|
Haplorchis Pumilio
''Haplorchis'' is a genus of intestinal flukes in the family Heterophyidae. Species include: * '' Haplorchis popelkae'' * '' Haplorchis pumilio'' * ''Haplorchis taichui'' * ''Haplorchis vagabundi ''Haplorchis'' is a genus of intestinal flukes in the family Heterophyidae. Species include: * '' Haplorchis popelkae'' * '' Haplorchis pumilio'' * '' Haplorchis taichui'' * '' Haplorchis vagabundi'' * '' Haplorchis yokogawai'' References ...'' * '' Haplorchis yokogawai'' References Heterophyidae Digenea genera {{Trematoda-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platyhelminthe
The flatworms, flat worms, Platyhelminthes, or platyhelminths (from the Greek πλατύ, ''platy'', meaning "flat" and ἕλμινς (root: ἑλμινθ-), ''helminth-'', meaning "worm") are a phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, unsegmented, soft-bodied invertebrates. Unlike other bilaterians, they are acoelomates (having no body cavity), and have no specialized circulatory and respiratory organs, which restricts them to having flattened shapes that allow oxygen and nutrients to pass through their bodies by diffusion. The digestive cavity has only one opening for both ingestion (intake of nutrients) and egestion (removal of undigested wastes); as a result, the food cannot be processed continuously. In traditional medicinal texts, Platyhelminthes are divided into Turbellaria, which are mostly non-parasitic animals such as planarians, and three entirely parasitic groups: Cestoda, Trematoda and Monogenea; however, since the turbellarians have since been proven not to be mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trematoda
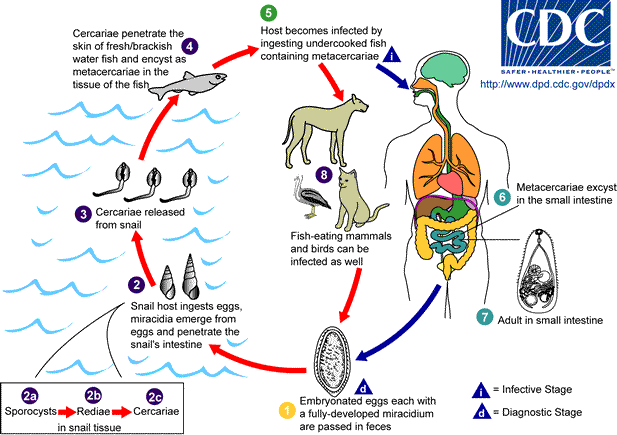
Trematoda is a Class (biology), class of flatworms known as flukes. They are obligate parasite, obligate internal Parasitism, parasites with a complex biological life cycle, life cycle requiring at least two Host_(biology), hosts. The intermediate host, in which asexual reproduction occurs, is usually a snail. The definitive host, where the flukes sexually reproduce, is a vertebrate. Infection by trematodes can cause disease in all five traditional vertebrate classes: mammals, birds, amphibians, reptiles, and fish. Etymology Trematodes are commonly referred to as flukes. This term can be traced back to the Old English name for flounder, and refers to the flattened, rhomboidal shape of the organisms. Taxonomy There are 18,000 to 24,000 known species of trematodes, divided into two subclasses — the Aspidogastrea and the Digenea. Aspidogastrea is the smaller subclass, comprising 61 species. These flukes mainly infect Bivalvia, bivalves and Osteichthyes, bony fishes.https://www.bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digenea
Digenea (Gr. ''Dis'' – double, ''Genos'' – race) is a class of trematodes in the Platyhelminthes phylum, consisting of parasitic flatworms (known as ''flukes'') with a syncytial tegument and, usually, two suckers, one ventral and one oral. Adults commonly live within the digestive tract, but occur throughout the organ systems of all classes of vertebrates. Once thought to be related to the Monogenea, it is now recognised that they are closest to the Aspidogastrea and that the Monogenea are more closely allied with the Cestoda. Around 6,000 species have been described to date. Morphology Key features Characteristic features of the Digenea include a syncytial tegument; that is, a tegument where the junctions between cells are broken down and a single continuous cytoplasm surrounds the entire animal. A similar tegument is found in other members of the Neodermata; a group of platyhelminths comprising the Digenea, Aspidogastrea, Monogenea and Cestoda. Digeneans possess a vermifo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opisthorchiida
Plagiorchiida is a large order of trematodes, synonymous to Echinostomida. They belong to the Digenea, a large subclass of flukes. This order contains relatively few significant parasites of humans. The following families are placed here, organised by superfamily and suborder:Jones, A., Bray, R. A., & Gibson, D. I. (Eds.). (2002). ''Keys to the Trematoda'' (Vol. 1). CABI Publishing and The Natural History Museum. * Apocreadiata ** Apocreadioidea Skrjabin, 1942 *** Apocreadiidae Skrjabin, 1942 * Bivesiculata ** Bivesiculoidea *** Bivesiculidae Yamaguti, 1934 * Bucephalata ** Bucephaloidea Poche, 1907 *** Bucephalidae Poche, 1907 *** Nuitrematidae Kurochkin, 1975 * Echinostomata ** Echinostomatoidea Looss, 1902 *** Caballerotrematidae Tkach, Kudlai & Kostadinova, 2016 *** Calycodidae Dollfus, 1929 *** Cyclocoelidae Stossich, 1902 *** Echinochasmidae Odhner, 1910 *** Echinostomatidae Looss, 1899 *** Fasciolidae Railliet, 1895 *** Himasthlidae Odhner, 1910 *** Philophthalmidae L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opisthorchiata
Opisthorchiata is a suborder of flatworms in the subclass Digenea. Families *Superfamily Opisthorchioidea Braun, 1901Braun, M. (1901). Zur revision der Trematoden der Vögel. ''Zentralblatt für Bakteriologie'', 1(29), 895–897. **Cryptogonimidae Ward, 1917Ward, H. B. (1917). On the structure and classification of North American parasitic worms. ''The Journal of Parasitology'', 4(1), 1–12. **Heterophyidae Leiper, 1909Leiper, R. T. (1909). London School of Tropical Medicine. Report of the helminthologist for the six months ending 30th April, 1908. In, ''Report of the Advisory Committee for the Tropical Diseases Research Fund for the Year 1908'' (pp. 35–39). London: Tropical Diseases Research Fund, Advisory Committee. **Opisthorchiidae Opisthorchiidae is a family of digenean trematodes. Opisthorchiidae have cosmopolitan distribution. The most medically important species in the family Opisthorchiidae are ''Clonorchis sinensis'', ''Opisthorchis viverrini'', and '' Opisthorch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opisthorchioidea
Opisthorchiata is a suborder of flatworms in the subclass Digenea. Families *Superfamily Opisthorchioidea Braun, 1901Braun, M. (1901). Zur revision der Trematoden der Vögel. ''Zentralblatt für Bakteriologie'', 1(29), 895–897. **Cryptogonimidae Ward, 1917Ward, H. B. (1917). On the structure and classification of North American parasitic worms. ''The Journal of Parasitology'', 4(1), 1–12. **Heterophyidae Leiper, 1909Leiper, R. T. (1909). London School of Tropical Medicine. Report of the helminthologist for the six months ending 30th April, 1908. In, ''Report of the Advisory Committee for the Tropical Diseases Research Fund for the Year 1908'' (pp. 35–39). London: Tropical Diseases Research Fund, Advisory Committee. **Opisthorchiidae Opisthorchiidae is a family of digenean trematodes. Opisthorchiidae have cosmopolitan distribution. The most medically important species in the family Opisthorchiidae are ''Clonorchis sinensis'', ''Opisthorchis viverrini'', and '' Opisthorch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterophyidae
Heterophyidae is a family of intestinal trematodes in the order Plagiorchiida. Description: " Tegument covered by spines. Oral sucker not armed or armed by cyrcumoral spines. Pharynx presented. Genital synus presented. Ventral and genital suckers usually not combined. Cirrus and bursa absent. Two testes located in posterior part of the body. Vitellaria in posterior part of the body." First intermediate hosts are molluscs of Prosobranchia, second intermediate hosts are fishes. Definite hosts are birds and mammals, including humans. Genera *'' Acanthotrema'' Travassos, 1928 *'' Alloheterophyes'' Pearson, 1999 *'' Apophallus'' Lühe, 1909 *''Ascocotyle'' Looss, 1899 *'' Centrocestus'' Looss, 1899 *'' Cercarioides'' Witenberg, 1929 *'' Condylocotyla'' Pearson & Prevot, 1985 *''Cryptocotyle'' Lühe, 1899 *'' Dermocystis'' Stafford, 1905 *''Galactosomum'' Looss, 1899 *'' Haplorchis'' Looss, 1899 *'' Haplorchoides'' Chen, 1949 *'' Heterophyes'' Cobbold, 1866 *'' Heterophyopsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trematoda
Trematoda is a Class (biology), class of flatworms known as flukes. They are obligate parasite, obligate internal Parasitism, parasites with a complex biological life cycle, life cycle requiring at least two Host_(biology), hosts. The intermediate host, in which asexual reproduction occurs, is usually a snail. The definitive host, where the flukes sexually reproduce, is a vertebrate. Infection by trematodes can cause disease in all five traditional vertebrate classes: mammals, birds, amphibians, reptiles, and fish. Etymology Trematodes are commonly referred to as flukes. This term can be traced back to the Old English name for flounder, and refers to the flattened, rhomboidal shape of the organisms. Taxonomy There are 18,000 to 24,000 known species of trematodes, divided into two subclasses — the Aspidogastrea and the Digenea. Aspidogastrea is the smaller subclass, comprising 61 species. These flukes mainly infect Bivalvia, bivalves and Osteichthyes, bony fishes.https://www.bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplorchis Popelkae
''Haplorchis'' is a genus of intestinal flukes in the family Heterophyidae. Species include: * '' Haplorchis popelkae'' * ''Haplorchis pumilio'' * ''Haplorchis taichui'' * ''Haplorchis vagabundi ''Haplorchis'' is a genus of intestinal flukes in the family Heterophyidae. Species include: * '' Haplorchis popelkae'' * '' Haplorchis pumilio'' * '' Haplorchis taichui'' * '' Haplorchis vagabundi'' * '' Haplorchis yokogawai'' References ...'' * '' Haplorchis yokogawai'' References Heterophyidae Digenea genera {{Trematoda-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplorchis Pumilio
''Haplorchis'' is a genus of intestinal flukes in the family Heterophyidae. Species include: * '' Haplorchis popelkae'' * '' Haplorchis pumilio'' * ''Haplorchis taichui'' * ''Haplorchis vagabundi ''Haplorchis'' is a genus of intestinal flukes in the family Heterophyidae. Species include: * '' Haplorchis popelkae'' * '' Haplorchis pumilio'' * '' Haplorchis taichui'' * '' Haplorchis vagabundi'' * '' Haplorchis yokogawai'' References ...'' * '' Haplorchis yokogawai'' References Heterophyidae Digenea genera {{Trematoda-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplorchis Taichui
''Haplorchis taichui'' is a species of intestinal fluke in the family Heterophyidae. It is a human parasite. Distribution This species occurs in: Taiwan, the Philippines, Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka, Palestine, Iraq, Egypt, Malaysia, Thailand, Laos, Vietnam, and South China. Life cycle The first intermediate hosts of ''Heterophyes nocens'' include freshwater snails '' Melania obliquegranosa'', '' Stenomelania juncea'', and ''Melanoides tuberculata''. The second intermediate host include freshwater fish: '' Cyclocheilichthys repasson'', goldfish ''Carassius auratus'', ''Cyprinus carpio'', ''Gambusia affinis'', ''Hampala dispar'', ''Labiobarbus leptocheilus'', ''Puntius binotatus'', ''Puntius brevis'', '' Puntius gonionotus'', Javean barb, '' Barbodes palata'', ''Pseudorasbora parva'', ''Rhodeus ocellatus'', '' Zacco platypus'', ''Raiamas guttatus'', '' Mystacoleucus marginatus'', and Siamese mud carp ''Henicorhynchus siamensis''. Natural definitive hosts are fish-eating anima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |