|
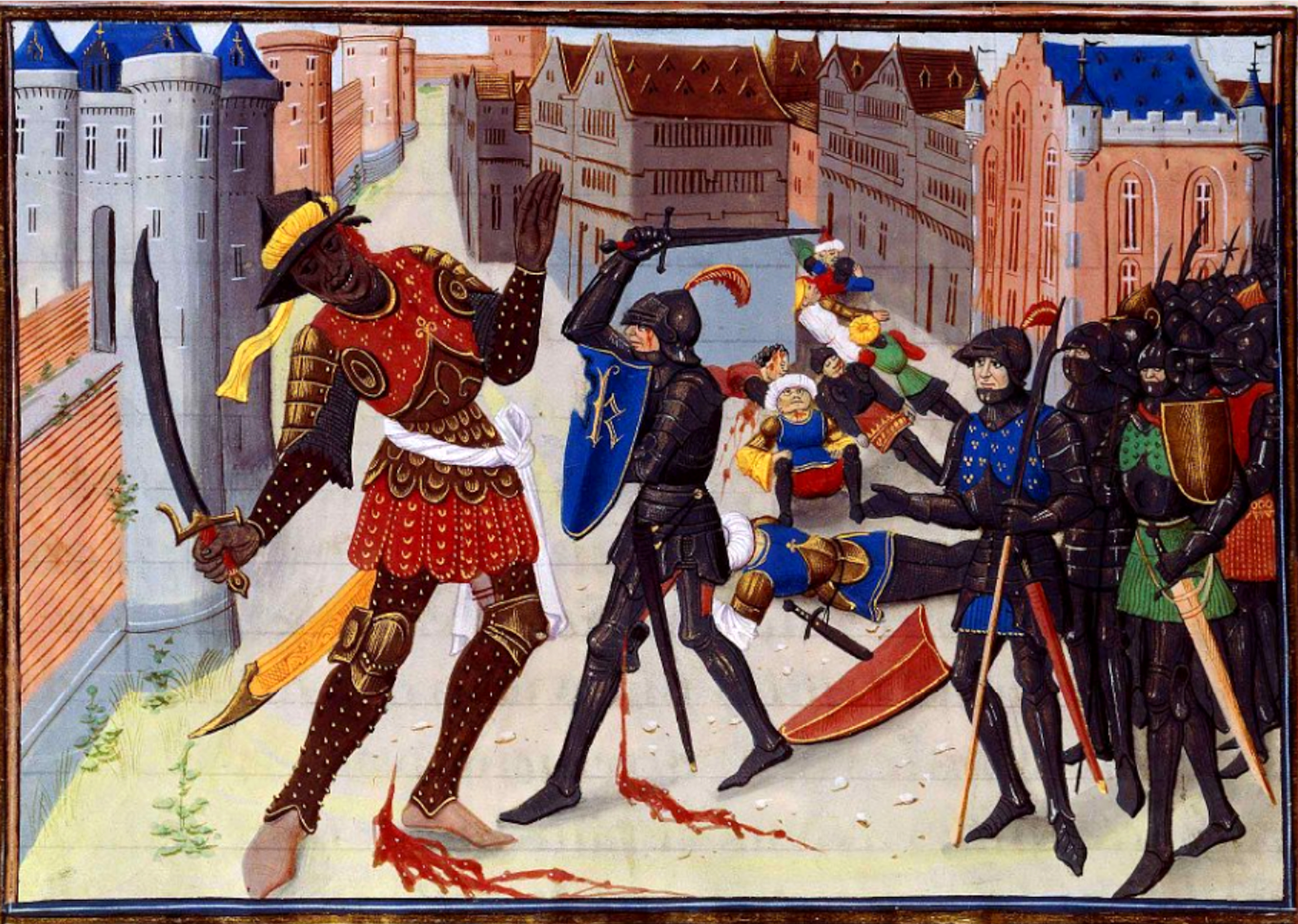
Harad
In J. R. R. Tolkien's high fantasy ''The Lord of the Rings'', Harad is the immense land south of Gondor and Mordor. Its main port is Umbar, the base of the Corsairs of Umbar whose ships serve as the Dark Lord Sauron's fleet. Its people are the dark-skinned Haradrim or Southrons; their warriors wear scarlet and gold, and are armed with swords and round shields; some ride gigantic elephants called ''mûmakil''. Tolkien based the Haradrim on ancient Aethiopians, people of Sub-Saharan Africa, following his philological research on the Old English word '' Sigelwara''. He deduced that this word referred to some kind of soot-black fire demon before it was applied to the Aethiopians. He based the Haradrim's use of war elephants, meanwhile, on that of Pyrrhus of Epirus in his war against Ancient Rome. Critics have debated whether Tolkien was racist in making the protagonists white and the antagonists black, but others have noted that Tolkien showed anti-xenophobic sentiments in real ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Man (Middle-earth)
In J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth fiction, Man and Men denote humans, whether male or female, in contrast to Elves, Dwarves, Orcs, and other humanoid races. Men are described as the second or younger people, created after the Elves, and differing from them in being mortal. Along with Ents and Dwarves, these are the "free peoples" of Middle-earth, differing from the enslaved peoples such as Orcs. Tolkien uses the Men of Middle-earth, interacting with immortal Elves, to explore a variety of themes in ''The Lord of the Rings'', especially death and immortality. This appears throughout, but is the central theme of an appendix, "The Tale of Aragorn and Arwen". Where the Hobbits stand for simple, earthbound, comfort-loving people, Men are far more varied, from petty villains and slow-witted publicans to the gentle warrior Faramir and the genuinely heroic Aragorn; Tolkien had wanted to create a heroic romance suitable for the modern age. Scholars have identified real-world analogue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigelwara Land
"Sigelwara Land" is an essay by J. R. R. Tolkien that appeared in two parts, in 1932 and 1934.J. R. R. Tolkien, "Sigelwara Land''Medium Aevum'' Vol. 1, No. 3. December 1932an''Medium Aevum'' Vol. 3, No. 2. June 1934./ref> It explores the etymology of the Old English word for the ancient Aethiopians, , and attempts to recover what it might originally have meant. Tolkien suggested that its two elements were most likely sun/jewel and coal/hearth, perhaps meaning something like a soot-black fire-demon. The Tolkien scholar and philologist Tom Shippey suggests that Tolkien's detailed study of the word may have influenced him in his creation of elements of his fantasy world of Middle-earth, including the Silmarils or forged sun-jewels, the Balrogs or dark fire-demons, and the Haradrim, men of the hot south. Essay Tolkien's essay treats the etymology of the Old English word for the ancient Aethiopians, . Tolkien concluded that, while the meaning of the first element was evidently " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gondor
Gondor is a fictional kingdom in J. R. R. Tolkien's writings, described as the greatest realm of Man (Middle-earth), Men in the west of Middle-earth at the end of the Third Age. The third volume of ''The Lord of the Rings'', ''The Return of the King'', is largely concerned with the events in Gondor during the War of the Ring and with the restoration of the realm afterward. The history of the kingdom is outlined in the appendices of the book. Gondor was founded by the brothers Isildur and Anárion, exiles from the downfallen island kingdom of Númenor. Along with Arnor in the north, Gondor, the South-kingdom, served as a last stronghold of the Dúnedain, Men of the West. After an early period of growth, Gondor gradually declined as the Third Age progressed, being continually weakened by internal strife and conflict with the allies of the Dark Lord Sauron. By the time of the War of the Ring, the throne of Gondor is empty, though its principalities and fiefdoms still pay deference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tolkien And Race
J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth fantasy writings have often been accused of embodying outmoded attitudes to race. However, scholars have noted that he was influenced by Victorian attitudes to race and to a literary tradition of monsters, and that he was anti-racist both in peacetime and during the two World Wars. With the late 19th century background of eugenics and a fear of moral decline, some critics believed that the mention of race mixing in ''The Lord of the Rings'' embodied scientific racism. Other commentators thought that Tolkien's description of the orcs was modelled on racist wartime propaganda caricatures of the Japanese. Critics have noted, too, that the work embodies a moral geography, with good in the West, evil in the East. Against this, Tolkien strongly opposed Nazi racial theories, as seen in a 1938 letter he wrote to his publisher, while in the Second World War he vigorously opposed anti-German propaganda. His Middle-earth has been described as definitely po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mordor
In J. R. R. Tolkien's fictional world of Middle-earth, Mordor (pronounced ; from Sindarin ''Black Land'' and Quenya ''Land of Shadow'') is the realm and base of the evil Sauron. It lay to the east of Gondor and the great river Anduin, and to the south of Mirkwood. Mount Doom, a volcano in Mordor, was the goal of the Fellowship of the Ring (characters), Fellowship of the Ring in the quest to destroy the One Ring. Mordor was surrounded by three mountain ranges, to the north, the west, and the south. These both protected the land from invasion and kept those living in Mordor from escaping. Commentators have noted that Mordor was influenced by Tolkien's own experiences in the industrial Black Country of the English Midlands, and by his time fighting in the trenches of the Western Front (World War I), Western Front in the First World War. Another forerunner that Tolkien was very familiar with is the account of the monster Grendel's unearthly landscapes in the Old English poem ''Beow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauron
Sauron (pronounced ) is the title character and the primary antagonist, through the forging of the One Ring, of J. R. R. Tolkien's ''The Lord of the Rings'', where he rules the land of Mordor and has the ambition of ruling the whole of Middle-earth. In the same work, he is identified as the "Necromancer" of Tolkien's earlier novel ''The Hobbit''. ''The Silmarillion'' describes him as the chief lieutenant of the first Dark Lord, Morgoth. Tolkien noted that the Ainur, the "angelic" powers of his constructed myth, "were capable of many degrees of error and failing", but by far the worst was "the absolute Satanic rebellion and evil of Morgoth and his satellite Sauron". Sauron appears most often as "the Eye", as if disembodied. Tolkien, while denying that absolute evil could exist, stated that Sauron came as near to a wholly evil will as was possible. Commentators have compared Sauron to the title character of Bram Stoker's 1897 novel ''Dracula'', and to Balor of the Evil Eye in C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Elephants
A war elephant was an elephant that was trained and guided by humans for combat. The war elephant's main use was to charge the enemy, break their ranks and instill terror and fear. Elephantry is a term for specific military units using elephant-mounted troops. Description War elephants played a critical role in several key battles in antiquity, especially in Ancient India. While seeing limited and periodic use in Ancient China, they became a permanent fixture in armies of historical kingdoms in Southeast Asia. During classical antiquity they were also used in ancient Persia and in the Mediterranean world within armies of Macedon, Hellenistic Greek states, the Roman Republic and later Empire, and Carthage in North Africa. In some regions they maintained a firm presence on the battlefield throughout the Middle Ages. However, their use declined with the spread of firearms and other gunpowder weaponry in early modern warfare. After this, war elephants became restricted to non- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saracens
file:Erhard Reuwich Sarazenen 1486.png, upright 1.5, Late 15th-century Germany in the Middle Ages, German woodcut depicting Saracens Saracen ( ) was a term used in the early centuries, both in Greek language, Greek and Latin writings, to refer to the people who lived in and near what was designated by the Roman Empire, Romans as Arabia Petraea and Arabia Deserta. The term's meaning evolved during its history of usage. During the Early Middle Ages, the term came to be associated with the tribes of Arabia. The oldest known source mentioning "Saracens" in relation to Islam dates back to the 7th century, in the Greek-language Christian tract Teaching of Jacob, ''Doctrina Jacobi''. Among other major events, the tract discusses the Muslim conquest of the Levant, which occurred after the rise of the Rashidun Caliphate following the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. The Roman-Catholic church and Christianity in Europe, European Christian leaders used the term during the Middle Ages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Ring
''The Lord of the Rings'' is an epic high-fantasy novel by English author and scholar J. R. R. Tolkien. Set in Middle-earth, intended to be Earth at some time in the distant past, the story began as a sequel to Tolkien's 1937 children's book ''The Hobbit'', but eventually developed into a much larger work. Written in stages between 1937 and 1949, ''The Lord of the Rings'' is one of the best-selling books ever written, with over 150 million copies sold. The title refers to the story's main antagonist, the Dark Lord Sauron, who, in an earlier age, created the One Ring to rule the other Rings of Power given to Men, Dwarves, and Elves, in his campaign to conquer all of Middle-earth. From homely beginnings in the Shire, a hobbit land reminiscent of the English countryside, the story ranges across Middle-earth, following the quest to destroy the One Ring mainly through the eyes of the hobbits Frodo, Sam, Merry and Pippin. Although often called a trilogy, the work was intended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Shadow
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akallabêth
''The Silmarillion'' () is a collection of myths and stories in varying styles by the English writer J. R. R. Tolkien. It was edited and published posthumously by his son Christopher Tolkien in 1977, assisted by the fantasy author Guy Gavriel Kay. It tells of Eä, a fictional universe that includes the Blessed Realm of Valinor, the once-great region of Beleriand, the sunken island of Númenor, and the continent of Middle-earth, where Tolkien's most popular works—''The Hobbit'' and ''The Lord of the Rings''—are set. After the success of ''The Hobbit'', Tolkien's publisher Stanley Unwin requested a sequel, and Tolkien offered a draft of the writings that would later become ''The Silmarillion''. Unwin rejected this proposal, calling the draft obscure and "too Celtic", so Tolkien began working on a new story that eventually became ''The Lord of the Rings''. ''The Silmarillion'' has five parts. The first, ''Ainulindalë'', tells in mythic style of the creation of Eä, the "worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle-earth
Middle-earth is the fictional setting of much of the English writer J. R. R. Tolkien's fantasy. The term is equivalent to the ''Miðgarðr'' of Norse mythology and ''Middangeard'' in Old English works, including ''Beowulf''. Middle-earth is the human-inhabited world, that is, the central continent of the Earth, in Tolkien's imagined mythological past. Tolkien's most widely read works, ''The Hobbit'' and ''The Lord of the Rings'', are set entirely in Middle-earth. "Middle-earth" has also become a short-hand term for Tolkien's legendarium, his large body of fantasy writings, and for the entirety of his fictional world. Middle-earth is the main continent of Earth (Arda) in an imaginary period of the Earth's past, ending with Tolkien's Third Age, about 6,000 years ago. Tolkien's tales of Middle-earth mostly focus on the north-west of the continent. This part of Middle-earth is suggestive of Europe, the north-west of the Old World, with the environs of the Shire reminiscent of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |