|
Hardware-based Encryption
Hardware-based encryption is the use of computer hardware to assist software, or sometimes replace software, in the process of data encryption. Typically, this is implemented as part of the processor's instruction set. For example, the AES encryption algorithm (a modern cipher) can be implemented using the AES instruction set on the ubiquitous x86 architecture. Such instructions also exist on the ARM architecture. However, more unusual systems exist where the cryptography module is separate from the central processor, instead being implemented as a coprocessor, in particular a secure cryptoprocessor or cryptographic accelerator, of which an example is the IBM 4758, or its successor, the IBM 4764. Hardware implementations can be faster and less prone to exploitation than traditional software implementations, and furthermore can be protected against tampering. History Prior to the use of computer hardware, cryptography could be performed through various mechanical or electro- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptography
Cryptography, or cryptology (from grc, , translit=kryptós "hidden, secret"; and ''graphein'', "to write", or ''-logia'', "study", respectively), is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of adversarial behavior. More generally, cryptography is about constructing and analyzing protocols that prevent third parties or the public from reading private messages. Modern cryptography exists at the intersection of the disciplines of mathematics, computer science, information security, electrical engineering, digital signal processing, physics, and others. Core concepts related to information security (data confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation) are also central to cryptography. Practical applications of cryptography include electronic commerce, chip-based payment cards, digital currencies, computer passwords, and military communications. Cryptography prior to the modern age was effectively synony ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scytale
In cryptography, a scytale (; also transliterated skytale, grc, σκυτάλη ''skutálē'' "baton, cylinder", also ''skútalon'') is a tool used to perform a transposition cipher, consisting of a cylinder with a strip of parchment wound around it on which is written a message. The ancient Greeks, and the Spartans in particular, are said to have used this cipher to communicate during military campaigns. The recipient uses a rod of the same diameter on which the parchment is wrapped to read the message. To cryptanalyse it is not difficult. Use a tapered cone. Wrap the strip around it. Somewhere plaintext will be visible. That is the diameter of the rods used. Encrypting Suppose the rod allows one to write four letters around in a circle and five letters down the side of it. The plaintext could be: "I am hurt very badly help". To encrypt, one simply writes across the leather: _____________________________________________________________ , , , , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Architecture
In computer engineering, computer architecture is a description of the structure of a computer system made from component parts. It can sometimes be a high-level description that ignores details of the implementation. At a more detailed level, the description may include the instruction set architecture design, microarchitecture design, logic design, and implementation. History The first documented computer architecture was in the correspondence between Charles Babbage and Ada Lovelace, describing the analytical engine. When building the computer Z1 (computer), Z1 in 1936, Konrad Zuse described in two patent applications for his future projects that machine instructions could be stored in the same storage used for data, i.e., the Stored-program computer, stored-program concept. Two other early and important examples are: * John von Neumann's 1945 paper, First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC, which described an organization of logical elements; and *Alan M. Turing, Alan Turing's mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Online Shopping
Online shopping is a form of electronic commerce which allows consumers to directly buy goods or services from a seller over the Internet using a web browser or a mobile app. Consumers find a product of interest by visiting the website of the retailer directly or by searching among alternative vendors using a shopping search engine, which displays the same product's availability and pricing at different e-retailers. As of 2020, customers can shop online using a range of different computers and devices, including desktop computers, laptops, tablet computers and smartphones. An online shop evokes the physical analogy of buying products or services at a regular "bricks-and-mortar" retailer or shopping center; the process is called business-to-consumer (B2C) online shopping. When an online store is set up to enable businesses to buy from another businesses, the process is called business-to-business (B2B) online shopping. A typical online store enables the customer to browse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW), commonly known as the Web, is an information system enabling documents and other web resources to be accessed over the Internet. Documents and downloadable media are made available to the network through web servers and can be accessed by programs such as web browsers. Servers and resources on the World Wide Web are identified and located through character strings called uniform resource locators (URLs). The original and still very common document type is a web page formatted in Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). This markup language supports plain text, digital image, images, embedded video and audio signal, audio contents, and scripting language, scripts (short programs) that implement complex user interaction. The HTML language also supports hyperlinks (embedded URLs) which provide immediate access to other web resources. Web navigation, or web surfing, is the common practice of following such hyperlinks across multiple websites. Web applicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcomputer
A microcomputer is a small, relatively inexpensive computer having a central processing unit (CPU) made out of a microprocessor. The computer also includes memory and input/output (I/O) circuitry together mounted on a printed circuit board (PCB). Microcomputers became popular in the 1970s and 1980s with the advent of increasingly powerful microprocessors. The predecessors to these computers, mainframes and minicomputers, were comparatively much larger and more expensive (though indeed present-day mainframes such as the IBM System z machines use one or more custom microprocessors as their CPUs). Many microcomputers (when equipped with a keyboard and screen for input and output) are also personal computers (in the generic sense). An early use of the term ''personal computer'' in 1962 predates microprocessor-based designs. ''(See "Personal Computer: Computers at Companies" reference below)''. A ''microcomputer'' used as an embedded control system may have no human-readable i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SIGSALY
SIGSALY (also known as the X System, Project X, Ciphony I, and the Green Hornet) was a secure speech system used in World War II for the highest-level Allied communications. It pioneered a number of digital communications concepts, including the first transmission of speech using pulse-code modulation. The name SIGSALY was not an acronym, but a cover name that resembled an acronym—the SIG part was common in Army Signal Corps names (e.g., SIGABA). The prototype was called the "Green Hornet" after the radio show ''The Green Hornet'', because it sounded like a buzzing hornet, resembling the show's theme tune, to anyone trying to eavesdrop on the conversation. Development At the time of its inception, long-distance telephone communications were broadcast using the "A-3" voice scrambler developed by Western Electric. The Germans had a listening station on the Dutch coast which could intercept and break A-3 traffic. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
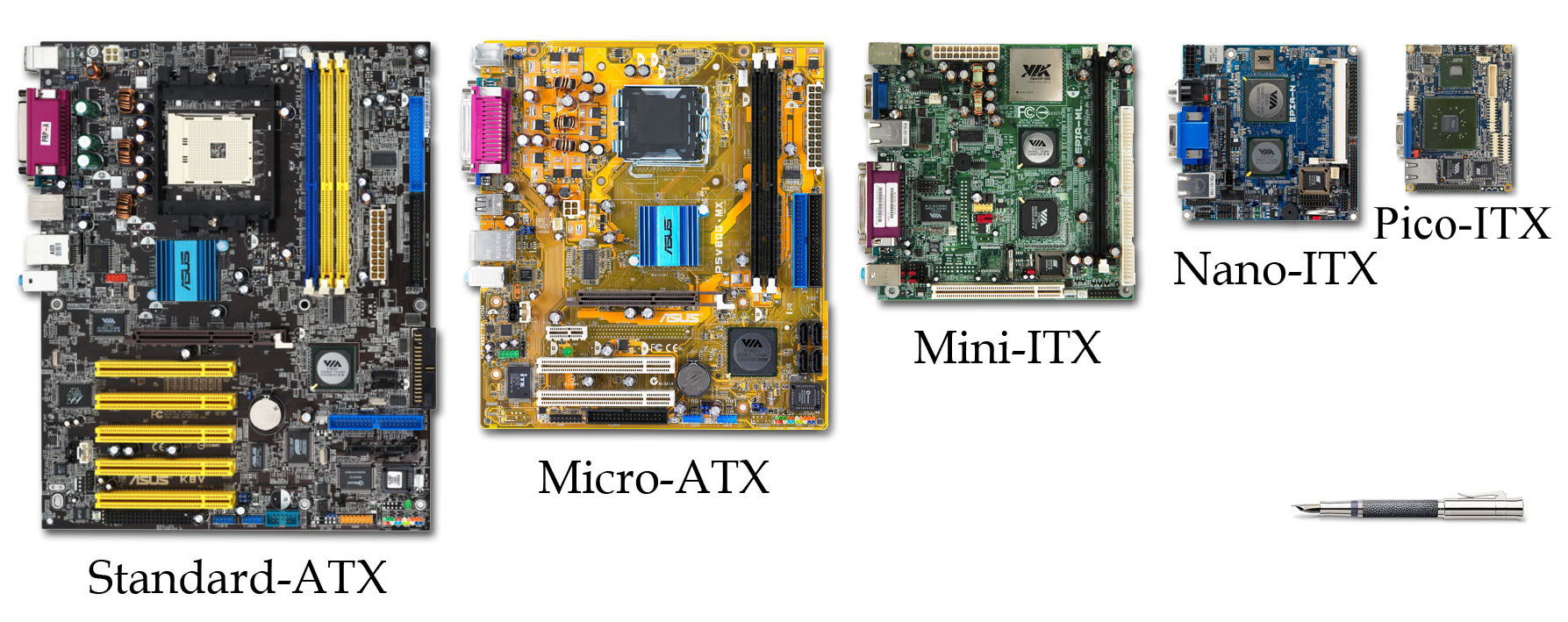
Form Factor (design)
Form factor is a hardware design aspect that defines and prescribes the size, shape, and other physical specifications of components, particularly in electronics. A form factor may represent a broad class of similarly sized components, or it may prescribe a specific standard. It may also define an entire system, as in a computer form factor. Evolution and standardization As electronic hardware has become smaller following Moore's law and related patterns, ever-smaller form factors have become feasible. Specific technological advances, such as PCI Express, have had a significant design impact, though form factors have historically been slower to evolve than individual components. Standardization of form factors is vital for compatibility of hardware from different manufacturers. Trade-offs Smaller form factors may offer more efficient use of limited space, greater flexibility in the placement of components within a larger assembly, reduced use of material, and greater ease of tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Transistor count, Large numbers of tiny MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) integrate into a small chip. This results in circuits that are orders of magnitude smaller, faster, and less expensive than those constructed of discrete electronic components. The IC's mass production capability, reliability, and building-block approach to integrated circuit design has ensured the rapid adoption of standardized ICs in place of designs using discrete transistors. ICs are now used in virtually all electronic equipment and have revolutionized the world of electronics. Computers, mobile phones and other home appliances are now inextricable parts of the structure of modern societies, made possible by the small size and low cost of ICs such as mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colossus Computer
Colossus was a set of computers developed by British codebreakers in the years 1943–1945 to help in the cryptanalysis of the Lorenz cipher. Colossus used thermionic valves (vacuum tubes) to perform Boolean and counting operations. Colossus is thus regarded as the world's first programmable, electronic, digital computer, although it was programmed by switches and plugs and not by a stored program. Colossus was designed by General Post Office (GPO) research telephone engineer Tommy Flowers to solve a problem posed by mathematician Max Newman at the Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS) at Bletchley Park. Alan Turing's use of probability in cryptanalysis (see Banburismus) contributed to its design. It has sometimes been erroneously stated that Turing designed Colossus to aid the cryptanalysis of the Enigma. (Turing's machine that helped decode Enigma was the electromechanical Bombe, not Colossus.) The prototype, Colossus Mark 1, was shown to be working in December ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bletchley Park
Bletchley Park is an English country house and estate in Bletchley, Milton Keynes (Buckinghamshire) that became the principal centre of Allied code-breaking during the Second World War. The mansion was constructed during the years following 1883 for the financier and politician Sir Herbert Leon in the Victorian Gothic, Tudor, and Dutch Baroque styles, on the site of older buildings of the same name. During World War II, the estate housed the Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS), which regularly penetrated the secret communications of the Axis Powersmost importantly the German Enigma and Lorenz ciphers. The GC&CS team of codebreakers included Alan Turing, Gordon Welchman, Hugh Alexander, Bill Tutte, and Stuart Milner-Barry. The nature of the work at Bletchley remained secret until many years after the war. According to the official historian of British Intelligence, the "Ultra" intelligence produced at Bletchley shortened the war by two to four years, and withou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Piracy
Copyright infringement (at times referred to as piracy) is the use of works protected by copyright without permission for a usage where such permission is required, thereby infringing certain exclusive rights granted to the copyright holder, such as the right to reproduce, distribute, display or perform the protected work, or to make derivative works. The copyright holder is typically the work's creator, or a publisher or other business to whom copyright has been assigned. Copyright holders routinely invoke legal and technological measures to prevent and penalize copyright infringement. Copyright infringement disputes are usually resolved through direct negotiation, a notice and take down process, or litigation in civil court. Egregious or large-scale commercial infringement, especially when it involves counterfeiting, is sometimes prosecuted via the criminal justice system. Shifting public expectations, advances in digital technology and the increasing reach of the Internet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


