Hamburg S-Bahn on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Hamburg S-Bahn is a suburban commuter railway network in the
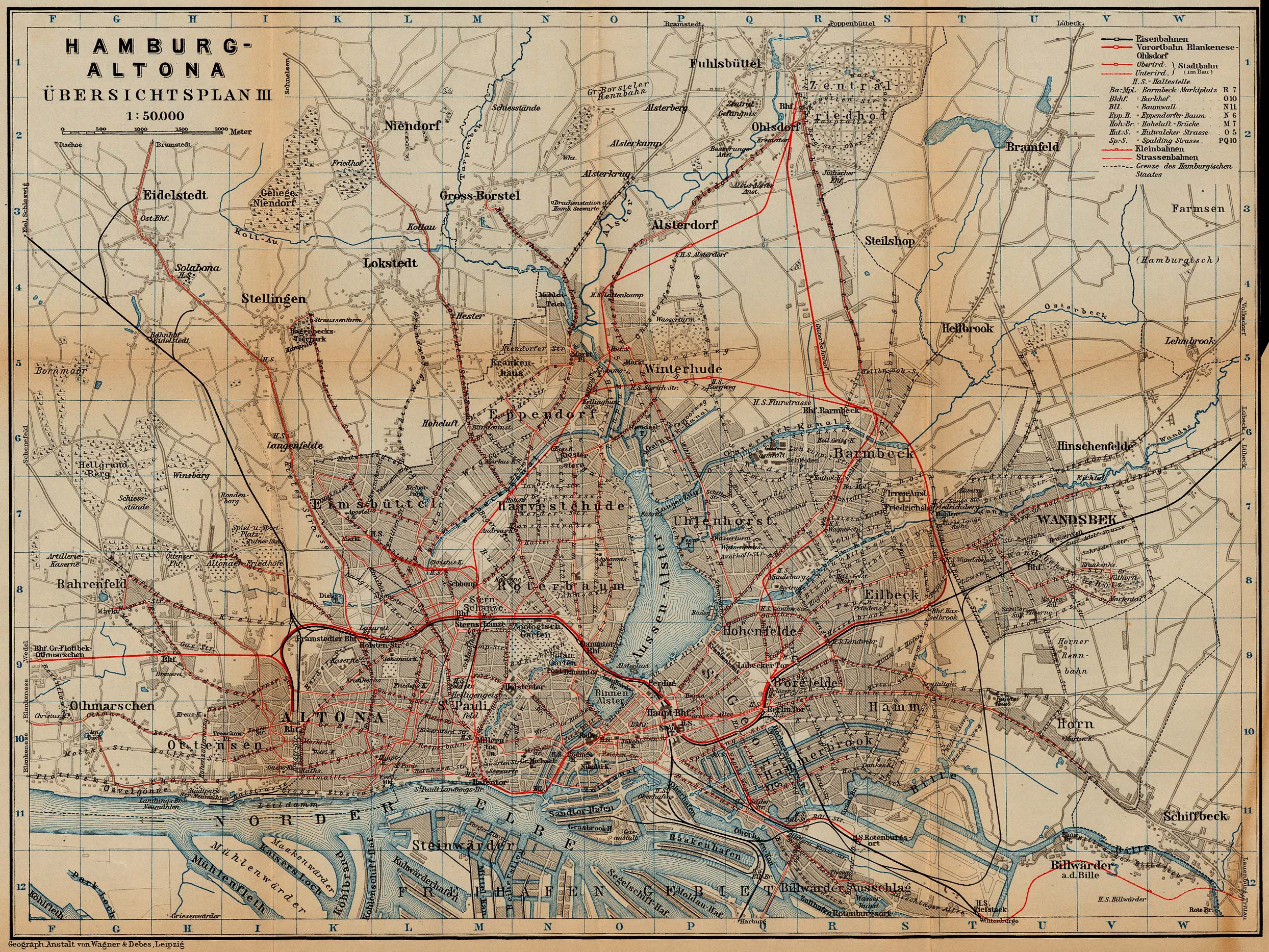
 The line was electrified with overhead lines supplying 6,600 V alternating current at 25 Hz. The electricity came from a coal-fired power station in ''Leverkusenstraße'' in Bahrenfeld, which also provided power to the Altona harbour railway.
The first electric trains ran on 1 October 1907, and from 29 January 1908 the line from Blankenese to Ohlsdorf was served exclusively by electric trains. These dates are considered the birthdates of the S-Bahn.
The basic unit of an AC train consisted of two articulated compartment carriages on six axles with motorised two-axle bogies under each cab end and a Jacobs bogie in the middle. The carriages, with doors on each side of the compartments, took their design and functionality from Prussian compartment carriages.
The line was electrified with overhead lines supplying 6,600 V alternating current at 25 Hz. The electricity came from a coal-fired power station in ''Leverkusenstraße'' in Bahrenfeld, which also provided power to the Altona harbour railway.
The first electric trains ran on 1 October 1907, and from 29 January 1908 the line from Blankenese to Ohlsdorf was served exclusively by electric trains. These dates are considered the birthdates of the S-Bahn.
The basic unit of an AC train consisted of two articulated compartment carriages on six axles with motorised two-axle bogies under each cab end and a Jacobs bogie in the middle. The carriages, with doors on each side of the compartments, took their design and functionality from Prussian compartment carriages.
 In the 1930s, after almost 30 years of service, the necessity to renew the trains and infrastructure had become apparent. Since the DC system had proved itself over more than a decade with the Berlin S-Bahn, where the 750 volt DC power was supplied by a third rail, the German Imperial Railway decided to adopt the same system for Hamburg in 1937 and to abandon overhead AC. In order to allow improved acceleration, the S-Bahn uses 1200 volts: as a consequence, Berlin and Hamburg rolling stock are not compatible with each other. The first DC trains, of the type ET 171, were delivered in 1939; daily service began in July 1940 alongside the AC trains. Due to the
In the 1930s, after almost 30 years of service, the necessity to renew the trains and infrastructure had become apparent. Since the DC system had proved itself over more than a decade with the Berlin S-Bahn, where the 750 volt DC power was supplied by a third rail, the German Imperial Railway decided to adopt the same system for Hamburg in 1937 and to abandon overhead AC. In order to allow improved acceleration, the S-Bahn uses 1200 volts: as a consequence, Berlin and Hamburg rolling stock are not compatible with each other. The first DC trains, of the type ET 171, were delivered in 1939; daily service began in July 1940 alongside the AC trains. Due to the
 Extensions were made in 1967 on separate tracks from Elbgaustraße to Pinneberg, and in 1969 on existing mainline tracks from Bergedorf to Aumühle.
To ease the strain on the central Verbindungsbahn ("connection railway"), a second main connection was constructed, the City S-Bahn, which traverses the city centre in a tunnel. The first section was opened in 1975 between Hauptbahnhof and Landungsbrücken, the extension to Altona in 1979 and was completed in 1981 with the connection above ground to ''Diebsteich''. 1983 saw the opening of the line via Wilhelmsburg to ''Harburg Rathaus'', a long stretch of which runs along the existing mainline. Through Hammerbrook the trains run on a concrete
Extensions were made in 1967 on separate tracks from Elbgaustraße to Pinneberg, and in 1969 on existing mainline tracks from Bergedorf to Aumühle.
To ease the strain on the central Verbindungsbahn ("connection railway"), a second main connection was constructed, the City S-Bahn, which traverses the city centre in a tunnel. The first section was opened in 1975 between Hauptbahnhof and Landungsbrücken, the extension to Altona in 1979 and was completed in 1981 with the connection above ground to ''Diebsteich''. 1983 saw the opening of the line via Wilhelmsburg to ''Harburg Rathaus'', a long stretch of which runs along the existing mainline. Through Hammerbrook the trains run on a concrete
 The network covers about , and serves 68 stations. It consists of two
The network covers about , and serves 68 stations. It consists of two
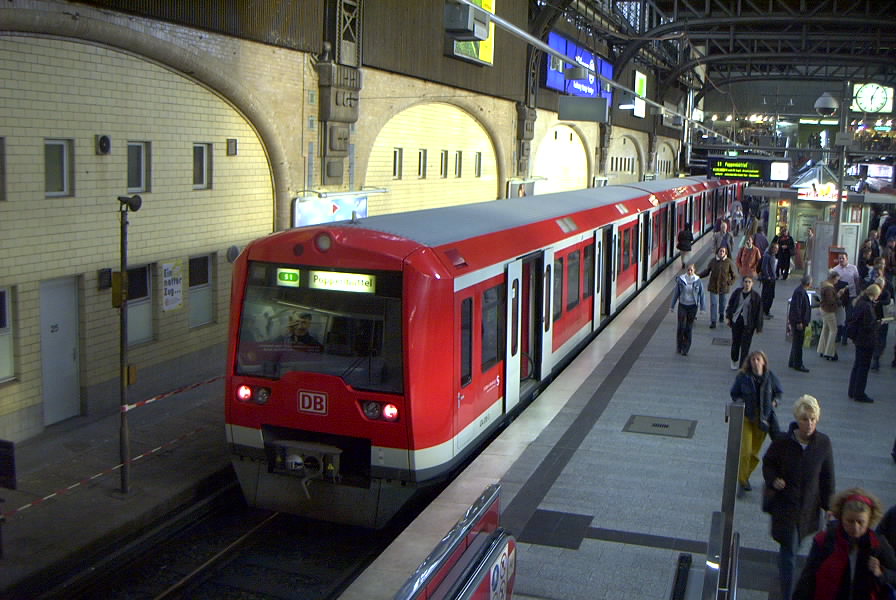 The S-Bahn uses three-car
The S-Bahn uses three-car
 The S-Bahn has 68 stations, of which ten are fully underground. These are the five stations along the City-S-Bahn (''Jungfernstieg'', ''Stadthausbrücke'', ''Landungsbrücken'', ''Reeperbahn'' and ''Königstraße''), the S-Bahn area of ''Altona'' station, the three stations in the centre of Harburg (''Harburg'', ''Harburg Rathaus'' and '' Heimfeld'') and at Hamburg Airport. At the Hauptbahnhof, the westbound platforms are also in tunnel.
Most stations consist of a single
The S-Bahn has 68 stations, of which ten are fully underground. These are the five stations along the City-S-Bahn (''Jungfernstieg'', ''Stadthausbrücke'', ''Landungsbrücken'', ''Reeperbahn'' and ''Königstraße''), the S-Bahn area of ''Altona'' station, the three stations in the centre of Harburg (''Harburg'', ''Harburg Rathaus'' and '' Heimfeld'') and at Hamburg Airport. At the Hauptbahnhof, the westbound platforms are also in tunnel.
Most stations consist of a single
''Die Hamburger S-Bahn'' by Martin Heimann
* ttp://www.kaemena360.net/FS/DB/ET474Hamburg1 Interactive Panorama of the inside of an S-Bahn Trainset ET 474
Interactive Panorama of new Airport Station
Homepage of the Historische S-Bahn Hamburg e.V.
{{coord missing, Hamburg S-Bahn 15 kV AC railway electrification Deutsche Bahn S-Bahn in Germany
Hamburg Metropolitan Region
The Hamburg Metropolitan Region (German: Metropolregion Hamburg) is a metropolitan area centred around the city of Hamburg in northern Germany, consisting of eight districts (''Landkreise'') in the federal state of Lower Saxony, six districts ('' ...
. Together, the S-Bahn, the Hamburg U-Bahn, the AKN railway
AKN Eisenbahn GmbH operates railway lines, commuter trains and freight trains in Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein. Its headquarters is in Kaltenkirchen. It is a member of the Hamburger Verkehrsverbund (HVV), which organises public transport in an ...
and the regional railway form the backbone of railway public transport in the city and the surrounding area. The network has operated since 1907 as a commuter rail system, under the direction of the state railway, and is a member of the Hamburger Verkehrsverbund
The Hamburger Verkehrsverbund (HVV) ( en, "Hamburg Transport Association") is a transport association coordinating public transport in and around Hamburg, Germany. Its main objectives are to provide a unified fare system, requiring only a sing ...
(HVV; Hamburg Transport Association). There are six lines, serving 68 stations, on of route. On an average working day the S-Bahn transports about 590,000 passengers; in 2010 about 221 million people used the S-Bahn.
The S-Bahn is the only railway in Germany that uses both 1,200 V DC supplied by a third rail and supplied by overhead lines. Most of the tracks are separated from other rail services. The S-Bahn is operated by S-Bahn Hamburg GmbH, a subsidiary of DB Regio.
Similarly to Berlin
Berlin is Capital of Germany, the capital and largest city of Germany, both by area and List of cities in Germany by population, by population. Its more than 3.85 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European U ...
but unlike Hanover, the S-Bahn is an important part of public transport within the city due to its dense schedule and good coverage of the metropolitan region. Unlike both Berlin and Hanover, the S-Bahn is of little importance for regional traffic since the network lies mostly within the city, though in 2007 the southwestern S3 line was extended about 32 km (20 miles) into the state of Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
(the ''Neugraben - Stade'' portion, which included seven new stations).
History

1906: Opening
On 5 December 1906, under the description , thePrussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
n '' Eisenbahndirektion'' (railway division) of Altona opened with steam trains between Blankenese, Altona (Elbe) and Hamburg.
The Stadt- und Vorortbahn (City and Suburban railway) included the Altona-Blankenese line (''Altona-Blankeneser Bahn'', opened in 1867), the local tracks of the Hamburg-Altona link line (''Verbindungsbahn'', opened in 1866) and a new section to Ohlsdorf.
The ''Verbindungsbahn'' had been extended from one track to four and level crossings eliminated between 1893 and 1903. The new double-track line adjoining it was completed in the summer of 1906 after an eight-year construction period. It ran alongside the Lübeck–Hamburg line of the Lübeck-Büchen Railway Company as far as Hasselbrook and then on its own tracks as far as the new Ohlsdorf cemetery. A new main cemetery with good transit connections was necessary in part due to the extension of the central railway lines, which had reduced the area of the existing already strained cemeteries near the city's medieval fortifications.
1907/08: First electric operation
 The line was electrified with overhead lines supplying 6,600 V alternating current at 25 Hz. The electricity came from a coal-fired power station in ''Leverkusenstraße'' in Bahrenfeld, which also provided power to the Altona harbour railway.
The first electric trains ran on 1 October 1907, and from 29 January 1908 the line from Blankenese to Ohlsdorf was served exclusively by electric trains. These dates are considered the birthdates of the S-Bahn.
The basic unit of an AC train consisted of two articulated compartment carriages on six axles with motorised two-axle bogies under each cab end and a Jacobs bogie in the middle. The carriages, with doors on each side of the compartments, took their design and functionality from Prussian compartment carriages.
The line was electrified with overhead lines supplying 6,600 V alternating current at 25 Hz. The electricity came from a coal-fired power station in ''Leverkusenstraße'' in Bahrenfeld, which also provided power to the Altona harbour railway.
The first electric trains ran on 1 October 1907, and from 29 January 1908 the line from Blankenese to Ohlsdorf was served exclusively by electric trains. These dates are considered the birthdates of the S-Bahn.
The basic unit of an AC train consisted of two articulated compartment carriages on six axles with motorised two-axle bogies under each cab end and a Jacobs bogie in the middle. The carriages, with doors on each side of the compartments, took their design and functionality from Prussian compartment carriages.
1924: Network expansion along the Alster valley railway
A railway line constructed and operated by a local company in 1914 and taken over by the district of Stormarn after bankruptcy, led from Ohlsdorf to Poppenbüttel inPrussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
, with the goal of connecting neighbouring settlements along the Alster river. It was known as the Alster Valley Railway. It opened in 1918 with petrol
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic c ...
-powered trains. The district of Stormarn gave the line to the German Imperial railway company, which electrified it and provided the extension of the Hamburg-Altona City and Suburban railway to Poppenbüttel in 1924.
1934: Designation as an S-Bahn
The term S-Bahn was first coined and used in Berlin from 1930, where a similar system on the '' City, Ring and Suburban lines'' had been operated since 1924; it was first used by the German Imperial railway with reference to its ''Hamburg-Altona City and Suburban railway'' in 1934. The term was also used to describe non-electric services on lines within the local suburban tariff: the steam-powered lines from Blankenese to Wedel, from Altona to Elmshorn, from Hamburg to Friedrichsruh and toHarburg Harburg may refer to:
Places in Germany
* Harburg (district), Lower Saxony
* Harburg, Bavaria
* Harburg, Hamburg, a borough of Hamburg
** Harburg (quarter), the former Hanoveran city of Harburg upon Elbe, now a quarter of Hamburg
* Harburg-Wilhe ...
. Since 2002, lines not served by S-Bahn have been designated "Regional railway lines".
1939/40: Moving to the DC system
 In the 1930s, after almost 30 years of service, the necessity to renew the trains and infrastructure had become apparent. Since the DC system had proved itself over more than a decade with the Berlin S-Bahn, where the 750 volt DC power was supplied by a third rail, the German Imperial Railway decided to adopt the same system for Hamburg in 1937 and to abandon overhead AC. In order to allow improved acceleration, the S-Bahn uses 1200 volts: as a consequence, Berlin and Hamburg rolling stock are not compatible with each other. The first DC trains, of the type ET 171, were delivered in 1939; daily service began in July 1940 alongside the AC trains. Due to the
In the 1930s, after almost 30 years of service, the necessity to renew the trains and infrastructure had become apparent. Since the DC system had proved itself over more than a decade with the Berlin S-Bahn, where the 750 volt DC power was supplied by a third rail, the German Imperial Railway decided to adopt the same system for Hamburg in 1937 and to abandon overhead AC. In order to allow improved acceleration, the S-Bahn uses 1200 volts: as a consequence, Berlin and Hamburg rolling stock are not compatible with each other. The first DC trains, of the type ET 171, were delivered in 1939; daily service began in July 1940 alongside the AC trains. Due to the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
and the post-war years with their shortages, mixed usage lasted until 1955.
The basic DC train unit consisted of three four-axle carriages, each with four sliding double doors per side. The middle carriages had upholstered seats for second class, while the motorised end carriages had third-class wooden seats.
Network extensions from 1950 to 1965
The DC S-Bahn was extended along the single-track suburban line from Blankenese to Sülldorf in 1950 and to Wedel in 1954. A section of the mainline railway between Hamburg and Berlin, which, due to the division of Germany, had very little traffic, between Haupbahnhof and Bergedorf was added to the network in 1959 by the addition of the third rail. This was the first section where S-Bahn and mainline trains (the number of the latter remained small until 1990) shared tracks. It was the second S-Bahn line, from Bergedorf via ''Berliner Tor'' to ''Altona''. In 1962 a connecting curve was constructed from the Verbindungsbahn at ''Holstenstraße'' to the Altona-Kaltenkirchen railway, whose terminus was relocated to ''Langenfelde''. The S-Bahn was extended in 1965 along the AKN to Eidelstedt and from there along the mainline tracks towardsKiel
Kiel () is the capital and most populous city in the northern German state of Schleswig-Holstein, with a population of 246,243 (2021).
Kiel lies approximately north of Hamburg. Due to its geographic location in the southeast of the Jutland pe ...
as far as ''Elbgaustraße''.
HVV and a line numbering system
In 1965, the German Railway, along with two local transport companies, founded theHamburger Verkehrsverbund
The Hamburger Verkehrsverbund (HVV) ( en, "Hamburg Transport Association") is a transport association coordinating public transport in and around Hamburg, Germany. Its main objectives are to provide a unified fare system, requiring only a sing ...
, a common tariff system for U-Bahn and bus lines. The S-Bahn joined in December 1966. From January 1967, the S-Bahn lines were designated ''S1''−''S6'' (see '' Network''). Line designations with a leading letter "S" have since been adopted for other S-Bahn systems in the German-speaking world. Analogically, U-Bahn lines got the leading letter "U".
Network extension after 1967
 Extensions were made in 1967 on separate tracks from Elbgaustraße to Pinneberg, and in 1969 on existing mainline tracks from Bergedorf to Aumühle.
To ease the strain on the central Verbindungsbahn ("connection railway"), a second main connection was constructed, the City S-Bahn, which traverses the city centre in a tunnel. The first section was opened in 1975 between Hauptbahnhof and Landungsbrücken, the extension to Altona in 1979 and was completed in 1981 with the connection above ground to ''Diebsteich''. 1983 saw the opening of the line via Wilhelmsburg to ''Harburg Rathaus'', a long stretch of which runs along the existing mainline. Through Hammerbrook the trains run on a concrete
Extensions were made in 1967 on separate tracks from Elbgaustraße to Pinneberg, and in 1969 on existing mainline tracks from Bergedorf to Aumühle.
To ease the strain on the central Verbindungsbahn ("connection railway"), a second main connection was constructed, the City S-Bahn, which traverses the city centre in a tunnel. The first section was opened in 1975 between Hauptbahnhof and Landungsbrücken, the extension to Altona in 1979 and was completed in 1981 with the connection above ground to ''Diebsteich''. 1983 saw the opening of the line via Wilhelmsburg to ''Harburg Rathaus'', a long stretch of which runs along the existing mainline. Through Hammerbrook the trains run on a concrete viaduct
A viaduct is a specific type of bridge that consists of a series of arches, piers or columns supporting a long elevated railway or road. Typically a viaduct connects two points of roughly equal elevation, allowing direct overpass across a wide va ...
and in a tunnel under the centre of Harburg Harburg may refer to:
Places in Germany
* Harburg (district), Lower Saxony
* Harburg, Bavaria
* Harburg, Hamburg, a borough of Hamburg
** Harburg (quarter), the former Hanoveran city of Harburg upon Elbe, now a quarter of Hamburg
* Harburg-Wilhe ...
. The line was extended in 1984 along the Niederelbebahn to Neugraben
[] is a Boroughs and quarters of Hamburg, quarter of Hamburg, Germany, belongs to the borough Harburg, Hamburg, Harburg. The quarter consists of the old settlements ''Neugraben'' and ''Fischbek'', and the more recently constructed area ''Neuwieden ...
.
The line to Bergedorf was placed on separate tracks due to increased traffic on the main line during the 1990s as a result of German reunification. For the same reason, S-Bahn service between Bergedorf and Aumühle was suspended in 1994. The section to Reinbek was reopened in 1997; completion to Aumühle was delayed until 2002 due to court challenges from local residents. In 1999, Allermöhe station (between Mittlerer Landweg and Nettelnburg) opened in the new housing development of Neuallermöhe-West.
Since December 2007, the S3 has served stations between Neugraben and Stade.
The groundbreaking for a 3.3 km long line from Ohlsdorf to the airport took place in 1991, and again in 2001; the line was opened on 11 December 2008 and has been fully operational since 12 December 2008. Northbound S1 trains split at Ohlsdorf, the front section to the airport, the rear section continues to Poppenbüttel.
Operating company
The S-Bahn is operated by ''S-Bahn Hamburg GmbH'', a subsidiary ofDeutsche Bahn AG
The (; abbreviated as DB or DB AG) is the national railway company of Germany. Headquartered in the Bahntower in Berlin, it is a joint-stock company ( AG). The Federal Republic of Germany is its single shareholder.
describes itself as the se ...
. The company is answerable to DB Regio Nord and was formed in 1997.
The S-Bahn is represented in German cities with a logo consisting of a white "S" in a green circle. In Hamburg the same logo with a red background was used for a few years before November 2007.
The company currently employs approximately 1200 personnel in the driving, maintenance, train departure and resource management divisions. Another 300 employees are responsible for security and cleaning, through subsidiaries.
Lines
trunk
Trunk may refer to:
Biology
* Trunk (anatomy), synonym for torso
* Trunk (botany), a tree's central superstructure
* Trunk of corpus callosum, in neuroanatomy
* Elephant trunk, the proboscis of an elephant
Computing
* Trunk (software), in rev ...
routes crossing the city in an east-west direction – the northern '' Hamburg-Altona link line'' and the southern '' City S-Bahn'' – and six connecting routes (two in the western part of the city and four in the eastern part). The trunk routes connect at Altona and Hauptbahnhof. 113.2 km are separated from other rail services, 31.9 km are shared with regional and cargo traffic. About 12.5 km is in tunnel, 7.9 km are single track.
There are four main lines (S1, S21, S3, S31) and two additional lines during peak hours (S11, S2). Lines with single-digit numbers use the "City-S-Bahn" via ''Jungfernstieg'', with two-digit numbers the ''Verbindungsbahn'' via Dammtor.
Until 2002, some Regionalbahn services were given S-Bahn numbers. Locomotive-hauled service between Hauptbahnhof and Ahrensburg was S4 (now RB 81); between Altona and Elmshorn was S5 (now RE 6 and RB 71); and, before the extension of electric services to Aumühle in 1969, the service between Bergedorf and Friedrichsruh was S6 (now RB 11 and RE 1). S3 was used for Regionalbahn services between Hauptbahnhof and Maschen
Maschen is a village in the municipality of Seevetal in Harburg district in the German state of Lower Saxony. It lies south of Hamburg on the northern edge of the Lüneburg Heath and within the commuter zone of the city of Hamburg. Maschen Mar ...
and Neugraben
[] is a Boroughs and quarters of Hamburg, quarter of Hamburg, Germany, belongs to the borough Harburg, Hamburg, Harburg. The quarter consists of the old settlements ''Neugraben'' and ''Fischbek'', and the more recently constructed area ''Neuwieden ...
(now RB 31 and RE 5) until the opening of the Harburg S-Bahn in 1983/1984.
(Stations with names bold in the following table offer a turning option)
Projected extensions
Plans, currently shelved, would have the S-Bahn network dramatically increased. S-Bahn trains would go as far as Kaltenkirchen (the private AKN Eisenbahn currently connects to Kaltenkirchen from Eidelstedt).S4 Hamburg - Bad Oldesloe
An expansion plan which is in proposal, is the opening (or reopening) of a line S4. Plans for this have been around since the 1960s. Whilst planning the City S-Bahn and network extensions of the 1960s, the German railway thought of building an S-Bahn line S4. This line will Altona in a north westerly direction towards Itzehoe via Elmshorn, being an Express line until Pinneberg. To the east of the city, the new line should have travelled with the current S1 and S11 to Hasselbrook and from there further to the northeast direction via Wandsbek to Ahrensburg along the existing regional train line. Only the eastern part of the line from Hauptbahnhof was implemented, as a regional railway line, which was designated a S-Bahn line, since the HVV did not offer travel with regional railways at the time, but wanted its fare system to be valid on the line. Since September 2000, a popular initiative in Stormarn has been working for the improvement of the S4, today the RB 81. The initiative is currently basing their arguments on a feasibility study which was ordered by S-Bahn Hamburg GmbH in the year 2002, and in principle dusted off the plans from the 1960s. According to the study, the extension involves upgrading the line to proper S-Bahn standards, served by EMUs and the addition of extra stations. The first step would be the improvement of the line as far as Ahrensburg, with a further intended step being the continuation to Bad Oldesloe. Dual-system trains would be necessary for the new line like those used on the extension to Stade. A third rail would be built as far as Ahrensburg, from where the trains would use the existing tracks with overhead lines. As of November 2019, those plans are already approved, with the construction of the line scheduled for 2020.Route and Stations
The route will be removed from the existing network at the '' Hasselbrook '' S and regional train stop and along the Lübeck – Hamburg route via Rahlstedt to Ahrensburg and Bad Oldesloe run. The route corresponds to the course of the regional train line RB81, which between 1966 and 2002 was already tariffed as an S-Bahn to '' Ahrensburg '' and operated under the name S4, but served by locomotive-hauled push-pull trains. For the expansion of the line, a double-track S-Bahn line will be created between '' Hasselbrook '' and '' Ahrensburg '', and a single-track S-Bahn line to '' Gartenholz '', then the S-Bahn trains will switch to the long-distance network and cross over this '' Bad Oldesloe ''. The new line has a length of around 20 km, the total length of the route between '' Hasselbrook '' and Bad Oldesloe is 35.9 km. The route is planning divided into the four sections `` Hasselbrook - Luetkensallee '', `` Luetkensallee - state border Hamburg / Schleswig-Holstein '', `` state border - garden wood '' and `` garden wood - Bad Oldesloe ''. The first three are also the sections that have been or will be individually plan approval. No separate approval procedure is required for the fourth section, as no construction work is planned for it. In the Hamburg area, the four new stops '' Wandsbek Rathaus '', '' Bovestraße '', '' Holstenhofweg '' and '' Am Pulverhof '' are being built, the existing regional train station '' Wandsbek '' will be replaced by '' Wandsbek Rathaus '' and '' Bovestrasse '' replaced. In Schleswig-Holstein, the establishment of an additional stopping point near the existing U-Bahn station ''Ahrensburg West'' is planned. The platforms of the existing stations will be adjusted in height and length for S-Bahn operations; In '' Tonndorf '', '' Ahrensburg '', '' Kupfermühle '' and '' Bad Oldesloe '' the existing systems can be raised to the height of 96 cm customary in the S-Bahn network, in '' Rahlstedt '', '' Gartenholz '' and '' Bargteheide '' this requires a completely new building. In the first step, all platforms will be built with a length of at least 140 m, a later expansion to serve the route with long trains was taken into account in the planning. Furthermore, the existing level crossings with other types of traffic along the Route eliminated. For nature conservation reasons, complex structures are sometimes required, such as a wide-span new bridge in the nature reserve ''Stellmoor-Ahrensburger Tunneltal'', which in the context of the planning process leads to delays and More costs resulted.Rolling stock
 The S-Bahn uses three-car
The S-Bahn uses three-car electrical multiple units
An electric multiple unit or EMU is a multiple-unit train consisting of self-propelled carriages using electricity as the motive power. An EMU requires no separate locomotive, as electric traction motors are incorporated within one or a number ...
(EMUs), 447 vehicles of the following types:
* Type 470
Type may refer to:
Science and technology Computing
* Typing, producing text via a keyboard, typewriter, etc.
* Data type, collection of values used for computations.
* File type
* TYPE (DOS command), a command to display contents of a file.
* ...
, built from 1959 until 1970, in service until 2002 (central carriage of type 870)
* Type 471, built from 1939 until 1958, in service until 2001 (central carriage of type 871)
* Type 472, built from 1974 until 1984, in service until 2022 (central carriage of type 473)
* Type 474, built from 1996 (central carriage of type 874)
* Type 490, built from 2017
Single three-carriage trains are designated ''short trains''. Units can be combined to form a ''full train'' with six carriages or a ''long train'' with nine carriages.
Until 2001, the S-Bahn was one of very few suburban railway systems to offer two classes of service. A quieter and more comfortable first class was available for a 50% supplement.
Only type 474 and type 490 trains are in regular service. The last remaining type 470 and type 471 trains were removed from service in 2002 and 2001 respectively and the 472 trains in 2022. The type 474 trains primarily serve lines S1, S11, S3 and S31, type 490 lines S2, S21 and S31.
With the extension of the S-Bahn to Stade, new dual-system trains have been deployed. These are identical to the type 474 units but with a pantograph on the central carriage to collect 15 kV alternate current from overhead lines.
With the introduction of type 474, the colour scheme of ivory and teal was replaced by a colour called "Traffic Red" ( RAL 3020). External advertising covering the entire bodies of trains was abandoned at this time.
The implementation of a consistent corporate design led to type 472 trains being updated with the new colour scheme. This has left the Berlin S-Bahn as the only German S-Bahn train types with an individual design.
Type 474 trains were initially in the same colour scheme as the type DT4 trains of the Hamburg U-Bahn (white, grey, red). This early experiment was quickly given up.
In 2013, 60 trains are ordered from Bombardier for 327 million euros. The trains are being delivered since 2016. These trains were at first, and to a lesser extent still are, notorious for their sensitive doors, making them more prone to delays.
There are three preserved trains, number 170 082 known as a 'museum train' and numbers 470 128 with 471 082 known as 'traditional trains'. These trains are used for different events throughout the year and in particular in the lead up to Christmas.
Stations
 The S-Bahn has 68 stations, of which ten are fully underground. These are the five stations along the City-S-Bahn (''Jungfernstieg'', ''Stadthausbrücke'', ''Landungsbrücken'', ''Reeperbahn'' and ''Königstraße''), the S-Bahn area of ''Altona'' station, the three stations in the centre of Harburg (''Harburg'', ''Harburg Rathaus'' and '' Heimfeld'') and at Hamburg Airport. At the Hauptbahnhof, the westbound platforms are also in tunnel.
Most stations consist of a single
The S-Bahn has 68 stations, of which ten are fully underground. These are the five stations along the City-S-Bahn (''Jungfernstieg'', ''Stadthausbrücke'', ''Landungsbrücken'', ''Reeperbahn'' and ''Königstraße''), the S-Bahn area of ''Altona'' station, the three stations in the centre of Harburg (''Harburg'', ''Harburg Rathaus'' and '' Heimfeld'') and at Hamburg Airport. At the Hauptbahnhof, the westbound platforms are also in tunnel.
Most stations consist of a single island platform
An island platform (also center platform, centre platform) is a station layout arrangement where a single platform is positioned between two tracks within a railway station, tram stop or transitway interchange. Island platforms are popular ...
. At the interchange stations ''Hauptbahnhof'' and ''Altona'' there are two island platforms, one for trains to the city centre and one for the other direction. At ''Neugraben'' and ''Pinneberg'' termini the two S-Bahn tracks are between a side platform
A side platform (also known as a marginal platform or a single-face platform) is a railway platform, platform positioned to the side of one or more railway tracks or guideways at a railway station, tram stop, or bus rapid transit, transitway. ...
and an island platform, on the other side of which regional rail trains stop. Side platforms are at the triple-track stations at ''Bergedorf'', ''Berliner Tor (lower level)'', ''Blankenese'' and ''Harburg Rathaus'', the twin-track station at ''Billwerder-Moorfleet'' and at the only single-track station, ''Iserbrook''.
All stations have electronic passenger information systems showing information about the line, destination, route, length and stopping position of the next train, missed connections and temporary disturbances to service.
Some stations, for example ''Landungsbrücken'' and ''Harburg Rathaus'', are designed as civilian shelters. The heavy protective entrance doors are the only sign of this dual use.
Service time and intervals
Trains run daily from about 04:30 to 01:00. There is an all-night service within the Hamburg section on the nights before Saturdays, Sundays, and public holidays in Germany. The base frequency for lines S1, S21, S3 and S31 during the day is 10 minutes; before 06:00, after 23:00 and during weekend night service, the frequency is 20 minutes. Multiple lines running on the same tracks, mainly through the city centre but also along the routes served by the S2/S21 and the S3/S31, have shorter intervals. Peak-time lines S2 and S11 decrease intervals in the morning and afternoon.See also
*List of Hamburg S-Bahn stations
The following is the list of the 68 stations of the Hamburg S-Bahn transit system. The Hamburg S-Bahn is operated by S-Bahn Hamburg GmbH (S-Bahn Hamburg plc) for the Hamburger Verkehrsverbund, the company coordinating public transport in Hamburg, ...
* Hamburg U-Bahn
* AKN Eisenbahn
* List of metro systems
This list of metro systems includes electrified rapid transit train systems worldwide. In some parts of the world, metro systems are referred to as subways, U-Bahn or undergrounds. , 205 cities in 61 countries have a metro system.
The Lond ...
References
Literature
* Erich Staisch: ''Die Hamburger S-Bahn. Chronik eines modernen Verkehrsmittels.'', Hamburg 1984, (German) * Erich Staisch (Hrsg.): ''Die Hamburger S-Bahn. Geschichte und Zukunft.'', Hamburg 1996, (German) * Wolfgang Pischek, Jan Borchers, Martin Heimann: ''Die Hamburger S-Bahn. Mit Gleichstrom durch die Hansestadt.'', Munich 2002, (German) * Michael Braun: "Hamburg lernt von Berlin. Punktsieg für Gleichstrom", in: ''LOK MAGAZIN'' Nr. 259, Munich 2003, p. 68–77, (German)External links
*''Die Hamburger S-Bahn'' by Martin Heimann
* ttp://www.kaemena360.net/FS/DB/ET474Hamburg1 Interactive Panorama of the inside of an S-Bahn Trainset ET 474
Interactive Panorama of new Airport Station
Homepage of the Historische S-Bahn Hamburg e.V.
{{coord missing, Hamburg S-Bahn 15 kV AC railway electrification Deutsche Bahn S-Bahn in Germany