|
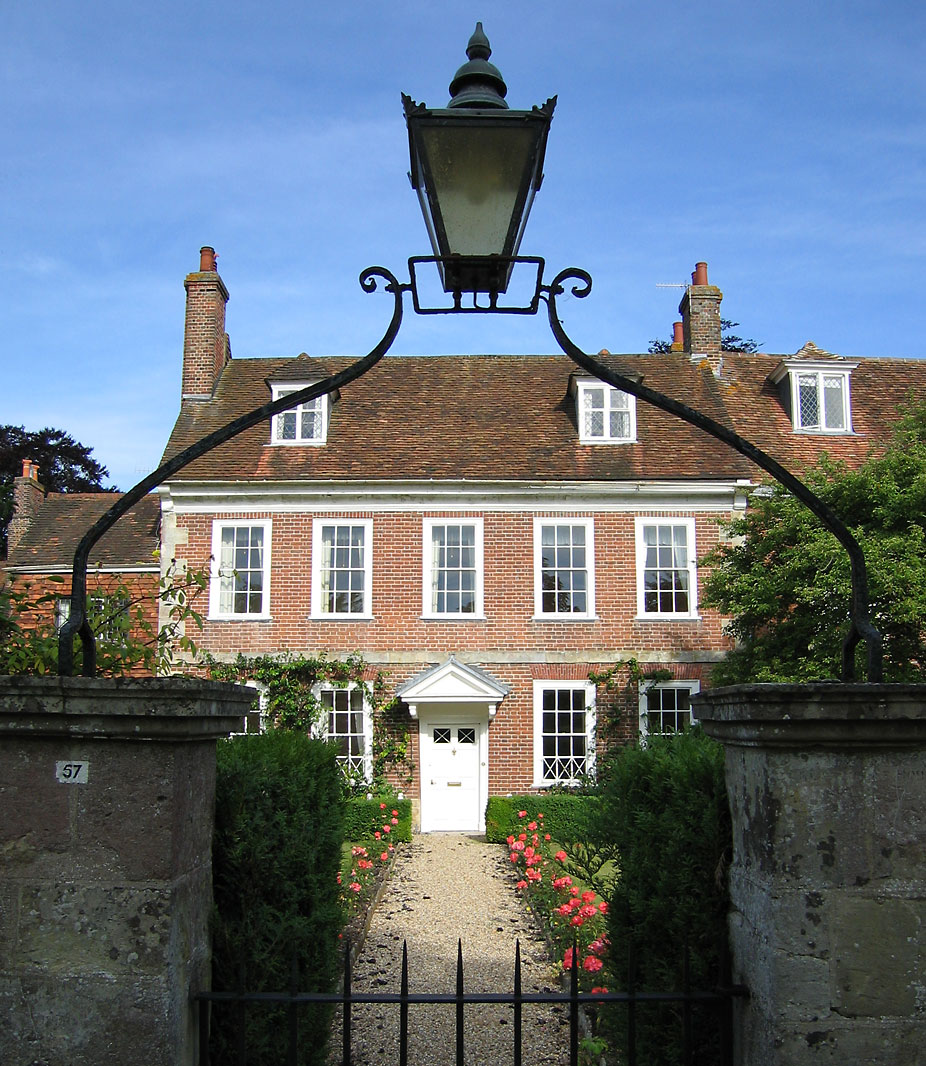
Hatherton, Staffordshire
Hatherton is a settlement and civil parish located south-east of Penkridge, and on the western edge of modern-day Cannock, Staffordshire, England, and lying adjacent to and north of Watling Street, now the A5. The civil parish include the village of Calf Heath. Hatherton was given to Wolverhampton monastery by Lady Wulfruna in 994. Its name, ''Hagerthorndun'' in the , means "the hill where Hawthorns grow". It was once a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe by the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south. The country covers five-eighths of the island of Great Britain, which lies in the North Atlantic, and includes over 100 smaller islands, such as the Isles of Scilly and the Isle of Wight. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic period, but takes its name from the Angles, a Germanic tribe deriving its name from the Anglia peninsula, who settled during the 5th and 6th centuries. England became a unified state in the 10th century and has had a significant cultural and legal impact on the wider world since the Age of Discovery, which began during the 15th century. The English language, the Anglican Church, and Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatherton Canal
The Hatherton Canal is a derelict branch of the Staffordshire and Worcestershire Canal in south Staffordshire, England. It was constructed in two phases, the first section opening in 1841 and connecting the main line to Churchbridge, from where a tramway connected to the Great Wyrley coal mines. The second section was a joint venture with the Birmingham Canal Navigations, and linked Churchbridge to the Cannock Extension Canal by a flight of 13 locks, which were opened with the Extension Canal in 1863. The coal traffic was very profitable, and the canal remained in use until 1949. It was formally abandoned in 1955, after which the Churchbridge flight and much of the Extension Canal were destroyed by open cast mining. Plans for its restoration began in 1975 and the forerunner to thLichfield and Hatherton Canals Restoration Trustwas formed in 1989. Since then they have worked hard to protect and restore the canal, which was threatened by the route of the M6 Toll motorway. Negotia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Parishes In Staffordshire
This is a list of civil parishes in the ceremonial county of Staffordshire, England. There are 195 civil parishes. There is no population data for some of the smallest parishes. The districts of Tamworth and Stoke-on-Trent are fully unparished. Parts of Cannock Chase District and the boroughs of Newcastle under Lyme and Stafford are unparished. These correspond to two separate parts of the former Cannock Urban District, the former municipal boroughs of Stafford, Newcastle-under-Lyme and Tamworth as well as the former county borough of Stoke-on-Trent. See also * List of civil parishes in England References External links Office for National Statistics : Geographical Area ListingsStaffordshire County Council {{Staffordshire Civil parishes Staffordshire Staffordshire (; postal abbreviation Staffs.) is a landlocked county in the West Midlands region of England. It borders Cheshire to the northwest, Derbyshire and Leicestershire to the east, Warwickshire to the so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
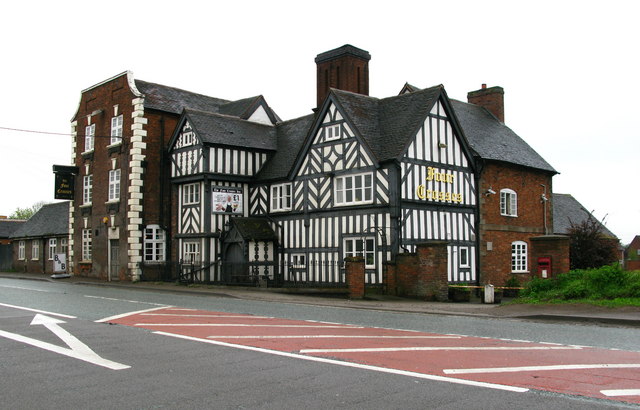
Listed Buildings In Hatherton, Staffordshire
Hatherton is a civil parish in the district of South Staffordshire, Staffordshire, England. It contains three listed buildings that are recorded in the National Heritage List for England. All the listed buildings are designated at Grade II, the lowest of the three grades, which is applied to "buildings of national importance and special interest". The listed buildings consist of a public house, a lodge and a small country house An English country house is a large house or mansion in the English countryside. Such houses were often owned by individuals who also owned a Townhouse (Great Britain), town house. This allowed them to spend time in the country and in the cit .... __NOTOC__ Buildings References Citations Sources * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Hatherton, Staffordshire Lists of listed buildings in Staffordshire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adelaide
Adelaide ( ) is the list of Australian capital cities, capital city of South Australia, the state's largest city and the list of cities in Australia by population, fifth-most populous city in Australia. "Adelaide" may refer to either Greater Adelaide (including the Adelaide Hills) or the Adelaide city centre. The demonym ''Adelaidean'' is used to denote the city and the residents of Adelaide. The Native title in Australia#Traditional owner, Traditional Owners of the Adelaide region are the Kaurna people. The area of the city centre and surrounding parklands is called ' in the Kaurna language. Adelaide is situated on the Adelaide Plains north of the Fleurieu Peninsula, between the Gulf St Vincent in the west and the Mount Lofty Ranges in the east. Its metropolitan area extends from the coast to the Adelaide Hills, foothills of the Mount Lofty Ranges, and stretches from Gawler in the north to Sellicks Beach in the south. Named in honour of Queen Adelaide, the city was founded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Private Hospital, Wakefield Street
The Calvary Wakefield Hospital, formerly Private Hospital, Wakefield Street (PHWS) and variants, Wakefield Street Private Hospital, Wakefield Memorial Hospital and Wakefield Hospital, referred to informally as "the Wakefield", was a private hospital founded in 1883 or 1884 on Wakefield Street in Adelaide, South Australia. In 1935, the hospital occupied new, purpose-built premises on the corner of Wakefield and Hutt Streets. In 2006 it was acquired by Little Company of Mary Health Care Ltd., known as Calvary Health Care, a Roman Catholic not-for-profit organisation. In 2020 it was vacated, being replaced by a newly constructed facility, the Calvary Adelaide Hospital. The hospital provided acute care with inpatient and outpatient facilities, orthopaedic, and neurosurgical services to patients. It specialised in cardiac care, and was the only private 24/7 accident and emergency unit in the city. It employed 600 staff. Beginnings The Wakefield was one of the first private hospit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories by area, and second smallest state by population. It has a total of 1.8 million people. Its population is the second most highly centralised in Australia, after Western Australia, with more than 77 percent of South Australians living in the capital Adelaide, or its environs. Other population centres in the state are relatively small; Mount Gambier, the second-largest centre, has a population of 33,233. South Australia shares borders with all of the other mainland states, as well as the Northern Territory; it is bordered to the west by Western Australia, to the north by the Northern Territory, to the north-east by Queensland, to the east by New South Wales, to the south-east by Victoria, and to the south by the Great Australian B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colony Of South Australia
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the '' metropolitan state'' (or "mother country"). This administrative colonial separation makes colonies neither incorporated territories nor client states. Some colonies have been organized either as dependent territories that are not sufficiently self-governed, or as self-governed colonies controlled by colonial settlers. The term colony originates from the ancient Roman '' colonia'', a type of Roman settlement. Derived from ''colon-us'' (farmer, cultivator, planter, or settler), it carries with it the sense of 'farm' and 'landed estate'. Furthermore the term was used to refer to the older Greek ''apoikia'' (), which were overseas settlements by ancient Greek city-states. The city that founded such a settlement became known as its ''metropolis'' ("mother-cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alice Tibbits
Alice Tibbits (1854–1932) was a South Australian nursing pioneer who was matron and owner of the Private Hospital, Wakefield Street in the 1880s. She was one of the first to train nurses in Australia and was known as the "Florence Nightingale of South Australia". Early life and education Alice Tibbits was born in Walsall, Staffordshire, England in 1854. She and her friend Kate Hill were influenced by Anglican community nurse Sister Dora (Dorothy Wyndlow Pattison) in Staffordshire. The two friends emigrated to South Australia in 1879 and began nursing at the newly opened Adelaide Children's Hospital. Tibbits was the first person to receive a certificate of training from the hospital in 1881. The training included care of sick children, maternity nursing, and secondment to the lying-in wards of the Destitute Asylum. Upon completion of the course, Tibbits went to London at her own expense to complete a further two years as a probationer at the London Hospital and six months train ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stucco
Stucco or render is a construction material made of aggregates, a binder, and water. Stucco is applied wet and hardens to a very dense solid. It is used as a decorative coating for walls and ceilings, exterior walls, and as a sculptural and artistic material in architecture. Stucco can be applied on construction materials such as metal, expanded metal lath, concrete, cinder block, or clay brick and adobe for decorative and structural purposes. In English, "stucco" sometimes refers to a coating for the outside of a building and " plaster" to a coating for interiors; as described below, however, the materials themselves often have little to no differences. Other European languages, notably Italian, do not have the same distinction; ''stucco'' means ''plaster'' in Italian and serves for both. Composition The basic composition of stucco is cement, water, and sand. The difference in nomenclature between stucco, plaster, and mortar is based more on use than composition. Until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgian Architecture
Georgian architecture is the name given in most English-speaking countries to the set of architectural styles current between 1714 and 1830. It is named after the first four British monarchs of the House of Hanover— George I, George II, George III, and George IV—who reigned in continuous succession from August 1714 to June 1830. The so-called great Georgian cities of the British Isles were Edinburgh, Bath, pre-independence Dublin, and London, and to a lesser extent York and Bristol. The style was revived in the late 19th century in the United States as Colonial Revival architecture and in the early 20th century in Great Britain as Neo-Georgian architecture; in both it is also called Georgian Revival architecture. In the United States the term "Georgian" is generally used to describe all buildings from the period, regardless of style; in Britain it is generally restricted to buildings that are "architectural in intention", and have stylistic characteristics that are ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatherton Hall
Hatherton may refer to: * Hatherton, Cheshire, England * Hatherton, Staffordshire, England ** The derelict Hatherton Canal ** Baron Hatherton * Hatherton Glacier Hatherton Glacier is a large glacier flowing from the Antarctic polar plateau generally eastward along the south side of the Darwin Mountains and entering Darwin Glacier at Junction Spur. It was mapped by the Darwin Glacier Party of the Commonwe ..., in East Antarctica, named for Trevor Hatherton {{geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)