|
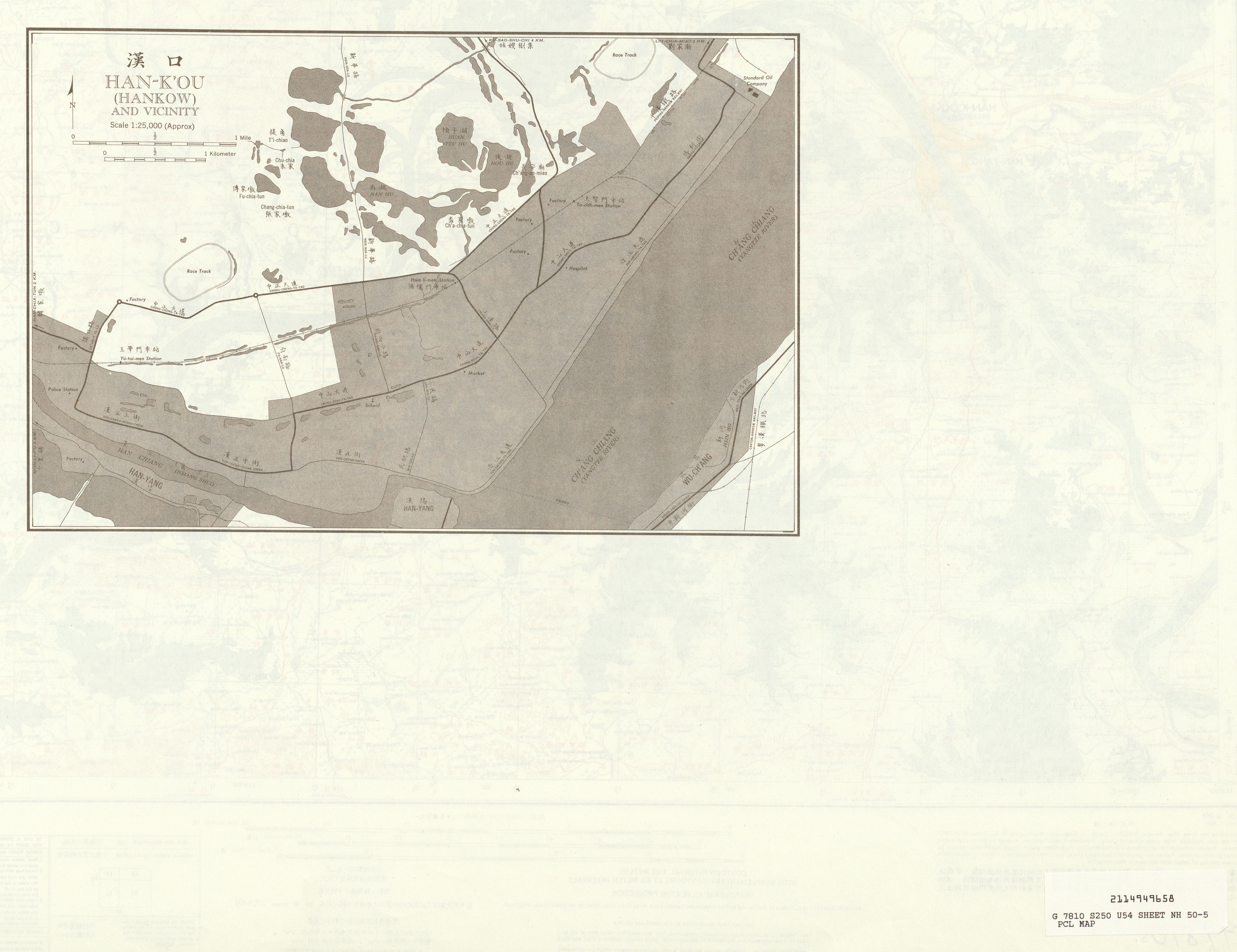
Hangkow
Hankou, alternately romanized as Hankow (), was one of the three towns (the other two were Wuchang and Hanyang) merged to become modern-day Wuhan city, the capital of the Hubei province, China. It stands north of the Han and Yangtze Rivers where the Han flows into the Yangtze. Hankou is connected by bridges to its triplet sister towns Hanyang (between Han and Yangtze) and Wuchang (on the south side of the Yangtze). Hankou is the main port of Hubei province and the single largest port in the middle reaches of Yangtze. History The city's name literally means " Mouth of the Han", from its position at the confluence of the Han with the Yangtze River. The name appears in a Tang Dynasty poem by Liu Changqing. Other historical names for the city include Xiakou (), Miankou (), and Lukou (). Hankou, from the Ming to late Qing, was under the administration of the local government in Hanyang, although it was already one of the four major national markets ( :zh:四大名镇) in Ming d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
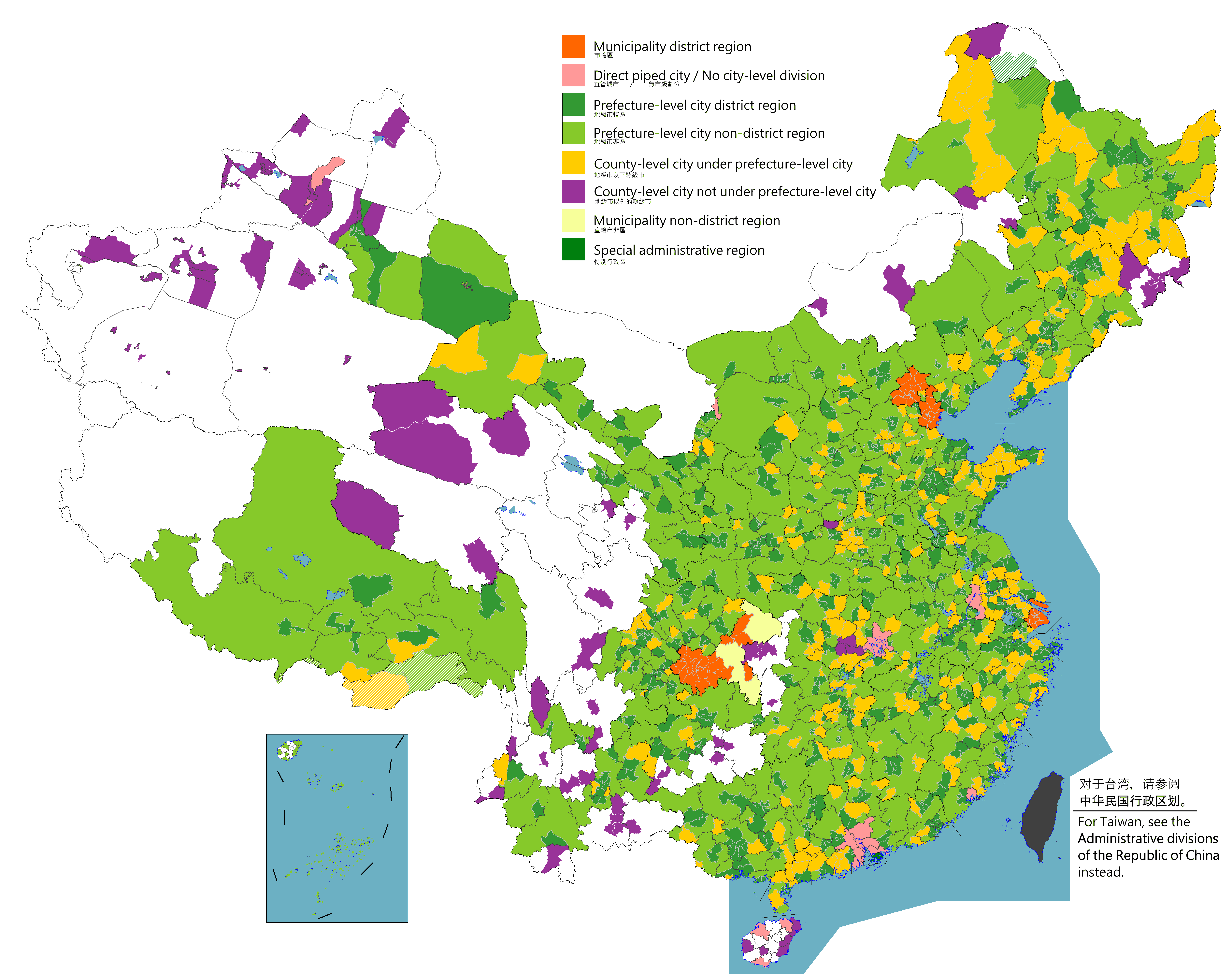
List Of Cities In China
According to the administrative divisions of the People's Republic of China there are three levels of cities, namely provincial-level (consists of municipalities ), prefecture-level cities, and county-level cities. As of June 2020 the PRC has a total of 687 cities: 4 municipalities, 2 SARs, 293 prefectural-level cities (including the 15 sub-provincial cities) and 388 county-level cities (including the 38 sub-prefectural cities and 10 XXPC cities). This list does not include any cities in the disputed Taiwan Province and portions of Fujian Province (see the List of cities in Taiwan), as these are controlled by the Republic of China and claimed by the PRC under the One-China policy. Four cities are centrally administered municipalities, which include dense urban areas, suburbs, and large rural areas: Chongqing (28.84 million), Shanghai (23.01 million), Beijing (19.61 million), and Tianjin (12.93 million). According to 2017 research from the Demographia research group, there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Mouth
A river mouth is where a river flows into a larger body of water, such as another river, a lake/reservoir, a bay/gulf, a sea, or an ocean. At the river mouth, sediments are often deposited due to the slowing of the current reducing the carrying capacity of the water. The water from a river can enter the receiving body in a variety of different ways. The motion of a river is influenced by the relative density of the river compared to the receiving water, the rotation of the earth, and any ambient motion in the receiving water, such as tides or seiches. If the river water has a higher density than the surface of the receiving water, the river water will plunge below the surface. The river water will then either form an underflow or an interflow within the lake. However, if the river water is lighter than the receiving water, as is typically the case when fresh river water flows into the sea, the river water will float along the surface of the receiving water as an overflow. Alon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boxer Rebellion
The Boxer Rebellion, also known as the Boxer Uprising, the Boxer Insurrection, or the Yihetuan Movement, was an anti-foreign, anti-colonial, and anti-Christian uprising in China between 1899 and 1901, towards the end of the Qing dynasty, by the Society of Righteous and Harmonious Fists (), known as the "Boxers" in English because many of its members had practised Chinese martial arts, which at the time were referred to as "Chinese boxing". After the Sino-Japanese War of 1895, villagers in North China feared the expansion of foreign spheres of influence and resented the extension of privileges to Christian missionaries, who used them to shield their followers. In 1898 Northern China experienced several natural disasters, including the Yellow River flooding and droughts, which Boxers blamed on foreign and Christian influence. Beginning in 1899, Boxers spread violence across Shandong and the North China Plain, destroying foreign property such as railroads and attacking or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct-controlled Municipality
A direct-controlled municipality is the highest level classification for cities used by unitary states, with status equal to that of the provinces in the respective countries. A direct-controlled municipality is similar to, but not the same as, a federal district, a common designation in various countries for a municipality that is not part of any state, and which usually hosts some governmental functions. Usually direct-controlled municipality are under central government control with limited power. Many countries have adopted this system with some different variations. Geographically and culturally, many of the municipalities are enclaves in the middle of provinces. Some occur in strategic positions in between provinces. References See also * Independent city * Federal city * Metropolitan Capitalism (Capital City) * Federal district A federal district is a type of administrative division of a federation, usually under the direct control of a federal government and or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. The city has 11 districts, an administrative area of , and a total recorded population of 9,314,685 . Situated in the Yangtze River Delta region, Nanjing has a prominent place in Chinese history and culture, having served as the capital of various Chinese dynasties, kingdoms and republican governments dating from the 3rd century to 1949, and has thus long been a major center of culture, education, research, politics, economy, transport networks and tourism, being the home to one of the world's largest inland ports. The city is also one of the fifteen sub-provincial cities in the People's Republic of China's administrative structure, enjoying jurisdictional and economic autonomy only slightly less than that of a province. Nanjing has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Expedition
The Northern Expedition was a military campaign launched by the National Revolutionary Army (NRA) of the Kuomintang (KMT), also known as the "Chinese Nationalist Party", against the Beiyang government and other regional warlords in 1926. The purpose of the campaign was to reunify China, which had become fragmented in the aftermath of the Revolution of 1911. The expedition was led by Generalissimo Chiang Kai-shek, and was divided into two phases. The first phase ended in a 1927 political split between two factions of the KMT: the right-leaning Nanjing faction, led by Chiang, and the left-leaning faction in Wuhan, led by Wang Jingwei. The split was partially motivated by Chiang's Shanghai Massacre of Communists within the KMT, which marked the end of the First United Front. In an effort to mend this schism, Chiang Kai-shek stepped down as the commander of the NRA in August 1927, and went into exile in Japan. The second phase of the Expedition began in January 1928, when Chiang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jianghan District
Jianghan District (, Yangtze and Han River) forms part of the urban core of and is one of 13 urban districts of the prefecture-level city of Wuhan, the capital of Hubei Province, China. The district is part of the historical Hankou. Geography Jianghan District is situated on the northwest (left) bank of the Yangtze River. It is both the least spacious and most densely populated of the districts of Wuhan. It borders Dongxihu to the north, Jiang'an to the northeast, Hanyang to the south, and Qiaokou to the west; on the opposite bank it borders Wuchang. Wuhan Center Wuhan Center () is a skyscraper in Wuhan near Wuhan Business District Station in Jianghan District, Wuhan, Hubei, China. The skyscraper's construction started in 2011, and was completed by 2019. The tower was topped out on April 16, 2015. It is ... is located in Jianghan District. Administrative divisions Jianghan District administers: References County-level divisions of Hubei Geography of Wuhan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang Zhidong
Zhang Zhidong () (4 September 18375 October 1909) was a Chinese politician who lived during the late Qing dynasty. Along with Zeng Guofan, Li Hongzhang and Zuo Zongtang, Zhang Zhidong was one of the four most famous officials of the late Qing dynasty. Known for advocating controlled reform and modernization of Chinese troops, he served as the governor of Shanxi Province and viceroy of Huguang, Liangguang and Liangjiang, and also as a member of the Grand Council. He took a leading role in the abolition of the Imperial examination system in 1905. The Red Guards destroyed his tomb in 1966 during the Cultural Revolution. His remains were rediscovered in 2007 and reburied with honors. Other names Zhang Zhidong was also known by other names. An older Wade–Giles form was Chang Chih-tung. His courtesy name was Xiaoda () or Xiangtao (). His pseudonyms were Xiangyan (), Hugong (), Wujing Jushi () and Baobing (). The posthumous name given to him by the Qing government was Wenxiang ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaking ethnic group who unified other Jurchen tribes to form a new "Manchu" ethnic identity. The dynasty was officially proclaimed in 1636 in Manchuria (modern-day Northeast China and Outer Manchuria). It seized control of Beijing in 1644, then later expanded its rule over the whole of China proper and Taiwan, and finally expanded into Inner Asia. The dynasty lasted until 1912 when it was overthrown in the Xinhai Revolution. In orthodox Chinese historiography, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China. The multiethnic Qing dynasty lasted for almost three centuries and assembled the territorial base for modern China. It was the largest imperial dynasty in the history of China and in 1790 the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ming Dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han Chinese, Han people, the majority ethnic group in China. Although the primary capital of Beijing fell in 1644 to a rebellion led by Li Zicheng (who established the short-lived Shun dynasty), numerous rump state, rump regimes ruled by remnants of the House of Zhu, Ming imperial family—collectively called the Southern Ming—survived until 1662. The Ming dynasty's founder, the Hongwu Emperor (r. 1368–1398), attempted to create a society of self-sufficient rural communities ordered in a rigid, immobile system that would guarantee and support a permanent class of soldiers for his dynasty: the empire's standing army exceeded one million troops and the naval history of China, navy's dockyards in Nanjin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |