|
Herman Ring
In the mathematical discipline known as complex dynamics, the Herman ring is a Fatou componentJohn Milnor''Dynamics in one complex variable'' Third Edition, Annals of Mathematics Studies, 160, Princeton Univ. Press, Princeton, NJ, 2006. where the rational function is conformally conjugate to an irrational rotation of the standard annulus. Formal definition Namely if ''ƒ'' possesses a Herman ring ''U'' with period ''p'', then there exists a conformal mapping :\phi:U\rightarrow\ and an irrational number \theta, such that :\phi\circ f^\circ\phi^(\zeta)=e^\zeta. So the dynamics on the Herman ring is simple. Name It was introduced by, and later named after, Michael Herman (1979) who first found and constructed this type of Fatou component. Function * Polynomials do not have Herman rings. * Rational functions can have Herman rings. According to the result of Shishikura, if a rational function ''ƒ'' possesses a Herman ring, then the degree of ''ƒ'' is at least ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herman Standard
Herman may refer to: People * Herman (name), list of people with this name * Saint Herman (other) * Peter Noone (born 1947), known by the mononym Herman Places in the United States * Herman, Arkansas * Herman, Michigan * Herman, Minnesota * Herman, Nebraska * Herman, Pennsylvania * Herman, Dodge County, Wisconsin * Herman, Shawano County, Wisconsin * Herman, Sheboygan County, Wisconsin Place in India * Herman (Village) Other uses * ''Herman'' (comic strip) * ''Herman'' (film), a 1990 Norwegian film * Herman the Bull, a bull used for genetic experiments in the controversial lactoferrin project of GenePharming, Netherlands * Herman the Clown ( fi, Pelle Hermanni), a Finnish TV clown from children's TV show performed by Veijo Pasanen * Herman's Hermits, a British pop combo * Herman cake (also called Hermann), a type of sourdough bread starter or Amish Friendship Bread starter * ''Herman'' (album) by 't Hof Van Commerce See also * Hermann (other) * Arman (na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herman Period=2
Herman may refer to: People * Herman (name), list of people with this name * Saint Herman (other) * Peter Noone (born 1947), known by the mononym Herman Places in the United States * Herman, Arkansas * Herman, Michigan * Herman, Minnesota * Herman, Nebraska * Herman, Pennsylvania * Herman, Dodge County, Wisconsin * Herman, Shawano County, Wisconsin * Herman, Sheboygan County, Wisconsin Place in India * Herman (Village) Other uses * ''Herman'' (comic strip) * ''Herman'' (film), a 1990 Norwegian film * Herman the Bull, a bull used for genetic experiments in the controversial lactoferrin project of GenePharming, Netherlands * Herman the Clown ( fi, Pelle Hermanni), a Finnish TV clown from children's TV show performed by Veijo Pasanen * Herman's Hermits, a British pop combo * Herman cake (also called Hermann), a type of sourdough bread starter or Amish Friendship Bread starter * ''Herman'' (album) by 't Hof Van Commerce See also * Hermann (other) * Arman (na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractals
In mathematics, a fractal is a geometric shape containing detailed structure at arbitrarily small scales, usually having a fractal dimension strictly exceeding the topological dimension. Many fractals appear similar at various scales, as illustrated in successive magnifications of the Mandelbrot set. This exhibition of similar patterns at increasingly smaller scales is called self-similarity, also known as expanding symmetry or unfolding symmetry; if this replication is exactly the same at every scale, as in the Menger sponge, the shape is called Affine geometry, affine self-similar. Fractal geometry lies within the mathematical branch of measure theory. One way that fractals are different from finite geometric figures is how they Scaling (geometry), scale. Doubling the edge lengths of a filled polygon multiplies its area by four, which is two (the ratio of the new to the old side length) raised to the power of two (the conventional dimension of the filled polygon). Likewise, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douady Rabbit
The Douady rabbit is any of various particular filled Julia sets associated with the parameter near the center period 3 buds of Mandelbrot set for complex quadratic map. It is named after French mathematician Adrien Douady. Formula The rabbit is generated by iterating the Mandelbrot set map z=z^2+c on the complex plane with c fixed to lie in the period three bulb off the main cardiod and z ranging over the plane. The pixels in the image are then colored to show whether for a particular value of z the iteration converged or diverged Variants Twisted rabbit or rabbits with twisted ears = is the composition of the “rabbit” polynomial with n-th powers of the Dehn twists about its ears. Corabbit is symmetrical image of rabbit. Here parameter c \approx -0.1226 -0.7449i It is one of 2 other polynomials inducing the same permutation of their post-critical set are the rabbit. 3D The julia set has no direct analog in 3D 4D Quaternion julia set with parameters c = −0,123 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siegel Disc
Siegel disc is a connected component in the Fatou set where the dynamics is analytically conjugate to an irrational rotation. Description Given a holomorphic endomorphism f:S\to S on a Riemann surface S we consider the dynamical system generated by the iterates of f denoted by f^n=f\circ\stackrel\circ f. We then call the orbit \mathcal^+(z_0) of z_0 as the set of forward iterates of z_0. We are interested in the asymptotic behavior of the orbits in S (which will usually be \mathbb, the complex plane or \mathbb=\mathbb\cup\, the Riemann sphere), and we call S the phase plane or ''dynamical plane''. One possible asymptotic behavior for a point z_0 is to be a fixed point, or in general a ''periodic point''. In this last case f^p(z_0)=z_0 where p is the period and p=1 means z_0 is a fixed point. We can then define the ''multiplier'' of the orbit as \rho=(f^p)'(z_0) and this enables us to classify periodic orbits as ''attracting'' if , \rho, 1 and indifferent if \rho=1. Indifferent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Critical Point (mathematics)
Critical point is a wide term used in many branches of mathematics. When dealing with functions of a real variable, a critical point is a point in the domain of the function where the function is either not differentiable or the derivative is equal to zero. When dealing with complex variables, a critical point is, similarly, a point in the function's domain where it is either not holomorphic or the derivative is equal to zero. Likewise, for a function of several real variables, a critical point is a value in its domain where the gradient is undefined or is equal to zero. The value of the function at a critical point is a critical value. This sort of definition extends to differentiable maps between and a critical point being, in this case, a point where the rank of the Jacobian matrix is not maximal. It extends further to differentiable maps between differentiable manifolds, as the points where the rank of the Jacobian matrix decreases. In this case, critical points are al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
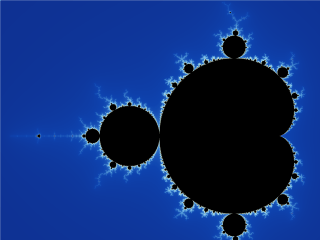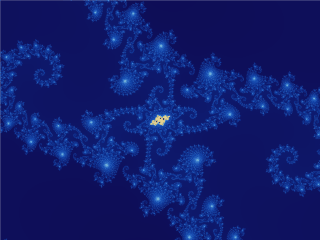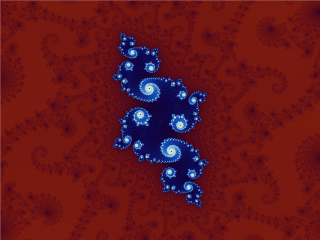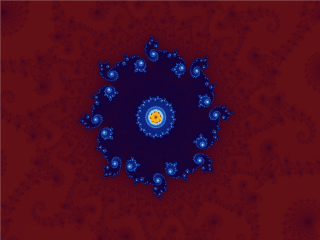
Mandelbrot Set
The Mandelbrot set () is the set of complex numbers c for which the function f_c(z)=z^2+c does not diverge to infinity when iterated from z=0, i.e., for which the sequence f_c(0), f_c(f_c(0)), etc., remains bounded in absolute value. This set was first defined and drawn by Robert W. Brooks and Peter Matelski in 1978, as part of a study of Kleinian groups. Afterwards, in 1980, Benoit Mandelbrot obtained high-quality visualizations of the set while working at IBM's Thomas J. Watson Research Center in Yorktown Heights, New York. Images of the Mandelbrot set exhibit an elaborate and infinitely complicated boundary that reveals progressively ever-finer recursive detail at increasing magnifications; mathematically, one would say that the boundary of the Mandelbrot set is a ''fractal curve''. The "style" of this recursive detail depends on the region of the set boundary being examined. Mandelbrot set images may be created by sampling the complex numbers and testing, for each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trial And Error
Trial and error is a fundamental method of problem-solving characterized by repeated, varied attempts which are continued until success, or until the practicer stops trying. According to W.H. Thorpe, the term was devised by C. Lloyd Morgan (1852–1936) after trying out similar phrases "trial and failure" and "trial and practice". Under Morgan's Canon, animal behaviour should be explained in the simplest possible way. Where behavior seems to imply higher mental processes, it might be explained by trial-and-error learning. An example is a skillful way in which his terrier Tony opened the garden gate, easily misunderstood as an insightful act by someone seeing the final behavior. Lloyd Morgan, however, had watched and recorded the series of approximations by which the dog had gradually learned the response, and could demonstrate that no insight was required to explain it. Edward Lee Thorndike was the initiator of the theory of trial and error learning based on the findings he sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siegel Disk
Siegel disc is a connected component in the Fatou set where the dynamics is analytically conjugate to an irrational rotation. Description Given a holomorphic endomorphism f:S\to S on a Riemann surface S we consider the dynamical system generated by the iterates of f denoted by f^n=f\circ\stackrel\circ f. We then call the orbit \mathcal^+(z_0) of z_0 as the set of forward iterates of z_0. We are interested in the asymptotic behavior of the orbits in S (which will usually be \mathbb, the complex plane or \mathbb=\mathbb\cup\, the Riemann sphere), and we call S the phase plane or ''dynamical plane''. One possible asymptotic behavior for a point z_0 is to be a fixed point, or in general a ''periodic point''. In this last case f^p(z_0)=z_0 where p is the period and p=1 means z_0 is a fixed point. We can then define the ''multiplier'' of the orbit as \rho=(f^p)'(z_0) and this enables us to classify periodic orbits as ''attracting'' if , \rho, 1 and indifferent if \rho=1. Indifferent p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitsuhiro Shishikura
is a Japanese mathematician working in the field of complex dynamics. He is professor at Kyoto University in Japan. Shishikura became internationally recognized for two of his earliest contributions, both of which solved long-standing open problems. * In his Master's thesis, he proved a conjectured of Fatou from 1920 by showing that a rational function of degree d\, has at most 2d-2\, nonrepelling periodic cycles. * He proved that the boundary of the Mandelbrot set has Hausdorff dimension two, confirming a conjecture stated by Mandelbrot and Milnor. For his results, he was awarded the Salem Prize in 1992, and the Iyanaga Spring Prize of the Mathematical Society of Japan in 1995. More recent results of Shishikura include * ''(in joint work with Kisaka)'' the existence of a transcendental entire function with a doubly connected wandering domain, answering a question of Baker from 1985; * ''(in joint work with Inou)'' a study of ''near-parabolic renormalization'' which is es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |