|
Hemamieh
Hemamieh (El-Hammamiya) is a village located in the Sohag Governorate in Middle Egypt on the east bank of the Nile. The site is significant in Egyptology because of its cemeteries from the Prehistoric Egypt, Prehistoric and Pharaoh, Pharaonic periods. From 1922 to 1931 the British archaeologists Gertrude Caton-Thompson and Guy Brunton excavated approximately 10,000 tombs from Qau el-Kebir in the south to Matmar in the north, across an area of about 36 km. At Hemamieh there were some smaller cemeteries, including important burials of the Badari culture and rock tombs of the Old Kingdom period belonging to the nomarchs of the Aphroditopolis Nome, Wadjit-nome. The best preserved one belongs to Kaikhenet (II), who lived at the beginning of the Fifth Dynasty. References *G. Brunton, G. Caton-Thompson: The Badarian civilisation and predynastic remains near Badari (= British School of Archeology in Egypt Publications Bd. 46). British School of Archaeology in Egypt, London 1928. *Guy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaikhenet (II)
Kaikhenet was an ancient Egyptian local governor in the Aphroditopolis Nome, 10th Upper Egyptian province; the latter called Wadjet in Egyptian language. Kaikhenet lived at the beginning of the Fifth Dynasty and is known from his decorated rock cut tomb at Hemamieh. Decorated rock cut tombs are very rare in the Egyptian province before the end of the Fifth Dynasty. The tombs at Hemamieh are an exception. They belong to the earliest ones in the provinces. Kaikhenet (II) was most likely the son of another governor also called Kaikhenet (I). The father-son relation of both governors is not fully certain but in the tomb of Kaikhenet (I) is depicted a son called Kaikhenet, that might be Kaikhenet (II). If this identification is correct, his mother was most likely Khentkaus, the wife of Kaikhenet (I). Kaikhenet's (II) wife was a woman called Iufi. She bore several titles, including ''acquaintance of the king'', ''priestess of Neith, north of the wall'', ''priestess of Hathor, lady of Den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gertrude Caton-Thompson
Gertrude Caton Thompson, (1 February 1888 – 18 April 1985) was an English archaeologist at a time when participation by women in the discipline was uncommon. Much of her archaeological work was conducted in Egypt. However, she also worked on expeditions in Zimbabwe, Malta, and South Arabia. Her notable contributions to the field of archaeology include creating a technique for excavating archaeological sites and information on Paleolithic to Predynastic civilizations in Zimbabwe and Egypt. Caton Thompson held many official positions in organizations such as the Prehistoric Society and the Royal Anthropological Institute. Early life Gertrude Caton Thompson was born to William Caton Thompson and Ethel Page in 1888 in London, England, and attended private schools in Paris and in Eastbourne, including the Links School, run by Miss Hawtrey. Her interest in archaeology began on a trip to Egypt with her mother in 1911, followed by a series of lectures on Ancient Greece given by Sarah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sohag Governorate
Sohag Governorate is one of the governorates of Egypt. It is located in the southern part of the country (Upper Egypt), and covers a stretch of the Nile Valley. Since 1960, its capital has been the city of Sohag. Prior to that, the capital was the city of Girga and the name of the governorate was Girga Governorate. Overview The rate of poverty is more than 60% in this governorate but recently some social safety networks have been provided in the form of financial assistance and job opportunities. The funding has been coordinated by the country's Ministry of Finance and with assistance from international organizations. In early 2019, some residents of the poorer villages of Sohag were able to move into their new homes built, in part, with aid from the National Bank of Kuwait. There was a celebration for the completion of 115 homes where residents also received cattle and other gifts. Archaeology In April 2019, the archaeological mission of the Ministry of Antiquities led by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Egypt
Middle Egypt () is the section of land between Lower Egypt (the Nile Delta) and Upper Egypt, stretching upstream from Asyut in the south to Memphis in the north. At the time, Ancient Egypt was divided into Lower and Upper Egypt, though Middle Egypt was technically a subdivision of Upper Egypt. It was not until the 19th century that archaeologists felt the need to divide Upper Egypt in two. As a result, they coined the term "Middle Egypt" for the stretch of river between Cairo and the Qena Bend. It was also associated with a region termed "Heptanomis" (; Greek: , in Ptol. iv. 5. § 55; more properly or , in Dionysius Periegetes 251; and sometimes ; meaning "Seven Nomes", a " nome" being a subdivision of ancient Egypt), generally as the district which separates the Thebaïd from the Delta. Middle Egypt today can be identified as the part of the Nile Valley that, while geographically part of Upper Egypt, is culturally closer to Lower Egypt. For instance, in terms of language, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin language, Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the List of rivers by length, longest river in the world, though this has been contested by research suggesting that the Amazon River is slightly longer.Amazon Longer Than Nile River, Scientists Say Of the world's major rivers, the Nile is one of the smallest, as measured by annual flow in cubic metres of water. About long, its drainage basin covers eleven countries: the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania, Burundi, Rwanda, Uganda, Kenya, Ethiopia, Erit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Egypt
Prehistoric Egypt and Predynastic Egypt span the period from the earliest human settlement to the beginning of the Early Dynastic Period around 3100 BC, starting with the first Pharaoh, Narmer for some Egyptologists, Hor-Aha for others, with the name Menes also possibly used for one of these kings. At the end of prehistory, "Predynastic Egypt" is traditionally defined as the period from the final part of the Neolithic period beginning c. 6000 BC to the end of the Naqada III period c. 3000 BC. The dates of the Predynastic period were first defined before widespread archaeological excavation of Egypt took place, and recent finds indicating very gradual Predynastic development have led to controversy over when exactly the Predynastic period ended. Thus, various terms such as " Protodynastic period", "Zero Dynasty" or "Dynasty 0" are used to name the part of the period which might be characterized as Predynastic by some and Early Dynastic by others. The Predynastic period is genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: ''pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the annexation of Egypt by the Roman Empire in 30 BC. However, regardless of gender, "king" was the term used most frequently by the ancient Egyptians for their monarchs through the middle of the Eighteenth Dynasty during the New Kingdom. The term "pharaoh" was not used contemporaneously for a ruler until a possible reference to Merneptah, c. 1210 BC during the Nineteenth Dynasty, nor consistently used until the decline and instability that began with the Twenty-Fifth Dynasty. In the early dynasties, ancient Egyptian kings had as many as three titles: the Horus, the Sedge and Bee ( ''nswt-bjtj''), and the Two Ladies or Nebty ( ''nbtj'') name. The Golden Horus and the nomen and prenomen titles were added later. In Egyptian society, religio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guy Brunton
Guy Brunton (1878 in London, England – 17 October 1948 in White River, Mpumalanga, South Africa) was an English archaeologist and Egyptologist who discovered the Badarian predynastic culture. He married Winifred Newberry on 28 April 1906. Her father built Prynnsberg Estate. He served in the First World War and returned to archaeology becoming assistant director of the Cairo Museum in 1931, he retired to South Africa. A student of Sir Flinders Petrie, Brunton became Assistant Director of the Egyptian Museum in Cairo Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo metro ... in 1931. References Publications * * * * * * 1878 births 1948 deaths British archaeologists English Egyptologists British expatriates in South Africa 20th-century archaeologists 20th-century English wr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Kingdom
In ancient Egyptian history, the Old Kingdom is the period spanning c. 2700–2200 BC. It is also known as the "Age of the Pyramids" or the "Age of the Pyramid Builders", as it encompasses the reigns of the great pyramid-builders of the Fourth Dynasty, such as King Sneferu, who perfected the art of pyramid-building, and the kings Khufu, Khafre and Menkaure, who constructed the pyramids at Giza. Egypt attained its first sustained peak of civilization during the Old Kingdom, the first of three so-called "Kingdom" periods (followed by the Middle Kingdom and New Kingdom), which mark the high points of civilization in the lower Nile Valley. The concept of an "Old Kingdom" as one of three "golden ages" was coined in 1845 by the German Egyptologist Baron von Bunsen, and its definition would evolve significantly throughout the 19th and the 20th centuries. Not only was the last king of the Early Dynastic Period related to the first two kings of the Old Kingdom, but the "capital", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomarchs
A nomarch ( grc, νομάρχης, egy, ḥrj tp ꜥꜣ Great Chief) was a provincial governor in ancient Egypt; the country was divided into 42 provinces, called nomes (singular , plural ). A nomarch was the government official responsible for a nome. Etymology The term ''nome'' is derived from grc, νομός ''nomós'' "province, district". ''Nomarch'' is derived from ''nomárkhēs'': "province" + "ruler". Egyptian history The division of the Egyptian kingdom into nomes can be documented as far back as the reign of Djoser of the 3rd Dynasty in the early Old Kingdom, c. 2670 BCE, and potentially dates even further back to the Predynastic kingdoms of the Nile valley. The earliest topographical lists of the nomes of Upper and Lower Egypt date back to the reign of Nyuserre Ini, of the mid 5th Dynasty, from which time the nomarchs no longer lived at royal capital but stayed in their nomes. The power of the nomarchs grew with the reforms of Nyuserre's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
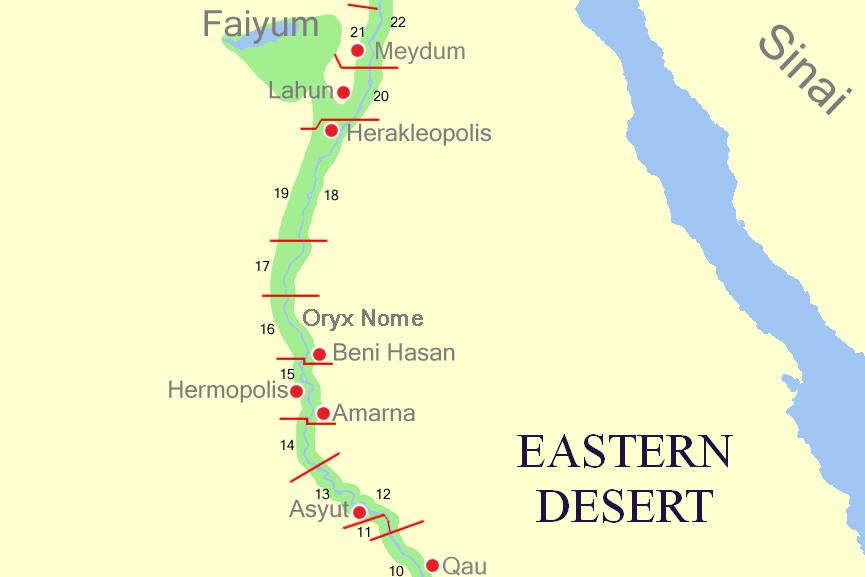
Aphroditopolis Nome
The Aphroditopolite Nome (also Wadjet) was a nome in ancient Egypt. The administrative region was the tenth nome of Upper Egypt. Its capital was Tjebu. During the Ptolemaic period, the nome's capital city was Aphroditopolis. Several governors of the province are known. These include Kaikhenet (II) Kaikhenet was an ancient Egyptian local governor in the Aphroditopolis Nome, 10th Upper Egyptian province; the latter called Wadjet in Egyptian language. Kaikhenet lived at the beginning of the Fifth Dynasty and is known from his decorated rock cut ... in the Old Kingdom. References Nomes of ancient Egypt {{AncientEgypt-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |