|
Henson Gletscher Formation
The Henson Gletscher Formation is a geologic formation in Greenland. It preserves fossils dating back to the Cambrian period. It is named after the Henson Glacier (Greenland). See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Greenland This is a list of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Greenland. List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Antarctica * Lists of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in North America * ... References * Cambrian Greenland Cambrian southern paleotropical deposits {{Greenland-geologic-formation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formation (stratigraphy)
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics (lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exposed in a geographical region (the stratigraphic column). It is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy, the study of strata or rock layers. A formation must be large enough that it can be mapped at the surface or traced in the subsurface. Formations are otherwise not defined by the thickness (geology), thickness of their rock strata, which can vary widely. They are usually, but not universally, tabular in form. They may consist of a single lithology (rock type), or of alternating beds of two or more lithologies, or even a heterogeneous mixture of lithologies, so long as this distinguishes them from adjacent bodies of rock. The concept of a geologic formation goes back to the beginnings of modern scientific geology. The term was used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized C with bar, Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago (mya) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period mya. Its subdivisions, and its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established as "Cambrian series" by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for 'Cymru' (Wales), where Britain's Cambrian rocks are best exposed. Sedgwick identified the layer as part of his task, along with Roderick Murchison, to subdivide the large "Transition Series", although the two geologists disagreed for a while on the appropriate categorization. The Cambrian is unique in its unusually high proportion of sedimentary deposits, sites of exceptional preservation where "soft" parts of organisms are preserved as well as their more resistant shells. As a result, our understanding of the Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
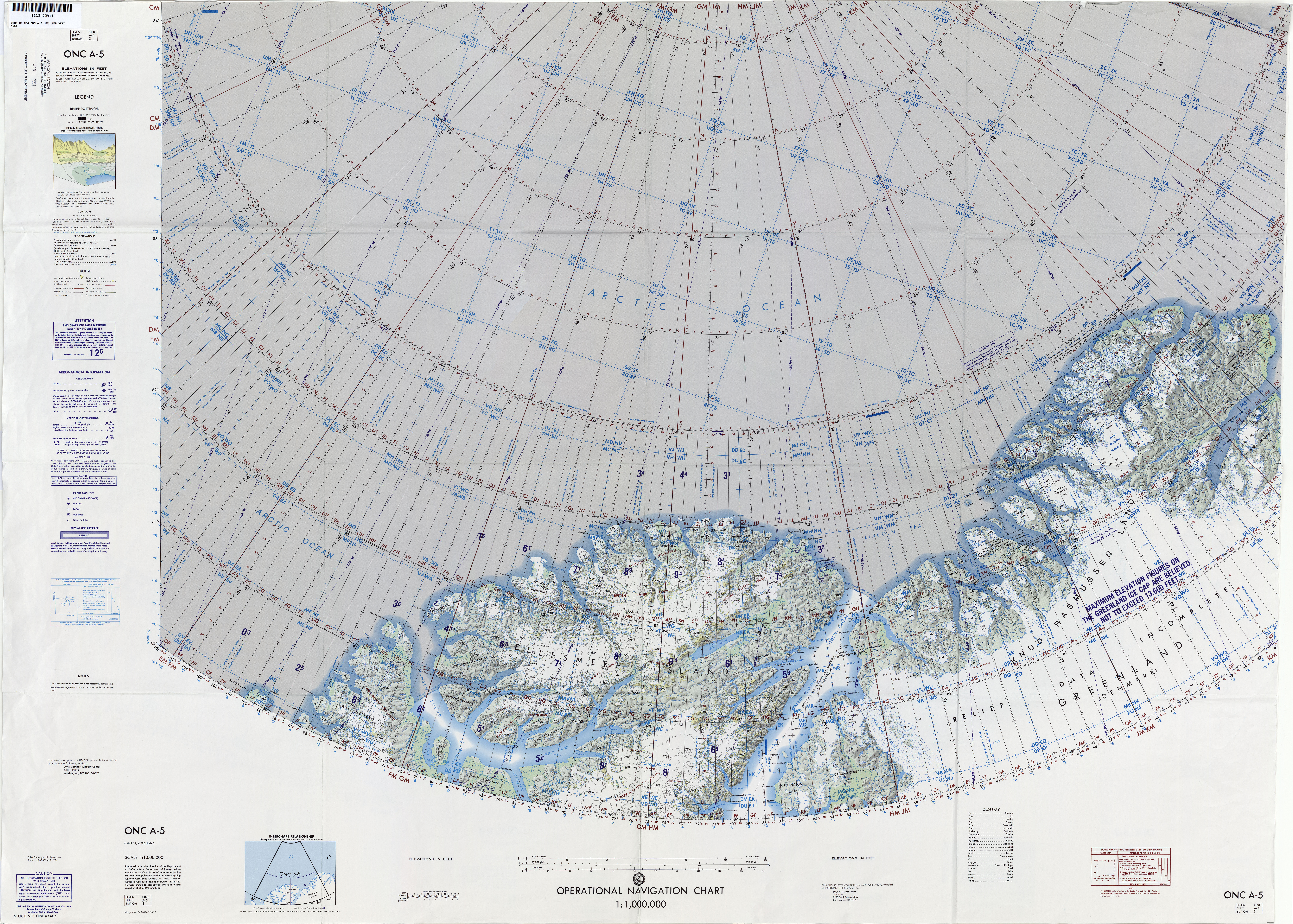
Henson Gletscher
Henson Glacier ( da, Henson Gletscher), is one of the major glaciers in northern Greenland. It was named in 1917 for African-American Arctic explorer Matthew Henson by Knud Rasmussen during the Second Thule Expedition to north Greenland. The Henson Gletscher Formation, which preserves trilobites and echinoderm fossils, among others, is named after this glacier. Geography The Henson Glacier originates in the Greenland Ice Cap. It is roughly north–south oriented and has its terminus at the head of the J.P. Koch Fjord. The Expedition Glacier discharges from the west north of the terminus of the Henson Glacier, between the head of the fjord and Navarana Fjord on the Freuchen Land side. The Hans Tausen Ice Cap is located to the east, close to the glacier tongue. Bibliography *H.P. Trettin (ed.), ''Geology of the Innuitian Orogen and Arctic Platform of Canada and Greenland''. Geological Survey of Canada (1991) See also *Henson Gletscher Formation *List of glaciers in Greenland *P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formation (geology)
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics ( lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exposed in a geographical region (the stratigraphic column). It is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy, the study of strata or rock layers. A formation must be large enough that it can be mapped at the surface or traced in the subsurface. Formations are otherwise not defined by the thickness of their rock strata, which can vary widely. They are usually, but not universally, tabular in form. They may consist of a single lithology (rock type), or of alternating beds of two or more lithologies, or even a heterogeneous mixture of lithologies, so long as this distinguishes them from adjacent bodies of rock. The concept of a geologic formation goes back to the beginnings of modern scientific geology. The term was used by Abraham Gottlob Wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is the world's largest island. It is one of three constituent countries that form the Kingdom of Denmark, along with Denmark and the Faroe Islands; the citizens of these countries are all citizens of Denmark and the European Union. Greenland's capital is Nuuk. Though a part of the continent of North America, Greenland has been politically and culturally associated with Europe (specifically Norway and Denmark, the colonial powers) for more than a millennium, beginning in 986.The Fate of Greenland's Vikings , by Dale Mackenzie Brown, ''Archaeological Institute of America'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossils
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absolute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Period (geology)
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronology (scientific branch of geology that aims to determine the age of rocks). It is used primarily by Earth scientists (including geologists, paleontologists, geophysicists, geochemists, and paleoclimatologists) to describe the timing and relationships of events in geologic history. The time scale has been developed through the study of rock layers and the observation of their relationships and identifying features such as lithologies, paleomagnetic properties, and fossils. The definition of standardized international units of geologic time is the responsibility of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), a constituent body of the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), whose primary objective is to precisely define ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henson Glacier (Greenland)
Henson Glacier ( da, Henson Gletscher), is one of the major glaciers in northern Greenland. It was named in 1917 for African-American Arctic explorer Matthew Henson by Knud Rasmussen during the Second Thule Expedition to north Greenland. The Henson Gletscher Formation, which preserves trilobites and echinoderm fossils, among others, is named after this glacier. Geography The Henson Glacier originates in the Greenland Ice Cap. It is roughly north–south oriented and has its terminus at the head of the J.P. Koch Fjord. The Expedition Glacier discharges from the west north of the terminus of the Henson Glacier, between the head of the fjord and Navarana Fjord on the Freuchen Land side. The Hans Tausen Ice Cap is located to the east, close to the glacier tongue. Bibliography *H.P. Trettin (ed.), ''Geology of the Innuitian Orogen and Arctic Platform of Canada and Greenland''. Geological Survey of Canada (1991) See also * Henson Gletscher Formation *List of glaciers in Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Fossiliferous Stratigraphic Units In Greenland
This is a list of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Greenland. List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Antarctica * Lists of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in North America ** List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in the Northwest Territories ** List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Nunavut ** List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Newfoundland and Labrador * Lists of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Europe ** List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Iceland ** List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Norway ** List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Russia ** List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Svalbard References Bibliography * * * * Further reading * C. B. Skovsted and J. S. Peel. 2011. ''Hyolithellus'' in life position from the Lower Cambrian of north Greenland. Journal of Paleontology 85(1):37-47 * A. C. Daley and J. S. Peel. 2010. A Possible Ano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian Greenland
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago (mya) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period mya. Its subdivisions, and its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established as "Cambrian series" by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for 'Cymru' (Wales), where Britain's Cambrian rocks are best exposed. Sedgwick identified the layer as part of his task, along with Roderick Murchison, to subdivide the large "Transition Series", although the two geologists disagreed for a while on the appropriate categorization. The Cambrian is unique in its unusually high proportion of sedimentary deposits, sites of exceptional preservation where "soft" parts of organisms are preserved as well as their more resistant shells. As a result, our understanding of the Cambrian biolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |