|
Hemoglobin D
Within the medical specialty of hematology, Hemoglobin D-Punjab is one of the sub-variants of Hemoglobin D, a variant of hemoglobin found in human blood. It is so named because of its higher prevalence in the Punjab region of India and Pakistan. It is also the most frequent abnormal hemoglobin variant in Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of China. Studies indicate that Hemoglobin D-Punjab accounts for over 55% of the total hemoglobin variants there. Hemoglobin D is a result of a mutation in the one or both of the Beta-chains that make up hemoglobin molecules. Having one gene effected is referred to as trait; having two is referred to as homozygous "disease" although the symptoms of this disease are mild. Hemoglobin D-Punjab was first discovered in the early 1950s in a mixed British and American family of Indian origin from the Los Angeles area; hence it is also sometimes called “D Los Angeles”. Hemoglobin D is the 4th most common hemoglobin variant. It developed as a respon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematology
Hematology ( always spelled haematology in British English) is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the cause, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to blood. It involves treating diseases that affect the production of blood and its components, such as blood cells, hemoglobin, blood proteins, bone marrow, platelets, blood vessels, spleen, and the mechanism of coagulation. Such diseases might include hemophilia, blood clots (thrombus), other bleeding disorders, and blood cancers such as leukemia, multiple myeloma, and lymphoma. The laboratory analysis of blood is frequently performed by a medical technologist or medical laboratory scientist. Specialization Physicians specialized in hematology are known as hematologists or haematologists. Their routine work mainly includes the care and treatment of patients with hematological diseases, although some may also work at the hematology laboratory viewing blood films and bone marrow slides under the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
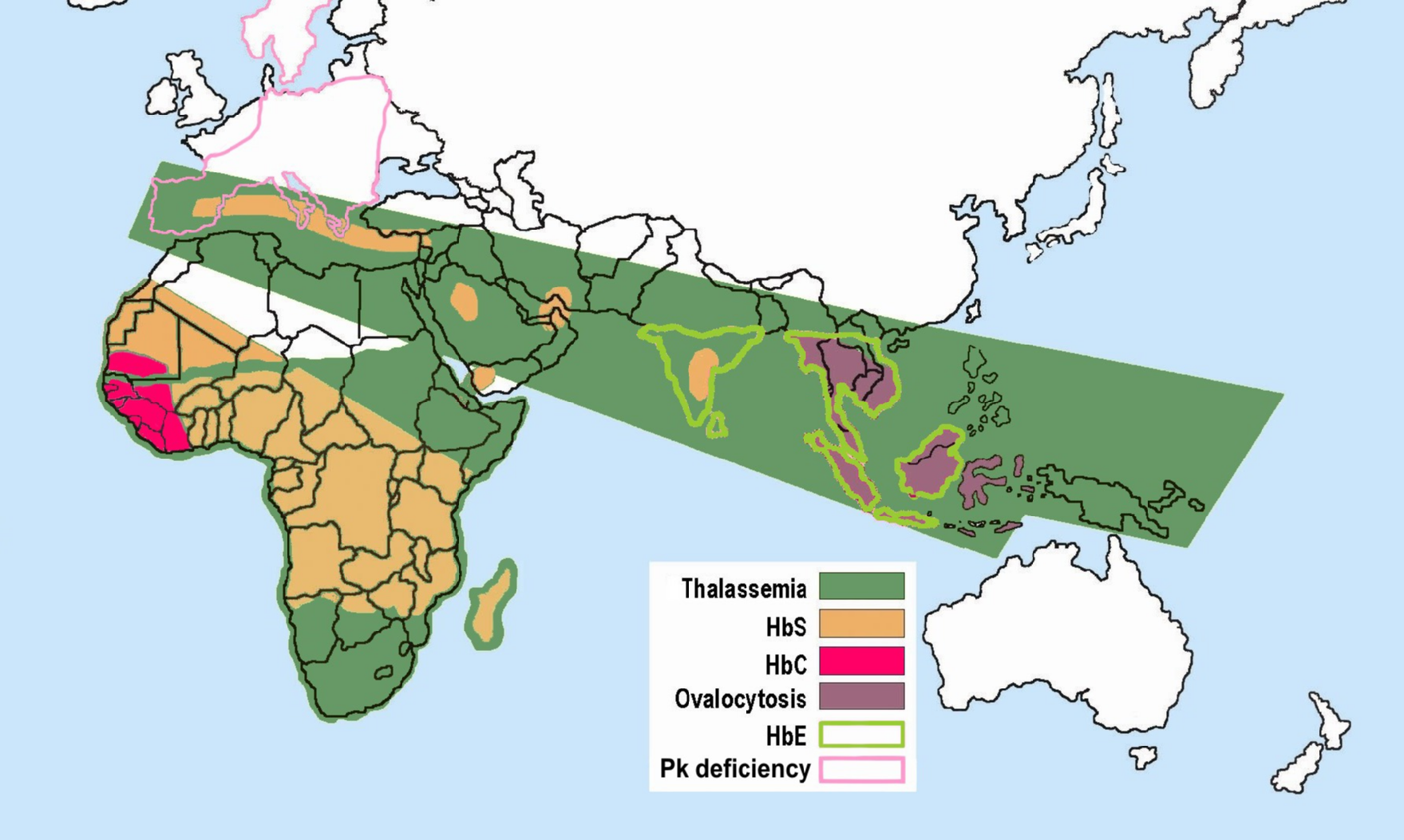
Beta-thalassemia
Beta thalassemias (β thalassemias) are a group of inherited blood disorders. They are forms of thalassemia caused by reduced or absent synthesis of the beta chains of hemoglobin that result in variable outcomes ranging from severe anemia to clinically asymptomatic individuals. Global annual incidence is estimated at one in 100,000. Beta thalassemias occur due to malfunctions in the hemoglobin subunit beta or HBB. The severity of the disease depends on the nature of the mutation. HBB blockage over time leads to decreased beta-chain synthesis. The body's inability to construct new beta-chains leads to the underproduction of HbA (adult hemoglobin). Reductions in HbA available overall to fill the red blood cells in turn leads to microcytic anemia. Microcytic anemia ultimately develops in respect to inadequate HBB protein for sufficient red blood cell functioning. Due to this factor, the patient may require blood transfusions to make up for the blockage in the beta-chains. Repeate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemoglobins
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythrocytes) of almost all vertebrates (the exception being the fish family Channichthyidae) as well as the tissues of some invertebrates. Hemoglobin in blood carries oxygen from the respiratory organs (''e.g.'' lungs or gills) to the rest of the body (''i.e.'' tissues). There it releases the oxygen to permit aerobic respiration to provide energy to power functions of an organism in the process called metabolism. A healthy individual human has 12to 20grams of hemoglobin in every 100mL of blood. In mammals, the chromoprotein makes up about 96% of the red blood cells' dry content (by weight), and around 35% of the total content (including water). Hemoglobin has an oxygen-binding capacity of 1.34mL O2 per gram, which increases the total blood oxygen ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemoglobin Lepore
Hemoglobin Lepore syndrome is typically an asymptomatic hemoglobinopathy, which is caused by an autosomal recessive genetic mutation. The Hb Lepore variant, consisting of two normal alpha globin chains (HBA) and two delta-beta globin fusion chains which occurs due to a "crossover" between the delta (HBD) and beta globin (HBB) gene loci during meiosis and was first identified in the Lepore family, an Italian-American family, in 1958. There are three varieties of Hb Lepore, Washington (Hb Lepore Washington, AKA Hb Lepore Boston or Hb Lepore Washington-Boston), Baltimore (Hb Lepore Baltimore) and Hollandia (Hb Hollandia). All three varieties show similar electrophoretic and chromatographic properties and hematological findings bear close resemblance to those of the beta-thalassemia trait; a blood disorder that reduces the production of the iron-containing protein hemoglobin which carries oxygen to cells and which may cause anemia. The homozygous state for Hb Lepore is rare. Patie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemoglobin E
Hemoglobin E (HbE) is an abnormal hemoglobin with a single point mutation in the β chain. At position 26 there is a change in the amino acid, from glutamic acid to lysine (E26K). Hemoglobin E is very common among people of Southeast Asian, Northeast Indian, Sri Lankan and Bangladeshi descent. The βE mutation affects β-gene expression creating an alternate splicing site in the mRNA at codons 25-27 of the β-globin gene. Through this mechanism, there is a mild deficiency in normal β mRNA and production of small amounts of anomalous β mRNA. The reduced synthesis of β chain may cause β-thalassemia. Also, this hemoglobin variant has a weak union between α- and β-globin, causing instability when there is a high amount of oxidant. HbE can be detected on electrophoresis. Hemoglobin E disease (EE) Hemoglobin E disease results when the offspring inherits the gene for HbE from both parents. At birth, babies homozygous for the hemoglobin E allele do not present symptoms because they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemoglobin C
Hemoglobin C (abbreviated as HbC) is an abnormal hemoglobin in which glutamic acid residue at the 6th position of the β-globin chain is replaced with a lysine residue due to a point mutation in the '' HBB'' gene. People with one copy of the gene for hemoglobin C do not experience symptoms, but can pass the abnormal gene on to their children. Those with two copies of the gene are said to have hemoglobin C disease and can experience mild anemia. It is possible for a person to have both the gene for hemoglobin S (the form associated with sickle cell anemia) and the gene for hemoglobin C; this state is called hemoglobin SC disease, and is generally more severe than hemoglobin C disease, but milder than sickle cell anemia. HbC was discovered by Harvey Itano and James V. Neel in 1950 in two African-American families. It has since been established that it is most common among people in West Africa. It confers survival benefits as individuals with HbC are naturally resistant to malaria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemoglobin S
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of blood disorders typically inherited from a person's parents. The most common type is known as sickle cell anaemia. It results in an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying protein haemoglobin found in red blood cells. This leads to a rigid, sickle-like shape under certain circumstances. Problems in sickle cell disease typically begin around 5 to 6 months of age. A number of health problems may develop, such as attacks of pain (known as a sickle cell crisis), anemia, swelling in the hands and feet, bacterial infections and stroke. Long-term pain may develop as people get older. The average life expectancy in the developed world is 40 to 60 years. Sickle cell disease occurs when a person inherits two abnormal copies of the β-globin gene (''HBB'') that makes haemoglobin, one from each parent. This gene occurs in chromosome 11. Several subtypes exist, depending on the exact mutation in each haemoglobin gene. An attack can be set off by tempera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splenomegaly
Splenomegaly is an enlargement of the spleen. The spleen usually lies in the left upper quadrant (LUQ) of the human abdomen. Splenomegaly is one of the four cardinal signs of ''hypersplenism'' which include: some reduction in number of circulating blood cells affecting granulocytes, erythrocytes or platelets in any combination; a compensatory proliferative response in the bone marrow; and the potential for correction of these abnormalities by splenectomy. Splenomegaly is usually associated with increased workload (such as in hemolytic anemias), which suggests that it is a response to hyperfunction. It is therefore not surprising that splenomegaly is associated with any disease process that involves abnormal red blood cells being destroyed in the spleen. Other common causes include congestion due to portal hypertension and infiltration by leukemias and lymphomas. Thus, the finding of an enlarged spleen, along with caput medusae, is an important sign of portal hypertension. Definiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, the symptoms are often vague, such as tiredness, weakness, shortness of breath, headaches, and a reduced ability to exercise. When anemia is acute, symptoms may include confusion, feeling like one is going to pass out, loss of consciousness, and increased thirst. Anemia must be significant before a person becomes noticeably pale. Symptoms of anemia depend on how quickly hemoglobin decreases. Additional symptoms may occur depending on the underlying cause. Preoperative anemia can increase the risk of needing a blood transfusion following surgery. Anemia can be temporary or long term and can range from mild to severe. Anemia can be caused by blood loss, decreased red blood cell production, and increased red blood cell breakdown. Causes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the world's most populous megacities. Los Angeles is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Southern California. With a population of roughly 3.9 million residents within the city limits , Los Angeles is known for its Mediterranean climate, ethnic and cultural diversity, being the home of the Hollywood film industry, and its sprawling metropolitan area. The city of Los Angeles lies in a basin in Southern California adjacent to the Pacific Ocean in the west and extending through the Santa Monica Mountains and north into the San Fernando Valley, with the city bordering the San Gabriel Valley to it's east. It covers about , and is the county seat of Los Angeles County, which is the most populous county in the United States with an estim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematology
Hematology ( always spelled haematology in British English) is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the cause, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to blood. It involves treating diseases that affect the production of blood and its components, such as blood cells, hemoglobin, blood proteins, bone marrow, platelets, blood vessels, spleen, and the mechanism of coagulation. Such diseases might include hemophilia, blood clots (thrombus), other bleeding disorders, and blood cancers such as leukemia, multiple myeloma, and lymphoma. The laboratory analysis of blood is frequently performed by a medical technologist or medical laboratory scientist. Specialization Physicians specialized in hematology are known as hematologists or haematologists. Their routine work mainly includes the care and treatment of patients with hematological diseases, although some may also work at the hematology laboratory viewing blood films and bone marrow slides under the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemoglobin Variants
Hemoglobin variants are mutant forms of hemoglobin in a population, caused by variations in genetics. Some well-known hemoglobin variants such as sickle-cell anemia Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of blood disorders typically inherited from a person's parents. The most common type is known as sickle cell anaemia. It results in an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying protein haemoglobin found in red bl ... are responsible for diseases, and are considered hemoglobinopathies. Other variants cause no detectable pathology, and are thus considered non-pathological variants. Some normal hemoglobin types are; Hemoglobin A (Hb A), which is 95–98% of hemoglobin found in adults, Hemoglobin A2 (Hb A2), which is 2–3% of hemoglobin found in adults, and Hemoglobin F (Hb F), which is found in adults up to 2.5% and is the primary hemoglobin that is produced by the fetus during pregnancy. Hemoglobin variants occur when there are genetic changes in specific genes, or globins, that ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |