Beta-thalassemia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Beta thalassemias (β thalassemias) are a group of inherited blood disorders. They are forms of
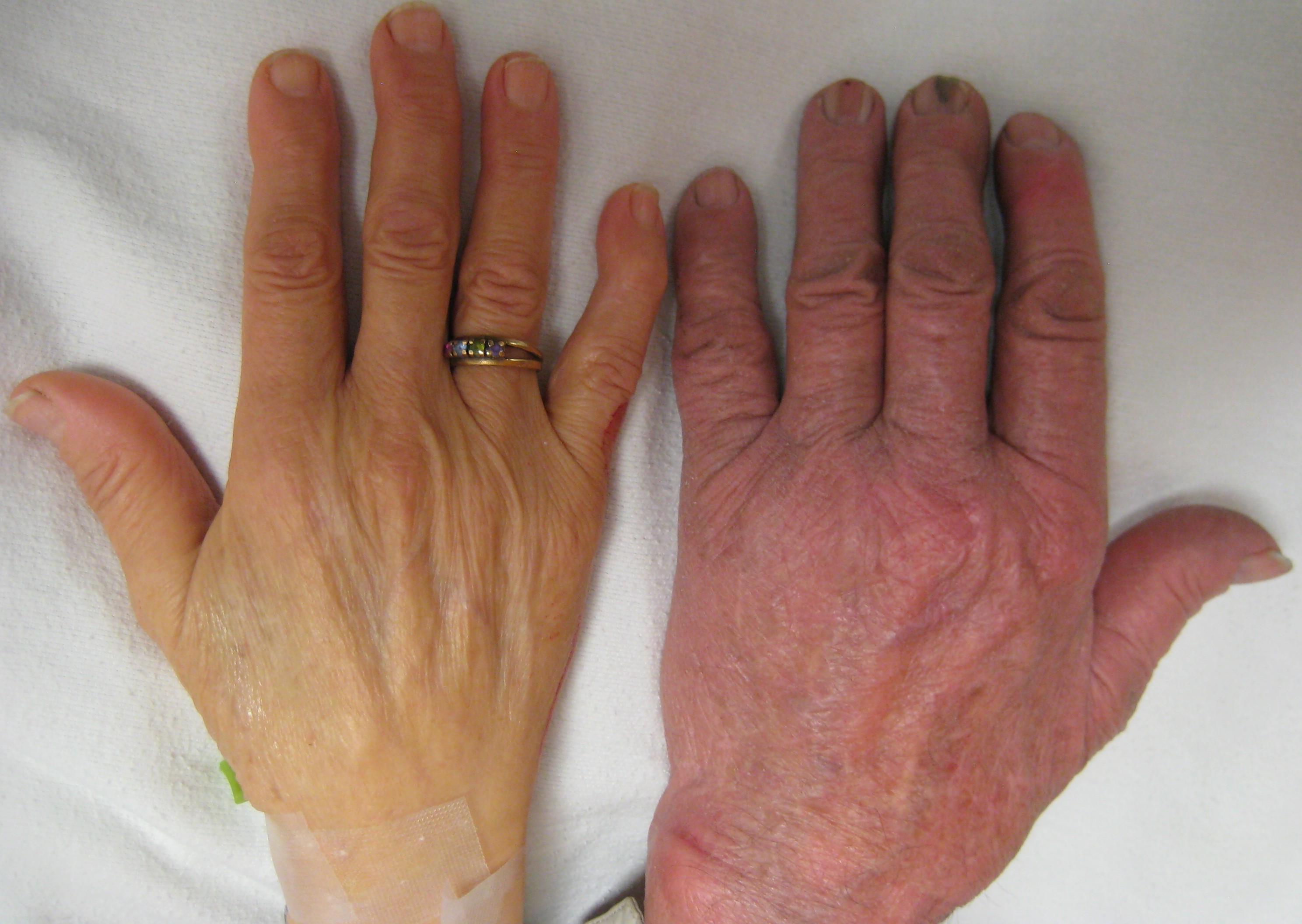 Three main forms have been described: thalassemia minor, thalassemia intermedia, and thalassemia major which vary from asymptomatic or mild symptoms to severe anemia requiring lifelong transfusions. Individuals with beta thalassemia major (those who are homozygous for thalassemia mutations, or inheriting 2 mutations) usually present within the first two years of life with symptomatic severe anemia, poor growth, and skeletal abnormalities. Untreated thalassemia major eventually leads to death, usually by
Three main forms have been described: thalassemia minor, thalassemia intermedia, and thalassemia major which vary from asymptomatic or mild symptoms to severe anemia requiring lifelong transfusions. Individuals with beta thalassemia major (those who are homozygous for thalassemia mutations, or inheriting 2 mutations) usually present within the first two years of life with symptomatic severe anemia, poor growth, and skeletal abnormalities. Untreated thalassemia major eventually leads to death, usually by
 Beta thalassemia is a hereditary disease affecting hemoglobin. As with about half of all hereditary diseases, an inherited mutation damages the assembly of the messenger-type RNA (mRNA) that is transcribed from a
Beta thalassemia is a hereditary disease affecting hemoglobin. As with about half of all hereditary diseases, an inherited mutation damages the assembly of the messenger-type RNA (mRNA) that is transcribed from a
 Abdominal pain due to hypersplenism,
Abdominal pain due to hypersplenism,
 Affected children require regular lifelong
Affected children require regular lifelong
thalassemia
Thalassemias are inherited blood disorders characterized by decreased hemoglobin production. Symptoms depend on the type and can vary from none to severe. Often there is mild to severe anemia (low red blood cells or hemoglobin). Anemia can resul ...
caused by reduced or absent synthesis of the beta chains of hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythroc ...
that result in variable outcomes ranging from severe anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, t ...
to clinically asymptomatic individuals. Global annual incidence is estimated at one in 100,000. Beta thalassemias occur due to malfunctions in the hemoglobin subunit beta or HBB. The severity of the disease depends on the nature of the mutation.
HBB blockage over time leads to decreased beta-chain synthesis. The body's inability to construct new beta-chains leads to the underproduction of HbA (adult hemoglobin). Reductions in HbA available overall to fill the red blood cells in turn leads to microcytic anemia. Microcytic anemia ultimately develops in respect to inadequate HBB protein for sufficient red blood cell functioning. Due to this factor, the patient may require blood transfusions to make up for the blockage in the beta-chains.
Repeated blood transfusions cause severe problems associated with iron overload
Iron overload or hemochromatosis (also spelled ''haemochromatosis'' in British English) indicates increased total accumulation of iron in the body from any cause and resulting organ damage. The most important causes are hereditary haemochromato ...
.
Signs and symptoms
heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, ...
; therefore, prenatal screening is very important. Those with beta thalassemia intermedia (those who are compound heterozygoutes for the beta thalassemia mutation) usually present later in life with mild to moderate symptoms of anemia. Beta thalassemia trait (also known as beta thalassemia minor) involves heterozygous
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
...
inheritance of a beta-thalassemia mutation and patients usually have borderline microcytic, hypochromic anemia and they are usually asymptomatic or have mild symptoms. Beta thalassemia minor can also present as beta thalassemia silent carriers; those who inherit a beta thalassemic mutation but have no hematologic abnormalities nor symptoms. Some people with thalassemia are susceptible to health complications that involve the spleen
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes .
(hypersplenism) and gallstone
A gallstone is a stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of mi ...
s (due to hyperbilirubinemia
Bilirubin (BR) (Latin for "red bile") is a red-orange compound that occurs in the normal catabolic pathway that breaks down heme in vertebrates. This catabolism is a necessary process in the body's clearance of waste products that arise from the ...
from peripheral hemolysis). These complications are mostly found in thalassemia major and intermedia patients.
Excess iron (from hemolysis
Hemolysis or haemolysis (), also known by several other names, is the rupturing ( lysis) of red blood cells (erythrocytes) and the release of their contents ( cytoplasm) into surrounding fluid (e.g. blood plasma). Hemolysis may occur in viv ...
or transfusions
Blood transfusion is the process of transferring blood products into a person's circulation intravenously. Transfusions are used for various medical conditions to replace lost components of the blood. Early transfusions used whole blood, but mo ...
) causes serious complications within the liver, heart, and endocrine gland
Endocrine glands are ductless glands of the endocrine system that secrete their products, hormones, directly into the blood. The major glands of the endocrine system include the pineal gland, pituitary gland, pancreas, ovaries, testes, thy ...
s. Severe symptoms include liver cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue repai ...
, liver fibrosis, and in extreme cases, liver cancer
Liver cancer (also known as hepatic cancer, primary hepatic cancer, or primary hepatic malignancy) is cancer that starts in the liver. Liver cancer can be primary (starts in liver) or secondary (meaning cancer which has spread from elsewhere to th ...
. Heart failure, growth impairment, diabetes and osteoporosis are life-threatening conditions which can be caused by beta thalassemia major. The main cardiac abnormalities seen as a result of beta thalassemia and iron overload include left ventricular systolic and diastolic dysfunction, pulmonary hypertension, valvulopathy, arrhythmias, and pericarditis. Increased gastrointestinal iron absorption is seen in all grades of beta thalassemia, and increased red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "hol ...
destruction by the spleen due to ineffective erythropoiesis
Erythropoiesis (from Greek 'erythro' meaning "red" and 'poiesis' "to make") is the process which produces red blood cells (erythrocytes), which is the development from erythropoietic stem cell to mature red blood cell.
It is stimulated by decrea ...
further releases additional iron into the bloodstream
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
.
Additional symptoms of beta thalassemia major or intermedia include the classic symptoms of moderate to severe anemia including fatigue, growth and developmental delay in childhood, leg ulcers and organ failure. Ineffective erythropoiesis
Erythropoiesis (from Greek 'erythro' meaning "red" and 'poiesis' "to make") is the process which produces red blood cells (erythrocytes), which is the development from erythropoietic stem cell to mature red blood cell.
It is stimulated by decrea ...
(red blood cell production) can also lead to compensatory bone marrow expansion which can then lead to bony changes/deformities, bone pain and craniofacial abnormalities. Extramedullary organs such as the liver and spleen that can also undergo erythropoiesis become activated leading to hepatosplenomegaly
Hepatosplenomegaly (commonly abbreviated HSM) is the simultaneous enlargement of both the liver (hepatomegaly) and the spleen (splenomegaly). Hepatosplenomegaly can occur as the result of acute viral hepatitis, infectious mononucleosis, and his ...
(enlargement of the liver and spleen). Other tissues in the body can also become sites of erythropoiesis, leading to extramedullary hematopoietic pseudotumors which may cause compressive symptoms if they occur in the thoracic cavity or spinal canal.
Cause
Mutations
Two major groups of mutations can be distinguished: * Nondeletion forms: These defects, in general, involve a single base substitution or small insertions near or upstream of the β globin gene. Most often, mutations occur in the promoter regions preceding the beta-globin genes. Less often, abnormal splice variants are believed to contribute to the disease. * Deletion forms: Deletions of different sizes involving the β globin gene produce different syndromes such as (βo) orhereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin
Hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin (HPFH) is a benign condition in which increased fetal hemoglobin (hemoglobin F, HbF) production continues well into adulthood, disregarding the normal shutoff point after which only adult-type hemoglobin s ...
syndromes.
Mutations are characterized as (βo) if they prevent any formation of β globin chains, mutations are characterized as (β+) if they allow some β globin chain formation to occur.
mRNA assembly
 Beta thalassemia is a hereditary disease affecting hemoglobin. As with about half of all hereditary diseases, an inherited mutation damages the assembly of the messenger-type RNA (mRNA) that is transcribed from a
Beta thalassemia is a hereditary disease affecting hemoglobin. As with about half of all hereditary diseases, an inherited mutation damages the assembly of the messenger-type RNA (mRNA) that is transcribed from a chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins ar ...
. DNA contains both the instructions (gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s) for stringing amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha ...
s together into protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
s, as well as stretches of DNA that play important roles in regulating produced protein levels.
In thalassemia, an additional, contiguous length or a discontinuous fragment of non-coding instructions is included in the mRNA. This happens because the mutation obliterates the boundary between the intron
An intron is any Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence within a gene that is not expressed or operative in the final RNA product. The word ''intron'' is derived from the term ''intragenic region'', i.e. a region inside a gene."The notion of ...
ic and exon
An exon is any part of a gene that will form a part of the final mature RNA produced by that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. The term ''exon'' refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and to the corresponding sequen ...
ic portions of the DNA template. Because all the coding sections may still be present, normal hemoglobin may be produced and the added genetic material, if it produces pathology, instead disrupts regulatory functions enough to produce anemia. Hemoblogin's normal alpha and beta subunits each have an iron-containing central portion (heme) that allows the protein chain of a subunit to fold around it. Normal adult hemoglobin contains 2 alpha and 2 beta subunits. Thalassemias typically affect only the mRNAs for production of the beta chains (hence the name). Since the mutation may be a change in only a single base (single-nucleotide polymorphism
In genetics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently ...
), on-going efforts seek gene therapies to make that single correction.
Risk factors
Family history and ancestry are factors that increase the risk of beta thalassemia. Depending on family history, if a person's parents or grandparents had beta thalassemia major or intermedia, there is a 75% (3 out of 4) probability (see inheritance chart at top of page) of the mutated gene being inherited by an offspring. Even if a child does not have beta thalassemia major or intermedia, they can still be a carrier, possibly resulting in future generations of their offspring having beta thalassemia. Another risk factor is ancestry. Beta thalassemia occurs most often in people of Italian, Greek, Middle Eastern, Southern Asian, and African ancestry.Diagnosis
 Abdominal pain due to hypersplenism,
Abdominal pain due to hypersplenism, splenic infarction
Splenic infarction is a condition in which blood flow supply to the spleen is compromised, leading to partial or complete infarction (tissue death due to oxygen shortage) in the organ. Splenic infarction occurs when the splenic artery or one of ...
and right-upper quadrant pain caused by gallstones
A gallstone is a stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of mi ...
are major clinical manifestations. However, diagnosing thalassemia from symptoms alone is inadequate. Physicians note these signs as associative due to this disease's complexity. The following associative signs can attest to the severity of the phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (biology), morphology or physical form and structure, its Developmental biology, developmental proc ...
: pallor, poor growth, inadequate food intake, splenomegaly
Splenomegaly is an enlargement of the spleen. The spleen usually lies in the left upper quadrant (LUQ) of the human abdomen. Splenomegaly is one of the four cardinal signs of ''hypersplenism'' which include: some reduction in number of circulatin ...
, jaundice
Jaundice, also known as icterus, is a yellowish or greenish pigmentation of the skin and sclera due to high bilirubin levels. Jaundice in adults is typically a sign indicating the presence of underlying diseases involving abnormal heme meta ...
, maxillary hyperplasia, dental malocclusion, cholelithiasis
A gallstone is a stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of mig ...
, systolic ejection murmur in the presence of severe anemia and pathologic fractures. Based on symptoms, tests are ordered for a differential diagnosis
In healthcare, a differential diagnosis (abbreviated DDx) is a method of analysis of a patient's history and physical examination to arrive at the correct diagnosis. It involves distinguishing a particular disease or condition from others that p ...
. These tests include complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blood cells, red blood cells and ...
; hemoglobin electrophoresis; serum transferrin, ferritin
Ferritin is a universal intracellular protein that stores iron and releases it in a controlled fashion. The protein is produced by almost all living organisms, including archaea, bacteria, algae, higher plants, and animals. It is the primary ...
, total iron-binding capacity; urine urobilin and urobilogen; peripheral blood smear, which may show codocytes, or target cells; hematocrit; and serum bilirubin. The expected pattern on hemoglobin electrophoresis in people with beta-thalassemia is an increased level of hemoglobin A2
Hemoglobin A2 (HbA2) is a normal variant of hemoglobin A that consists of two alpha and two delta chains (α2δ2) and is found at low levels in normal human blood. Hemoglobin A2 may be increased in beta thalassemia or in people who are heterozy ...
and slightly increased hemoglobin F
Fetal hemoglobin, or foetal haemoglobin (also hemoglobin F, HbF, or α2γ2) is the main oxygen carrier protein in the human fetus. Hemoglobin F is found in fetal red blood cells, and is involved in transporting oxygen from the mother's bloodstrea ...
. The diagnosis is confirmed with hemoglobin electrophoresis or high performance liquid chromatography.
Skeletal changes associated with expansion of the bone marrow:
* Chipmunk facies
Chipmunks are small, striped rodents of the family Sciuridae. Chipmunks are found in North America, with the exception of the Siberian chipmunk which is found primarily in Asia.
Taxonomy and systematics
Chipmunks may be classified either as a ...
: bossing of the skull, prominent malar eminence, depression of the bridge of the nose, tendency to a mongoloid slant of the eye, and exposure of the upper teeth due to hypertrophy of the maxillae.
* Hair-on-end (or "crew cut") on skull X-ray: new bone formation due to the inner table.
DNA analysis
All beta thalassemias may exhibit abnormal red blood cells; a family history is followed by DNA analysis. This test is used to investigate deletions and mutations in the alpha- and beta-globin-producing genes. Family studies can be done to evaluate carrier status and the types of mutations present in other family members. DNA testing is not routine, but can help diagnose thalassemia and determine carrier status. In most cases the treating physician uses a clinical prediagnosis assessing anemia symptoms: fatigue, breathlessness and poor exercise tolerance. Further genetic analysis may includeHPLC
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), formerly referred to as high-pressure liquid chromatography, is a technique in analytical chemistry used to separate, identify, and quantify each component in a mixture. It relies on pumps to p ...
should routine electrophoresis prove difficult.
Prevention
Beta thalassemia is a hereditary disease allowing for a preventative treatment by carrier screening and prenatal diagnosis. It can be prevented if one parent has normal genes, giving rise to screenings that empower carriers to select partners with normal hemoglobin. A study aimed at detecting the genes that could give rise to offspring with sickle cell disease. Patients diagnosed with beta thalassemia have MCH ≤ 26 pg and an RDW < 19. Of 10,148 patients, 1,739 patients had a hemoglobin phenotype and RDW consistent with beta thalassemia. After the narrowing of patients, the HbA2 levels were tested presenting 77 patients with beta thalassemia. This screening procedure proved insensitive in populations of West African ancestry because of the indicators has high prevalence of alpha thalassemia. Countries have programs distributing information about the reproductive risks associated with carriers of haemoglobinopathies. Thalassemia carrier screening programs have educational programs in schools, armed forces, and through mass media as well as providing counseling to carriers and carrier couples. Screening has shown reduced incidence; by 1995 the prevalence in Italy reduced from 1:250 to 1:4000, and a 95% decrease in that region. The decrease in incidence has benefitted those affected with thalassemia, as the demand for blood has decreased, therefore improving the supply of treatment.Treatment
Beta thalassemia major
 Affected children require regular lifelong
Affected children require regular lifelong blood transfusion
Blood transfusion is the process of transferring blood products into a person's circulation intravenously. Transfusions are used for various medical conditions to replace lost components of the blood. Early transfusions used whole blood, but mo ...
s. Bone marrow transplants can be curative for some children. Patients receive frequent blood transfusions that lead to or potentiate iron overload
Iron overload or hemochromatosis (also spelled ''haemochromatosis'' in British English) indicates increased total accumulation of iron in the body from any cause and resulting organ damage. The most important causes are hereditary haemochromato ...
. Iron chelation treatment is necessary to prevent damage to internal organs in cases of iron overload. Advances in iron chelation treatments allow patients with thalassemia major to live long lives with access to proper treatment. Popular chelators include deferoxamine
Deferoxamine (DFOA), also known as desferrioxamine and sold under the brand name Desferal, is a medication that binds iron and aluminium. It is specifically used in iron overdose, hemochromatosis either due to multiple blood transfusions or an ...
and deferiprone.
The oral chelator deferasirox
Deferasirox, sold under the brand name Exjade & Asunra (in injectable form) & Oleptiss (Tablet formulation) both by Novartis among others, is an oral iron chelator. Its main use is to reduce chronic iron overload in patients who are receiving ...
was approved for use in 2005 in some countries. Bone marrow transplant
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood in order to replicate inside of a patient and to produce ...
ation is the only cure and is indicated for patients with severe thalassemia major. Transplantation can eliminate a patient's dependence on transfusions. Absent a matching donor, a savior sibling
A savior baby or savior sibling is a child who is conceived in order to provide a stem cell transplant to a sibling that is affected with a fatal disease, such as cancer or Fanconi anemia, that can best be treated by hematopoietic stem cell transp ...
can be conceived by preimplantation genetic diagnosis
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD or PIGD) is the genetic profiling of embryos prior to implantation (as a form of embryo profiling), and sometimes even of oocytes prior to fertilization. PGD is considered in a similar fashion to prenatal ...
(PGD) to be free of the disease as well as to match the recipient's human leukocyte antigen
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system or complex is a complex of genes on chromosome 6 in humans which encode cell-surface proteins responsible for the regulation of the immune system. The HLA system is also known as the human version of th ...
(HLA) type.
Serum ferritin
Ferritin is a universal intracellular protein that stores iron and releases it in a controlled fashion. The protein is produced by almost all living organisms, including archaea, bacteria, algae, higher plants, and animals. It is the primary ...
(the storage form of iron) is routinely measured in those with beta thalassemia to determine the degree of iron overload; with increased ferritin levels directing the use of iron chelation therapy. The three iron chelators; subcutaneous deferoxamine
Deferoxamine (DFOA), also known as desferrioxamine and sold under the brand name Desferal, is a medication that binds iron and aluminium. It is specifically used in iron overdose, hemochromatosis either due to multiple blood transfusions or an ...
, oral deferiprone and oral deferasirox
Deferasirox, sold under the brand name Exjade & Asunra (in injectable form) & Oleptiss (Tablet formulation) both by Novartis among others, is an oral iron chelator. Its main use is to reduce chronic iron overload in patients who are receiving ...
can be used as monotherapy or in combination, they have all been shown to decrease serum/systemic iron levels, hepatic and cardiac iron levels as well as decreasing the risk of cardiac arrhythmia, heart failure and death. Hepatic and myocardial MRI is also used to quantify the iron deposition in target organs, especially the heart and liver, to guide therapy.
Scientists at Weill Cornell Medical College
The Joan & Sanford I. Weill Medical College of Cornell University is Cornell University's biomedical research unit and medical school located in Upper East Side, Manhattan, New York City, New York.
Weill Cornell Medicine is affiliated with ...
have developed a gene therapy strategy that could feasibly treat both beta-thalassemia and sickle cell disease. The technology is based on delivery of a lentiviral vector carrying both the human β-globin gene and an ankyrin insulator to improve gene transcription and translation, and boost levels of β-globin production.
On June 10, 2022, a U.S. federal advisory panel recommended that the FDA approve a gene therapy treatment for use with beta thalassemia.
Surgical
Patients with thalassemia major are more inclined to have a splenectomy. The use of splenectomies have been declining in recent years due to decreased prevalence of hypersplenism in adequately transfused patients. Splenectomy is also associated with increased risk of infections and increased morbidity due to vascular disease, as the spleen is involved in scavenging to rid the body of pathologic or abnormal red blood cells. Patients with hypersplenism are more likely to have a lower amount of healthy blood cells in their body than normal and reveal symptoms of anemia. The different surgical techniques are the open and laparoscopic method. The laparoscopic method requires longer operating time but a shorter recovery period with a smaller and less prominent surgical scar. If it is unnecessary to remove the entire spleen a partial splenectomy may occur; this method preserves some of the immune function while reducing the probability of hypersplenism. Those undergoing splenectomy should receive an appropriate pneumococcal vaccine at least one week (preferably three weeks) before the surgery.Therapeutic
Long-term transfusion therapy (in those with transfusion dependent beta thalassemia) is a treatment used to maintain hemoglobin levels at a target pre-transfusion hemoglobin level of 9–10.5 g/dL (11-12 g/dL in those with concomitant heart disease). To ensure quality blood transfusions, the packed red blood cells should be leucoreduced. By having leucoreduced blood packets, the patient is at a lower risk to develop adverse reactions by contaminated white cells and preventing platelet alloimmunisation. Patients with allergic transfusion reactions or unusual red cell antibodies must receive washed red cells or cryopreserved red cells. Washed red cells have been removed of plasma proteins that would have become a target of the patient's antibodies allowing the transfusion to be carried out safely. Cryopreserved red cells are used to maintain a supply of rare donor units for patients with unusual red cell antibodies or missing common red cell antigens. These regular transfusions promote normal growth, physical activities and suppress bone marrow hyperactivity.Pharmaceutical
During normal iron homeostasis the circulating iron is bound to transferrin. But with iron overload (such as with frequent blood transfusions), the ability for transferrin to bind iron is exceeded and non-transferrin bound iron accumulated. This unbound iron is toxic due to its high propensity to induce oxygen species and is responsible for cellular damage. The prevention of iron overload protects patients from morbidity and mortality. The primary aim is to bind to and remove iron from the body and a rate equal to the rate of transfusional iron input or greater than iron input. Iron chelation is a medical therapy that may prevent the complications of iron overload. Every unit of transfused blood contains 200–250 mg of iron and the body has no natural mechanism to remove excess iron. The excess iron can be removed by iron chelators (deferoxamine, deferiprone and deferasirox). Luspatercept (ACE-536) is a recombinant fusion protein that is used as a treatment in adults with transfusion dependent beta thalassemia. It consists of a modified extra-cellular domain of human activin receptor type IIB bound to the Fc portion of the human IgG1 antibody. The molecule binds to select transforming growth factor beta superfamily ligands to block SMAD2 and 3 signaling, thus enhancing erythroid maturation. The medication has been shown to reduce the transfusion burden by 33% in adults with transfusion dependent beta thalassemia as compared to placebo and was also associated with decreased ferritin levels (with no significant decreases in liver or cardiac iron levels).Beta thalassemia intermedia
Patients with beta thalassemia intermedia require no transfusions or may require episodic blood transfusions during certain circumstances (infection, pregnancy, surgery). Patients with frequent transfusions may developiron overload
Iron overload or hemochromatosis (also spelled ''haemochromatosis'' in British English) indicates increased total accumulation of iron in the body from any cause and resulting organ damage. The most important causes are hereditary haemochromato ...
and require chelation therapy
Chelation therapy is a medical procedure that involves the administration of chelating agents to remove heavy metals from the body. Chelation therapy has a long history of use in clinical toxicology and remains in use for some very specific me ...
. Transmission is autosomal recessive
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant ( allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant an ...
; however, dominant mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, m ...
s and compound heterozygotes have been reported. Genetic counseling
Genetic counseling is the process of investigating individuals and families affected by or at risk of genetic disorders to help them understand and adapt to the medical, psychological and familial implications of genetic contributions to disease; t ...
is recommended and prenatal diagnosis may be offered.
Beta thalassemia minor
Patients with beta thalassemia minor are usually asymptomatic and are often monitored without treatment. Beta thalassemia minor may coexist with other conditions such as chronic hepatitis B, chronic hepatitis C,non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), also known as metabolic (dysfunction) associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), is excessive fat build-up in the liver without another clear cause such as alcohol use. There are two types; non-alcoholic ...
and alcoholic liver disease
Alcoholic liver disease (ALD), also called alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD), is a term that encompasses the liver manifestations of alcohol overconsumption, including fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and chronic hepatitis with liver fibros ...
that, when combined or co-existing, may cause a person to have iron overload of the liver and more severe liver disease.
Epidemiology
The beta form of thalassemia is particularly prevalent among theMediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
peoples and this geographical association is responsible for its naming: ''thalassa
Thalassa (; grc-gre, Θάλασσα, Thálassa, sea; Attic Greek: , ''Thálatta'') was the general word for 'sea' and for its divine female personification in Greek mythology. The word may have been of Pre-Greek origin.
Mythology
According to ...
'' (''θάλασσα'') is the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
word for sea and ''haima'' (''αἷμα'') is the Greek word for blood. In Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
, the highest concentrations of the disease are found in Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wi ...
and the Turkish coastal regions. The major Mediterranean islands
The following is a list of islands in the Mediterranean Sea. The two main island countries in the region are Malta and Cyprus, while other countries with islands in the Mediterranean Sea include Italy, France, Greece, Spain, Tunisia, Croatia, ...
(except the Balearics) such as Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label=Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label= Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, aft ...
, Corsica
Corsica ( , Upper , Southern ; it, Corsica; ; french: Corse ; lij, Còrsega; sc, Còssiga) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the 18 regions of France. It is the fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of ...
, Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ...
, Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
and Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, ...
are heavily affected in particular. Other Mediterranean people
The Mediterranean race (also Mediterranid race) was a historical race concept that was a sub-race of the Caucasian race as categorised by anthropologists in the late 19th to mid-20th centuries. According to various definitions, it was said to be ...
s, as well as those in the vicinity of the Mediterranean, also have high incidence rates, including people from West Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes ...
and North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
. The data indicate that 15% of the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and Turkish Cypriots
Turkish Cypriots or Cypriot Turks ( tr, Kıbrıs Türkleri or ''Kıbrıslı Türkler''; el, Τουρκοκύπριοι, Tourkokýprioi) are ethnic Turks originating from Cyprus. Following the Ottoman conquest of the island in 1571, about 30,0 ...
are carriers of beta-thalassaemia genes, while 10% of the population carry alpha-thalassaemia genes.
Evolutionary adaptation
The thalassemia trait may confer a degree of protection againstmalaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. ...
, which is or was prevalent in the regions where the trait is common, thus conferring a selective survival advantage on carriers (known as heterozygous advantage
A heterozygote advantage describes the case in which the heterozygous genotype has a higher relative fitness than either the homozygous dominant or homozygous recessive genotype. Loci exhibiting heterozygote advantage are a small minority of lo ...
), thus perpetuating the mutation. In that respect, the various thalassemias resemble another genetic disorder
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders ...
affecting hemoglobin, sickle-cell disease
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of blood disorders typically inherited from a person's parents. The most common type is known as sickle cell anaemia. It results in an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying protein haemoglobin found in red ...
.
Incidence
The disorder is more prevalent in certain ethnicities and age groups. Beta thalassemia is most prevalent in the "thalassemia belt" which includes areas in Sub-Saharan Africa, the Mediterranean extending into the Middle East and Southeast Asia. This geographical distribution is thought to be due to beta-thalassemia carrier state (beta thalassemia minor) conferring a resistance to malaria. In the United States, thalassemia's prevalence is approximately 1 in 272,000 or 1,000 people. There have been 4,000 hospitalized cases in England in 2002 and 9,233 consultant episodes for thalassemia. Men accounted for 53% of hospital consultant episodes and women accounted for 47%. The mean patient age is 23, with only 1% of consultants being older than 75, and 69% being 15–59. It is estimated that 1.5% of the world's population are carriers and 40,000 affected infants are born with the disease annually. Beta thalassemia major is usually fatal in infancy if blood transfusions are not initiated immediately.See also
*Alpha-thalassemia
Alpha-thalassemia (α-thalassemia, α-thalassaemia) is a form of thalassemia involving the genes '' HBA1'' and '' HBA2''. Thalassemias are a group of inherited blood conditions which result in the impaired production of hemoglobin, the molecule ...
* Anisopoikilocytosis (variance in red blood cell size, usually as a result of beta thalassemia)
* Delta-thalassemia
Delta-beta thalassemia is a rare form of thalassemia in which there is a reduced production of hemoglobin subunit delta and hemoglobin subunit beta and raised levels of hemoglobin subunit gamma. It is an autosomal recessive disorder.
Signs and ...
* Hemoglobinopathy
References
Further reading
* *External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Beta-Thalassemia Disorders of globin and globulin proteins Hereditary hemolytic anemias Rare diseases