|
Head Crash
A head crash is a hard-disk failure that occurs when a read–write head of a hard disk drive makes contact with its rotating platter, slashing its surface and permanently damaging its magnetic media. It is most often caused by a sudden severe motion of the disk, for example the jolt caused by dropping a laptop to the ground while it is operating or physically shocking a computer. Head details A head normally rides on a thin film of moving air entrapped at the surface of its platter (some drives manufactured by Conner Peripherals in the mid-1990s used a thin liquid layer instead). The distance between the head and platter is called the flying height. The topmost layer of the platter is made of a Teflon-like material that acts like a lubricant. Underneath is a layer of sputtered carbon. These two layers protect the magnetic layer (data storage area) from most accidental touches of the read-write head. The disk read-and-write head is made using thin film techniques that in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Disk Head Crash
Hard may refer to: * Hardness, resistance of physical materials to deformation or fracture * Hard water, water with high mineral content Arts and entertainment * ''Hard'' (TV series), a French TV series * Hard (band), a Hungarian hard rock supergroup * Hard (music festival), in the U.S. * ''Hard'' (EP), Goodbye Mr Mackenzie, 1993 * ''Hard'' (Brainpower album), 2008 * ''Hard'' (Gang of Four album), 1983 * ''Hard'' (Jagged Edge album), 2003 * "Hard" (song), a 2009 song by Rihanna * "Hard", a song by Royce da 5'9" from the 2016 album ''Layers'' * "Hard", a song by Why Don't We from the 2018 album ''8 Letters'' * ''Hard'', a 2017 EP from the band The Neighbourhood *"Hard", a song by Sophie from the 2015 compilation album ''Product'' Places * Hard, Austria * Hard (Zürich), Switzerland Other uses * Hard (surname) * Nickname of Masaki Sumitani ( HardGay / HardoGay ) * Hard (nautical), a beach or slope convenient for hauling out vessels * Hard (video game player), Anthony Barkho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
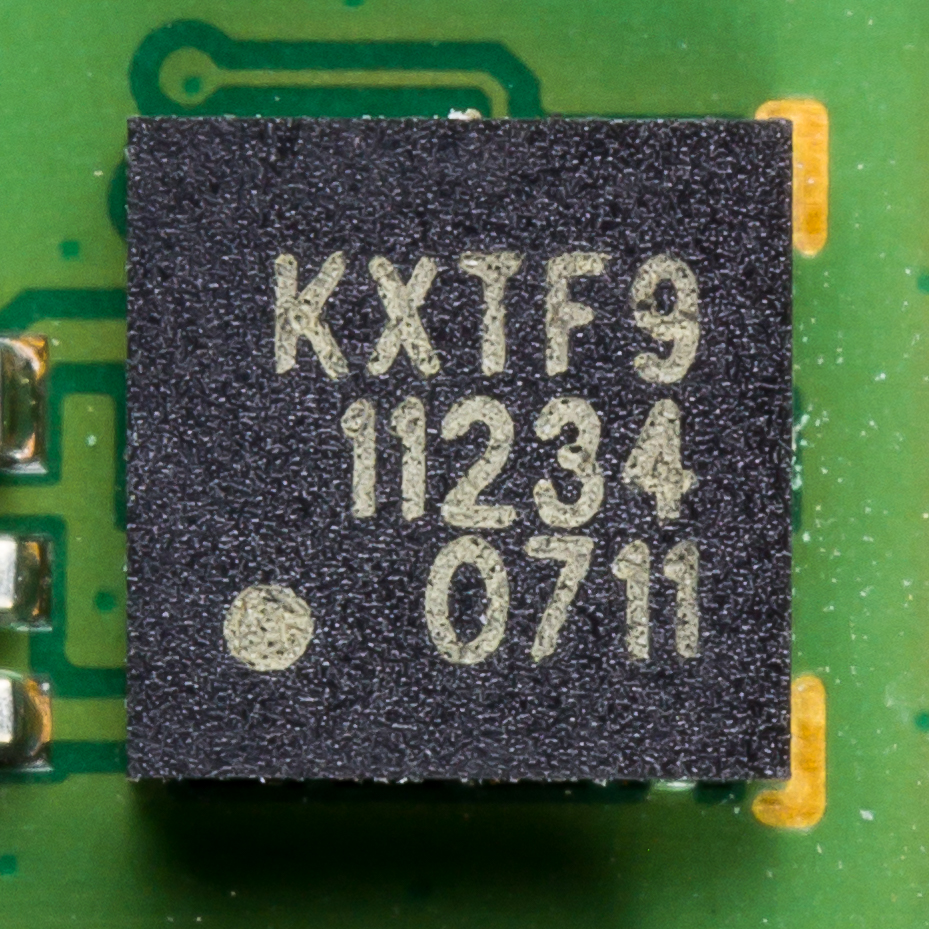
Free Fall Sensor
An accelerometer is a tool that measures proper acceleration. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change of velocity) of a body in its own instantaneous rest frame; this is different from coordinate acceleration, which is acceleration in a fixed coordinate system. For example, an accelerometer at rest on the surface of the Earth will measure an acceleration due to Earth's gravity, straight upwards (by definition) of g ≈ 9.81 m/s2. By contrast, accelerometers in free fall (falling toward the center of the Earth at a rate of about 9.81 m/s2) will measure zero. Accelerometers have many uses in industry and science. Highly sensitive accelerometers are used in inertial navigation systems for aircraft and missiles. Vibration in rotating machines is monitored by accelerometers. They are used in tablet computers and digital cameras so that images on screens are always displayed upright. In unmanned aerial vehicles, accelerometers help to stabilise flight. W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Disk Drives
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating hard disk platter, platters coated with magnetic material. The platters are paired with disk read-and-write head, magnetic heads, usually arranged on a moving actuator arm, which read and write data to the platter surfaces. Data is accessed in a random-access manner, meaning that individual Block (data storage), blocks of data can be stored and retrieved in any order. HDDs are a type of non-volatile storage, retaining stored data when powered off. Modern HDDs are typically in the form of a small disk enclosure, rectangular box. Introduced by IBM in 1956, HDDs were the dominant secondary storage device for History of general-purpose CPUs, general-purpose computers beginning in the early 1960s. HDDs maintained this position into the modern era of server (computing), se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Click Of Death
Click of death is a term that had become common in the late 1990s referring to the clicking sound in disk storage systems that signals a disk drive has failed, often catastrophically. The clicking sound itself arises from the unexpected movement of the disk's read/write actuator. At startup, and during use, the disk head must move correctly and be able to confirm that it is correctly tracking data on the disk. If the head fails to move as expected or upon moving cannot track the disk surface correctly, the disk controller may attempt to recover from the error by returning the head to its home position and then retrying, at times causing an audible "click". In some devices, the process automatically retries, causing a repeated or rhythmic clicking sound, sometimes accompanied by the whirring sound of the drive plate spinning. Origin of the term The phrase "click of death" originated to describe a failure mode of the Iomega ZIP drives, appearing in print as early as January 30, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bad Sector
A bad sector in computing is a disk sector on a disk storage unit that is permanently damaged. Upon taking damage, all information stored on that sector is lost. When a bad sector is found and marked, the operating system like Windows or Linux will skip it in the future. Details A bad sector is the result of mechanical damage, most commonly caused by a head crash, manufacturing flaw(s), wear-and-tear, physical shock, sudden power outages, or dust intrusion. Bad sectors are a threat to information security in the sense of data remanence. Very often physical damages can interfere with parts of many different files. Operating system Bad sectors may be detected by the operating system or the disk controller. Most file systems contain provisions for sectors to be marked as bad, so that the operating system avoids them in the future. Disk diagnostic utilities, such as CHKDSK ( Microsoft Windows), Disk Utility (on macOS), or badblocks (on Linux) can actively look for bad sectors upon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Hard-drive Protection
In computer hardware, active hard-drive protection refers to technology that attempts to avoid or reduce mechanical damage to hard disk drives by preparing the disk prior to impact. This approach is mainly used in laptop computers that are frequently carried around and more prone to impacts than desktop computers. Implementation Usually the system consists of accelerometers that alert the system when excess acceleration or vibration is detected. The software then tells the hard disk to unload its heads to prevent them from coming in contact with the platter, thus potentially preventing head crash. Many laptop vendors have implemented this technology under different names. Some hard-disk drives also include this technology, needing no cooperation from the system. See also * Hard disk drive failure * Head crash A head crash is a hard-disk failure that occurs when a read–write head of a hard disk drive makes contact with its rotating platter, slashing its surface and per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
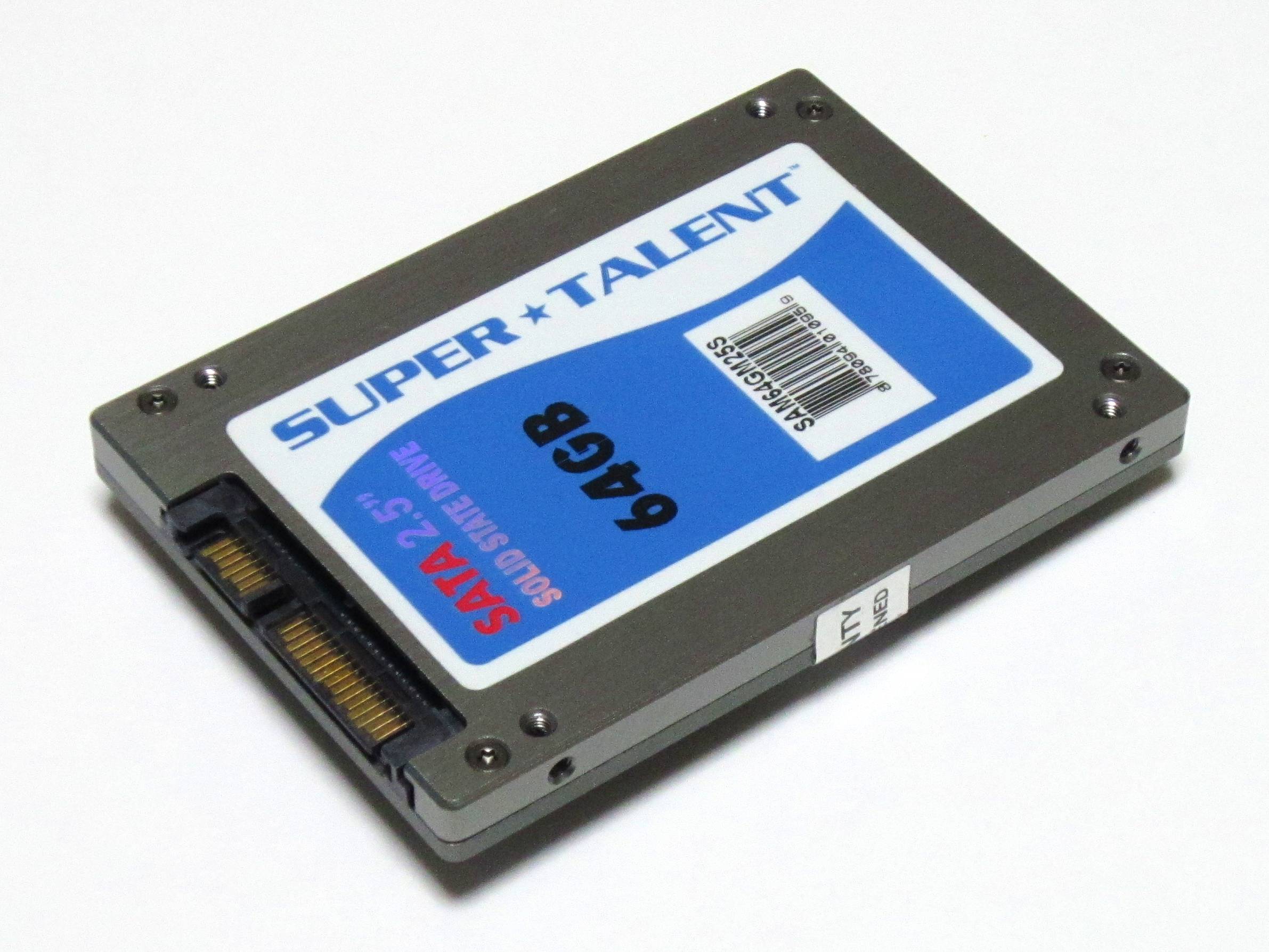
Solid-state Drives
A solid-state drive (SSD) is a solid-state storage device that uses integrated circuit assemblies to store data persistently, typically using flash memory, and functioning as secondary storage in the hierarchy of computer storage. It is also sometimes called a semiconductor storage device, a solid-state device or a solid-state disk, even though SSDs lack the physical spinning disks and movable read–write heads used in hard disk drives (HDDs) and floppy disks. SSD also has rich internal parallelism for data processing. In comparison to hard disk drives and similar electromechanical media which use moving parts, SSDs are typically more resistant to physical shock, run silently, and have higher input/output rates and lower latency. SSDs store data in semiconductor cells. cells can contain between 1 and 4 bits of data. SSD storage devices vary in their properties according to the number of bits stored in each cell, with single-bit cells ("Single Level Cells" or "SLC") ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ThinkPad
ThinkPad is a line of business-oriented laptop computers and tablet computers, tablets designed, developed and marketed by Lenovo, and formerly by IBM until 2005, when IBM's Personal computer, PC business was acquired by Lenovo. ThinkPads have a distinct black, boxy design language, inspired by a Japanese ''bento'' lunchbox, which originated in 1990 and is still used in some models. Most models also feature a red-colored trackpoint on the keyboard, which has become an iconic and distinctive design characteristic associated with the ThinkPad line. The ThinkPad line was first developed at the IBM Yamato Facility in Japan, and the first ThinkPads were released in October 1992. It has seen significant success in the business market. ThinkPad laptops have been used in outer space and for many years were the only laptops certified for use on the International Space Station. ThinkPads have also for several years been one of the preferred laptops used by the United Nations. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Hard-drive Protection
In computer hardware, active hard-drive protection refers to technology that attempts to avoid or reduce mechanical damage to hard disk drives by preparing the disk prior to impact. This approach is mainly used in laptop computers that are frequently carried around and more prone to impacts than desktop computers. Implementation Usually the system consists of accelerometers that alert the system when excess acceleration or vibration is detected. The software then tells the hard disk to unload its heads to prevent them from coming in contact with the platter, thus potentially preventing head crash. Many laptop vendors have implemented this technology under different names. Some hard-disk drives also include this technology, needing no cooperation from the system. See also * Hard disk drive failure * Head crash A head crash is a hard-disk failure that occurs when a read–write head of a hard disk drive makes contact with its rotating platter, slashing its surface and per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAMAC 305 Disk
{{disambiguation ...
RAMAC may refer to: *IBM 305 RAMAC, a computing system introduced in 1956 *IBM 350 RAMAC, a disk storage unit introduced in 1956 as a bundled component of the IBM 305 RAMAC * IBM 650 RAMAC, a computing system consisting of an IBM 650 with an IBM 355 Disk Storage unit and introduced in 1956 * IBM 9394 RAMAC Array, a disk storage array and controller unit introduced in 1994 which uses data striping In computer data storage, data striping is the technique of segmenting logically sequential data, such as a file, so that consecutive segments are stored on different physical storage devices. Striping is useful when a processing device request ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolutions Per Minute
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequency for rotating machines. Standards ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a unit of rotation as the dimensionless unit equal to 1, which it refers to as a revolution, but does not define the revolution as a unit. It defines a unit of rotational frequency equal to s−1. The superseded standard ISO 80000-3:2006 did however state with reference to the unit name 'one', symbol '1', that "The special name revolution, symbol r, for this unit is widely used in specifications on rotating machines." The International System of Units (SI) does not recognize rpm as a unit, and defines the unit of frequency, Hz, as equal to s−1. :\begin 1~&\text &&=& 60~&\text \\ \frac~&\text &&=& 1~&\text \end A corresponding but distinct quantity for describing rotation is angular velocity, for which the SI unit is the ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Loss
Data loss is an error condition in information systems in which information is destroyed by failures (like failed spindle motors or head crashes on hard drives) or neglect (like mishandling, careless handling or storage under unsuitable conditions) in storage, transmission, or processing. Information systems implement backup and disaster recovery equipment and processes to prevent data loss or restore lost data. Data loss can also occur if the physical medium containing the data is lost or stolen. Data loss is distinguished from data unavailability, which may arise from a network outage. Although the two have substantially similar consequences for users, data unavailability is temporary, while data loss may be permanent. Data loss is also distinct from data breach, an incident where data falls into the wrong hands, although the term data loss has been used in those incidents. Types *''Procedural'' * ''Intentional action'' ** Intentional deletion of a file or program * ''Unin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |