|
Henricus Grammateus
Henricus Grammateus (also known as Henricus Scriptor, Heinrich Schreyber or Heinrich Schreiber; 1495 – 1525 or 1526) was a German mathematician. He was born in Erfurt Erfurt () is the capital and largest city in the Central German state of Thuringia. It is located in the wide valley of the Gera river (progression: ), in the southern part of the Thuringian Basin, north of the Thuringian Forest. It sits .... In 1507 he started to study at the University of Vienna, where he subsequently taught. Christoph Rudolff was one of his students. From 1514 to 1517 he studied in Cracow and then returned to Vienna. But when the plague affected Vienna Schreiber left the city and went to Nuremberg. In 1518 he published details of a new musical temperament, which is now named after him, for the harpsichord. It was a precursor of the equal temperament. In 1525 Schreiber was back in Vienna, where he is listed as "Examinator", i.e. eligible to work holding exams. Works * ''A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
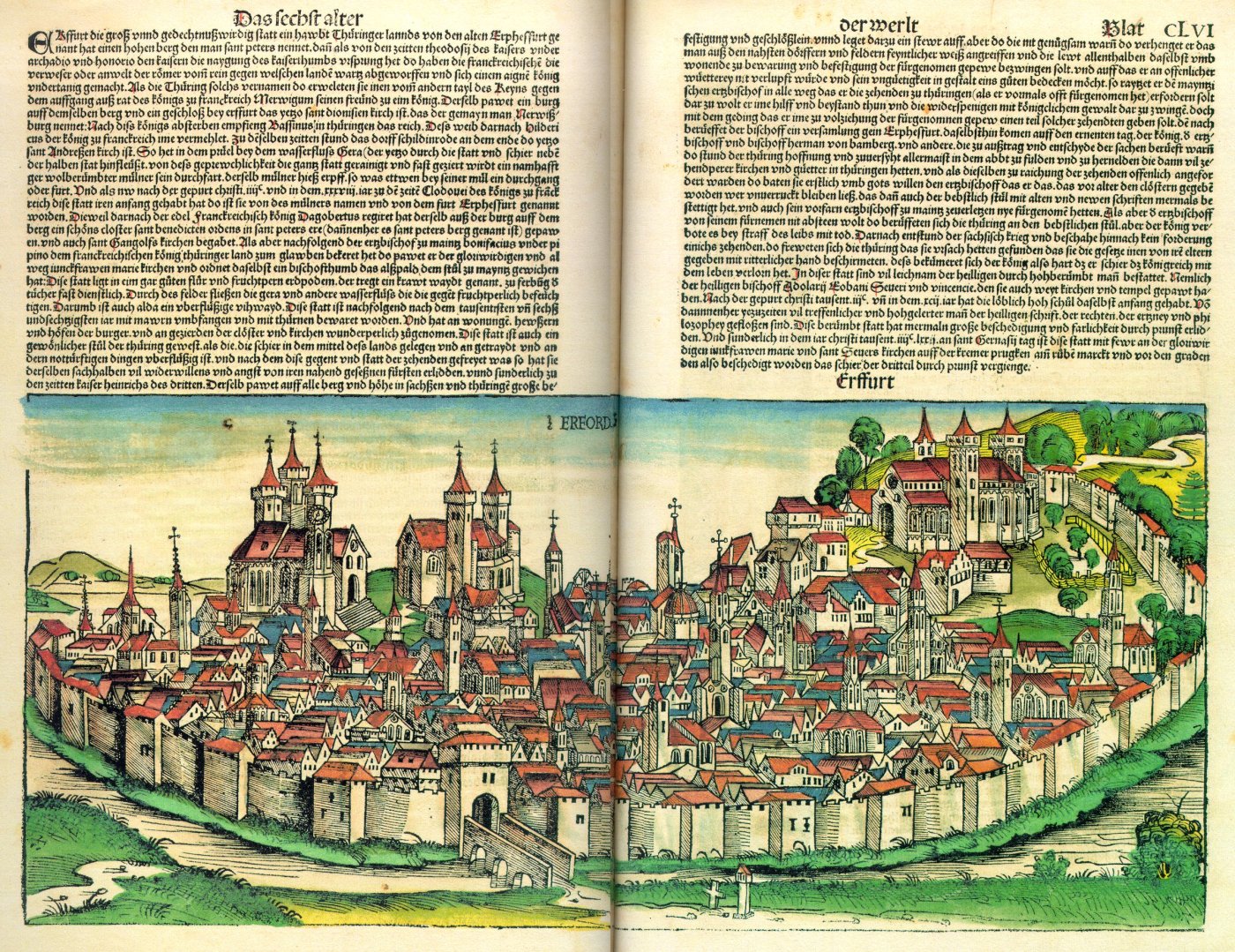
Erfurt
Erfurt () is the capital and largest city in the Central German state of Thuringia. It is located in the wide valley of the Gera river (progression: ), in the southern part of the Thuringian Basin, north of the Thuringian Forest. It sits in the middle of an almost straight line of cities consisting of the six largest Thuringian cities forming the central metropolitan corridor of the state, the "Thuringian City Chain" ('' Thüringer Städtekette'') with more than 500,000 inhabitants, stretching from Eisenach in the west, via Gotha, Erfurt, Weimar and Jena, to Gera in the east. Erfurt and the city of Göttingen in southern Lower Saxony are the two cities with more than 100,000 inhabitants closest to the geographic center of Germany. Erfurt is located south-west of Leipzig, north-east of Frankfurt, south-west of Berlin and north of Munich. Erfurt's old town is one of the best preserved medieval city centres in Germany. Tourist attractions include the Merchants' Bridge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harpsichord
A harpsichord ( it, clavicembalo; french: clavecin; german: Cembalo; es, clavecín; pt, cravo; nl, klavecimbel; pl, klawesyn) is a musical instrument played by means of a musical keyboard, keyboard. This activates a row of levers that turn a trigger mechanism that plucks one or more strings with a small plectrum made from quill or plastic. The strings are under tension on a Sound board (music), soundboard, which is mounted in a wooden case; the soundboard amplifies the vibrations from the strings so that the listeners can hear it. Like a pipe organ, a harpsichord may have more than one keyboard Manual (music), manual, and even a #Pedal harpsichord, pedal board. Harpsichords may also have Organ stop, stop buttons which add or remove additional octaves. Some harpsichords may have a buff stop, which brings a strip of buff leather or other material in contact with the strings, muting their sound to simulate the sound of a plucked lute. The term denotes the whole family of similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Music Theorists
German(s) may refer to: * Germany (of or related to) **Germania (historical use) * Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language ** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law **Germanic peoples (Roman times) * German language **any of the Germanic languages * German cuisine, traditional foods of Germany People * German (given name) * German (surname) * Germán, a Spanish name Places * German (parish), Isle of Man * German, Albania, or Gërmej * German, Bulgaria * German, Iran * German, North Macedonia * German, New York, U.S. * Agios Germanos, Greece Other uses * German (mythology), a South Slavic mythological being * Germans (band), a Canadian rock band * "German" (song), a 2019 song by No Money Enterprise * ''The German'', a 2008 short film * "The Germans", an episode of ''Fawlty Towers'' * ''The German'', a nickname for Congolese rebel André Kisase Ngandu See also * Germanic (other) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16th-century German Mathematicians
The 16th century begins with the Julian year 1501 ( MDI) and ends with either the Julian or the Gregorian year 1600 ( MDC) (depending on the reckoning used; the Gregorian calendar introduced a lapse of 10 days in October 1582). The 16th century is regarded by historians as the century which saw the rise of Western civilization and the Islamic gunpowder empires. The Renaissance in Italy and Europe saw the emergence of important artists, authors and scientists, and led to the foundation of important subjects which include accounting and political science. Copernicus proposed the heliocentric universe, which was met with strong resistance, and Tycho Brahe refuted the theory of celestial spheres through observational measurement of the 1572 appearance of a Milky Way supernova. These events directly challenged the long-held notion of an immutable universe supported by Ptolemy and Aristotle, and led to major revolutions in astronomy and science. Galileo Galilei became a champion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientists From Erfurt
A scientist is a person who conducts scientific research to advance knowledge in an area of the natural sciences. In classical antiquity, there was no real ancient analog of a modern scientist. Instead, philosophers engaged in the philosophical study of nature called natural philosophy, a precursor of natural science. Though Thales (circa 624-545 BC) was arguably the first scientist for describing how cosmic events may be seen as natural, not necessarily caused by gods,Frank N. Magill''The Ancient World: Dictionary of World Biography'', Volume 1 Routledge, 2003 it was not until the 19th century that the term ''scientist'' came into regular use after it was coined by the theologian, philosopher, and historian of science William Whewell in 1833. In modern times, many scientists have advanced degrees in an area of science and pursue careers in various sectors of the economy such as academia, industry, government, and nonprofit environments.'''' History The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1525 Deaths
Fifteen or 15 may refer to: * 15 (number), the natural number following 14 and preceding 16 *one of the years 15 BC, AD 15, 1915, 2015 Music *Fifteen (band), a punk rock band Albums * ''15'' (Buckcherry album), 2005 * ''15'' (Ani Lorak album), 2007 * ''15'' (Phatfish album), 2008 * ''15'' (mixtape), a 2018 mixtape by Bhad Bhabie * ''Fifteen'' (Green River Ordinance album), 2016 * ''Fifteen'' (The Wailin' Jennys album), 2017 * ''Fifteen'', a 2012 album by Colin James Songs * "Fifteen" (song), a 2008 song by Taylor Swift *"Fifteen", a song by Harry Belafonte from the album '' Love Is a Gentle Thing'' *"15", a song by Rilo Kiley from the album '' Under the Blacklight'' *"15", a song by Marilyn Manson from the album ''The High End of Low'' *" The 15th", a 1979 song by Wire Other uses *Fifteen, Ohio, a community in the United States * ''15'' (film), a 2003 Singaporean film * ''Fifteen'' (TV series), international release name of ''Hillside'', a Canadian-American teen drama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1495 Births
Year 1495 ( MCDXCV) was a common year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events January–December * February – King's College, Aberdeen, predecessor of the University of Aberdeen in Scotland, is founded on the petition of William Elphinstone, Bishop of Aberdeen. It is the first English-speaking university to teach medicine. * February 22 – Italian War of 1494–98: King Charles VIII of France enters Naples, to claim the city's throne. A few months later, he decides to return to France, and leaves Naples with most of his army, leaving a force under his cousin Gilbert, Count of Montpensier as viceroy. Syphilis is first definitely recorded in Europe during this invasion. (perhaps from French forces who may have contacted Croats fleeing an Ottoman army in the east). * May 26 – A Spanish army under Gonzalo Fernández de Córdoba lands in Calabria, with the purpose of ousting the French and restoring Ferd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florian Cajori
Florian Cajori (February 28, 1859 – August 14 or 15, 1930) was a Swiss-American historian of mathematics. Biography Florian Cajori was born in Zillis, Switzerland, as the son of Georg Cajori and Catherine Camenisch. He attended schools first in Zillis and later in Chur. In 1875, Florian Cajori emigrated to the United States at the age of sixteen, and attended the State Normal school in Whitewater, Wisconsin. After graduating in 1878, he taught in a country school, and then later began studying mathematics at University of Wisconsin–Madison. In 1883, Cajori received both his bachelor's and master's degrees from the University of Wisconsin–Madison, briefly attended Johns Hopkins University for 8 months in between degrees. He taught for a few years at Tulane University, before being appointed as professor of applied mathematics there in 1887. He was then driven north by tuberculosis. He founded the Colorado College Scientific Society and taught at Colorado College wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plus And Minus Signs
The plus and minus signs, and , are mathematical symbols used to represent the notions of positive and negative, respectively. In addition, represents the operation of addition, which results in a sum, while represents subtraction, resulting in a difference. Their use has been extended to many other meanings, more or less analogous. ''Plus'' and ''minus'' are Latin terms meaning "more" and "less", respectively. History Though the signs now seem as familiar as the alphabet or the Hindu-Arabic numerals, they are not of great antiquity. The Egyptian hieroglyphic sign for addition, for example, resembled a pair of legs walking in the direction in which the text was written ( Egyptian could be written either from right to left or left to right), with the reverse sign indicating subtraction: Nicole Oresme's manuscripts from the 14th century show what may be one of the earliest uses of as a sign for plus. In early 15th century Europe, the letters "P" and "M" were gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Widmann
Johannes Widmann (c. 1460 – after 1498) was a German mathematician. The + and - symbols first appeared in print in his book ''Mercantile Arithmetic'' or ''Behende und hüpsche Rechenung auff allen Kauffmanschafft'' published in Leipzig in 1489 in reference to surpluses and deficits in business problems. Born in Eger, Bohemia, Widmann attended the University of Leipzig in the 1480s. In 1482 he earned his " Baccalaureus" (Bachelor of Art degree) and in 1485 his "Magister" (doctorate). Widman published ''Behende und hübsche Rechenung auff allen Kauffmanschafft'' ( German; i.e. Nimble and neat calculation in all trades), his work making use of the signs, in Leipzig in 1489. Further editions were published in Pforzheim, Hagenau, and Augsburg. Handwritten entries in a surviving collection show that after earning his "Magister" Widman announced holding lectures on e.g. calculating on the lines of a calculating board and on algebra. There is evidence that the lecture on algebra act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
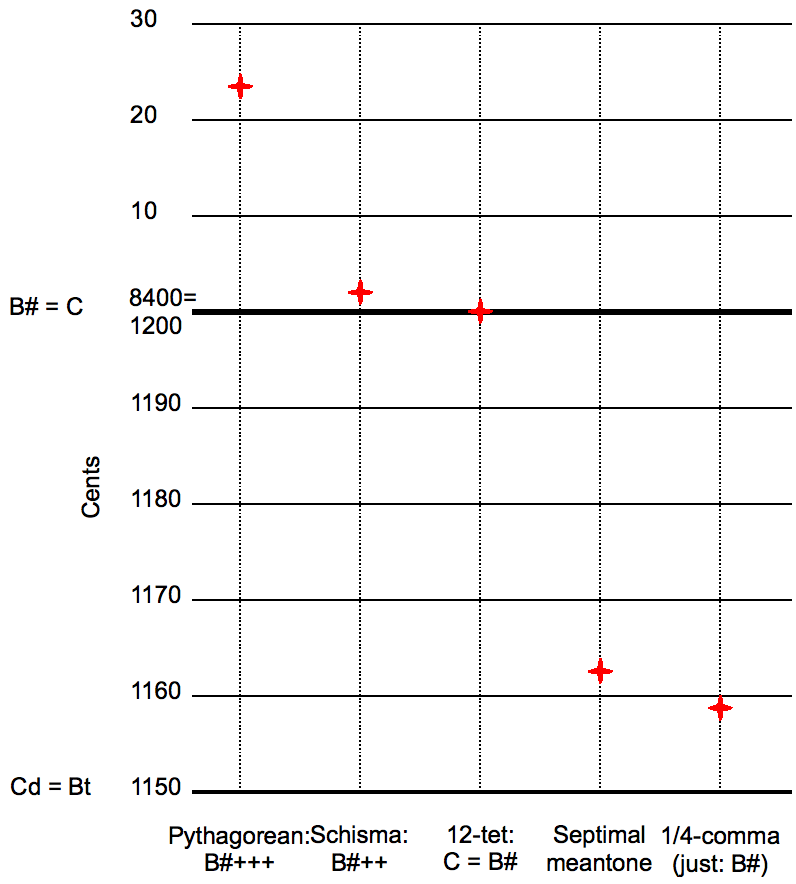
Equal Temperament
An equal temperament is a musical temperament or tuning system, which approximates just intervals by dividing an octave (or other interval) into equal steps. This means the ratio of the frequencies of any adjacent pair of notes is the same, which gives an equal perceived step size as pitch is perceived roughly as the logarithm of frequency. In classical music and Western music in general, the most common tuning system since the 18th century has been twelve-tone equal temperament (also known as 12 equal temperament, 12-TET or 12-ET; informally abbreviated to twelve equal), which divides the octave into 12 parts, all of which are equal on a logarithmic scale, with a ratio equal to the 12th root of 2 ( ≈ 1.05946). That resulting smallest interval, the width of an octave, is called a semitone or half step. In Western countries the term ''equal temperament'', without qualification, generally means 12-TET. In modern times, 12-TET is usually tuned relative to a standard pit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical Temperament
In musical tuning, a temperament is a tuning system that slightly compromises the pure intervals of just intonation to meet other requirements. Most modern Western musical instruments are tuned in the equal temperament system. Tempering is the process of altering the size of an interval by making it narrower or wider than pure. "Any plan that describes the adjustments to the sizes of some or all of the twelve fifth intervals in the circle of fifths so that they accommodate pure octaves and produce certain sizes of major thirds is called a ''temperament''." Temperament is especially important for keyboard instruments, which typically allow a player to play only the pitches assigned to the various keys, and lack any way to alter pitch of a note in performance. Historically, the use of just intonation, Pythagorean tuning and meantone temperament meant that such instruments could sound "in tune" in one key, or some keys, but would then have more dissonance in other keys. In the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |