|
Havre Trough
The Havre Trough (Havre Basin) is a currently actively rifting back-arc basin about to wide, between the Australian Plate and Kermadec microplate. The trough extends northward from New Zealand's offshore Taupō Volcanic Zone commencing at Zealandia's continental shelf margin and continuing as a tectonic feature, as the Lau Basin which currently contains active seafloor spreading centers. Its eastern margin is defined by the Kermadec Ridge created by Pacific Plate subduction under the Kermadec microplate, while the western margin is the remnant Lau-Colville Ridge. Geology The Havre Trough is characterised by a number of basins up to deep in the south, with several more shallow volcanic edifices that may rise to within of the ocean surface. It is a back-arc domain where rifting is universally oblique to the bounding ridges and consists of rifted horsts and grabens, extrusive magmatism and partially sedimented rifts. The western basins have flat floors and sediment in fill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taupō Volcanic Zone
The Taupō Volcanic Zone (TVZ) is a volcanic area in the North Island of New Zealand that has been active for the past two million years and is still highly active. Mount Ruapehu marks its south-western end and the zone runs north-eastward through the Taupō and Rotorua areas and offshore into the Bay of Plenty. It is part of the larger Central Volcanic Region that extends further westward through the western Bay of Plenty to the eastern side of the Coromandel Peninsula and has been active for four million years. At Taupō the rift volcanic zone is widening east–west at the rate of about 8 mm per year while at Mount Ruapehu it is only 2–4 mm per year but this increases at the north eastern end at the Bay of Plenty coast to 10–15 mm per year. It is named after Lake Taupō, the flooded caldera of the largest volcano in the zone, the Taupō Volcano and contains a large central volcanic plateau as well as other landforms associated with its containing tecton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90% of all volcanic rock on Earth is basalt. Rapid-cooling, fine-grained basalt is chemically equivalent to slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro. The eruption of basalt lava is observed by geologists at about 20 volcanoes per year. Basalt is also an important rock type on other planetary bodies in the Solar System. For example, the bulk of the plains of Venus, which cover ~80% of the surface, are basaltic; the lunar maria are plains of flood-basaltic lava flows; and basalt is a common rock on the surface of Mars. Molten basalt lava has a low viscosity due to its relatively low silica content (between 45% and 52%), resulting in rapidly moving lava flows that can spread over great areas before cooling and solidifying. Flood basalts are thick sequence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of Oceania
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great ocean basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, stratification, rock exposure and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, mounds, hills, ridges, cliffs, valleys, rivers, peninsulas, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodies and sub-surface features. Mountains, hills, plateaux, and plains are the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Basins Of The Pacific Ocean
Oceanic may refer to: *Of or relating to the ocean *Of or relating to Oceania **Oceanic climate **Oceanic languages **Oceanic person or people, also called "Pacific Islander(s)" Places *Oceanic, British Columbia, a settlement on Smith Island, British Columbia, Canada * Oceanic, New Jersey, an unincorporated community within Rumson Borough, Monmouth County, New Jersey, United States Ships named Oceanic * , the White Star Line's first ocean liner * , a transatlantic ocean liner built for the White Star Line * , a project of the 1930s * , built as SS ''Independence'' in 1950 * , also named ''Big Red Boat I'' by Premier Cruises Art, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * Oceanic Airlines or Oceanic Airways, often used in disaster movies * Oceanic Flight 815, a flight in the television series ''Lost'' Literature * "Oceanic" (novella), a 1998 sci-fi novella by Greg Egan Music ;Artists * Oceanic (band), a 1990s UK dance/house act ;Albums * ''Oceanic'' (Isis album) * ''O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
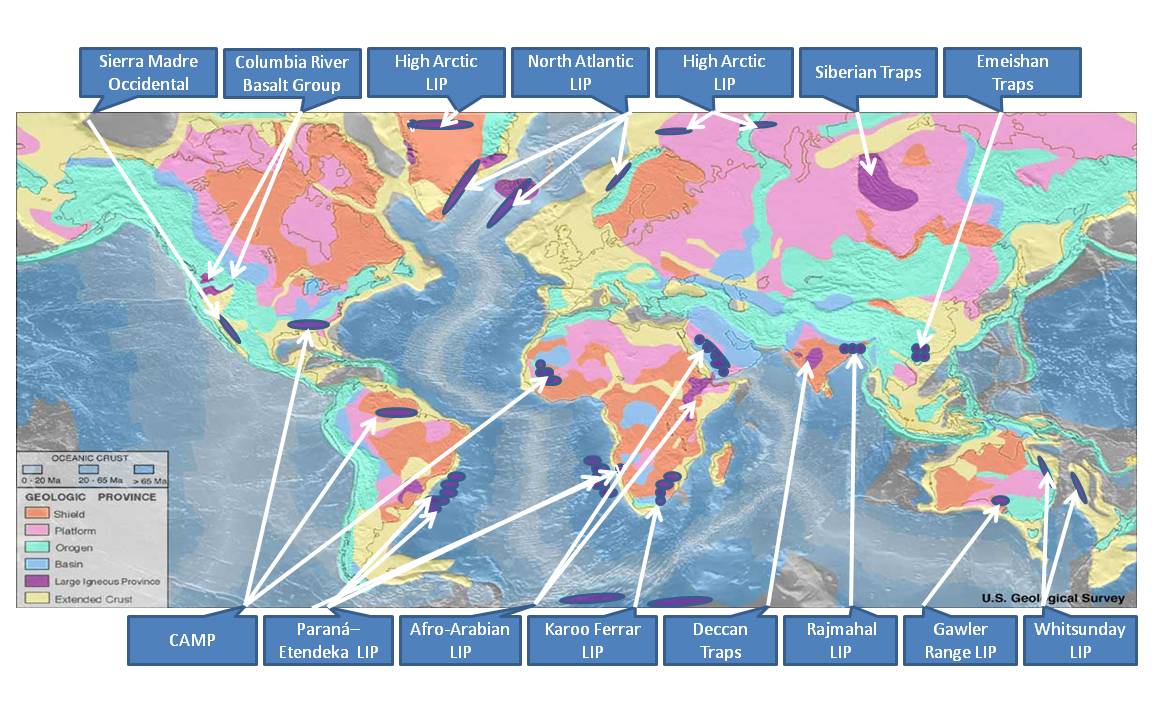
Large Igneous Province
A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including intrusive (sills, dikes) and extrusive (lava flows, tephra deposits), arising when magma travels through the crust towards the surface. The formation of LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with divergent plate tectonics. The formation of some of the LIPs in the past 500 million years coincide in time with mass extinctions and rapid climatic changes, which has led to numerous hypotheses about causal relationships. LIPs are fundamentally different from any other currently active volcanoes or volcanic systems. Definition In 1992 researchers first used the term ''large igneous province'' to describe very large accumulations—areas greater than 100,000 square kilometers (approximately the area of Iceland)—of mafic igneous rocks that were erupted or emplaced at depth within an extremely short geological time interval: a few million years or less. Maf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin ''creta'', " chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation ''Kreide''. The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now-extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was ice free, and forests extended to the poles. During this time, new groups of mammals and birds appeared. During the Early Cretaceous, flowering plants appeared and began to rapidly diversify, becoming the dominant group of plants across the Ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hikurangi Plateau
The Hikurangi Plateau is an oceanic plateau in the South Pacific Ocean east of the North Island of New Zealand. It is part of a large igneous province (LIP) together with Manihiki and Ontong Java, now located and north of Hikurangi respectively. Mount Hikurangi, in Māori mythology the first part of the North Island to emerge from the ocean, gave its name to the plateau. Geological setting The Hikurangi Plateau covers approximately and reaches below sea level. Hikurangi Plateau is cut by the Hikurangi Channel, a 2000 km abyssal channel that starts at Kaikoura and runs along the Hikurangi Trench as far as the Māhia Peninsula before crossing the plateau and ending in the South-west Pacific abyssal plain. Tectonic evolution Two models have been proposed for the formation of Hikurangi. It can be derived from the mantle plume that caused the break-up of Gondwana and the separation of Zealandia from Antarctica 107 Ma. Alternatively, it could have formed toget ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kermadec And Tonga Plates ''
*
{{disambiguation, geo, surname ...
Kermadec or de Kermadec may refer to: Geography * Kermadec Islands, a subtropical island arc in the South Pacific Ocean northeast of New Zealand * Kermadec Plate, a long narrow tectonic plate located west of the Kermadec Trench * Kermadec Trench, one of Earth's deepest oceanic trenches, reaching a depth of 10047 m * Kermadec-Tonga subduction zone, a convergent plate boundary People * Eugène de Kermadec (1899–1976), a French painter * Jean-Michel Huon de Kermadec (1748–1792), an 18th-century French navigator * Liliane de Kermadec (born 1928), a French film director and screenwriter See also * ''Kermadecia ''Kermadecia'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Proteaceae. The genus comprises five species, all endemic to New Caledonia. Its closest relatives are '' Sleumerodendron'' (New Caledonia) and '' Turrillia'' ( Fiji, Vanuatu Vanu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mayor Island / Tūhua
Mayor Island / Tūhua is a dormant shield volcano located off the Bay of Plenty coast of New Zealand's North Island. It lies north of Tauranga and covers . Geography The island is quite steep along its coast and rises to above sea level. A saddle about deep separates it from the North Island, while the other side of the volcano rises from the seafloor some beneath the waves. Approximately 18,000 years ago during the Last Glacial Maximum when sea levels were over 100 metres lower than present day levels, Mayor Island / Tūhua was connected to the rest of New Zealand. Sea levels began to rise 7,000 years ago, separating Mayor Island / Tūhua from the mainland. Hot springs abound, and there are two small crater lakes, Green Lake and Black Lake. These lie within two overlapping calderas formed in explosive eruptions 36,000 and 6,340 years ago. Geology Mayor Island is characterised as a peralkaline volcano and has exhibited a wide range of eruptive styles, including lava ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhyolite
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained ( aphanitic) in texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals ( phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained groundmass. The mineral assemblage is predominantly quartz, sanidine, and plagioclase. It is the extrusive equivalent to granite. Rhyolitic magma is extremely viscous, due to its high silica content. This favors explosive eruptions over effusive eruptions, so this type of magma is more often erupted as pyroclastic rock than as lava flows. Rhyolitic ash-flow tuffs are among the most voluminous of continental igneous rock formations. Rhyolitic tuff has been extensively used for construction. Obsidian, which is rhyolitic volcanic glass, has been used for tools from prehistoric times to the present day because it can be shaped to an extremely sharp edge. Rhyolitic pumice finds use as an abrasive, in concrete, and as a soil amendment. Description R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caldera Volcano
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is gone. The ground surface then collapses into the emptied or partially emptied magma chamber, leaving a large depression at the surface (from one to dozens of kilometers in diameter). Although sometimes described as a crater, the feature is actually a type of sinkhole, as it is formed through subsidence and collapse rather than an explosion or impact. Compared to the thousands of volcanic eruptions that occur each century, the formation of a caldera is a rare event, occurring only a few times per century. Only seven caldera-forming collapses are known to have occurred between 1911 and 2016. More recently, a caldera collapse occurred at Kīlauea, Hawaii in 2018. Etymology The term ''caldera'' comes from Spanish ', and Latin ', meani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacite
Dacite () is a volcanic rock formed by rapid solidification of lava that is high in silica and low in alkali metal oxides. It has a fine-grained ( aphanitic) to porphyritic texture and is intermediate in composition between andesite and rhyolite. It is composed predominantly of plagioclase feldspar and quartz. Dacite is relatively common, occurring in many tectonic settings. It is associated with andesite and rhyolite as part of the subalkaline tholeiitic and calc-alkaline magma series. Composition Dacite consists mostly of plagioclase feldspar and quartz with biotite, hornblende, and pyroxene ( augite or enstatite). The quartz appears as rounded, corroded phenocrysts, or as an element of the ground-mass. The plagioclase in dacite ranges from oligoclase to andesine and labradorite. Sanidine occurs, although in small proportions, in some dacites, and when abundant gives rise to rocks that form transitions to the rhyolites. The relative proportions of feldspars a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)