|
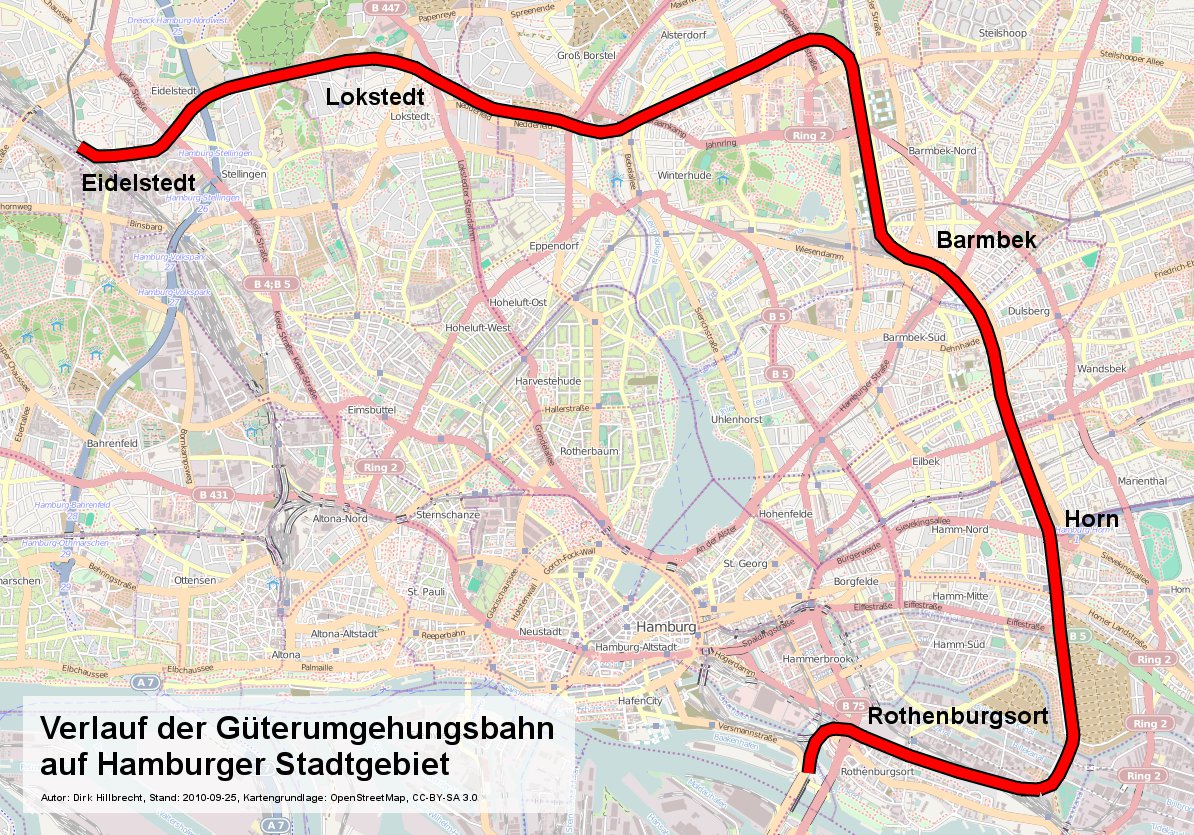
Hamburg Freight Bypass
The Hamburg freight rail bypass (german: Güterumgehungsbahn) is a railway line in the German city of Hamburg. It runs from Hamburg-Eidelstedt via Hamburg-Rothenburgsort to Hamburg-Harburg and connects the long-distance railways approaching Hamburg, bypassing the link line and the railway junctions on the approaches to Hamburg-Altona station and Hamburg Hauptbahnhof. The line is mainly used for rail freight. History The first part of the freight bypass was opened in 1902 by the Lübeck-Büchen Railway Company (''Lübeck-Büchener Eisenbahn'') as a link connecting Wandsbek station on the Lübeck–Hamburg railway and Rothenburgsort station on the Berlin–Hamburg railway. On 21 February 1903, the bypass was connected to Hamburg Hauptbahnhof via the main freight yard (''Hauptgüterbahnhof'') at the former ''Hannoverscher Bahnhof'' (the original terminal station on the line to Hanover). An extension to Ohlsdorf was completed from the link line before the First World War, alo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
15 KV AC Railway Electrification
Railway electrification systems using at are used on transport railways in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Sweden, and Norway. The high voltage enables high power transmission with the lower frequency reducing the losses of the traction motors that were available at the beginning of the 20th century. Railway electrification in late 20th century tends to use AC systems which has become the preferred standard for new railway electrifications but extensions of the existing networks are not completely unlikely. In particular, the Gotthard Base Tunnel (opened on 1 June 2016) still uses 15 kV, 16.7 Hz electrification. Due to high conversion costs, it is unlikely that existing systems will be converted to despite the fact that this would reduce the weight of the on-board step-down transformers to one third that of the present devices. History The first electrified railways used series-wound DC motors, first at 600 V and then 1,500 V. Areas with 3 kV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wandsbek-Gartenstadt (Hamburg U-Bahn Station)
Wandsbek-Gartenstadt is a major rapid transit station on the Hamburg U-Bahn lines U1 and U3. For line U1, Wandsbek-Gartenstadt is a through station; for line U3, it is terminus station. The station is located in the Gartenstadt (garden city) of Wandsbek, Germany. Wandsbek is center of the Hamburg borough of Wandsbek. History The station was opened in 1918 by the name "Hinschenfelde" and as part of Hamburg's Walddörferbahn. In 1920 the station was electrified, renamed "Wandsbek-Gartenstadt" and integrated into the Hamburger Hochbahn network. On 4 August 1963 the second rail line was opened. Since 2014, ongoing modernization works on the station building and the station platforms are underway, including raised platforms for handicap-accessibility and new platform roofs. Since May 2014, the northbound trains are accessible via an elevator, the southbound trains are expected to be equipped accordingly by the end of 2014. Layout The station is located on the northern side of O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harburg S-Bahn
The Harburg S-Bahn line is a railway line in southern Hamburg, Germany. It starts at Hamburg Hauptbahnhof and runs via Harburg to Stade. It mostly runs parallel with the line to Hanover and the Lower Elbe line and is now part of the Hamburg S-Bahn lines S3 and S31. Route The route begins at the Hauptbahnhof, where it climbs a steep ramp before crossing the tracks of the main lines to Berlin and to Lübeck. After running on a concrete viaduct, on which, Hammerbrook station is located, the line crosses the southern freight railway bypass and the Northern Elbe bridge. The line now runs directly parallel with the line to Hanover. After Veddel and Wilhelmsburg stations the line moves away from the Hanover line and dives into a tunnel. The line passes through the stations of Harburg, Harburg Rathaus (which has three platforms) and Heimfeld and then climbs to the surface and runs parallel with the Lower Elbe line. It then passes through the stations of Neuwiedenthal and Neugra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamburg Berliner Bahnhof
The Berliner Bahnhof (Berlin line station) in the German city of Hamburg was the western terminus of the Berlin-Hamburg railway opened in 1846. It was previously the site of the station built in 1844 to a design by Alexis de Chateauneuf for the Hamburg-Bergedorf Railway. Berliner Bahnhof was completed in 1857 and closed in 1903. Structural features The former Bergedorfer Bahnhof was extended for the needs of the Berlin-Hamburg railway using red brick with plastered cornices and provided with a 148-meter-long and 23.5 m-high wooden train shed with four tracks. This train shed was considered at the time to be the most substantial wooden structure in Germany. The station building was divided into departure and arrival areas with a baggage check-in and check-out and waiting rooms of different classes. It also had a ladies room. The commissioning took place on 15 December 1846, but the renovation and construction of the 173 m-long building complex, the freight tracks and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiefstack Station
Tiefstack is a station on the Berlin-Hamburg railway line and served by the trains of Hamburg S-Bahn lines S2 and S21. The station was originally opened in 1842 and is located in the Hamburg district of Rothenburgsort, Germany. Rothenburgsort is part of the borough of Hamburg-Mitte. History The station was originally opened by the Hamburg-Bergedorf Railway Company in 1842 to serve the commuter rail in Hamburg's south-eastern quarters. In 1958 Tiefstack station was electrified and integrated into the Hamburg S-Bahn network. Service The lines S2 and S21 of Hamburg S-Bahn call at Tiefstack station. See also * Hamburger Verkehrsverbund The Hamburger Verkehrsverbund (HVV) ( en, "Hamburg Transport Association") is a transport association coordinating public transport in and around Hamburg, Germany. Its main objectives are to provide a unified fare system, requiring only a single ... (HVV) * List of Hamburg S-Bahn stations References External links Line and route ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Billwerder Industriebahn
Billwerder () is a quarter of Hamburg, Germany, in the borough of Bergedorf. It is located on the northwestern border of the borough adjacent to the borough of Hamburg-Mitte. At the same time Billwerder means a greater area south of the river Bille. Name The name derives from ''Bilnawerthere'', meaning ''island in the Bille''. A Werder is an island between rivers or other bodies of water, in this case Bille and Elbe/Dove Elbe rivers. Until 1949 Billwerder was also named ''Billwärder an der Elbe''. Geography Billwerder borders the quarters of Lohbrügge, Bergedorf, Neuallermöhe, Allermöhe, Moorfleet, Billbrook, and Billstedt. Billwerder is part of the Marschlande (''marshlands'') area in Hamburg, which is known for its wet and muddy grounds. It is sparsely populated. Billwerder's landscape is formed by the transition of rural Vierlande into the industrial and commercial areas near the Port of Hamburg, such as nearby Billbrook. Billwerder is largely characterized by ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Billstedt (Hamburg U-Bahn Station)
Billstedt is a major rapid transit station on the Hamburg U-Bahn lines U2 and U4. For line U2, Billstedt is a through station; for line U4, it is currently terminus station. Intermodal connections are available to local and regional buses. The station is located in the Hamburg district of Billstedt, Germany. Billstedt is part of the borough of Hamburg-Mitte. History The station was opened in 1969, and initially served as terminus station for line U3 until opening of Merkenstraße station in May 1970. Layout The station's layout is using a natural depression for the rail tracks to sit below street level, but nevertheless above ground level. The platforms for the U-Bahn trains are capped by the ZOB Billstedt, a central bus station. Adjacent to the bus station is Billstedt-Center, a large shopping mall. Service Trains Billstedt U-Bahn station is served by Hamburg U-Bahn lines U2 and U4; departures into the inner-city are every 5 minutes; trains out east run every 10 minut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berliner Tor Station
Berliner Tor (; literally "Berlin Gate") is a transport hub in Hamburg, Germany, served by the Hamburg U-Bahn (underground railway) and the Hamburg S-Bahn (suburban railway). The station is located in St. Georg, part of the borough of Hamburg-Mitte. The railway station is listed by the German railway company, because S-Bahn call at this station, and the S-Bahn part of it is managed by DB Station&Service. History Berliner Tor S-Bahn station opened in 1906. The original Berliner Tor U-Bahn station was designed by the architect, Erich Elingius, and built between 1908 and 1910, opening on 1 March 1912. It had a brick wall on the North, and some glass walls on the South. During the British Operation Gomorrah (air raids) in 1943, the damage to the station was so severe that the U-Bahn was no longer able to serve the line. On 19 January 1948, the station re-opened as a terminus for trains to Barmbek via Schlump, and from 1 July 1949, trains continued again to Mundsburg. From 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lübeck–Hamburg Railway
The Hamburg–Lübeck railway is one of the most important mainline railways of the German states of Schleswig-Holstein and Hamburg. It connects the two Hanseatic cities of Hamburg and Lübeck, and is part of the line to Denmark. The line was opened in 1865. Route The line runs the south-west from Lübeck through mostly agricultural, undulating land. The Trave river is crossed three times. The most important intermediate stop is Bad Oldesloe, where the line connects with hourly services on the line to Bad Segeberg and Neumünster, operated by Nordbahn. Between Ahrensburg and Hamburg-Rahlstedt the line runs along the Stellmoor tunnel valley. In the city of Hamburg the line crosses the rail freight bypass and then runs parallel to the S-Bahn line until Hamburg Hauptbahnhof is reached from the east. History The first plans to build a direct rail link between Hamburg and Lübeck were put forward in 1831. Because of the refusal of the Danish authorities to allow a direct line to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamburg S-Bahn
The Hamburg S-Bahn is a suburban commuter railway network in the Hamburg Metropolitan Region. Together, the S-Bahn, the Hamburg U-Bahn, the AKN railway and the regional railway form the backbone of railway public transport in the city and the surrounding area. The network has operated since 1907 as a commuter rail system, under the direction of the state railway, and is a member of the Hamburger Verkehrsverbund (HVV; Hamburg Transport Association). There are six lines, serving 68 stations, on of route. On an average working day the S-Bahn transports about 590,000 passengers; in 2010 about 221 million people used the S-Bahn. The S-Bahn is the only railway in Germany that uses both 1,200 V DC supplied by a third rail and supplied by overhead lines. Most of the tracks are separated from other rail services. The S-Bahn is operated by S-Bahn Hamburg GmbH, a subsidiary of DB Regio. Similarly to Berlin but unlike Hanover, the S-Bahn is an important part of public transport within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wandsbeker Chaussee Station
Wandsbeker Chaussee is a U-Bahn and S-Bahn hub of the rail network in the district of Eilbek in the German city of Hamburg. It is now served by Hamburg S-Bahn lines S1 and S11 and Hamburg U-Bahn line U1 and consists of two separate stations for the S-Bahn and U-Bahn. It is classified by Deutsche Bahn The (; abbreviated as DB or DB AG) is the national railway company of Germany. Headquartered in the Bahntower in Berlin, it is a joint-stock company ( AG). The Federal Republic of Germany is its single shareholder. describes itself as the se ... as a category 4 station. History Today's S-Bahn station was established in 1906 as part of the extension of the link line to Ohlsdorf as a station for the ''Hamburg-Altonaer Stadt- und Vorortbahn'' (Hamburg-Altona City and Suburban railway, the predecessor of the S-Bahn). The name ''S-Bahn'' was not used not until 1934. The U-Bahn station was taken into service in 1962 with the opening of the new U-Bahn line to Wandsbek. The i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


Bergedorf_Reinbek.jpg)
