|
Health In The Cayman Islands
In 2003, the Cayman Islands became the first country in the world to mandate health insurance for all residents. There are four hospitals in the Cayman Islands. Grand Cayman is home to the private Health City Cayman Islands, as well as the Chrissie Tomlinson Memorial Hospital. The public hospitals are the Cayman Islands Hospital (commonly known as the George Town Hospital); and Faith Hospital on Cayman Brac. Resources Emergency Medical Services are provided by paramedics and Emergency Medical Technicians using ambulances based in George Town, West Bay and North Side in Grand Cayman and in Cayman Brac. EMS is managed by the Government's Health Services Authority. In 2007, a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) unit was installed at the Chrissie Tomlinson Memorial Hospital, replacing the one destroyed by Hurricane Ivan in 2004. In 2009, a stand-alone open MRI facility was opened. This centre provides MRI, CT, X-ray and DEXA (bone density) scanning. Also housed in this building is the He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health City Cayman Islands
Health City Cayman Islands is a JCI accredited tertiary care hospital in the Cayman Islands, a British Overseas Territory. Background Dr. Devi Shetty founded Health City Cayman Islands. History The 107,000 square foot facility, opened in February 2014, becoming the first advanced medical facility and tertiary care hospital in the Cayman Islands. Facility and Current Operations The 104-bed tertiary care hospital features a reinforced roof, walls, doors and windows and was built to withstand the rigors of a Category 5 Hurricane and shield all of its critical assets from flooding. Location and Satellite Offices The tertiary care hospital is located on 1283 Sea View Road, near High Rock in the East End District of Grand Cayman. In 2016, Health City opened a Canadian satellite office located in Hamilton, Ontario Hamilton is a port city in the Canadian Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Ontario. Hamilton has a Canada 2016 Census, population of 569,35 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cayman Islands Hospital
The Cayman Islands Hospital, also known locally as the George Town Hospital (GT Hospital), is the principal government hospital in the Cayman Islands, located in George Town on Grand Cayman. It is run by the Cayman Islands Health Services Authority. History The hospital was completed in 1999. Facilities The hospital is a two-storey facility with 124 beds and four operating theatres. Other facilities include an accident and emergency department An emergency department (ED), also known as an accident and emergency department (A&E), emergency room (ER), emergency ward (EW) or casualty department, is a medical treatment facility specializing in emergency medicine, the acute care of pati ..., critical care unit, dialysis unit, pharmacy, laboratory and forensic unit. Services The hospital provides services in most medical specialities. References {{Reflist External links Official site Buildings and structures in George Town, Cayman Islands Hospitals in the Cayman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from CT and PET scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft-tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, though "Open" MRI designs mostly relieve this. Additionally, implants and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Ivan
Hurricane Ivan was a large, long-lived, Cape Verde hurricane that caused widespread damage in the Caribbean and United States. The cyclone was the ninth named storm, the sixth hurricane and the fourth major hurricane of the active 2004 Atlantic hurricane season. Ivan formed in early September, and reached Category 5 strength on the Saffir–Simpson Hurricane Scale (SSHS). Ivan caused catastrophic damage in Grenada as a strong Category 3 storm, heavy damage in Jamaica as a strong Category 4 storm, and then severe damage in Grand Cayman, Cayman Islands, and the western tip of Cuba as a Category 5 hurricane. After peaking in strength, the hurricane moved north-northwest across the Gulf of Mexico to strike Pensacola/ Milton, Florida and Alabama as a strong Category 3 storm, causing significant damage. Ivan dropped heavy rain on the Southeastern United States as it progressed northeastward and eastward through the Eastern United States, becoming an extratropical cyclone on Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DEXA
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA, or DEXA) is a means of measuring bone mineral density (BMD) using spectral imaging. Two X-ray beams, with different energy levels, are aimed at the patient's bones. When soft tissue absorption is subtracted out, the bone mineral density (BMD) can be determined from the absorption of each beam by bone. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry is the most widely used and most thoroughly studied bone density measurement technology. The DXA scan is typically used to diagnose and follow osteoporosis, as contrasted to the nuclear bone scan, which is sensitive to certain metabolic diseases of bones in which bones are attempting to heal from infections, fractures, or tumors. It is also sometimes used to assess body composition. Physics Soft tissue and bone have different attenuation coefficients to X-rays. A single X-ray beam passing through the body will be attenuated by both soft tissue and bone, and it is not possible to determine, from a single beam, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
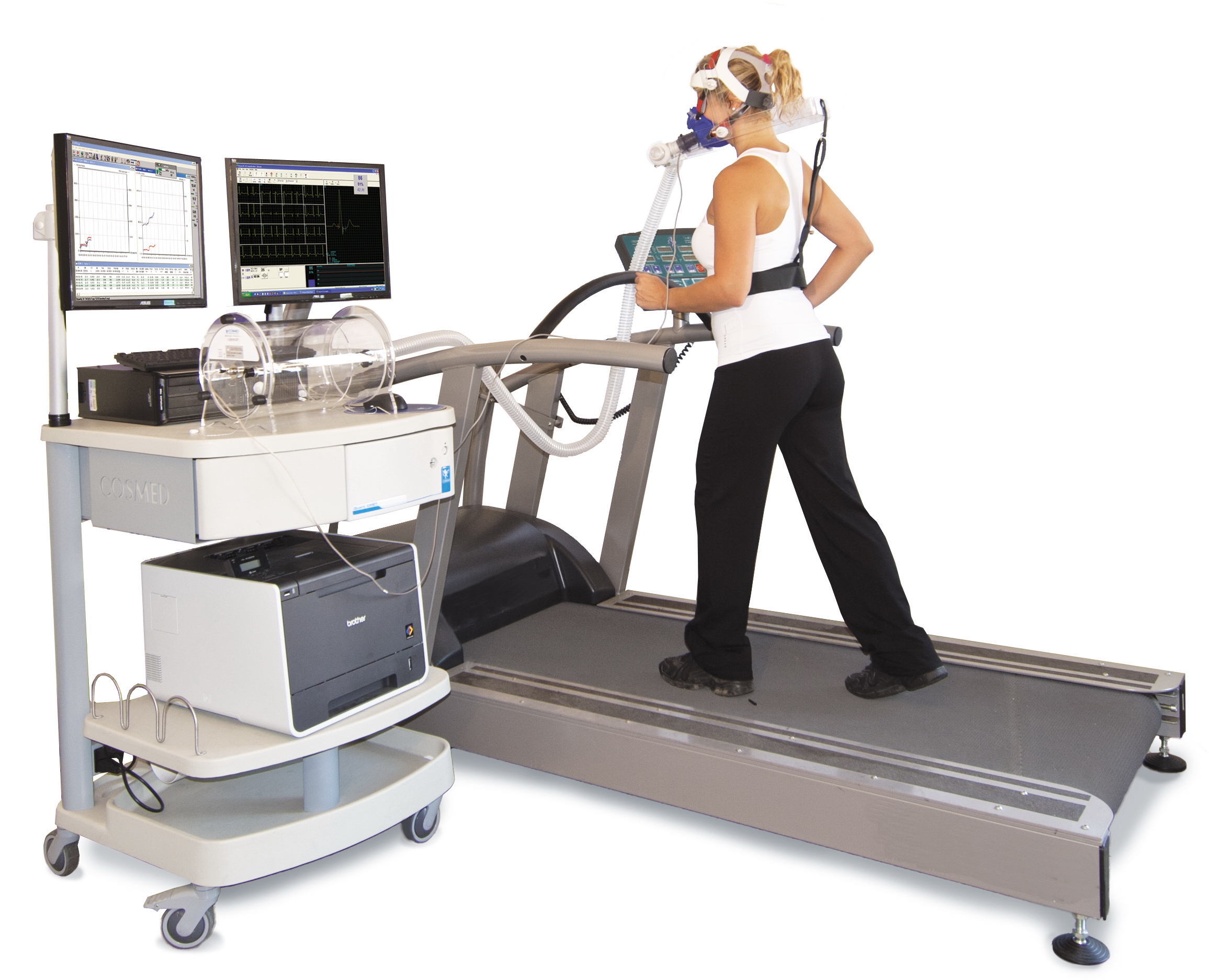
Cardiac Stress Test
A cardiac stress test (also referred to as a cardiac diagnostic test, cardiopulmonary exercise test, or abbreviated CPX test) is a cardiological test that measures the heart's ability to respond to external stress in a controlled clinical environment. The stress response is induced by exercise or by intravenous pharmacological stimulation. Cardiac stress tests compare the coronary circulation while the patient is at rest with the same patient's circulation during maximum cardiac exertion, showing any abnormal blood flow to the myocardium (heart muscle tissue). The results can be interpreted as a reflection on the general physical condition of the test patient. This test can be used to diagnose coronary artery disease (also known as ischemic heart disease) and assess patient prognosis after a myocardial infarction (heart attack). Exercise-induced stressors are most commonly either exercise on a treadmill or pedalling a stationary exercise bicycle ergometer. The level of stress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
Hyperbaric medicine is medical treatment in which an ambient pressure greater than sea level atmospheric pressure is a necessary component. The treatment comprises hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), the medical use of oxygen at an ambient pressure higher than atmospheric pressure, and therapeutic recompression for decompression illness, intended to reduce the injurious effects of systemic gas bubbles by physically reducing their size and providing improved conditions for elimination of bubbles and excess dissolved gas. The equipment required for hyperbaric oxygen treatment consists of a pressure chamber, which may be of rigid or flexible construction, and a means of delivering 100% oxygen. Operation is performed to a predetermined schedule by trained personnel who monitor the patient and may adjust the schedule as required. HBOT found early use in the treatment of decompression sickness, and has also shown great effectiveness in treating conditions such as gas gangrene and carbon mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recompression Chamber
A diving chamber is a vessel for human occupation, which may have an entrance that can be sealed to hold an internal pressure significantly higher than ambient pressure, a pressurised gas system to control the internal pressure, and a supply of breathing gas for the occupants. There are two main functions for diving chambers: * as a simple form of submersible vessel to transport divers underwater and to provide a temporary base and retrieval system in the depths; * as a land, ship or offshore platform-based hyperbaric chamber or system, to artificially reproduce the hyperbaric conditions under the sea. Internal pressures above normal atmospheric pressure are provided for diving-related applications such as saturation diving and diver decompression, and non-diving medical applications such as hyperbaric medicine. Basic types of diving chambers There are two basic types of submersible diving chambers, differentiated by the way in which the pressure in the diving chamber is p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |