|
Harold H. Purcell
Harold Hidmore Purcell (February 7, 1920 – July 14, 2007) was an American lawyer, judge and politician affiliated with the Byrd Organization who served in both houses of the Virginia General Assembly representing his native Louisa County and adjacent counties (1948-1965), and later as Circuit Judge for what was then the 16th Judicial Circuit (1966-1979)(also covering Louisa County). Early life Born in Louisa County to the former Mary Elizabeth (Bessie) Walton (1886-1970), his father John S. Purcell (1876--1961) had moved from nearby Goochland County to operate a store at Bells Cross Roads, which the elder Purcell expanded into a sawmill and wholesale lumber supply business. This man's great-grandfather, John Pedie Purcell (1804-1881) had emigrated from Ireland and moved to Louisa County. His son (this boy's grandfather), Charles Daniel Purcell, had been born in Louisa County and fought with the 23rd Virginia Infantry during the Civil War. John Purcell had been appointed to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louisa, Virginia
Louisa (originally named Louisa Court House) is a town in Louisa County, Virginia, United States. The population was 1,555 at the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Louisa County. History Louisa Court House was named because of the county courthouse constructed in 1742, near the intersection of Courthouse Road (now SR 208) and Main Street/Louisa Road (now SR-22/ US-33). The village of Louisa Court House had been the county seat for over a century when it became a strategic location during the American Civil War for Virginia's supply and communication lines. Chartered in 1836 as the Louisa Railroad by the Virginia General Assembly, the Virginia Central Railroad mainline passed through the village. On 10 June 1864, thousands of men and horses of Gen. Fitzhugh Lee's cavalry division camped around the courthouse prior to the Battle of Trevilian Station. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Captain (United States O-3)
In the United States Army (), U.S. Marine Corps (USMC), U.S. Air Force (USAF), and U.S. Space Force (USSF), captain (abbreviated "CPT" in the and "Capt" in the USMC, USAF, and USSF) is a company-grade officer rank, with the pay grade of O-3. It ranks above first lieutenant and below major. It is equivalent to the rank of lieutenant in the Navy/Coast Guard officer rank system and should not be confused with the Navy/Coast Guard rank of captain. The insignia for the rank consists of two silver bars, with slight stylized differences between the Army/Air Force version and the Marine Corps version. History The U.S. military inherited the rank of captain from its British Army forebears. In the British Army, the captain was designated as the appropriate rank for the commanding officer of infantry companies, artillery batteries, and cavalry troops, which were considered as equivalent-level units. Captains also served as staff officers in regimental and brigade headquarters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
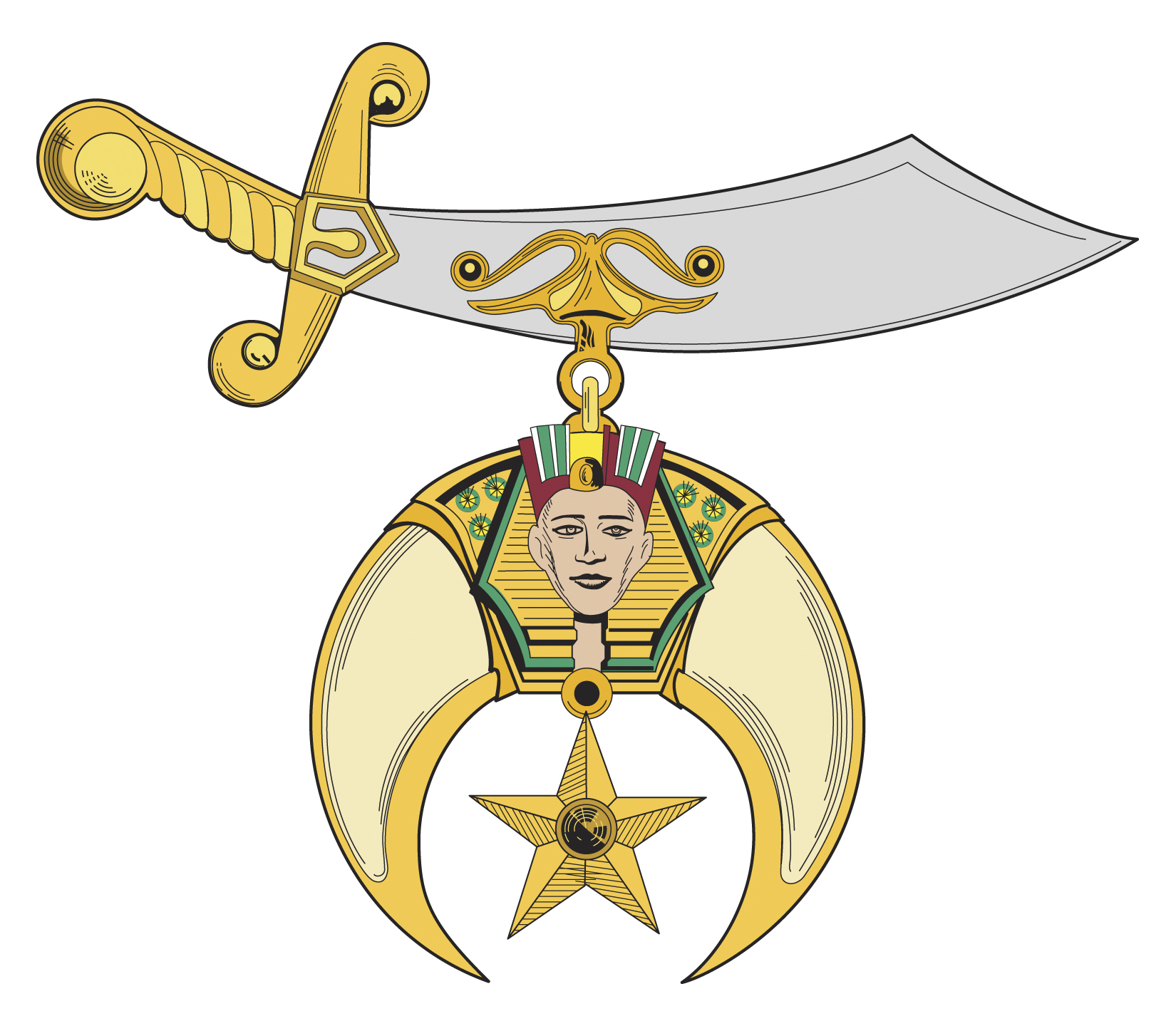
Shriners
Shriners International, formally known as the Ancient Arabic Order of the Nobles of the Mystic Shrine (AAONMS), is an American Masonic society established in 1870 and is headquartered in Tampa, Florida. Shriners International describes itself as a fraternity based on fun, fellowship, and the Masonic principles of brotherly love, relief, and truth. There are approximately 350,000 members from 196 temples (chapters) in the US, Canada, Brazil, Bolivia, Mexico, Panama, the Philippines, Europe, and Australia. The organization is best known for the Shriners Hospitals for Children that it administers, and the red fezzes that members wear. The organization was previously known as "Shriners North America". The name was changed in 2010 across North America, Central America, South America, Europe, and Southeast Asia. History In 1870, there were several thousand Freemasons in Manhattan, many of whom lunched at the Knickerbocker Cottage at a special table on the second floor. There, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theta Delta Phi
Theta (, ; uppercase: Θ or ; lowercase: θ or ; grc, ''thē̂ta'' ; Modern: ''thī́ta'' ) is the eighth letter of the Greek alphabet, derived from the Phoenician letter Teth . In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 9. Greek In Ancient Greek, θ represented the aspirated voiceless dental plosive , but in Modern Greek it represents the voiceless dental fricative . Forms In its archaic form, θ was written as a cross within a circle (as in the Etruscan or ), and later, as a line or point in circle ( or ). The cursive form was retained by Unicode as , separate from . (There is also ). For the purpose of writing Greek text, the two can be font variants of a single character, but are also used as distinct symbols in technical and mathematical contexts. Extensive lists of examples follow below at Mathematics and Science. is also common in biblical and theological usage e.g. instead of πρόθεσις (means placing in public or laying out a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigma Phi Epsilon
Sigma Phi Epsilon (), commonly known as SigEp, is a social college fraternity for male college students in the United States. It was founded on November 1, 1901, at Richmond College (now the University of Richmond), and its national headquarters remains in Richmond, Virginia. It was founded on three principles: Virtue, Diligence, and Brotherly Love (often abbreviated as "VDBL"). Sigma Phi Epsilon is one of the largest social fraternities in the United States in terms of current undergraduate membership. History Founding In the fall of 1900 18-year-old divinity student Carter Ashton Jenkens, the son of a Baptist minister, transferred from Rutgers College of New Jersey to Richmond College, a Baptist institution in the Virginia capital. At Rutgers Jenkens had been initiated into the Chi Phi fraternity. At Richmond, which did not have a chapter of Chi Phi, Jenkens was part of group of friends who were meeting regularly under the unofficial name the "Saturday Night Club". By ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freemasons
Freemasonry or Masonry refers to fraternal organisations that trace their origins to the local guilds of stonemasons that, from the end of the 13th century, regulated the qualifications of stonemasons and their interaction with authorities and clients. Modern Freemasonry broadly consists of two main recognition groups: * Regular Freemasonry insists that a volume of scripture be open in a working lodge, that every member profess belief in a Supreme Being, that no women be admitted, and that the discussion of religion and politics be banned. * Continental Freemasonry consists of the jurisdictions that have removed some, or all, of these restrictions. The basic, local organisational unit of Freemasonry is the Lodge. These private Lodges are usually supervised at the regional level (usually coterminous with a state, province, or national border) by a Grand Lodge or Grand Orient. There is no international, worldwide Grand Lodge that supervises all of Freemasonry; each Grand Lod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brian Balogh
Brian Balogh is an American historian, and professor at the University of Virginia. Balogh is the director of the National Fellowship Program hosted by the Jefferson Scholars Foundation. He also co-hosts the radio program, " Backstory with the American History Guys". In 2015, he received a Nancy Lyman Roelker Award. Education He graduated from Harvard University, and from Johns Hopkins University Johns Hopkins University (Johns Hopkins, Hopkins, or JHU) is a private university, private research university in Baltimore, Maryland. Founded in 1876, Johns Hopkins is the oldest research university in the United States and in the western hem .... Works * * * * * * References External links * https://millercenter.org/experts/brian-balogh * http://www.backstoryradio.org/ * {{DEFAULTSORT:Balogh, Brian Living people University of Virginia faculty Harvard University alumni Johns Hopkins University alumni 21st-century American historians 21st-century American ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlottesville, Virginia
Charlottesville, colloquially known as C'ville, is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia. It is the county seat of Albemarle County, which surrounds the city, though the two are separate legal entities. It is named after Queen Charlotte. At the 2020 census, the population was 46,553. The Bureau of Economic Analysis combines the City of Charlottesville with Albemarle County for statistical purposes, bringing its population to approximately 150,000. Charlottesville is the heart of the Charlottesville metropolitan area, which includes Albemarle, Buckingham, Fluvanna, Greene, and Nelson counties. Charlottesville was the home of two presidents, Thomas Jefferson and James Monroe. During their terms as Governor of Virginia, they lived in Charlottesville, and traveled to and from Richmond, along the historic Three Notch'd Road. Orange, located northeast of the city, was the hometown of President James Madison. The University of Virginia, founded by Jefferson, stradd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augusta Military Academy
The Augusta Military Academy (AMA) was a secondary education military academy in Fort Defiance, Virginia, United States. The school was established in by Confederate veteran Charles Summerville Roller as the Augusta Male Academy and formally became a military academy in . It combined classical studies with a military curriculum and was officially named Augusta Military Academy in 1890. At the time, it was one of the first military preparatory schools in the Commonwealth of Virginia. It was one of the first such schools in the United States to adopt the Junior Reserve Officers' Training Corps program in 1919. Until its closure in , the Academy had attracted over 7,000 students from the United States and abroad. Today it is owned and operated as a campground for the Virginia District of the United Pentecostal Church International. It is located on U.S. Route 11, also known as the Lee Highway. History 19th century Charles Summerville Roller was born in Mt. Sidney Virginia on May 8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louisa High School
Louisa High School is a historic high school building located at Louisa, Louisa County, Virginia Louisa County is a county located in the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 37,596. The county seat is Louisa. History Prior to colonial settlement, the area comprising Louisa County was occupied by severa .... It was designed by noted Richmond architect Charles M. Robinson and built in 1907, as a 1 1/2-story, stone building. About 1916, a second story was added along with an auditorium addition to the rear. Early in 1924 a fire gutted the building, leaving only the granite walls. It was rebuilt in its two-story configuration in 1925. The school served as an elementary school after 1940, and closed in 1987. The building was restored starting in 2002, and reopened in 2006 as a town hall, art gallery, and performing arts center. an''Accompanying four photos''/ref> It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2011. Reference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagion began around September and led to the Wall Street stock market crash of October 24 (Black Thursday). It was the longest, deepest, and most widespread depression of the 20th century. Between 1929 and 1932, worldwide gross domestic product (GDP) fell by an estimated 15%. By comparison, worldwide GDP fell by less than 1% from 2008 to 2009 during the Great Recession. Some economies started to recover by the mid-1930s. However, in many countries, the negative effects of the Great Depression lasted until the beginning of World War II. Devastating effects were seen in both rich and poor countries with falling personal income, prices, tax revenues, and profits. International trade fell by more than 50%, unemployment in the U.S. rose to 23% and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richmond Times-Dispatch
The ''Richmond Times-Dispatch'' (''RTD'' or ''TD'' for short) is the primary daily newspaper in Richmond, Virginia, Richmond, the capital of Virginia, and the primary newspaper of record for the state of Virginia. Circulation The ''Times-Dispatch'' has the second-highest circulation of any Virginia newspaper, after Norfolk, Virginia, Norfolk's ''The Virginian-Pilot''. In addition to the Richmond area (Petersburg, Virginia, Petersburg, Chester, Virginia, Chester, Hopewell, Virginia, Hopewell, Colonial Heights, Virginia, Colonial Heights and surrounding areas), the ''Times-Dispatch'' has substantial readership in Charlottesville, Lynchburg, Virginia, Lynchburg, and Waynesboro, Virginia, Waynesboro. As the primary paper of the state's capital, the ''Times-Dispatch'' serves as a newspaper of record for rural regions of the state that lack large local papers. The ''Times-Dispatch'' lists itself as "Virginia's News Leader" on its Nameplate (publishing), masthead. History and notable ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |