|
Henry De Bracton
Henry of Bracton (c. 1210 – c. 1268), also known as Henry de Bracton, Henricus Bracton, Henry Bratton, and Henry Bretton, was an English cleric and jurist. He is famous now for his writings on law, particularly ''De legibus et consuetudinibus Angliæ'' ("On the Laws and Customs of England"), and his ideas on ''mens rea'' (criminal intent). According to Bracton, it was only through the examination of a combination of action and intention that the commission of a criminal act could be established. He also wrote on kingship, arguing that a ruler should be called king only if he obtained and exercised power in a lawful manner. In his writings, Bracton manages to set out coherently the law of the royal courts through his use of categories drawn from Roman law, thus incorporating into English law several developments of medieval Roman law. Life Plucknett describes Bracton in this way: "Two generations after Ranulf de Glanvill we come to the flower and crown of English jurispr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windsor Castle At Sunset - Nov 2006
Windsor may refer to: Places * Detroit–Windsor, Michigan-Ontario, USA-Canada, North America; a cross-border metropolitan region Australia New South Wales *Windsor, New South Wales ** Municipality of Windsor, a former local government area Queensland * Windsor, Queensland, a suburb of Brisbane, Queensland ** Shire of Windsor, a former local government authority around Windsor, Queensland ** Town of Windsor, a former local government authority around Windsor, Queensland * Windsor Tablelands, a series of plateaus in Far North Queensland South Australia * Windsor, South Australia, a small town in the northern Adelaide Plains * Windsor Gardens, South Australia, a suburb of Adelaide Victoria * Windsor, Victoria, a suburb of Melbourne ** Windsor railway station, Melbourne Canada * Grand Falls-Windsor, Newfoundland and Labrador * Windsor, Nova Scotia *Windsor, Ontario; in Essex County ** Windsor (Ontario provincial electoral district) *Windsor-Essex, Essex County, Ontario; a metropol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornwall
Cornwall (; or ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is also one of the Celtic nations and the homeland of the Cornish people. The county is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, Devon to the east, and the English Channel to the south. The largest urban area is the Redruth and Camborne conurbation. The county is predominantly rural, with an area of and population of 568,210. After the Redruth-Camborne conurbation, the largest settlements are Falmouth, Cornwall, Falmouth, Penzance, Newquay, St Austell, and Truro. For Local government in England, local government purposes most of Cornwall is a Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area, with the Isles of Scilly governed by a Council of the Isles of Scilly, unique local authority. The Cornish nationalism, Cornish nationalist movement disputes the constitutional status of Cornwall and seeks greater autonomy within the United Kingdom. Cornwall is the weste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chantry
A chantry is an ecclesiastical term that may have either of two related meanings: # a chantry service, a set of Christian liturgical celebrations for the dead (made up of the Requiem Mass and the Office of the Dead), or # a chantry chapel, a building on private land, or an area in a parish church or cathedral reserved for the performance of these celebrations. In the Medieval Era through to the Age of Enlightenment it was commonly believed such liturgies might help atone for misdeeds and assist the soul to obtain eternal peace. Etymology The word "chantry" derives from Old French ''chanter'' and from the Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... ''chanter'' and from the Latin ''cantare'' (to sing). Its medieval derivative ''cantaria'' means "licence to sing mass". The French term for this commemorative institution is ''chapellenie'' (chaplaincy). Overview Liturgy for the dead Firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exeter Cathedral
Exeter Cathedral, properly known as the Cathedral Church of Saint Peter in Exeter, is an Anglican cathedral, and the seat of the Bishop of Exeter, in the city status in the United Kingdom, city of Exeter, Devon, in South West England. The present building was complete by about 1400 and has several notable features, including an early set of misericords, an astronomical clock and the longest uninterrupted medieval stone Vault (architecture), vaulted ceiling in the world. History The site where Exeter Cathedral was constructed was home to Roman Britain, Roman buildings. A legionary fortress was constructed between 50–75 AD. A Roman bathhouse was discovered in 1971. The founding of the cathedral at Exeter, England, Exeter, dedicated to Saint Peter, dates from 1050, when the seat of the bishop of United sees of Devon and Cornwall, Devon and Cornwall was transferred from Crediton because of a fear of sea-raids. A Anglo-Saxons, Saxon minster already existing within the town (an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barnstaple
Barnstaple ( or ) is a river-port town and civil parish in the North Devon district of Devon, England. The town lies at the River Taw's lowest crossing point before the Bristol Channel. From the 14th century, it was licensed to export wool from which it earned great wealth. Later it imported Irish wool, but its harbour silted up and other trades developed such as shipbuilding, foundries and sawmills. A Victorian market building survives, with a high glass and timber roof on iron columns. Toponymy The name is first recorded in the 10th century and is thought to derive from the Early English ''bearde'', meaning "battle-axe", and ''stapol'', meaning "pillar", i.e. a post or pillar to mark a religious or administrative meeting place. The derivation from ''staple'' meaning "market", indicating a market from its foundation, is likely to be incorrect, as the use of ''staple'' in that sense first appears in 1423. Barnstaple was formerly referred to as "Barum", as a contraction of the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bideford
Bideford ( ) is a historic port town on the estuary of the River Torridge in north Devon, South West England. It is the main town of the Torridge District, Torridge Districts of England, local government district. Toponymy In ancient records Bideford is recorded as ''Bedeford'', ''Byddyfrod'', ''Bedyford'', ''Bydeford'', ''Bytheford'' and ''Biddeford''. The etymology of the name means "by the ford," and records show that, before there was a bridge, there was a Ford (crossing), ford at Bideford where River Torridge is estuarine; and at low tide, it is possible (but not advisable) to cross the river by wading on foot. History Early history Ubba, Hubba the Dane was said to have attacked Devon in the area around Bideford near Northam, Devon, Northam or near Kenwith Castle, and was repelled either by Alfred the Great (849–899) or by the Saxon Earl of Devon. The Manorialism, manor of Bideford was recorded in the Domesday Book of 1086 as held at some time tenant in chief, in chief ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combe-in-Teignhead
Combeinteignhead or Combe-in-Teignhead is a village in Teignbridge, South Devon, England. It lies within the civil parish of Haccombe with Combe, between Newton Abbot and Shaldon, about half a mile (1 km) inland from the estuary of the River Teign. Despite this closeness to the River Teign, the name ''Combeinteignhead'' is not derived from it: in the Domesday Book the district contained thirteen manors which totalled an area of ten hides and the whole area was known as the "Ten Hide". This was later corrupted to ''Teignhead'' through the influence of the river name. It is one of the longest place names in England, with 16 letters. The name of the nearby village of Stokeinteignhead has a similar derivation. The village has two historic pubs: the Wild Goose Inn, originally called the Country House Inn, a 17th-century tavern in the centre of the village, and the Coombe Cellars Inn, right on the estuary of the River Teign. Coombe Cellars was an early base for the local fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
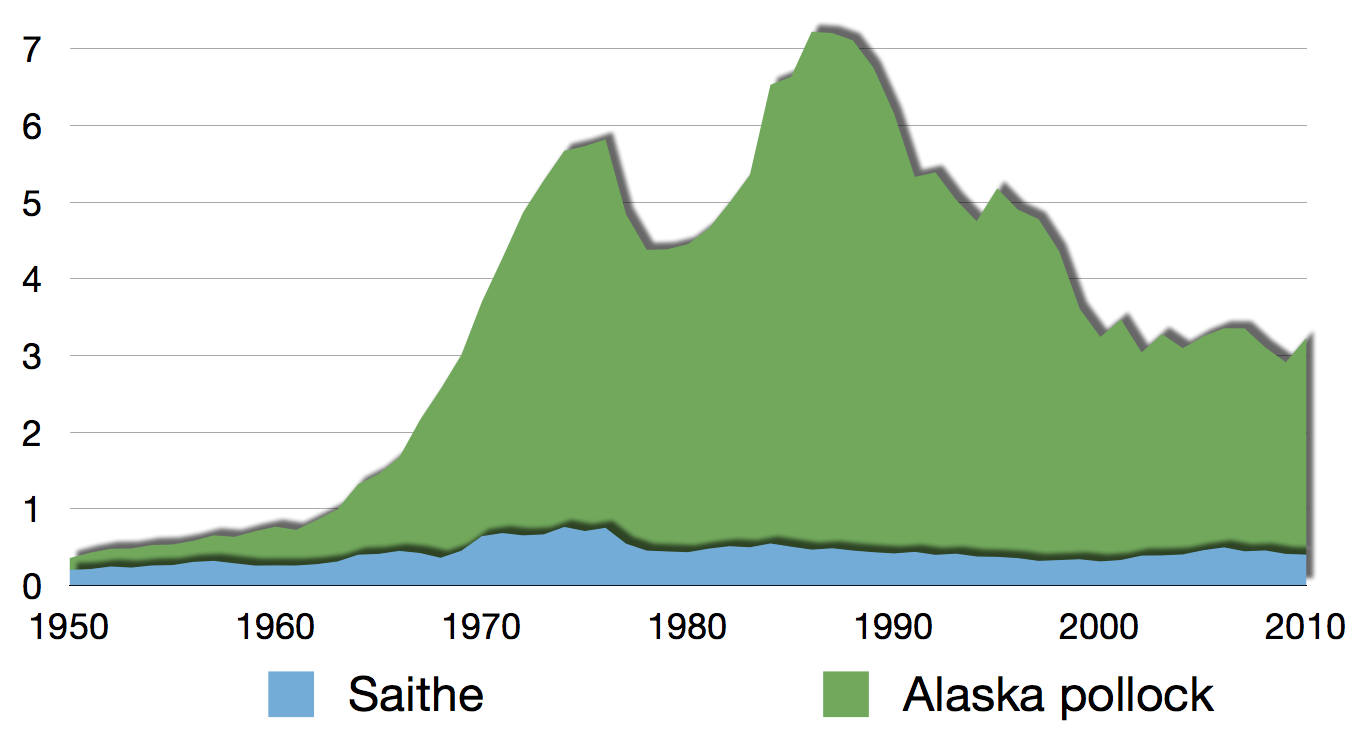
Pollock
Pollock or pollack (pronounced ) is the common name used for either of the two species of North Atlantic ocean, marine fish in the genus ''Pollachius''. ''Pollachius pollachius'' is referred to as "pollock" in North America, Ireland and the United Kingdom, while ''Pollachius virens'' is usually known as saithe or coley in Great Britain and Ireland (derived from the older name coalfish). Other names for ''P. pollachius'' include the Atlantic pollock, European pollock, ''lieu jaune'', and lythe or lithe; while ''P. virens'' is also known as Boston blue (distinct from bluefish) and silver bill. Species The recognized species in this genus are: * ''Pollachius pollachius'' (Carl Linnaeus, Linnaeus, 1758) (pollack) * ''Pollachius virens'' (Linnaeus, 1758) (coalfish) Description Both species can grow to . ''P. virens'' can weigh up to and ''P. pollachius'' can weigh up to . ''P. virens'' has a strongly defined, silvery lateral line running down the sides. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon De Montfort, 6th Earl Of Leicester
Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester, 1st Earl of Chester ( – 4 August 1265), also known as Simon V de Montfort, was an English nobleman of French origin and a member of the Peerage of England, English peerage, who led the baronial opposition to the rule of King Henry III of England, culminating in the Second Barons' War. Following his initial victories over royal forces, he became ''de facto'' ruler of the country, and played a major role in the constitutional development of England. During his rule, Montfort called two famous parliaments: the Oxford Parliament (1258), Oxford Parliament stripped Henry of his unlimited authority, while Simon de Montfort's Parliament, the second included ordinary citizens from the towns. For this reason, Montfort is regarded today as one of the wikt:progenitor, progenitors of modern parliamentary democracy. As Earl of Leicester he expelled Jews from Leicester, that city; as he became ruler of England he also cancelled debts owed to Jews thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William De Raley
William de Raley (died 1250) was a medieval judge, administrator and bishop. Most historians now believe that he was the author of the great law book ''Bracton''. Life In 1212 Raley was presented by the King to the church living at Bratton Fleming, in the archdeaconry of Barnstaple, wherein his occupation was described as "clerk", when he studied law.Pegues "''Clericus'' in Legal Administration" ''English Historical Review'' p. 543 He is known to have served as a clerk of the bench in 1214, and again from 1219 to 1229. From 1225 to 1229 he was the personal clerk of Martin of Pattishall, with whom he travelled the Eyre (legal term), Eyre in Cumberland and Northumberland between 1226 and 1227, where he acted as a commissioner for the assessment of Tallage. He became justice of the bench in 1229 following Pattishall's retirement, with Roger of Thirkleby being appointed as his clerk in 1231.Pegues "''Clericus'' in Legal Administration" ''English Historical Review'' p. 544 Raley took p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Pateshull
Martin of Pattishall (died 14 November 1229) was an English judge. He took his name from the village of Pattishall in Northamptonshire and was the clerk of Simon of Pattishall, although they were apparently unrelated. By 1201 he was already respected enough to be collecting the Plea rolls from the clerks of other judges on Eyre. After the end of the First Barons' War Pattishall became the leader of Henry III's professional legal servants, and was instrumental in reestablishing the courts. Between 1217 and 1218 he was a justice on Eyre in Yorkshire and Northumberland, in 1220–1221 in Hertfordshire and at the Tower of London, in March and April 1226 again at the Tower of London; from September 1226 to February 1227 in Lincolnshire, Yorkshire, Lancashire, and Westmorland; and between September 1227 and October 1228 in Kent, Essex, Hertfordshire, Norfolk, and Suffolk. One of his clerks wrote that: In 1217 he was made Chief Justice of the Common Pleas, a position his former mast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |