|
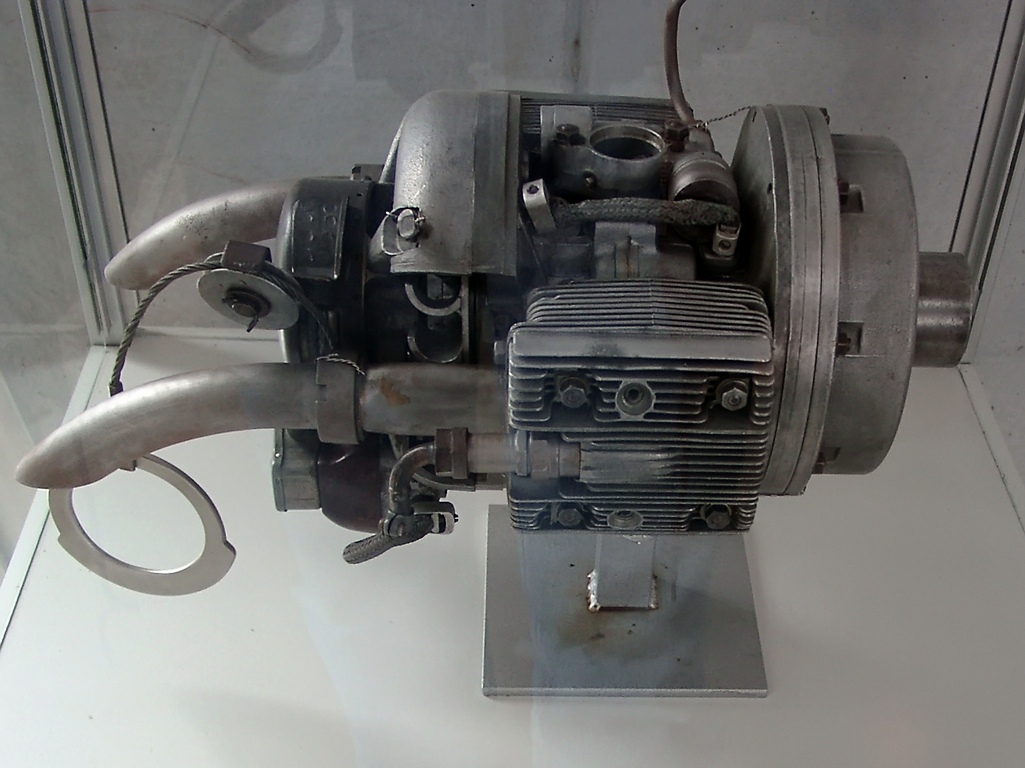
Heinkel HeS 011A
The Heinkel HeS 011 or Heinkel-Hirth 109-011 ''(HeS - Heinkel Strahltriebwerke)'' was an advanced World War II jet engine built by Heinkel-Hirth. It featured a unique compressor arrangement, starting with a low-compression impeller in the intake, followed by a "diagonal" stage similar to a centrifugal compressor, and then a three-stage axial compressor. Many of the German jet-powered aircraft designs at the end of the war were designed to use the HeS 011, but the HeS 011 engine was not ready for production before the war ended in Europe and only small numbers of prototypes were produced. Design and development Starting in 1936, Junkers started a jet engine development project under the direction of Wagner and Müller, who worked on axial compressor designs. By 1940 they had progressed to the point of having a semi-working prototype, which could not run under its own power and required an external supply of compressed air. Meanwhile, Hans Mauch, in charge of engine development at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinkel HeS 8
The Heinkel HeS 8 (prefix being an abbreviation for "Heinkel Strahltriebwerke 8" - ''Heinkel Jet Engine 8'') was an early jet engine designed by Hans von Ohain while working at Heinkel. It was the first jet engine to be financially supported by the RLM, bearing the official name 109-001. Had development continued it would have been known as the Heinkel 001, but it does not appear this was used in practice. The HeS 8 was intended to power the Heinkel He 280 twin-engine fighter, although both Heinkel and von Ohain preferred the axial HeS 30. A lengthy gestation period meant it was finally becoming ready for production at about the same time as the Junkers Jumo 004 and BMW 003. In 1942 work was ended on the HeS 8 and HeS 30, and Heinkel was ordered to move on to the larger Heinkel HeS 011 instead. The He 280 was left engineless, and was eventually abandoned. Design and development By the time the HeS 3 program wound down in 1939, it appears that von Ohain no longer favoured the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bomber B
Bomber B was a German military aircraft design competition organised just before the start of World War II to develop a second-generation high-speed bomber for the ''Luftwaffe''. The new designs would be a direct successor to the ''Schnellbomber'' philosophy of the Dornier Do 17 and Junkers Ju 88, relying on high speed as its primary defence. Bomber B would be a much larger and more capable aircraft, with range and payload far greater than the ''Schnellbomber'', besting the largest conventional designs then under consideration. The winning design was intended to form the backbone of the ''Luftwaffe's'' bomber force, replacing the wide collection of semi-specialized designs then in service. The Reich Air Ministry was so optimistic that more modest projects were generally cancelled; when the project failed the ''Luftwaffe'' was left with hopelessly outdated aircraft. Background By the late 1930s, airframe construction methods had progressed to the point where airframes could be bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinkel He 111
The Heinkel He 111 is a German airliner and bomber designed by Siegfried and Walter Günter at Heinkel Flugzeugwerke in 1934. Through development, it was described as a "wolf in sheep's clothing". Due to restrictions placed on Germany after the First World War prohibiting bombers, it was presented solely as a civil airliner, although from conception the design was intended to provide the nascent Luftwaffe with a heavy bomber. Perhaps the best-recognised German bomber of World War II due to the distinctive, extensively glazed "greenhouse" nose of the later versions, the Heinkel He 111 was the most numerous Luftwaffe bomber during the early stages of the war. It fared well until it met serious fighter opposition during the Battle of Britain, when its defensive armament was found to be inadequate. As the war progressed, the He 111 was used in a wide variety of roles on every front in the European theatre. It was used as a strategic bomber during the Battle of Britain, a torpedo bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daimler-Benz
The Mercedes-Benz Group Aktiengesellschaft, AG (previously named Daimler-Benz, DaimlerChrysler and Daimler) is a German Multinational corporation, multinational automotive corporation headquartered in Stuttgart, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is one of the world's leading car manufacturers. Daimler-Benz was formed with the merger of Benz & Cie. and Daimler Motoren Gesellschaft in 1926. The company was renamed DaimlerChrysler upon acquiring the American automobile manufacturer Chrysler Corporation in 1998, and was again renamed Daimler AG upon divestment of Chrysler in 2007. In 2021, Daimler AG was the second-largest German automaker and the sixth-largest worldwide by production. In February 2022, Daimler was renamed Mercedes-Benz Group. The Mercedes-Benz Group's marques are Mercedes-Benz for cars and vans (including Mercedes-AMG and Maybach#Mercedes-Maybach, Mercedes-Maybach) and Smart (marque), Smart. It has shares in other vehicle manufactures such as Daimler Truck, Denza, BA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinkel Wespe
The Heinkel Wespe ( en, Wasp) was a project study by the German company Heinkel for a tail-sitting, vertical take off and landing-interceptor aircraft. The aircraft did not have conventional wings, but instead featured a large rotor. Completed in 1945, it remained untested due to a lack of material at the end of the Second World War. A related project was the Heinkel Lerche. Design The aircraft was to be powered by a turboprop in the center of the airframe which was unusual for having a circular wing and would have had a small frontal area, making it a good platform for attacking bombers. It may have been designed for point defense, but due to the situation in Germany at the time, the engine was not completed and none were ever built. Specifications See related aircraft Heinkel Lerche Focke-Wulf Triebflugel Lockheed XFV Convair XFY Pogo Notes References * {{Heinkel aircraft Wespe The Sd.Kfz. 124 ''Wespe'' (German for "wasp"), also known as ''Leichte Feldhaubitze 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auxiliary Power Unit
An auxiliary power unit (APU) is a device on a vehicle that provides energy for functions other than propulsion. They are commonly found on large aircraft and naval ships as well as some large land vehicles. Aircraft APUs generally produce 115 V AC voltage at 400 Hz (rather than 50/60 Hz in mains supply), to run the electrical systems of the aircraft; others can produce 28 V DC voltage. APUs can provide power through single or three-phase systems. Transport aircraft History During World War I, the British Coastal class blimps, one of several types of airship operated by the Royal Navy, carried a ABC auxiliary engine. These powered a generator for the craft's radio transmitter and, in an emergency, could power an auxiliary air blower. One of the first military fixed-wing aircraft to use an APU was the British, World War 1, Supermarine Nighthawk, an anti-Zeppelin night fighter.Andrews and Morgan 1987, p. 21. During World War II, a number of large Ameri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turboprop
A turboprop is a turbine engine that drives an aircraft propeller. A turboprop consists of an intake, reduction gearbox, compressor, combustor, turbine, and a propelling nozzle. Air enters the intake and is compressed by the compressor. Fuel is then added to the compressed air in the combustor, where the fuel-air mixture then combusts. The hot combustion gases expand through the turbine stages, generating power at the point of exhaust. Some of the power generated by the turbine is used to drive the compressor and electric generator. The gases are then exhausted from the turbine. In contrast to a turbojet or turbofan, the engine's exhaust gases do not provide enough energy to create significant thrust, since almost all of the engine's power is used to drive the propeller. Technological aspects Exhaust thrust in a turboprop is sacrificed in favor of shaft power, which is obtained by extracting additional power (beyond that necessary to drive the compressor) from turbine ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixed Flow Compressor
A mixed flow compressor, or diagonal compressor, combines axial and radial components to produce a diagonal airflow compressor stage. The exit mean radius is greater than at the inlet, like a centrifugal design, but the flow tends to exit in an axial rather than radial direction. This eliminates the need for a relatively large diameter exit diffuser associated with centrifugal compressors. The impeller can be machined from solid using NC machines, in much the same way as that of a centrifugal design. Diagonal compressors were widely experimented during and just after World War II, but did not see much service use. A diagonal-flow compressor is featured since 2001 in the Pratt & Whitney Canada PW600 series turbofan engines used in the Phenom 100, Eclipse 500, Cessna Citation Mustang and other very light jet aircraft. See also * Gas compressor A compressor is a mechanical device that increases the pressure of a gas by reducing its volume. An air compressor is a specific type of g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junkers Jumo 004
The Junkers Jumo 004 was the world's first production turbojet engine in operational use, and the first successful axial compressor turbojet engine. Some 8,000 units were manufactured by Junkers in Germany late in World War II, powering the Messerschmitt Me 262 fighter and the Arado Ar 234 reconnaissance/bomber, along with prototypes, including the Horten Ho 229. Variants and copies of the engine were produced in Eastern Europe and the USSR for several years following the end of WWII. Design and development The feasibility of jet propulsion had been demonstrated in Germany in early 1937 by Hans von Ohain working with the Heinkel company. Most of the Reich Air Ministry ( RLM) remained uninterested, but Helmut Schelp and Hans Mauch saw the potential of the concept and encouraged Germany's aero engine manufacturers to begin their own programmes of jet engine development. The companies remained skeptical and little new development was carried out. In 1939 Schelp and Mauch visited th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMW 003
The BMW 003 (full RLM designation 109-003) is an early axial turbojet engine produced by BMW AG in Germany during World War II. The 003 and the Junkers Jumo 004 were the only German turbojet engines to reach production during World War II. Work had begun on the design of the BMW 003 before its contemporary, the Jumo 004, but prolonged developmental problems meant that the BMW 003 entered production much later, and the aircraft projects that had been designed with it in mind were re-engined with the Jumo powerplant instead. The most famous case of this was the Messerschmitt Me 262, which used the 003 in two of the V-series prototypes and in the two experimental A-1b aircraft. The only production aircraft to use the BMW 003 were the Heinkel He 162 and the later C-series, four-engined versions of the Arado Ar 234. About 3500 BMW 003 engines were built in Germany, but very few were ever installed in aircraft. The engine also formed the basis for turbojet development in Japan du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |