|
Hausman Baboe
Hausman Baboe was a colonial head of Kuala Kapuas district of Central Kalimantan in the Dutch East Indies; he was also an early Dayak journalist and an Indonesian nationalist. Baboe was born into an aristocratic family of Dayak Ngaju people and served as head of Kuala Kapuas under the Dutch colonial government but was dismissed from his post due to his anti-colonial remarks. He became a prominent Dayak political figure and was several times accused of being a communist due to his close association with the left-wing political party Sarekat Rakjat. Despite being a Christian, his Indonesian nationalist ideals drew him close to Sarekat Islam. Baboe started several congresses of native Kalimantan organizations and attempted to invite Oemar Said Tjokroaminoto to his congress, which caused unrest across Kalimantan and a subsequent travel ban by the Dutch East Indies government. Baboe was executed in 1943 after the occupying Japanese military accused him of collaborating with forme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies ( nl, Nederlands(ch)-Indië; ), was a Dutch colony consisting of what is now Indonesia. It was formed from the nationalised trading posts of the Dutch East India Company, which came under the administration of the Dutch government in 1800. During the 19th century, the Dutch possessions and hegemony expanded, reaching the greatest territorial extent in the early 20th century. The Dutch East Indies was one of the most valuable colonies under European rule, and contributed to Dutch global prominence in spice and cash crop trade in the 19th to early 20th centuries. The colonial social order was based on rigid racial and social structures with a Dutch elite living separate from but linked to their native subjects. The term ''Indonesia'' came into use for the geographical location after 1880. In the early 20th century, local intellectuals began developing the concept of Indonesia as a nation state, and set the stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
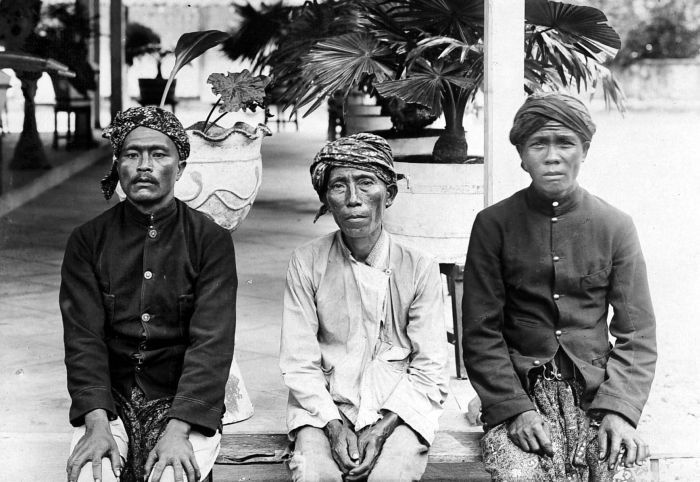
Banjar People
The Banjar or Banjarese ( bjn, Urang Banjar; ) are an indigenous ethnic group native to the Banjar regions (notably Banjarmasin, Banjarbaru, Banjar Regency, etc.) in the southeastern Kalimantan hemisphere of Indonesia. Nowadays, Banjarese diaspora can be found in neigbouring Banjar regions as well; including Kotabaru Regency, the southeastern regions of Central Kalimantan, southernmost regions of East Kalimantan, and some provinces of Indonesia in general. The Banjarese diaspora community also can be found in neighbouring countries of Indonesia, such as Brunei, Malaysia (notably in Sabah and Perak), and Singapore. Etymology Etymologically, the word ''Banjar'' is derived from terminology in the Janyawai dialect of Ma'anyan language, which rooted from Old Javanese language. It is initially used to identified the Ma'anyan, Meratus Dayak, and Ngaju people who are already "Javanized" when the Javanese people arrived in southeastern Kalimantan regions to established their ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch East Indies Campaign
The Dutch East Indies campaign of 1941–1942 was the conquest of the Dutch East Indies (present-day Indonesia) by forces from the Empire of Japan in the early days of the Pacific campaign of World War II. Forces from the Allies attempted unsuccessfully to defend the islands. The East Indies were targeted by the Japanese for their rich oil resources which would become a vital asset during the war. The campaign and subsequent three and a half year Japanese occupation was also a major factor in the end of Dutch colonial rule in the region. Background The East Indies was one of Japan's primary targets if and when it went to war because the colony possessed abundant valuable resources, the most important of which were its rubber plantations and oil fields; the colony was the fourth-largest exporter of oil in the world, behind the U.S., Iran, and Romania. The oil made the islands enormously important to the Japanese, so they sought to secure the supply for themselves. They sent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madurese People
id, Orang Madura , image = , image_caption = A portrait of Madurese village head. , population = 7,179,356 , popplace = : , region1 = East Java , pop1 = 6,520,403 , region2 = West Kalimantan , pop2 = 274,869 , region3 = Jakarta , pop3 = 79,925 , region4 = South Kalimantan , pop4 = 53,002 , region5 = East Kalimantan , pop5 = 46,823 , region6 = West Java , pop6 = 43,001 , region7 = Central Kalimantan , pop7 = 42,668 , region8 = Bali , pop8 = 29,864 , region9 = Bangka Belitung , pop9 = 15,429 , region10 = Central Java , pop10 = 12,920 , langs = Native MadureseAlsoIndonesian Javanese , rels = Islam , related = Javanese people, Sundanese people The Madurese (sometimes Madurace or Madhurâ; also known as Orang Madura and Suku Madura in Indonesian) are an ethnic group originally from the island o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indonesian National Awakening
The Indonesian National Awakening ( id, Kebangkitan Nasional Indonesia) is a term for the period in the first half of the 20th century, during which people from many parts of the archipelago of Indonesia first began to develop a national consciousness as "Indonesians". In the pursuit of profits and administrative control, the Dutch imposed an authority of the Dutch East Indies on an array of peoples who had not previously shared a unified political identity. By the start of the 20th century, the Dutch had formed the territorial boundaries of a colonial state that became the precursor to modern Indonesia. In the first half of the 20th century, new organisations and leadership developed. Under its Ethical Policy, the Netherlands helped create an educated Indonesian elite. These profound changes amongst the indigenous Indonesian population are often referred to as the "Indonesian National Revival". They were accompanied by increased political activism and culminated in Indonesian n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makassar
Makassar (, mak, ᨆᨀᨔᨑ, Mangkasara’, ) is the capital of the Indonesian province of South Sulawesi. It is the largest city in the region of Eastern Indonesia and the country's fifth-largest urban center after Jakarta, Surabaya, Medan, and Bandung.Ministry of Internal AffairsRegistration Book for Area Code and Data of 2013/ref> The city is located on the southwest coast of the island of Sulawesi, facing the Makassar Strait. Throughout its history, Makassar has been an important trading port, hosting the center of the Gowa Sultanate and a Portuguese naval base before its conquest by the Dutch East India Company in the 17th century. It remained an important port in the Dutch East Indies, serving Eastern Indonesian regions with Makassarese fishers going as far south as the Australian coast. For a brief period after Indonesian independence, Makassar became the capital of the State of East Indonesia, during which an uprising occurred. The city's area is , and it had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Java
East Java ( id, Jawa Timur) is a Provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia located in the easternmost hemisphere of Java island. It has a land border only with the province of Central Java to the west; the Java Sea and the Indian Ocean border its northern and southern coasts, respectively, while the narrow Bali Strait to the east separates Java from Bali by around . Located in eastern Java (island), Java, the province also includes the island of Madura Island, Madura (which is connected to Java by the longest bridge in Indonesia, the Suramadu Bridge), as well as the Kangean Islands, Kangean islands and other smaller island groups located further east (in the northern Bali Sea) and Masalembu Islands, Masalembu archipelagos in the north. Its capital is Surabaya, the Largest cities in Indonesia, second largest city in Indonesia, a major industrial center and also a major business center. Banyuwangi is the largest regency in East Java and the largest on the island of Java. The p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volksraad (Dutch East Indies)
The ''Volksraad'' (People's Council) an advisory, and later semi-legislative institution for the Dutch East Indies, was provided for by law in 1916 but was only established with the actual installation of the Council in 1918. It was a hesitant and slow attempt at democratisation of the Dutch East Indies as part of the "ethical policy" adopted by the Dutch government. The power of the ''Volksraad'' was limited as it only had advisory powers. Although part of the council was elected only a small proportion of the population had voting rights. Initially the ''Volksraad'' had 39 members, eventually rising to 60. It was reconstituted every four years. The members were partly elected, partly appointed by the colonial administration. Background The idea of a representative body in the Dutch East Indies arose partly became of the Ethical Policy implemented by the Dutch government as part of a move away from simple exploration of the colony towards expressing concern for the Indonesian p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agus Salim
''Haji'' Agus Salim (; October 8, 1884 – November 4, 1954) was an Indonesian journalist, diplomat, and statesman. He served as Indonesia's Minister of Foreign Affairs between 1947 and 1949. Early life Agus Salim was born Masjhoedoelhaq Salim on October 8, 1884, in the village of Koto Gadang, a suburb of Fort de Kock. His father, Sutan Mohammad Salim, was a colonial prosecutor and judge whose highest rank was chief judge for the indigenous court in Tanjung Pinang. His birth name, which translates into "defender of truth", was changed into Agus Salim early in his childhood. Salim received his elementary education at ''Europeesche Lagere School''; at that time, it was considered a privilege for a non-European child to attend an all-European school. He continued his studies at the ''Hogere Burgerschool'' in Batavia, and graduated with the highest score in the whole Dutch East Indies. Salim's father had applied (and was granted) for his two sons, Agus and Jacob, to be granted equ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
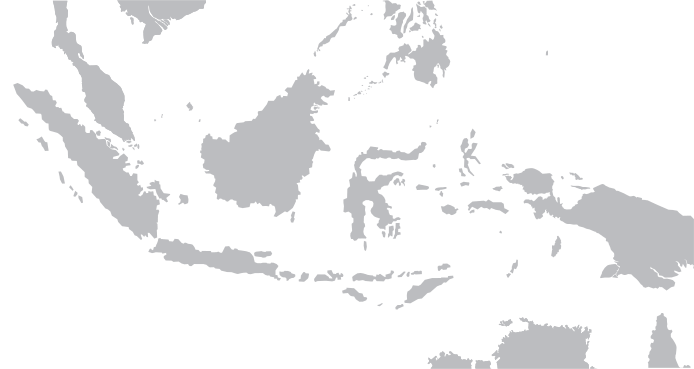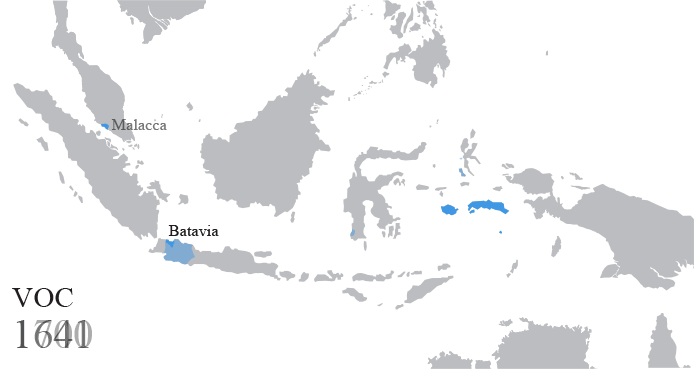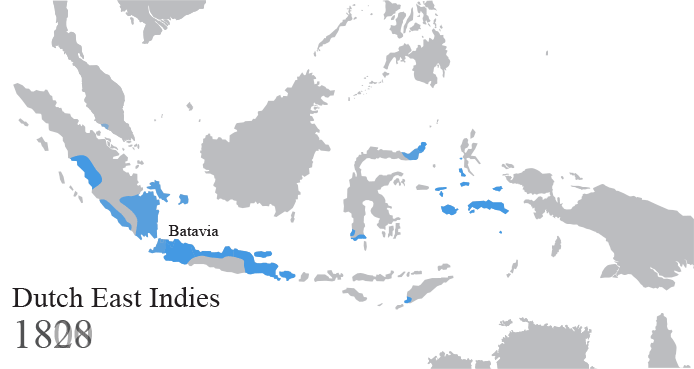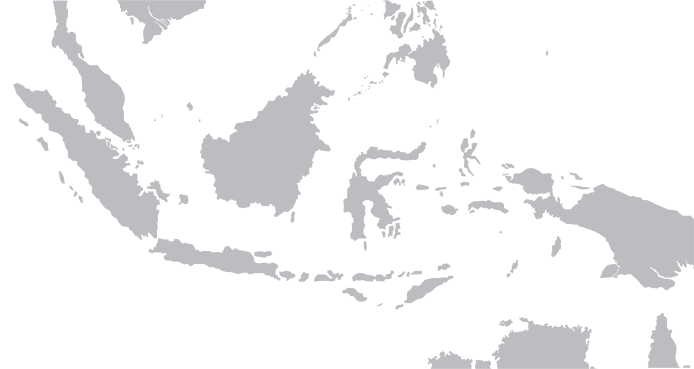
Batavia, Dutch East Indies
Batavia was the capital of the Dutch East Indies. The area corresponds to present-day Jakarta, Indonesia. Batavia can refer to the city proper or its suburbs and hinterland, the Ommelanden, which included the much-larger area of the Residency of Batavia in the present-day Indonesian provinces of Jakarta, Banten and West Java. The founding of Batavia by the Dutch in 1619, on the site of the ruins of Jayakarta, led to the establishment of a Dutch colony; Batavia became the center of the Dutch East India Company's trading network in Asia. Monopolies on local produce were augmented by non-indigenous cash crops. To safeguard their commercial interests, the company and the colonial administration absorbed surrounding territory. Batavia is on the north coast of Java, in a sheltered bay, on a land of marshland and hills crisscrossed with canals. The city had two centers: Oud Batavia (the oldest part of the city) and the relatively-newer city, on higher ground to the south. It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's List of islands by population, most populous island, home to approximately 56% of the Demographics of Indonesia, Indonesian population. Indonesia's capital city, Jakarta, is on Java's northwestern coast. Many of the best known events in Indonesian history took place on Java. It was the centre of powerful Hindu-Buddhist empires, the Islamic sultanates, and the core of the colonial Dutch East Indies. Java was also the center of the History of Indonesia, Indonesian struggle for independence during the 1930s and 1940s. Java dominates Indonesia politically, economically and culturally. Four of Indonesia's eight UNESCO world heritage sites are located in Java: Ujung Kulon National Park, Borobudur Temple, Prambanan Temple, and Sangiran Early Man Site. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pangkalan Bun
Pangkalan Bun is the capital of West Kotawaringin Regency in Borneo, Indonesia. It has a population of around 200,000 It is also the administrative headquarters of South Arut (''Arut Selatan'') district (''kecamatan''). Pangkalan Bun is served by Iskandar Airport. Several airlines fly to this airport. Shipping services provide connections to Jakarta, Surabaya, and Semarang. Birutė Galdikas established her base, Camp Leakey, for the study and conservation of orangutans about from Pangkalan Bun up the Sekonyer River. The site has expanded from the original hut in 1971. Its facilities, supported by the Orangutan Foundation International, are a part of the Tanjung Puting National Park. Crash of AirAsia QZ 8501 Iskandar Airport, Iskandar International Airport was one of the operation centres being used to support search operations following the crash of Indonesia AirAsia Flight 8501, AirAsia QZ 8501 on 28 December 2014 in nearby Karimata Strait. Shortly after the crash, the Nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |