|
Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4 Alpha
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha (HNF4A) also known as NR2A1 (nuclear receptor subfamily 2, group A, member 1) is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the ''HNF4A'' gene. Function HNF-4α is a nuclear transcription factor that binds DNA as a homodimer. The encoded protein controls the expression of several genes, including hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha, a transcription factor which regulates the expression of several hepatic genes. This gene plays a role in development of the liver, kidney, and intestines. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. HNF4A is required for the PXR and CAR-mediated transcriptional activation of CYP3A4. Genetic mutations in the ''HNF4A'' gene can influence the activity of HNF4α's downstream proteins such as CYP2D6, ''in vitro'' and ''in vivo''. The alkaloid berberine upregulates the expression of HNF4A. This gene also plays a pivotal role in the expression and synthesis of SHBG, an important glyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Receptor
In the field of molecular biology, nuclear receptors are a class of proteins responsible for sensing steroids, thyroid hormones, vitamins, and certain other molecules. These receptors work with other proteins to regulate the expression of specific genes thereby controlling the development, homeostasis, and metabolism of the organism. Nuclear receptors bind directly to DNA regulating the expression of adjacent genes; hence these receptors are classified as transcription factors. The regulation of gene expression by nuclear receptors often occurs in the presence of a ligand—a molecule that affects the receptor's behavior. Ligand binding to a nuclear receptor results in a conformational change activating the receptor. The result is up- or down-regulation of gene expression. A unique property of nuclear receptors that differentiates them from other classes of receptors is their direct control of genomic DNA. Nuclear receptors play key roles in both embryonic development a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MODY 1
MODY 1 is a form of maturity onset diabetes of the young. MODY 1 is due to a loss-of-function mutation in the ''HNF4A'' (''MODY1'') gene on chromosome 12. This gene codes for hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha (HNF4-α) protein also known as transcription factor 14 (TCF14). HNF4α controls function of HNF1α (see MODY 3; ) and perhaps HNF1β ( MODY 5) as well. This transcription network plays a role in the early development of the pancreas, liver, and intestines. In the pancreas these genes influence expression of, among others, the genes for insulin, the principal glucose transporter (GLUT2), and several proteins involved in glucose and mitochondrial metabolism. Although pancreatic beta cells produce adequate insulin in infancy, the capacity for insulin production declines thereafter. Diabetes (persistent hyperglycemia) typically develops by early adult years, but may not appear until later decades. The degree of insulin deficiency is slowly progressive. Many patients with MODY 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatocyte Nuclear Factors
Hepatocyte nuclear factors (HNFs) are a group of phylogenetically unrelated transcription factors that regulate the transcription of a diverse group of genes into proteins. These proteins include blood clotting factors and in addition, enzymes and transporters involved with glucose, cholesterol, and fatty acid transport and metabolism. Function As the name suggests, hepatocyte nuclear factors are expressed predominantly in the liver. However HNFs are also expressed and play important roles in a number of other tissues so that the name ''hepatocyte nuclear factor'' is somewhat misleading. Nevertheless, the liver is the only tissue in which a significant number of different HNFs are expressed at the same time. In addition, there are a number of genes which contain multiple promoter and enhancer regions each regulated by a different HNF. Furthermore, efficient expression of these genes require synergistic activation by multiple HNFs. Hence hepatocyte nuclear factors functio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4
HNF4 (Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4) is a nuclear receptor protein mostly expressed in the liver, gut, kidney, and pancreatic beta cells that is critical for liver development. In humans, there are two isoforms of HNF4, HNF4α and HNF4γ, encoded by two separate genes and respectively. Ligands HNF4 was originally classified as an orphan receptor that exhibits constitutive transactivation activity apparently by being continuously bound to a variety of fatty acids. The existence of a ligand for HNF4 has been somewhat controversial, but linoleic acid (LA) has been identified as the endogenous ligand of native HNF4 expressed in mouse liver; the binding of LA to HNF4 is reversible. The ligand binding domain of HNF4, as with other nuclear receptors, adopts a canonical alpha helical sandwich fold and interacts with co-activator proteins. HNF4 binds to the consensus sequence AGGTCAaAGGTCA in order to activate transcription. Pathology Mutations in the ''HNF4A'' gene have been lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testicular Receptor 4
Testicular receptor 4 also known as NR2C2 (nuclear receptor subfamily 2, group C, member 2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NR2C2'' gene. The testicular receptor 4 is a member of the nuclear receptor family of transcription factors. Interactions Testicular receptor 4 has been shown to interact with * Androgen receptor, * Estrogen receptor alpha, and * Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha. See also * Testicular receptor The testicular receptor proteins are members of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular transcription factor In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the ra ... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * Intracellular receptors Transcription factors {{gene-3-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Heterodimer Partner
The small heterodimer partner (SHP) also known as NR0B2 (nuclear receptor subfamily 0, group B, member 2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NR0B2'' gene. SHP is a member of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular transcription factors. SHP is unusual for a nuclear receptor in that it lacks a DNA binding domain. Therefore, it is technically neither a transcription factor nor nuclear receptor but nevertheless it is still classified as such due to relatively high sequence homology with other nuclear receptor family members. Function The principal role of SHP appears to be repression of other nuclear receptors through association to produce a non-productive heterodimer. The protein has also been identified as a mediating factor in the metabolic circadian clock Research shows that it interacts with retinoid and thyroid hormone receptors, inhibiting their ligand-dependent transcriptional activation. In addition, interaction with estrogen receptors has been demo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MED14
Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 14 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MED14'' gene. The activation of gene transcription is a multistep process that is triggered by factors that recognize transcriptional enhancer sites in DNA. These factors work with co-activators to direct transcriptional initiation by the RNA polymerase II apparatus. The protein encoded by this gene is a subunit of the CRSP (cofactor required for SP1 activation) complex, which, along with TFIID, is required for efficient activation by SP1. This protein is also a component of other multisubunit complexes e.g. thyroid hormone receptor-(TR-) associated proteins which interact with TR and facilitate TR function on DNA templates in conjunction with initiation factors and cofactors. This protein contains a bipartite nuclear localization signal. This gene is known to escape chromosome X-inactivation. Interactions MED14 has been shown to interact with PPARGC1A, Estrogen receptor alpha, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MED1
Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 1 also known as DRIP205 or Trap220 is a subunit of the Mediator complex and is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MED1'' gene. MED1 functions as a nuclear receptor coactivator. Function The activation of gene transcription is a multistep process that is triggered by factors that recognize transcriptional enhancer sites in DNA. These factors work with co-activators to direct transcriptional initiation by the RNA polymerase II apparatus. The mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 1 protein is a subunit of the CRSP (cofactor required for SP1 activation) complex, which, along with TFIID, is required for efficient activation by SP1. This protein is also a component of other multisubunit complexes .g., thyroid hormone receptor-(TR-) associated proteins that interact with TR and facilitate TR function on DNA templates in conjunction with initiation factors and cofactors]. It also regulates p53-dependent ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
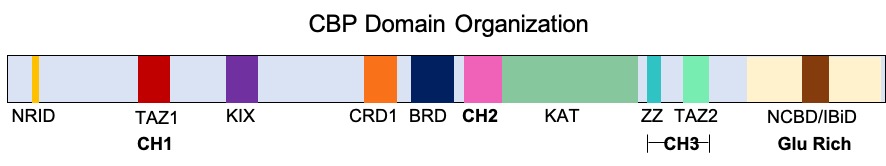
CREB Binding Protein
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate Response Element Binding protein Binding Protein (CREB-binding protein), also known as CREBBP or CBP or KAT3A, is a coactivator encoded by the ''CREBBP'' gene in humans, located on chromosome 16p13.3. CBP has intrinsic acetyltransferase functions; it is able to add acetyl groups to both transcription factors as well as histone lysines, the latter of which has been shown to alter chromatin structure making genes more accessible for transcription. This relatively unique acetyltransferase activity is also seen in another transcription enzyme, EP300 (p300). Together, they are known as the p300-CBP coactivator family and are known to associate with more than 16,000 genes in humans; however, while these proteins share many structural features, emerging evidence suggests that these two co-activators may promote transcription of genes with different biological functions. For example, CBP alone has been implicated in a wide variety of pathophysiologies includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-catenin
Catenin beta-1, also known as beta-catenin (β-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene. Beta-catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcription. In humans, the CTNNB1 protein is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene. In ''Drosophila'', the homologous protein is called ''armadillo''. β-catenin is a subunit of the cadherin protein complex and acts as an intracellular signal transducer in the Wnt signaling pathway. It is a member of the catenin protein family and homologous to γ-catenin, also known as plakoglobin. Beta-catenin is widely expressed in many tissues. In cardiac muscle, beta-catenin localizes to adherens junctions in intercalated disc structures, which are critical for electrical and mechanical coupling between adjacent cardiomyocytes. Mutations and overexpression of β-catenin are associated with many cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma, colorectal carcinoma, lun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fanconi Syndrome
Fanconi syndrome or Fanconi's syndrome (, ) is a syndrome of inadequate reabsorption in the proximal renal tubules of the kidney. The syndrome can be caused by various underlying congenital or acquired diseases, by toxicity (for example, from toxic heavy metals), or by adverse drug reactions. It results in various small molecules of metabolism being passed into the urine instead of being reabsorbed from the tubular fluid (for example, glucose, amino acids, uric acid, phosphate, and bicarbonate). Fanconi syndrome affects the proximal tubules, namely, the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT), which is the first part of the tubule to process fluid after it is filtered through the glomerulus, and the proximal straight tubule (pars recta), which leads to the descending limb of loop of Henle. Different forms of Fanconi syndrome can affect different functions of the proximal tubule, and result in different complications. The loss of bicarbonate results in type 2 or proximal renal tubular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |