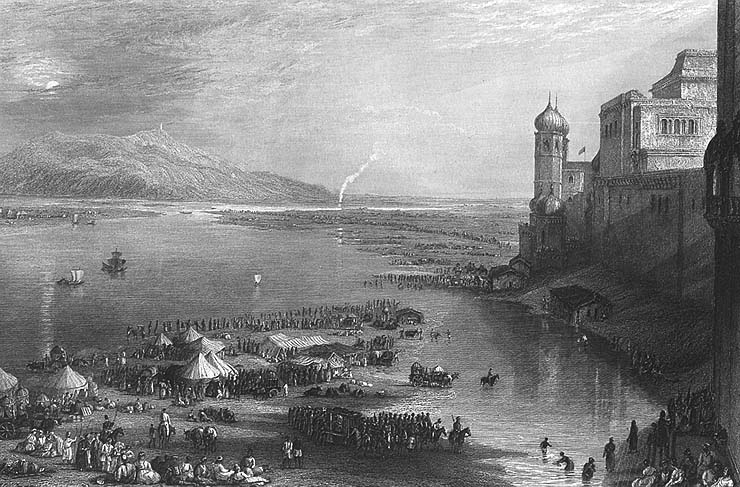|
Haridwar Kumbh Mela
The Kumbh Mela at Haridwar is a mela held every 12 years at Haridwar, India. The exact date is determined according to Hindu astrology: the Mela is held when Jupiter is in Aquarius and the Sun enters Aries. The event possesses deep religious significance to Hindus as well as other spiritual seekers. Historically, it was an important commercial event and was attended by merchants from as far as Arabia. The Haridwar Kumbh Mela had happened from 1 April to 30 April in the year 2021 amidst the COVID-19 pandemic. An Ardh Kumbh ("Half Kumbh") Mela is held six years after a Kumbh Mela. The last Ardh Kumbh Mela took place in 2016. Early records Haridwar is one of the four sites of Kumbh Mela, the others being Prayag (Allahabad), Trimbak (Nashik), and Ujjain. Although there are several references to riverside bathing festivals in ancient Indian literature, the exact age of the Kumbh Mela is uncertain. The fair at Haridwar appears to be the original Kumbh Mela, since it is hel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Har Ki Pauri
Har Ki Pauri is a famous ghat on the banks of the Ganges in Haridwar in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. This revered place is the major landmark of the holy city of Haridwar. Literally, " Har" means "God", "Ki" means " 's " and "Pauri" means "steps". Lord Vishnu is believed to have visited the Brahmakund in Har Ki Pauri in the Vedic times. It is believed that it is the precise spot where the Ganges leaves the mountains and enters the plains. The ghat is on the west bank of Ganges canal through which the Ganges is diverted just to the north. Har Ki Pauri is also the area where thousands of pilgrims converge and the festivities commence during the Kumbha Mela, which takes place every twelve years, and the Ardh Kumbh Mela, which takes place every six years and the Punjabi festival of Vaisakhi, a harvest festival occurring every year in the month of April. History King Vikramaditya is said to have built it in 1st century BC in the memory of his brother, Bharthari who ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ujjain
Ujjain (, Hindustani pronunciation: �d͡ːʒɛːn is a city in Ujjain district of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It is the fifth-largest city in Madhya Pradesh by population and is the administrative centre of Ujjain district and Ujjain division. It is one of the Hindu pilgrimage centres of Sapta Puri famous for the ''Kumbh Mela'' held there every 12 years. The famous temple of Mahakaleshwar Jyotirlinga is located in the center of the city. An ancient city situated on the eastern bank of the Shipra River, Ujjain was the most prominent city on the Malwa plateau of central India for much of its history. It emerged as the political centre of central India around 600 BCE. It was the capital of the ancient Avanti kingdom, one of the sixteen Mahajanapadas. During the 18th century, the city briefly became the capital of Scindia state of the Maratha Empire, when Ranoji Scindia established his capital at Ujjain in 1731. It remained an important political, commercial and cultural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakh
A lakh (; abbreviated L; sometimes written lac) is a unit in the Indian numbering system equal to one hundred thousand (100,000; scientific notation: 105). In the Indian 2,2,3 convention of digit grouping, it is written as 1,00,000. For example, in India, 150,000 rupees becomes 1.5 ''lakh'' rupees, written as 1,50,000 or INR 1,50,000. It is widely used both in official and other contexts in Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Myanmar, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. It is often used in Bangladeshi, Indian, Pakistani, and Sri Lankan English. Usage In Indian English, the word is used both as an attributive and non-attributive noun with either an unmarked or marked ("-s") plural, respectively. For example: "1 ''lakh'' people"; "''lakhs'' of people"; "20 ''lakh'' rupees"; "''lakhs'' of rupees". In the abbreviated form, usage such as "5L" or "5 lac" (for "5 ''lakh'' rupees") is common. In this system of numeration, 100 ''lakh'' is called one '' crore'' and is e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaisakha
Vaisakha; hi, बैसाख, Baisākh; pa, ਵਿਸਾਖ/وساکھ , te, వైశాఖ, kn, ವೈಶಾಖ, Vaiśākha; ml, വൈശാഖം, Vaiśākham; mr, वैशाख, Vaiśākh; ta, வைகாசி, Vaikāci; ne, बैशाख, or, ବୈଶାଖ, Baiśākh; as, ব’হাগ, Bohag, name=, group= is a month of the Hindu calendar that corresponds to April/May in the Gregorian Calendar. In the Indian national calendar, Vaisakha is the second month of the year. It is the first month of the Vikram Samvat calendar, Odia calendar, Punjabi calendar, Assamese calendar (where it is called ''Bohag'') and the Bengali calendar (where it is called ''Boishakh''). This month lies between the second half of April And The First Half Of May. Regional calendars used in the Indian subcontinent have two aspects: lunar and solar. Lunar months begin with Chaitra and solar months start with Vaisakha Sankranti. However, regional calendars mark when the officia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alms
Alms (, ) are money, food, or other material goods donated to people living in poverty. Providing alms is often considered an act of virtue or charity. The act of providing alms is called almsgiving, and it is a widespread practice in a number of different religions and cultures. Etymology The word ''alms'' comes from the Old English ', ', which comes from Late Latin ', from Greek ' ("pity, alms"), from , ' ("merciful"), from , ', meaning "pity or mercy". Buddhism ''Dāna'' in Buddhism In Buddhism, both "almsgiving" and "giving" are called "dāna" (Pāli). Such giving is one of the three elements of the path of practice as formulated by the Buddha for laypeople. This path of practice for laypeople is dāna, sīla, and bhāvanā. Generosity towards other sentient beings is also emphasized in Mahayana as one of the perfections ( paramita). As shown in Lama Tsong Khapa's 'The Abbreviated Points of the Graded Path' (): The giving of alms is the beginning of one's jou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaisakhi
Vaisakhi (Punjabi: ), also pronounced Baisakhi, marks the first day of the month of Vaisakh and is traditionally celebrated annually on 13 April and sometimes 14 April as a celebration of spring harvest primarily in Northern India. Further, other Indian cultures and diaspora celebrate this festival too. Whilst it is culturally significant as a festival of harvest, in many parts of India, Vaisakhi is also the date for the Indian Solar New Year. For Sikhs, in addition to its significance as the harvest festival, during which Sikhs hold kirtans, visit local Gurdwaras, community fairs, hold ''nagar kirtan'' processions, raise the Nishan Sahib flag, and gather to socialize and share festive foods, Vaisakhi observes major events in the history of Sikhism and the Indian subcontinent that happened in the Punjab region. Vaisakhi as a major Sikh festival marks the birth of the Khalsa order by Guru Gobind Singh, the tenth Guru of Sikhism, on 13 April 1699. Later, Ranjit Singh was procl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subah (country Subdivision)
A Subah was the term for a province (State) in the Mughal Empire. The word is derived from Arabic and Persian. The governor/ruler of a ''Subah'' was known as a ''subahdar'' (sometimes also referred to as a "''Subeh''"), which later became ''subedar'' to refer to an officer in the Indian Army and Pakistan Army. The ''subahs'' were established by badshah (emperor) Akbar during his administrative reforms of years 1572–1580; initially they numbered to 12, but his conquests expanded the number of ''subahs'' to 15 by the end of his reign. ''Subahs'' were divided into '' Sarkars'', or districts. ''Sarkars'' were further divided into ''Parganas'' or '' Mahals''. His successors, most notably Aurangzeb, expanded the number of ''subahs'' further through their conquests. As the empire began to dissolve in the early 18th century, many ''subahs'' became effectively independent, or were conquered by the Marathas or the British. In modern context subah ( ur, ) is a word used for province in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders with the state of Uttar Pradesh in the east and with the state of Haryana in the remaining directions. The NCT covers an area of . According to the 2011 census, Delhi's city proper population was over 11 million, while the NCT's population was about 16.8 million. Delhi's urban agglomeration, which includes the satellite cities of Ghaziabad, Faridabad, Gurgaon and Noida in an area known as the National Capital Region (India), National Capital Region (NCR), has an estimated population of over 28 million, making it the List of metropolitan areas in India, largest metropolitan area in India and the List of urban areas by population, second-largest in the world (after Tokyo). The topography of the medieval fort Purana Qila on the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akhara
Akhara or Akhada ( Sanskrit and Hindi: अखाड़ा, shortened to ''khara'' Hindi: खाड़ा) is an Indian word for a place of practice with facilities for boarding, lodging and training, both in the context of Indian martial artists or a '' sampradaya'' monastery for religious renunciates in Guru–shishya tradition. it is similar to the Greek-origin word ''academy'' and the English word ''school'', can be used to mean both a physical institution or a group of them which share a common lineage or are under a single leadership, such as the school of monastic thought or the school of martial arts. Unlike the gurukul in which students live and study at the home of a guru, members of an akhara although train under a guru but they do not live a domestic life. Some strictly practice Brahmacharya (celibacy) and others may require complete renunciation of worldly life. For example, wrestlers are expected to live a pure life while living at akhara with other fellow wrestl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohsin Fani
Mohsin Fani was a noted Persian historian from Iran. Some suggest he is the author of Dabistan-E-Mazahib. Life & works Born around 1615 in Iran, Mohsin Fani was once migrated to India, for the study of the religions there, in the time of the sixth Sikh guru, Guru Hargobind Sahib with whom he had friendly relationships. Bhai Kahn Singh Nabha gave some references to him and his (Fani's) book Dabistan-E-Mazahib to claim his point on Sikhs not following Hindu rituals in Ham Hindu Nahin ''Ham Hindu Nahin'' ( pa, ਹਮ ਹਿੰਦੂ ਨਹੀਂ, lit=We are not Hindus), also spelled as Hum Hindu Nahin, is a 19th-century Punjabi book by Kahn Singh Nabha, on the distinction of the Sikhism and identity. First published in 1898, .... See also * Kahn Singh Nabha References {{DEFAULTSORT:Fani, Mohsin 17th-century Iranian historians Iranian historians of religion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dabestan-e Mazaheb
The ''Dabestān-e Mazāheb'' ( fa, دبستان مذاهب) "school of religions" is a Persian language work that examines and compares Abrahamic religions, Dharmic religions and sects of the mid-17th century Southern Eurasia. The work, whose authorship is uncertain, was probably composed in about 1655 CE. The text's title is also transliterated as ''Dabistān-i Mazāhib'' , ''Dabistan-e Madahib'', or ''Dabestan-e Madaheb''. The text is best known for its chapter on the Dīn-i Ilāhī, the syncretic religion propounded by the Mughal emperor Jalāl ud-Dīn Muḥammad Akbar ("Akbar the Great") after 1581 and is possibly the most reliable account of the ''Ibādat Khāna'' discussions that led up to this. Authorship Several manuscripts have been discovered that identifies the author as Mīr Du’l-feqār Ardestānī (also known as Mollah Mowbad). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timur
Timur ; chg, ''Aqsaq Temür'', 'Timur the Lame') or as ''Sahib-i-Qiran'' ( 'Lord of the Auspicious Conjunction'), his epithet. ( chg, ''Temür'', 'Iron'; 9 April 133617–19 February 1405), later Timūr Gurkānī ( chg, ''Temür Küregen''), was a Turco-Mongol tradition, Turco-Mongol conqueror who founded the Timurid Empire in and around modern-day Afghanistan, Iran, and Central Asia, becoming the first ruler of the Timurid dynasty. An undefeated commander, he is widely regarded as one of the greatest military leaders and tacticians in history, as well as one of the most brutal. Timur is also considered a great patron of art and architecture as he interacted with intellectuals such as Ibn Khaldun, Hafez, and Hafiz-i Abru and his reign introduced the Timurid Renaissance. Born into the Barlas confederation in Transoxiana (in modern-day Uzbekistan) on 9 April 1336, Timur gained control of the western Chagatai Khanate by 1370. From that base, he led military campaigns acr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |