modify ''current'' or ''voltage''. The usual waveform of alternating current in most electric power circuits is a sine wave, whose positive half-period corresponds with positive direction of the current and vice versa. In certain applications, like guitar amplifiers, different waveforms are used, such as triangular waves or square waves. Audio a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three-phase
Three-phase electric power (abbreviated 3φ) is a common type of alternating current used in electricity generation, Electric power transmission, transmission, and Electric power distribution, distribution. It is a type of polyphase system employing three wires (or four including an optional neutral return wire) and is the most common method used by electrical grids worldwide to transfer power. Three-phase electrical power was developed in the 1880s by multiple people. Three-phase power works by the voltage and currents being 120 degrees phase shift, out of phase on the three wires. As an AC system it allows the voltages to be easily stepped up using transformers to high voltage for transmission, and back down for distribution, giving high efficiency. A three-wire three-phase circuit is usually more economical than an equivalent two-wire Single-phase electric power, single-phase circuit at the same line to ground voltage because it uses less conductor material to transmit a giv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eponymous
An eponym is a person, a place, or a thing after whom or which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. The adjectives which are derived from the word eponym include ''eponymous'' and ''eponymic''. Usage of the word The term ''eponym'' functions in multiple related ways, all based on an explicit relationship between two named things. A person, place, or thing named after a particular person share an eponymous relationship. In this way, Elizabeth I of England is the eponym of the Elizabethan era. When Henry Ford is referred to as "the ''eponymous'' founder of the Ford Motor Company", his surname "Ford" serves as the eponym. The term also refers to the title character of a fictional work (such as Rocky Balboa of the ''Rocky'' film series), as well as to ''self-titled'' works named after their creators (such as the album ''The Doors'' by the band the Doors). Walt Disney created the eponymous Walt Disney Company, with his name similarly extended to theme parks such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wattmeter
The wattmeter is an instrument for measuring the electric active power (or the average of the rate of flow of electrical energy) in watts of any given circuit. Electromagnetic wattmeters are used for measurement of utility frequency and audio frequency power; other types are required for radio frequency measurements. A wattmeter reads the average value of the product ''v(t)i(t) = p(t)'', where ''v(t)'' is the voltage with positive reference polarity at the ± terminal with respect to the other terminal of the potential coil, and ''i(t)'' is the current with reference direction flowing into the ± terminal of the current coil. The wattmeter reads ''P = (1/T) ∫0T v(t)i(t) dt'', which in sinusoidal steady-state reduces to ''V''rms ''I''rms cos(φ), where ''T'' is the period of ''p(t)'' and φ is the angle by which the current lags the voltage. History On 14 August 1888, Oliver B. Shallenberge patented a watt-hour meter. The Hungarian Ottó Bláthy patented his AC wattmeter. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Electric Company Plc
The General Electric Company (GEC) was a major British industrial conglomerate involved in consumer and defence electronics, communications, and engineering. The company was founded in 1886, was Britain's largest private employer with over 250,000 employees in the 1980s, and at its peak in the 1990s, made profits of over £1 billion a year. In June 1998, GEC sold its share of the joint venture GEC-Alsthom on the Paris stock exchange. In December 1999, GEC's defence arm, Marconi Electronic Systems, was sold to British Aerospace, forming BAE Systems. The rest of GEC, mainly telecommunications equipment manufacturing, continued as Marconi Communications. After buying several US telecoms manufacturers at the top of the market, losses following the bursting of the dot-com bubble in 2001 led to the restructuring in 2003 of Marconi plc into Marconi Corporation plc. In 2005, Ericsson acquired the bulk of that company. What was left of the business was renamed Telent. History E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugo Hirst
Hugo Hirst, 1st Baron Hirst (26 November 1863 – 22 January 1943), known as Sir Hugo Hirst, Bt, between 1925 and 1934, was a German-born British industrialist. Born near Munich, Hugo Hirsch became a naturalized British subject in 1883 and changed his surname to Hirst. He was co-founder with Gustav Binswanger of the General Electric Company plc, and in 1910 became its chairman. He was created a baronet, of Witton in the County of Warwick, on 2 July 1925 and elevated to the peerage as Baron Hirst, of Witton in the County of Warwick, on 28 June 1934. Hirst's eldest daughter Muriel married Leslie Gamage, the elder son of Arthur Walter Gamage, the founder of Gamages Gamages was a department store in Holborn, London. Trading between 1878 and 1972, it was particularly well known for its toy and hardware departments. History Gamages began life in 1878 in a rented watch repair shop and, after quickly becoming ... department store. Leslie joined GEC and became chairman and managin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-winding Clock
An automatic watch, also known as a self-winding watch or simply an automatic, is a mechanical watch where the natural motion of the wearer provides energy to wind the mainspring, making manual winding unnecessary if worn enough. It is distinguished from a ''manual watch'' in that a manual watch must have its mainspring wound by hand at regular intervals. Operation In a mechanical watch the watch's gears are turned by a spiral spring called a mainspring. In a ''manual watch'' energy is stored in the mainspring by turning a knob, the ''crown'' on the side of the watch. Then the energy from the mainspring powers the watch movement until it runs down, requiring the spring to be wound again. A self-winding watch movement has a mechanism which winds the mainspring using the natural motions of the wearer's body. The watch contains an oscillating weight that turns on a pivot. The normal movements of the watch in the user's pocket (for a pocketwatch) or on the user's arm (for a wristwat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



.jpg)