|
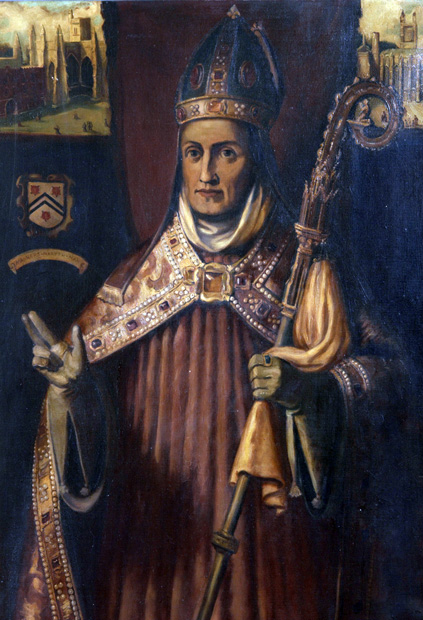
Henry, Bishop Of Winchester
Henry of Blois ( c. 1096 8 August 1171), often known as Henry of Winchester, was Abbot of Glastonbury Abbey from 1126, and Bishop of Winchester from 1129 to his death. He was a younger son of Stephen Henry, Count of Blois by Adela of Normandy, daughter of William the Conqueror and Matilda of Flanders. Thus, he was a younger brother of Stephen, King of England, and a grandchild of William the Conqueror. Henry was also a major patron of the arts. Early life and education Henry was one of five sons of Stephen II, Count of Blois, by Adela of Normandy (daughter of William the Conqueror) and the younger brother of King Stephen.British History Online: Bishops of Winchester ; accessed on 2 November 2007 His birth date is uncertain, along with his siblings but he was the 4th or youngest son and he was mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Winchester
The Bishop of Winchester is the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of Winchester in the Church of England. The bishop's seat (''cathedra'') is at Winchester Cathedral in Hampshire. The Bishop of Winchester has always held ''ex officio'' (except during the period of the Commonwealth until the Restoration of the Monarchy) the office of Prelate of the Most Noble Order of the Garter since its foundation in 1348, and Bishops of Winchester often held the positions of Lord Treasurer and Lord Chancellor ''ex officio''. During the Middle Ages, it was one of the wealthiest English sees, and its bishops have included a number of politically prominent Englishmen, notably the 9th century Saint Swithun and medieval magnates including William of Wykeham and Henry of Blois. The Bishop of Winchester is appointed by the Crown, and is one of five Church of England bishops who sit ''ex officio'' among the 26 Lords Spiritual in the House of Lords, regardless of their length of service. The Diocese o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chartres
Chartres () is the prefecture of the Eure-et-Loir department in the Centre-Val de Loire region in France. It is located about southwest of Paris. At the 2019 census, there were 170,763 inhabitants in the metropolitan area of Chartres (as defined by the INSEE), 38,534 of whom lived in the city (commune) of Chartres proper. Chartres is famous worldwide for its cathedral. Mostly constructed between 1193 and 1250, this Gothic cathedral is in an exceptional state of preservation. The majority of the original stained glass windows survive intact, while the architecture has seen only minor changes since the early 13th century. Part of the old town, including most of the library associated with the School of Chartres, was destroyed by Allies of World War II, Allied bombs in 1944. History Chartres was one of the principal towns in Gaul of the Carnutes, a Celts, Celtic tribe. In the Gallo-Roman period, it was called ''Autricum'', name derived from the river ''Autura'' (Eure), and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter The Venerable
Peter the Venerable ( – 25 December 1156), also known as Peter of Montboissier, was the abbot of the Benedictine abbey of Cluny. He has been honored as a saint, though he was never canonized in the Middle Ages. Since in 1862 Pope Pius IX confirmed his historical cult, and the ''Martyrologium Romanum'', issued by the Holy See in 2004, regards him as a Blessed. Life Born to Blessed Raingarde in Auvergne, Peter was "Dedicated to God" at birth and given to the monastery at Sauxillanges of the Congregation of Cluny where he took his vows at age seventeen. By the age of twenty he gained a professorship and was appointed prior of the monastery of Vézelay, transferring later to the monastery at Domène. Success at Vézelay and Domène led to his election as abbot general of the order, aged thirty. After his predecessor, the abbot Pontius, had been deposed by the pope, Peter became a tireless reformer of the Cluniac order, in the face of criticism from other orders and prominent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Of Ypres
William of Ypres ( nl, Willem van Yper; 1090 – 24 January 116524 January 1164 O.S., 1165 N.S.) was a Flemish nobleman and one of the first mercenary captains of the Middle Ages. Following two unsuccessful bids for the County of Flanders, William became King Stephen of England's chief lieutenant during the civil war of 1139–54 known as the Anarchy. He held Kent, though not the title of earl, until the early years of King Henry II's reign, when he returned to Flanders. Struggle for Flanders William was an illegitimate son of Philip of Loo, who was the son of the Flemish count Robert the Frisian and younger brother of Robert II.Richard Ealesof Ypres, styled count of Flanders (d. 1164/5)"''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' William's mother was a wool carder, which further diminished his status; King Louis VI of France pointed out that she never rose from that station. The exact date of his birth is unknown, and although 1090 is the commonly used date of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empress Matilda
Empress Matilda ( 7 February 110210 September 1167), also known as the Empress Maude, was one of the claimants to the English throne during the civil war known as the Anarchy. The daughter of King Henry I of England, she moved to Germany as a child when she married the future Holy Roman Emperor Henry V. She travelled with her husband to Italy in 1116, was controversially crowned in St Peter's Basilica, and acted as the imperial regent in Italy. Matilda and Henry V had no children, and when he died in 1125, the imperial crown was claimed by his rival Lothair of Supplinburg. Matilda's younger and only full brother, William Adelin, died in the ''White Ship'' disaster of 1120, leaving Matilda's father and realm facing a potential succession crisis. On Emperor Henry V's death, Matilda was recalled to Normandy by her father, who arranged for her to marry Geoffrey of Anjou to form an alliance to protect his southern borders. Henry I had no further legitimate children and nominated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Lincoln (1141)
The Battle of Lincoln, or the First Battle of Lincoln, occurred on 2 February 1141 in Lincoln, England between King Stephen of England and forces loyal to Empress Matilda. Stephen was captured during the battle, imprisoned, and effectively deposed while Matilda ruled for a short time. Account The forces of King Stephen of England had been besieging Lincoln Castle but were themselves attacked by a relief force loyal to Empress Matilda and commanded by Robert, 1st Earl of Gloucester, Matilda's half-brother. The Angevin army consisted of the divisions of Robert's men, those of Ranulf, Earl of Chester and those disinherited by Stephen, while on the flank was a mass of Welsh troops led by Madog ap Maredudd, Lord of Powys, and Cadwaladr ap Gruffydd. Cadwaladr was the brother of Owain, King of Gwynedd, but Owain did not support any side in the Anarchy. Stephen's force included William of Ypres; Simon of Senlis; Gilbert of Hertford; William of Aumale, Alan of Richmond and Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
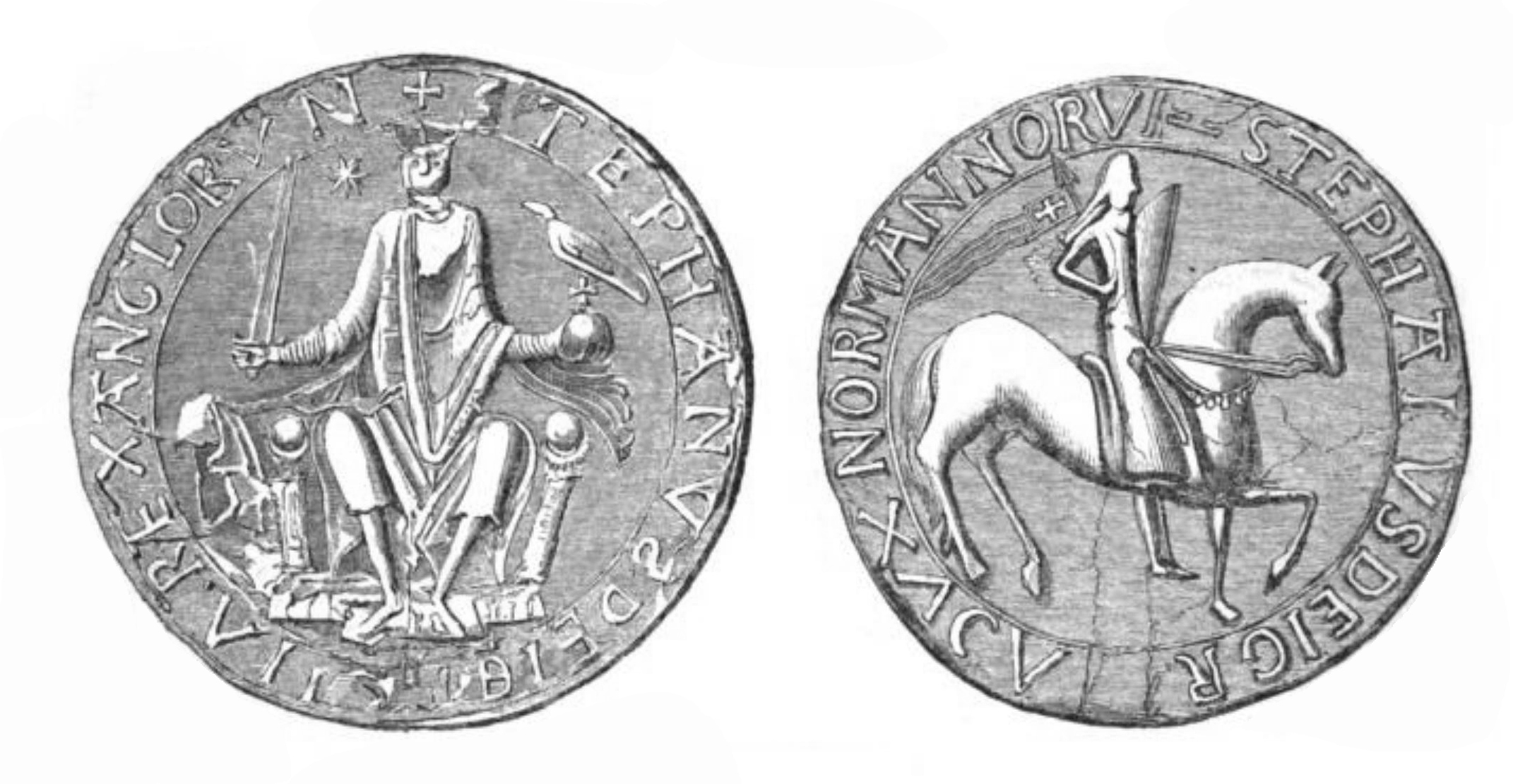
The Anarchy
The Anarchy was a civil war in England and Normandy between 1138 and 1153, which resulted in a widespread breakdown in law and order. The conflict was a war of succession precipitated by the accidental death of William Adelin, the only legitimate son of King Henry I, who drowned in the sinking of the ''White Ship'' in 1120. Henry sought to be succeeded by his daughter, known as Empress Matilda, but was only partially successful in convincing the nobility to support her. On Henry's death in 1135, his nephew Stephen of Blois seized the throne, with the help of Stephen's brother Henry of Blois, who was the bishop of Winchester. Stephen's early reign saw fierce fighting with disloyal English barons, rebellious Welsh leaders, and Scottish invaders. Following a major rebellion in the south-west of England, Matilda invaded in 1139 with the help of her half-brother Robert of Gloucester. In the initial years of civil war, neither side was able to achieve a decisive advantage; the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theobald Of Bec
Theobald of Bec ( c. 1090 – 18 April 1161) was a Norman archbishop of Canterbury from 1139 to 1161. His exact birth date is unknown. Some time in the late 11th or early 12th century Theobald became a monk at the Abbey of Bec, rising to the position of abbot in 1137. King Stephen of England chose him to be Archbishop of Canterbury in 1138. Canterbury's claim to Primacy of Canterbury, primacy over the Welsh ecclesiastics was resolved during Theobald's term of office when Pope Eugene III decided in 1148 in Canterbury's favour. Theobald faced challenges to his authority from a subordinate bishop, Henry of Blois, Bishop of Winchester and King Stephen's younger brother, and his relationship with King Stephen was turbulent. On one occasion Stephen forbade him from attending a Council of Reims (1148), papal council, but Theobald defied the king, which resulted in the confiscation of his property and temporary exile. Theobald's relations with his cathedral clergy and the mona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papal Legate
300px, A woodcut showing Henry II of England greeting the pope's legate. A papal legate or apostolic legate (from the ancient Roman title ''legatus'') is a personal representative of the pope to foreign nations, or to some part of the Catholic Church. He is empowered on matters of Catholic faith and for the settlement of ecclesiastical matters. The legate is appointed directly by the pope—the bishop of Rome and head of the Catholic Church. Hence a legate is usually sent to a government, a sovereign or to a large body of believers (such as a national church) or to take charge of a major religious effort, such as an ecumenical council, a crusade to the Holy Land, or even against a heresy such as the Cathars. The term ''legation'' is applied both to a legate's mandate and to the territory concerned (such as a state, or an ecclesiastical province). The relevant adjective is ''legatine''. History 200px, Cardinal Thomas Wolsey, papal legate to England during the reign of Hen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Country
The West Country (occasionally Westcountry) is a loosely defined area of South West England, usually taken to include all, some, or parts of the counties of Cornwall, Devon, Dorset, Somerset, Bristol, and, less commonly, Wiltshire, Gloucestershire and Herefordshire. "Which counties make up the West Country?", ''YouGov.co.uk'', 23 October 2019 Retrieved 22 June 2021 The West Country has a distinctive regional English dialect and accent, and is also home to the . Extent ...
|
Archbishop Of Canterbury
The archbishop of Canterbury is the senior bishop and a principal leader of the Church of England, the ceremonial head of the worldwide Anglican Communion and the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of Canterbury. The current archbishop is Justin Welby, who was enthroned at Canterbury Cathedral on 21 March 2013. Welby is the 105th in a line which goes back more than 1400 years to Augustine of Canterbury, the "Apostle to the English", sent from Rome in the year 597. Welby succeeded Rowan Williams. From the time of Augustine until the 16th century, the archbishops of Canterbury were in full communion with the See of Rome and usually received the pallium from the pope. During the English Reformation, the Church of England broke away from the authority of the pope. Thomas Cranmer became the first holder of the office following the English Reformation in 1533, while Reginald Pole was the last Roman Catholic in the position, serving from 1556 to 1558 during the Counter-Reformation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
See Of Winchester
The Diocese of Winchester forms part of the Province of Canterbury of the Church of England. Founded in 676, it is one of the older dioceses in England. It once covered Wessex, many times its present size which is today most of the historic enlarged version of Hampshire. Territory The area of the diocese is an area of eastern Dorset, and modern Hampshire, including the city of Southampton, with four exceptions: *the south-eastern quarter of the county (which together with the Isle of Wight constitutes the Diocese of Portsmouth) *an area in the north-east (in the Diocese of Guildford) *a small area in the west (in the Diocese of Salisbury) *one parish in the north (in the Diocese of Oxford) The diocese historically covered a much larger area, see below. In the most recent major revision in 1927, the Archdeaconry of Surrey was removed to form the new Diocese of Guildford, and south-eastern Hampshire and the Isle of Wight were removed to form the Diocese of Portsmouth. The Bisho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |