|
Hdatta
Hdatta or Haditha ( syc, ܚܕܬܐ ', ar, الحديثة '), was a historical city on the East bank of the Tigris just below its confluence with the Upper Zab. The city flourished during the Sasanian and early Islamic periods. The town was apparently established by the Sasanians, hence its Middle Persian name Newkart (literally "Newly Founded"), which corresponds with its Syriac and later Arabic names. According to al-Baladhuri, the town gained its name when the inhabitants of Firuz Shabur (Pirisabora; Anbar) of central Mesopotamia migrated to this location and transferred the name of their newly founded city with them. The city became renowned as a bishopric centre of the Church of the East within the ecclesiastical province of Adiabene. There existed also a substantial number of Jews, many of whom were converted to Christianity at the hand of its bishop Titus of Hdatta in the 6th century. The city prospered and expanded during the Abbasid period, and the fourth Caliph Al-Hadi mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adiabene (East Syriac Ecclesiastical Province)
Metropolitanate of Adiabene ( syr, Hadyab ܚܕܝܐܒ) was an East Syriac metropolitan province of the Church of the East between the 5th and 14th centuries, with more than fifteen known suffragan dioceses at different periods in its history. Although the name Hadyab normally connoted the region around Erbil and Mosul in present-day Iraq, the boundaries of the East Syriac metropolitan province went well beyond the Erbil and Mosul districts. Its known suffragan dioceses included Beth Bgash (the Hakkari region of eastern Turkey) and Adarbaigan (the Ganzak district, to the southeast of Lake Urmi), well to the east of Adiabene proper. Ecclesiastical history The bishop of Erbil, present-day Iraqi Kurdistan, became metropolitan of Adiabene in 410, responsible also for the six suffragan dioceses of Beth Nuhadra (), Beth Bgash, Beth Dasen, Ramonin, Beth Mahqart and Dabarin. Bishops of the dioceses of Beth Nuhadra, Beth Bgash and Beth Dasen, which covered the modern ʿAmadiya and Hakkari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeshudad Of Merv
Mar Ishodad of Merv ( syc, , Māri Ishoʿdād Maruzāyā; fl. AD 850) was a bishop of Hdatta and prominent theologian of the Church of the East, best known for his ''Commentaries'' on the Old and New Testaments. Life Very little is known of Ishodad's life, but a few details have survived in annotations to the list of patriarchs compiled by Mari ibn Suleiman and Amr ibn Matta. His epithet "of Merv" may denote a birthplace, meaning that he was born in the city of Merv in Khorasan, but this inference remains conjectural: his relationship to Merv is not known with certainty.. A member of the Church of the East—historically, though inaccurately, known as the Nestorian church—he became bishop of Hdatta,. a town close to the mouth of the Great Zab in modern Iraq, perhaps in 837 after Abraham of Marga left the see to become patriarch. Ishodad was a candidate for the patriarchate of the Church of the East around 853 after Abraham's death.. At the time the patriarchate was subject ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abraham II (Nestorian Patriarch)
Abraham II was Patriarch of the Church of the East from 837 to 850. He was a monk at Beth Abe and was later appointed a bishop of Hdatta before being elected to the patriarchate. Brief accounts of Abraham's patriarchate are given in the ''Ecclesiastical Chronicle'' of the Jacobite writer Bar Hebraeus (''floruit'' 1280) and in the ecclesiastical histories of the Nestorian writers Mari (twelfth-century), Amr (fourteenth-century) and Sliba (fourteenth-century). The following account of Abraham's patriarchate is given by Bar Hebraeus: Sabrisho II Sabrishoʿ II was Patriarch of the Church of the East The Patriarch of the Church of the East (also known as Patriarch of the East, Patriarch of Babylon, the Catholicose of the East or the Grand Metropolitan of the East) is the patriarch, or lea ... was succeeded by Abraham II, from the monastery of Beth Abe, who was a man pure and chaste in body but not learned, and not up to the task of governing the church. His nephew Ephrem, his sister' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anbar (town)
Anbar ( ar, الأنبار, al-Anbār, syr, ܐܢܒܐܪ, Anbar,) also known by its original ancient name, Peroz-Shapur, was an ancient and medieval town in central Iraq. It played a role in the Roman–Persian Wars of the 3rd–4th centuries, and briefly became the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate before the founding of Baghdad in 762. It remained a moderately prosperous town through the 10th century, but quickly declined thereafter. As a local administrative centre, it survived until the 14th century, but was later abandoned. Its ruins are near modern Fallujah. The city gives its name to the Al-Anbar Governorate. History Origins The city is located on the left bank of the Middle Euphrates, at the junction with the Nahr Isa canal, the first of the navigable canals that link the Euphrates to the River Tigris to the east. The origins of the city are unknown, but ancient, perhaps dating to the Babylonian era and even earlier: the local artificial mound of Tell Aswad dates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Hadi
Abū Muḥammad Mūsā ibn al-Mahdī al-Hādī ( ar, أبو محمد موسى بن المهدي الهادي; 26 April 764 CE 14 September 786 CE) better known by his laqab Al-Hādī (الهادي) was the fourth Arab Abbasid caliph who succeeded his father Al-Mahdi and ruled from 169 AH (785 CE) until his death in 170 AH (786 CE). His short reign ended with internal chaos and power struggles with his mother. Biography Al-Hadi was the eldest son of Al-Mahdi and Al-Khayzuran and the older brother of Harun al-Rashid. He was very dear to his father and was appointed as the first crown prince by his father at the age of 16 and was chosen as the leader of the army. Prior to his death, Al-Mahdi supposedly favored his second son, Harun al-Rashid, as his successor, taking him on multiple military expeditions in 779 and 781 to train him to be the next caliph, as his own father prepared him, but died before the formal transfer of the crown prince title could occur. Alternatively, Al-R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibn Batish
Ibn Bāṭīsh (June 1179 – June 1257) was a Muslim scholar and jurist belonging to the Shāfiʿī '' maddhab'' (legal school of thought). He was the '' muftī'' of Aleppo from 1230 until his death. Life Ibn Bāṭīsh, whose given name was Ismāʿīl, was born on 24 June 1179 in Mosul (as the ''nisba'' al-Mawṣilī indicates) to a humble family. His father, Hibatallāh, had moved to Mosul from al-Ḥadītha. Ibn Bāṭīsh records two things he learned from his father: a ''ḥadīth'' (tradition) his father had learned from al-Shahrazūrī and some poetry of Laylā al-Akhyaliyya and her lover that his father learned from al-Ṭūsī, who taught at Mosul and died in 1182. The only other family member about whom anything is known is Ibn Batish's younger brother Ibrāhīm, who was born in Mosul on 16 March 1189 and died during the siege of Aleppo in January 1260, according to al-Dimyāṭī. Ibn Bāṭīsh excelled in ''fiqh'' (jurisprudence) at the Madrasa al-Niẓāmīyya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigris
The Tigris () is the easternmost of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, and empties into the Persian Gulf. Geography The Tigris is 1,750 km (1,090 mi) long, rising in the Taurus Mountains of eastern Turkey about 25 km (16 mi) southeast of the city of Elazığ and about 30 km (20 mi) from the headwaters of the Euphrates. The river then flows for 400 km (250 mi) through Southeastern Turkey before becoming part of the Syria-Turkey border. This stretch of 44 km (27 mi) is the only part of the river that is located in Syria. Some of its affluences are Garzan, Anbarçayi, Batman, and the Great and the Little Zab. Close to its confluence with the Euphrates, the Tigris splits into several channels. First, the artificial Shatt al-Hayy branches off, to join the Euphrates near Nasiriyah. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Mesopotamia Under The Abbasid Caliphate
Upper may refer to: * Shoe upper or ''vamp'', the part of a shoe on the top of the foot * Stimulant, drugs which induce temporary improvements in either mental or physical function or both * ''Upper'', the original film title for the 2013 found footage film '' The Upper Footage'' See also {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nineveh Governorate
Nineveh Governorate ( ar, محافظة نينوى, syr, ܗܘܦܪܟܝܐ ܕܢܝܢܘܐ, Hoparkiya d’Ninwe, ckb, پارێزگای نەینەوا, Parêzgeha Neynewa), also known as Ninawa Governorate, is a governorate in northern Iraq. It has an area of and an estimated population of 2,453,000 people as of 2003. Its largest city and provincial capital is Mosul, which lies across the Tigris river from the ruins of ancient Nineveh. Before 1976, it was called ''Mosul Province'' and included the present-day Dohuk Governorate. The second largest city is Tal Afar, which has an almost exclusively Turkmen population. An ethnically, religiously and culturally diverse region, it was partly conquered by ISIS in 2014. Iraqi government forces retook the city of Mosul in 2017. Recent history and administration Its two cities endured the 2003 U.S.-led invasion of Iraq and emerged unscathed. In 2004, however, Mosul and Tal Afar were the scenes of fierce battles between US-led troops an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capitals Of Caliphates
Capital may refer to: Common uses * Capital city, a municipality of primary status ** List of national capital cities * Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences * Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used for further production *Economic capital * Financial capital, an economic resource measured in terms of money * Capital (Marxism), a central concept in Marxian critique of political economy *Capital good *Natural capital *Public capital *Human capital *Instructional capital *Social capital Architecture and buildings * Capital (architecture), the topmost member of a column or pilaster * Capital (fortification), a proportion of a bastion * The Capital (building), a commercial building in Mumbai, India Arts, entertainment and media Literature Books * ''Das Kapital'' ('Capital: Critique of Political Economy'), a foundational theoretical text by Karl Marx * '' Capital: The Eruption of Delhi'', a 2014 book by Rana Dasgupta * ''Capital'' (no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kashkar
Kashkar, also known as Kaskar, ( syc, ܟܫܟܪ), was a city in southern Mesopotamia. Its name appears to originate from Syriac ' meaning "citadel" or "town". Other sources connect it to ' "farming". It was originally built on the Tigris, across the river from the later medieval city of Wasit. The city was originally a significant Sasanian city built on the west bank of the Tigris where Greek speaking deportees from north-western Syria were settled by Shapur I in the mid third century A.D. According to Syriac tradition, Mar Mari is said to have preached and performed miracles and converted many of its inhabitants to Christianity. Kashkar became an important centre of Christianity in lower Mesopotamia and had its own diocese which lay under the jurisdiction of the Patriarchal Province of Seleucia-Ctesiphon. During a flood the Tigris burst its banks leaving Kashkar on its east bank. The medieval city of Wasit was built on the west bank of the new channel by al-Hajjaj ibn Yusuf, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol Conquests
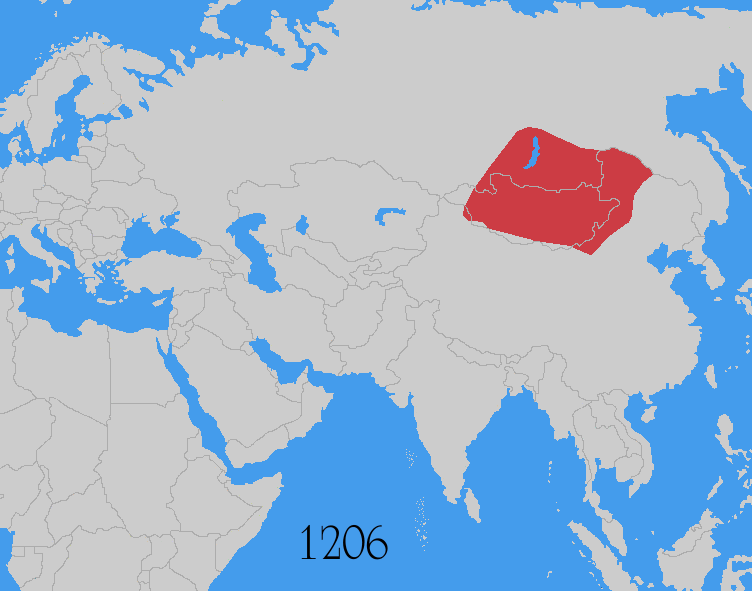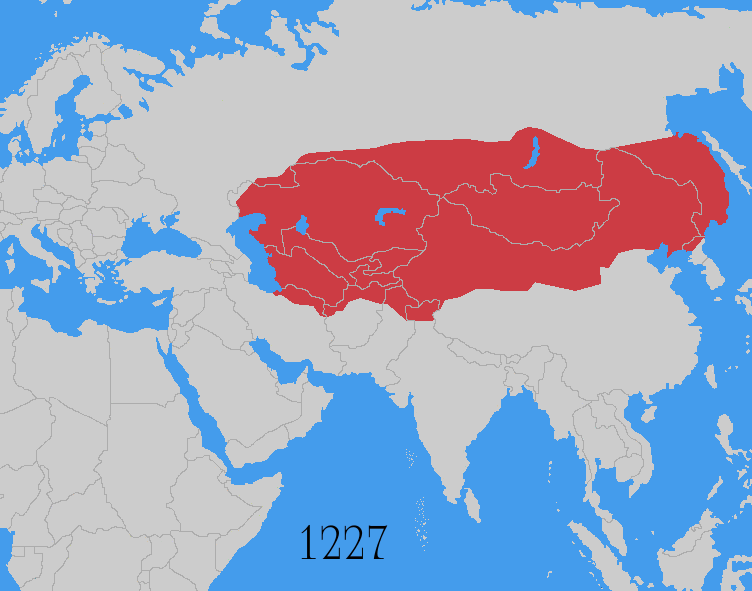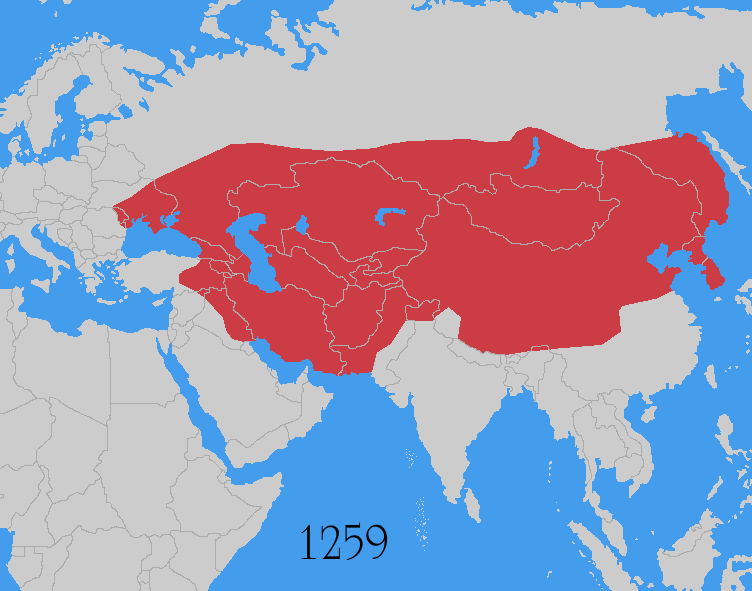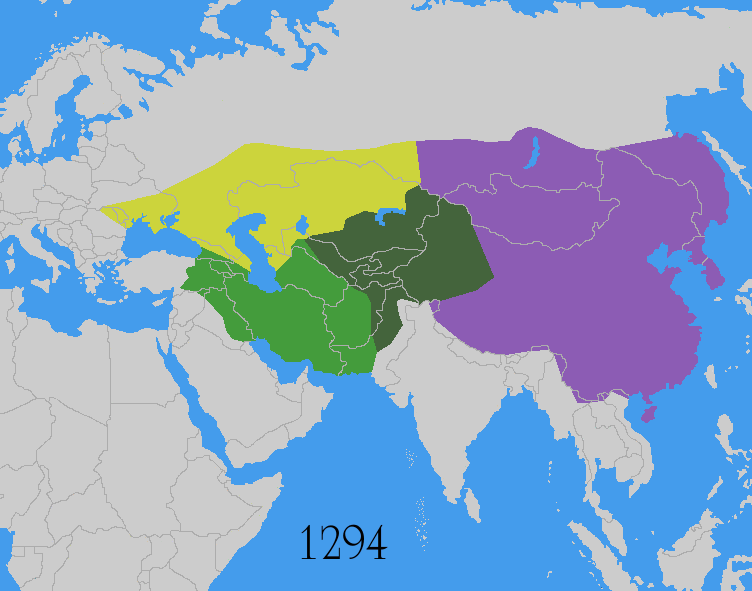
The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire: the Mongol Empire ( 1206- 1368), which by 1300 covered large parts of Eurasia. Historians regard the Mongol devastation as one of the deadliest episodes in history. In addition, Mongol expeditions may have spread the bubonic plague across much of Eurasia, helping to spark the Black Death of the 14th century. The Mongol Empire developed in the course of the 13th century through a series of victorious campaigns throughout Asia, reaching Eastern Europe by the 1240s. In contrast with later "empires of the sea" such as European colonial powers, the Mongol Empire was a land power, fueled by the grass-foraging Mongol cavalry and cattle. Thus most Mongol conquest and plundering took place during the warmer seasons, when there was sufficient grazing for their herds. The rise of the Mongols was preceded by 15 years of wet and warm weather conditions from 1211 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


%2C_(033)_der_geladene_Gastredner_Athiel_al-Nudschafi%2C_Gouverneur_von_Ninive.jpg)