|
Hasmonean Civil War
The Hasmonean Civil War was a civil war between two claimants to the Hasmonean Jewish Crown. What began as an inter-Jewish conflict became a highly decisive conflict that included the Nabataean Kingdom and ended with Roman involvement. This conflict resulted in the loss of Jewish independence. Background The Hasmonean Dynasty had been established after the Maccabean Revolt and had gained independence from the Seleucid Empire, after which it became a powerful regional kingdom. The kingdom reached its greatest extent during the reigns of Alexander Jannaeus and Salome Alexandra, who had two sons, Hyrcanus and Aristobulus. Hyrcanus, the elder son, was not as popular with the people and mostly sided with the Pharisees, while his younger brother Aristobulus was very ambitious and popular and tended to side with the Sadducees. For this reason, Aristobulus began making connections with military officials and owners of bastions even during his mother's lifetime. Early stages Brothers p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Fouquet
Jean (or Jehan) Fouquet (ca.1420–1481) was a French painter and miniaturist. A master of panel painting and manuscript illumination, and the apparent inventor of the portrait miniature, he is considered one of the most important painters from the period between the late Gothic and early Renaissance. He was the first French artist to travel to Italy and experience first-hand the early Italian Renaissance. Little is known of Fouquet's early life and education. Though long assumed to have been an apprentice of the so-called Bedford Master of Paris it is now suggested that he may have studied under the Jouvenal Master in Nantes, whose works were formerly assumed to be early works by Fouquet. Sometime between 1445 and 1447 he travelled to Italy where he came under the influence of Roman Quattrocento artists such as Fra Angelico and Filarete. During the 1450s he began working at the French court, where he counted kings Charles VII and his successor Louis XI among his many patrons. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and marine infantry. Although disused in modern times, heavy infantry also commonly made up the bulk of many historic armies. Infantry, cavalry, and artillery have traditionally made up the core of the combat arms professions of various armies, with the infantry almost always comprising the largest portion of these forces. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French ''infanterie'', from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' īnfāns'' (without speech, newborn, foolish), from which English also gets '' infant''. The individual-soldier term ''infantry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple Mount
The Temple Mount ( hbo, הַר הַבַּיִת, translit=Har haBayīt, label=Hebrew, lit=Mount of the House f the Holy}), also known as al-Ḥaram al-Sharīf (Arabic: الحرم الشريف, lit. 'The Noble Sanctuary'), al-Aqsa Mosque compound, or simply al-Aqsa Mosque (, ''al-Masjid al-Aqṣā'', lit. 'The Furthest Mosque'), * ''Where Heaven and Earth Meet'', page 13: "Nowadays, while oral usage of the term Haram persists, Palestinians tend to use in formal texts the name Masjid al-Aqsa, habitually rendered into English as 'the Aqsa Mosque'" * * * * PEF Survey of Palestine, 1883, volume III Jerusalem, p.119: "The Jamia el Aksa, or 'distant mosque' (that is, distant from Mecca), is on the south, reaching to the outer wall. The whole enclosure of the Haram is called by Moslem writers Masjid el Aksa, 'praying-place of the Aksa,' from this mosque." * Yitzhak Reiter: "This article deals with the employment of religious symbols for national identities and national narratives by us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. is a city in Western Asia. Situated on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea, it is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world and is considered to be a holy city for the three major Abrahamic religions: Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Both Israelis and Palestinians claim Jerusalem as their Capital city, capital, as Israel maintains its primary governmental institutions there and the State of Palestine ultimately foresees it as its seat of power. Because of this dispute, Status of Jerusalem, neither claim is widely recognized internationally. Throughout History of Jerusalem, its long history, Jerusalem has been destroyed at least twice, Sie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salome Alexandra
Salome Alexandra, or Shlomtzion ( grc-gre, Σαλώμη Ἀλεξάνδρα; he, , ''Šəlōmṣīyyōn''; 141–67 BCE), was one of three women to rule over Judea, the other two being Athaliah and Devora. The wife of Aristobulus I, and afterward of Alexander Jannaeus, she was the last regnant queen of Judea, and the last ruler of Judea to die as the sovereign of an independent kingdom. Family Salome Alexandra's personal genealogy is not given by Josephus, nor does it appear in any of the books of Maccabees. Rabbinical sources designate the rabbi, Simeon ben Shetah, as her brother, making her the daughter of Shetah as well. Salome Alexandra's oldest son by Alexander Jannaeus was Hyrcanus II who fought his younger brother Aristobulus II in 73 BCE over the Jewish High Priesthood. Hyrcanus II was eventually successful after enlisting the help of the Nabataean king, Aretas III; bribing Roman officials, including Scaurus; and gaining the favour of Pompey the Great, who defeate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Jannaeus
Alexander Jannaeus ( grc-gre, Ἀλέξανδρος Ἰανναῖος ; he, ''Yannaʾy''; born Jonathan ) was the second king of the Hasmonean dynasty, who ruled over an expanding kingdom of Judea from 103 to 76 BCE. A son of John Hyrcanus, he inherited the throne from his brother Aristobulus I, and married his brother's widow, Queen Salome Alexandra. From his conquests to expand the kingdom to a bloody civil war, Alexander's reign has been generalised as cruel and oppressive with never-ending conflict. The major historical sources of Alexander's life are Josephus's '' Antiquities of the Jews'' and ''The Jewish War''. The kingdom of Alexander Jannaeus was the largest and strongest known Jewish State outside of biblical sources, having conquered most of Palestine's Mediterranean coastline and regions surrounding the Jordan River. Alexander also had many of his subjects killed for their disapproval of his handling of state affairs. Due to his territorial expansion and interac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire originally founded by Alexander the Great. After receiving the Mesopotamian region of Babylonia in 321 BC, Seleucus I began expanding his dominions to include the Near Eastern territories that encompass modern-day Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, Syria, all of which had been under Macedonian control after the fall of the former Persian Achaemenid Empire. At the Seleucid Empire's height, it had consisted of territory that had covered Anatolia, Persia, the Levant, and what are now modern Iraq, Kuwait, Afghanistan, and parts of Turkmenistan. The Seleucid Empire was a major center of Hellenistic culture. Greek customs and language were privileged; the wide varie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maccabean Revolt
The Maccabean Revolt ( he, מרד החשמונאים) was a Jewish rebellion led by the Maccabees against the Seleucid Empire and against Hellenistic influence on Jewish life. The main phase of the revolt lasted from 167–160 BCE and ended with the Seleucids in control of Judea, but conflict between the Maccabees, Hellenized Jews, and the Seleucids continued until 134 BCE, with the Maccabees eventually attaining independence. Seleucid King Antiochus IV Epiphanes launched a massive campaign of repression against the Jewish religion in 168 BCE. The reason he did so is not entirely clear, but it seems to have been related to the King mistaking an internal conflict among the Jewish priesthood as a full-scale rebellion. Jewish practices were banned, Jerusalem was placed under direct Seleucid control, and the Second Temple in Jerusalem was made the site of a syncretic Pagan-Jewish cult. This repression triggered exactly the revolt that Antiochus IV had feared, with a group o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hasmonean Dynasty
The Hasmonean dynasty (; he, ''Ḥašmōnaʾīm'') was a ruling dynasty of Judea and surrounding regions during classical antiquity, from BCE to 37 BCE. Between and BCE the dynasty ruled Judea semi-autonomously in the Seleucid Empire, and from roughly 110 BCE, with the empire disintegrating, Judea gained further autonomy and expanded into the neighboring regions of Perea, Samaria, Idumea, Galilee, and Iturea. Some modern scholars regard the Hasmonean realm as an independent Israel. The Hasmonean rulers took the Greek title '' basileus'' ("king" or "emperor"). Forces of the Roman Republic conquered the Hasmonean kingdom in 63 BCE and made it into a client state; Herod the Great displaced the last reigning Hasmonean client-ruler in 37 BCE. Simon Thassi established the dynasty in 141 BCE, two decades after his brother Judas Maccabeus ( ''Yehudah HaMakabi'') had defeated the Seleucid army during the Maccabean Revolt of 167 to 141 BCE. According to 1 Maccabees, 2 Maccabee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
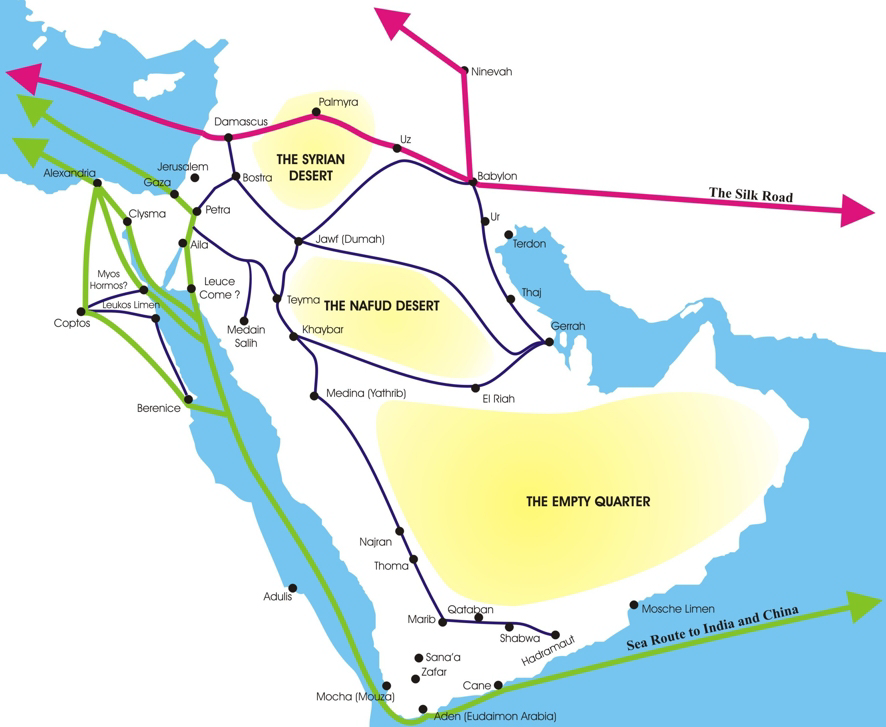
Nabataean Kingdom
The Nabataean Kingdom (Nabataean Aramaic: 𐢕𐢃𐢋𐢈 ''Nabāṭū''), also named Nabatea (), was a political state of the Arab Nabataeans during classical antiquity. The Nabataean Kingdom controlled many of the trade routes of the region, amassing large wealth and drawing the envy of its neighbors. It stretched south along the Red Sea coast into the Hejaz, up as far north as Damascus, which it controlled for a short period (85–71 BC). Nabataea remained an independent political entity from the mid-3rd century BC until it was annexed in AD 106 by the Roman Empire, which renamed it Arabia Petraea. History Nabataeans The Nabataeans were one among several nomadic Bedouin tribes that roamed the Arabian Desert and moved with their herds to wherever they could find pasture and water. They became familiar with their area as seasons passed, and they struggled to survive during bad years when seasonal rainfall diminished. Although the Nabataeans were initially embedded in Aramaic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies. James Fearon"Iraq's Civil War" in ''Foreign Affairs'', March/April 2007. For further discussion on civil war classification, see the section "Formal classification". The term is a calque of Latin '' bellum civile'' which was used to refer to the various civil wars of the Roman Republic in the 1st century BC. Most modern civil wars involve intervention by outside powers. According to Patrick M. Regan in his book ''Civil Wars and Foreign Powers'' (2000) about two thirds of the 138 intrastate conflicts between the end of World War II and 2000 saw international intervention, with the United States intervening in 35 of these conflicts. A civil war is a high-intensity conflict, often involving regular armed forces, that is sustained, org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)





.jpg)