|
Helium Dilution Technique
The helium dilution technique is the way of measuring the functional residual capacity of the lungs (the volume left in the lungs after normal expiration). This technique is a closed-circuit system where a spirometer is filled with a mixture of helium (He) and oxygen. The amount of He in the spirometer is known at the beginning of the test (concentration × volume = amount). The patient is then asked to breathe (normal breaths) in the mixture starting from FRC (functional residual capacity), which is the gas volume in the lung after a normal breath out. The spirometer measures helium concentration. The helium spreads into the lungs of the patient, and settles at a new concentration (C2). Because there is no leak of substances in the system, the amount of helium remains constant during the test, and the FRC is calculated by using the following equation: C_1V_1=C_2V_2 C_1 V_1 = C_2 (V_1 + FRC) FRC = \frac- V1 V2 = total gas volume (FRC + volume of spirometer) V1 = volume of g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Residual Capacity
Functional residual capacity (FRC) is the volume of air present in the lungs at the end of passive expiration. At FRC, the opposing elastic recoil forces of the lungs and chest wall are in equilibrium and there is no exertion by the diaphragm or other respiratory muscles. FRC is the sum of expiratory reserve volume (ERV) and residual volume (RV) and measures approximately 2500 mL in a 70 kg, average-sized male (or approximately 30ml/kg). It cannot be estimated through spirometry, since it includes the residual volume. In order to measure RV precisely, one would need to perform a test such as nitrogen washout, helium dilution or body plethysmography. A lowered or elevated FRC is often an indication of some form of respiratory disease. For instance, in emphysema, FRC is increased, because the lungs are more compliant and the equilibrium between the inward recoil of the lungs and outward recoil of the chest wall is disturbed. As such, patients with emphysema often have no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the air and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their different muscles to support and foster breathing. In earlier tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the main muscle of respiration that drives breathing is the diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes vocal sounds including human speech possible. Humans have two lungs, one on the left and on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exhalation
Exhalation (or expiration) is the flow of the breath out of an organism. In animals, it is the movement of air from the lungs out of the airways, to the external environment during breathing. This happens due to elastic properties of the lungs, as well as the internal intercostal muscles which lower the rib cage and decrease thoracic volume. As the thoracic diaphragm relaxes during exhalation it causes the tissue it has depressed to rise superiorly and put pressure on the lungs to expel the air. During forced exhalation, as when blowing out a candle, expiratory muscles including the abdominal muscles and internal intercostal muscles generate abdominal and thoracic pressure, which forces air out of the lungs. Exhaled air is 4% carbon dioxide, a waste product of cellular respiration during the production of energy, which is stored as ATP. Exhalation has a complementary relationship to inhalation which together make up the respiratory cycle of a breath. Exhalation and gas e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling and melting point are the lowest among all the elements. It is the second lightest and second most abundant element in the observable universe (hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant). It is present at about 24% of the total elemental mass, which is more than 12 times the mass of all the heavier elements combined. Its abundance is similar to this in both the Sun and in Jupiter, due to the very high nuclear binding energy (per nucleon) of helium-4, with respect to the next three elements after helium. This helium-4 binding energy also accounts for why it is a product of both nuclear fusion and radioactive decay. The most common isotope of helium in the universe is helium-4, the vast majority of which was formed during t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
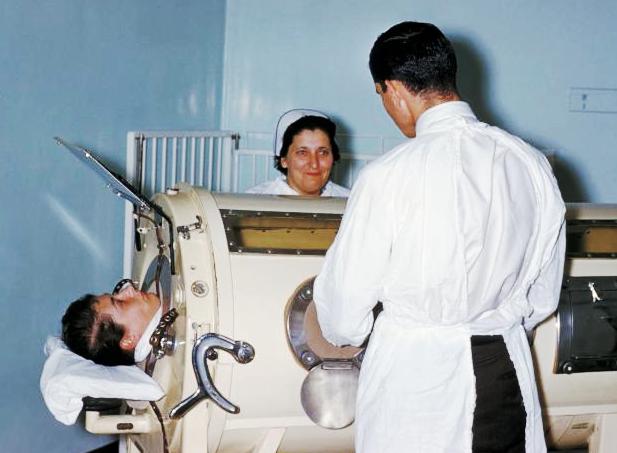
Mechanical Ventilation
Mechanical ventilation, assisted ventilation or intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV), is the medical term for using a machine called a ventilator to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air into and out of the lungs, with the main goal of helping the delivery of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide. Mechanical ventilation is used for many reasons, including to protect the airway due to mechanical or neurologic cause, to ensure adequate oxygenation, or to remove excess carbon dioxide from the lungs. Various healthcare providers are involved with the use of mechanical ventilation and people who require ventilators are typically monitored in an intensive care unit. Mechanical ventilation is termed invasive if it involves an instrument to create an airway that is placed inside the trachea. This is done through an endotracheal tube or nasotracheal tube. For non-invasive ventilation in people who are conscious, face or nasal mask ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
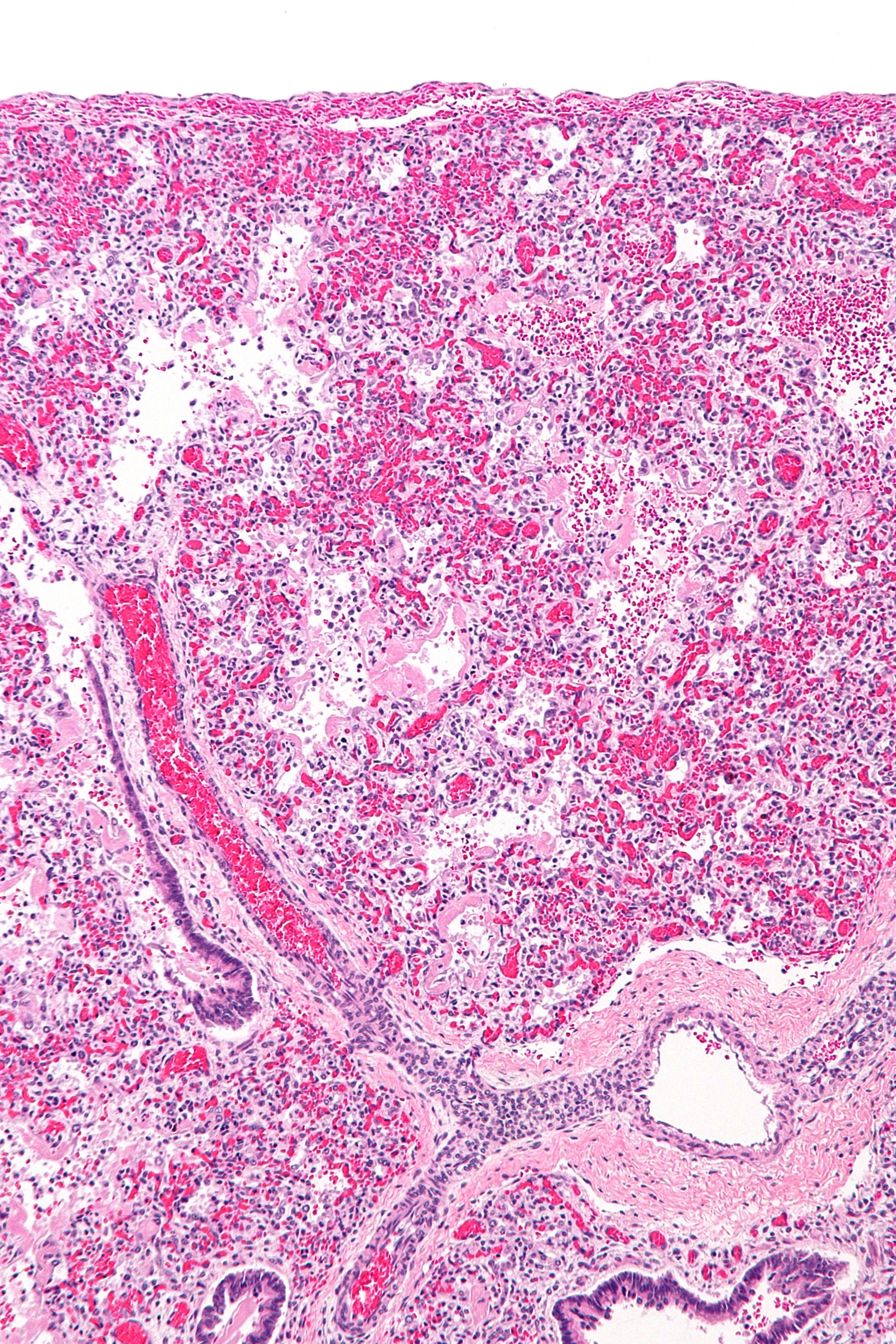
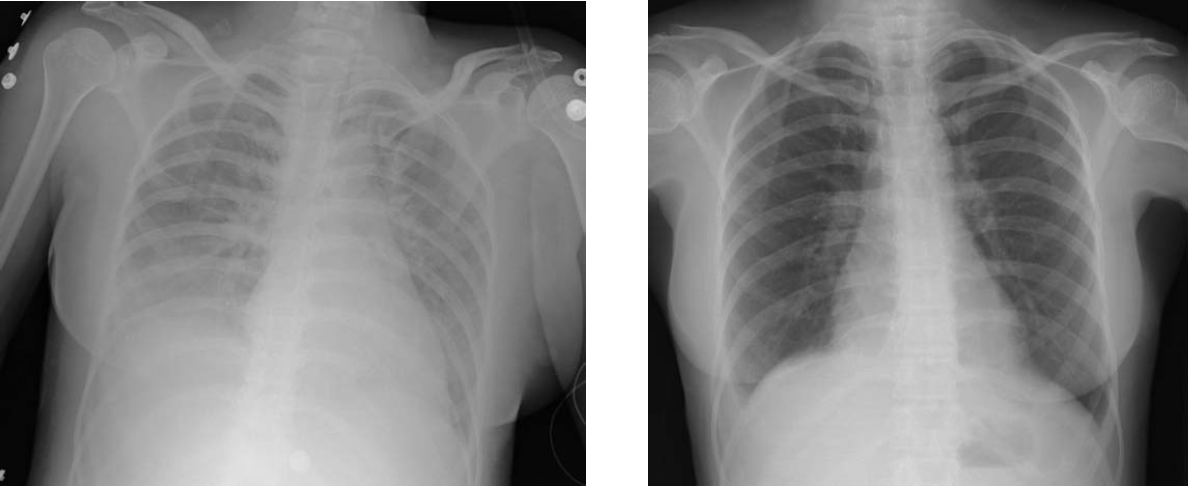
Acute Lung Injury
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a type of respiratory failure characterized by rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath (dyspnea), rapid breathing (tachypnea), and bluish skin coloration (cyanosis). For those who survive, a decreased quality of life is common. Causes may include sepsis, pancreatitis, trauma, pneumonia, and aspiration. The underlying mechanism involves diffuse injury to cells which form the barrier of the microscopic air sacs of the lungs, surfactant dysfunction, activation of the immune system, and dysfunction of the body's regulation of blood clotting. In effect, ARDS impairs the lungs' ability to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide. Adult diagnosis is based on a PaO2/FiO2 ratio (ratio of partial pressure arterial oxygen and fraction of inspired oxygen) of less than 300 mm Hg despite a positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) of more than 5 cm H2O. Cardiogenic pulmonary edema, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARDS
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a type of respiratory failure characterized by rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath (dyspnea), rapid breathing (tachypnea), and bluish skin coloration (cyanosis). For those who survive, a decreased quality of life is common. Causes may include sepsis, pancreatitis, trauma, pneumonia, and aspiration. The underlying mechanism involves diffuse injury to cells which form the barrier of the microscopic air sacs of the lungs, surfactant dysfunction, activation of the immune system, and dysfunction of the body's regulation of blood clotting. In effect, ARDS impairs the lungs' ability to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide. Adult diagnosis is based on a PaO2/FiO2 ratio (ratio of partial pressure arterial oxygen and fraction of inspired oxygen) of less than 300 mm Hg despite a positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) of more than 5 cm H2O. Cardiogenic pulmonary edema, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-sectional
Cross-sectional data, or a cross section of a study population, in statistics and econometrics, is a type of data collected by observing many subjects (such as individuals, firms, countries, or regions) at the one point or period of time. The analysis might also have no regard to differences in time. Analysis of cross-sectional data usually consists of comparing the differences among selected subjects. For example, if we want to measure current obesity levels in a population, we could draw a sample of 1,000 people randomly from that population (also known as a cross section of that population), measure their weight and height, and calculate what percentage of that sample is categorized as obese. This cross-sectional sample provides us with a snapshot of that population, at that one point in time. Note that we do not know based on one cross-sectional sample if obesity is increasing or decreasing; we can only describe the current proportion. Cross-sectional data differs from time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiratory System Procedures
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies greatly, depending on the size of the organism, the environment in which it lives and its evolutionary history. In land animals the respiratory surface is internalized as linings of the lungs. Gas exchange in the lungs occurs in millions of small air sacs; in mammals and reptiles these are called alveoli, and in birds they are known as atria. These microscopic air sacs have a very rich blood supply, thus bringing the air into close contact with the blood. These air sacs communicate with the external environment via a system of airways, or hollow tubes, of which the largest is the trachea, which branches in the middle of the chest into the two main bronchi. These enter the lungs where they branch into progressively narrower secondary and ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiratory Therapy
A respiratory therapist is a specialized healthcare professional, healthcare practitioner trained in Intensive care medicine, critical care and cardio-pulmonary medicine in order to work therapeutically with people who have acute critical conditions, Cardiovascular disease, cardiac and Respiratory disease, pulmonary disease. Respiratory therapists graduate from a college or university with a degree in respiratory therapy and have passed a national board certifying examination. The NBRC (National Board for Respiratory Care) is responsible for credentialing as a CRT (Certified Respiratory Therapist, certified respiratory therapist), or RRT (Registered Respiratory Therapist, registered respiratory therapist), The specialty certifications of respiratory therapy include: CPFT and RPFT (Certified or Registered Pulmonary Function Technologist), ACCS (Adult Critical Care Specialist), NPS (Neonatal/Pediatric Specialist), and SDS (Sleep disorder specialist, Sleep Disorder Specialist). Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |