|
Hamburg-Altstadt
Altstadt (, literally: "Old town"), more precisely Hamburg-Altstadt – as not to be mistaken with Hamburg-Altona-Altstadt – is one of the inner-city districts of the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg, Germany. History The area of today's Altstadt had a minor Bronze Age settlement dating from the 9th or 8th century BC. An Ingaevonian settlement at this location was known by the name " Treva" – a strategic trading node on amber routes during Iron Age and Late Antiquity. In the 8th century CE, Saxon merchants established what was to become the nucleus of Hamburg: the " Hammaburg", then a refuge fort located at today's Domplatz, the site of the former cathedral. , |
Kontorhaus District
The Kontorhaus District is the southeastern part of Altstadt, Hamburg, between Steinstraße, Meßberg, Klosterwall and Brandstwiete. The streetscape is characterised by large office buildings in the style of Brick Expressionism of the early 20th century. Since 5 July 2015, parts of the Kontorhaus district and the adjacent Speicherstadt district have been UNESCO World Heritage Sites. Historical background Since the 17th century, the area has been densely built-up; the result was a so-called ''Gängeviertel'' (''"corridor quarter"'') with many narrow alleys. The density of the buildings increased even more when there was a housing shortage after the Hamburg fire in 1842. In 1892, a cholera epidemic broke out and the poor hygienic conditions in the neighbourhood caused the disease to spread dramatically – it was then decided to redevelop the area. As a result, many inhabitants were resettled. Fritz Schumacher, who had been Director of Construction and Head of Building ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chilehaus
The Chilehaus (, "Chile House") is a ten-story office building in Hamburg, Germany. It is located in the Kontorhaus District. It is an exceptional example of the 1920s Brick Expressionism style of architecture. This large angular building is located on a site of approximately , spanning the Fischertwiete Street in Hamburg. It was designed by the German architect Fritz Höger and finished in 1924. As part of Kontorhaus District, it was inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2015. Design The Chilehaus building is famed for its top, which is reminiscent of a ship's prow, and the facades, which meet at a very sharp angle at the corner of the ''Pumpen-'' and ''Niedernstrasse''. The best view of the building is from the east. Because of the accentuated vertical elements and the recessed upper stories, as well as the curved facade on the Pumpen street, the building has, despite its enormous size, a touch of lightness. The building has a reinforced concrete structure and has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamburg-Mitte
Hamburg-Mitte (Hamburg Central) is one of the seven boroughs of Hamburg, Germany, covering most of the city's urban center. The quarters of Hamburg-Altstadt and Neustadt cover much of the city's historic core. In 2020 the population was 301,231. History In 1937 several settlements (e.g. Finkenwerder), villages and rural areas were passed into Hamburg enforced by the Greater Hamburg Act. On 1 March 2008 due to a law of Hamburg, the quarter Wilhelmsburg was transferred from the borough Harburg. The neighborhood HafenCity was formed from parts of the quarters Klostertor, Altstadt and Rothenburgsort. The other part of Klostertor was transferred to Hammerbrook. From small parts of the borough Hamburg-Mitte (And Altona and Eimsbüttel) the neighborhood Sternschanze was created as a quarter in the borough Altona. Geography The borough severs Hamburg from the east to the west. In 2006, according to the statistical office of Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein, Hamburg-Mitte has a tot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boroughs And Quarters Of Hamburg
The city of Hamburg in Germany is made up of seven boroughs (German: ''Bezirke'', also known as ''districts'' or ''administrative districts'') and subdivided into 104 quarters (German: ''Stadtteile''). Most of the quarters were former independent settlements. The areal organisation is regulated by the constitution of Hamburg and several laws. The subdivision into boroughs and quarters was last modified in March 2008. Borough overview History The first official administrative divisions of Hamburg were the parishes of four churches, the St. Peter's, St. Catherine's, St. James's and St. Nicholas's Churches (or their preceding buildings). On 24 February, 1529 a compromise of 132 articles between the senate of Hamburg and the citizens (German: ''Langer Rezeß'') established a council of citizens. The twelve councilmen were called ''Oberalte'' (eldermen) and were the three oldest deacons of each parish. Each parish was given a confirmed border. 1871 In 1871 at the declaration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; nds, label=Hamburg German, Low Saxon, Hamborg ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg (german: Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg; nds, label=Low Saxon, Friee un Hansestadt Hamborg),. is the List of cities in Germany by population, second-largest city in Germany after Berlin, as well as the overall List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 7th largest city and largest non-capital city in the European Union with a population of over 1.85 million. Hamburg's urban area has a population of around 2.5 million and is part of the Hamburg Metropolitan Region, which has a population of over 5.1 million people in total. The city lies on the River Elbe and two of its tributaries, the River Alster and the Bille (Elbe), River Bille. One of Germany's 16 States of Germany, federated states, Hamburg is surrounded by Schleswig-Holstein to the north and Lower Saxony to the south. The official name reflects History of Hamburg, Hamburg's history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Town
A market town is a Human settlement, settlement most common in Europe that obtained by custom or royal charter, in the Middle Ages, a market right, which allowed it to host a regular marketplace, market; this distinguished it from a village or city. In Britain, small rural towns with a hinterland of villages are still commonly called market towns, as sometimes reflected in their names (e.g. Downham Market, Market Rasen, or Market Drayton). Modern markets are often in special halls, but this is a recent development, and the rise of permanent retail establishments has reduced the need for periodic markets. Historically the markets were open-air, held in what is usually called (regardless of its actual shape) the market square (or "Market Place" etc), and centred on a market cross (mercat cross in Scotland). They were and are typically open one or two days a week. History The primary purpose of a market town is the provision of goods and services to the surrounding locality. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first Emperor of the Romans from 800. Charlemagne succeeded in uniting the majority of western and central Europe and was the first recognized emperor to rule from western Europe after the fall of the Western Roman Empire around three centuries earlier. The expanded Frankish state that Charlemagne founded was the Carolingian Empire. He was canonized by Antipope Paschal III—an act later treated as invalid—and he is now regarded by some as beatified (which is a step on the path to sainthood) in the Catholic Church. Charlemagne was the eldest son of Pepin the Short and Bertrada of Laon. He was born before their canonical marriage. He became king of the Franks in 768 following his father's death, and was initially co-ruler with his brother ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
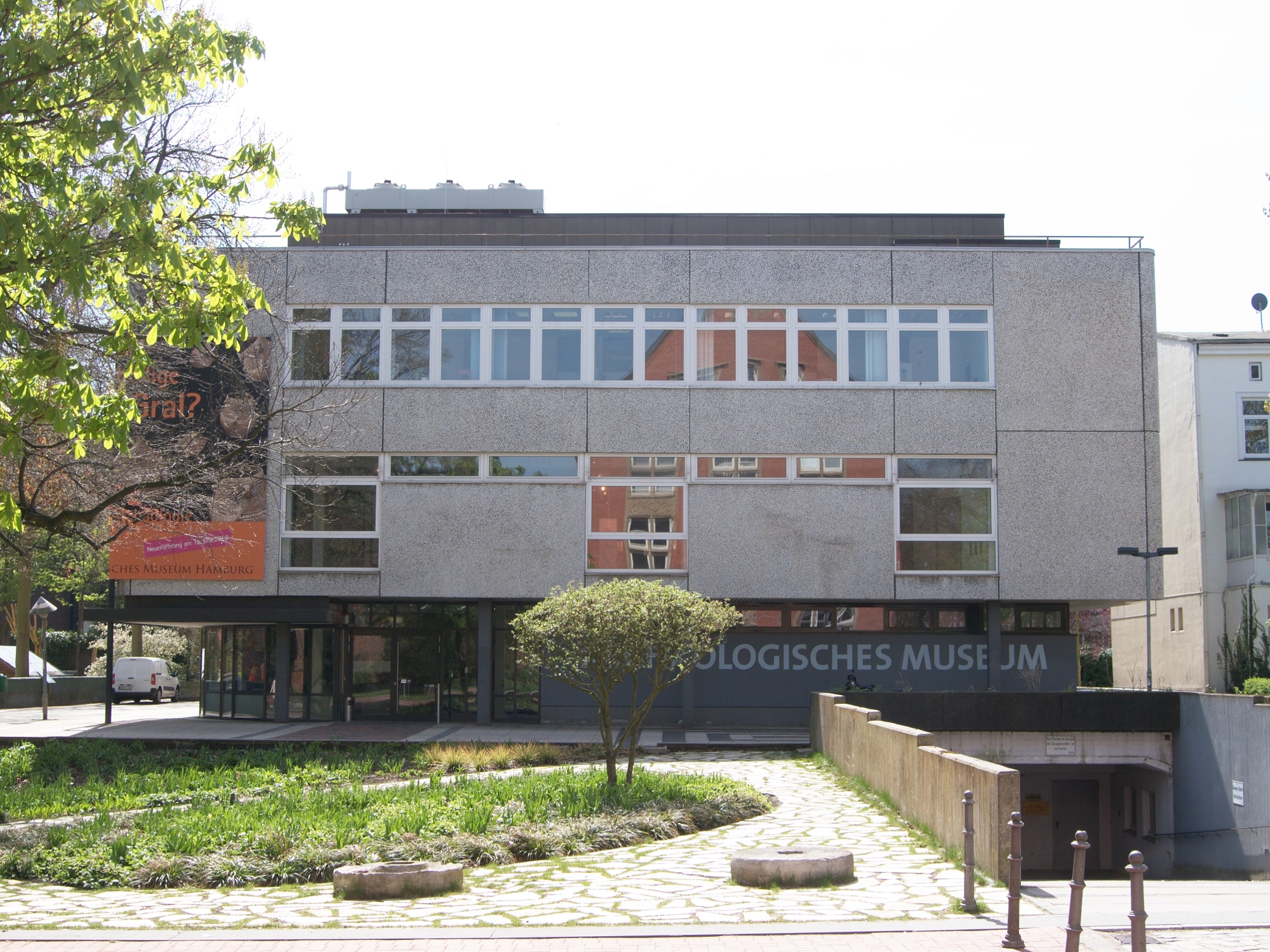
Archäologisches Museum Hamburg
The (Hamburg Archaeological Museum; formerly the ') is an archaeological museum in the Harburg borough of Hamburg, Germany. It houses the archaeological finds of the city of Hamburg and the neighbouring counties to the south of the city. It focuses on northern German prehistory and early history as well as the history of the former city of Harburg. The museum is also home to the cultural heritage landmarks commission of the city of Hamburg and the adjacent district of Harburg in Lower-Saxony and thus supervises all archaeological undertakings in the region. The museum has two major exhibition spaces. The future City Museum of Harburg, temporary exhibitions, the library, offices and small storage facilities are located in the main building, which is shared with the Harburger Theater at . The permanent archaeological exhibition and education facilities are located nearby, at . In addition, the Museum maintains as external branches the exhibition area of the 12th-century (Bishop's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
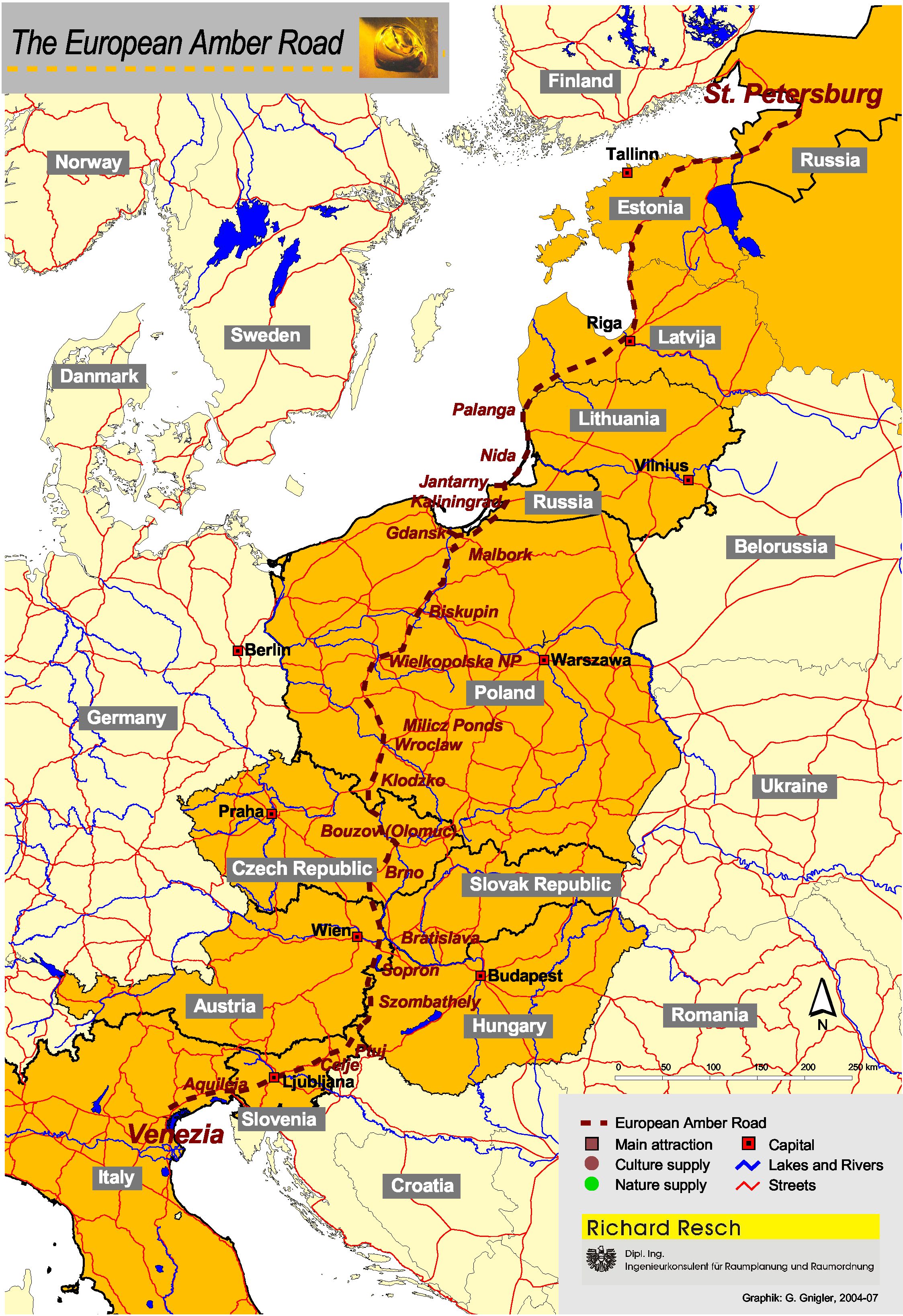
Amber Road
The Amber Road was an ancient trade route for the transfer of amber from coastal areas of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea to the Mediterranean Sea. Prehistoric trade routes between Northern and Southern Europe were defined by the amber trade. As an important commodity, sometimes dubbed "the gold of the north", amber was transported from the North Sea and Baltic Sea coasts overland by way of the Vistula and Dnieper rivers to Italy, Greece, the Black Sea, Syria and Egypt over a period of thousands of years. Antiquity The oldest trade in amber started from Sicily. The Sicilian amber trade was directed to Greece, North Africa and Spain. Sicilian amber was also discovered in Mycenae by the archaeologist Heinrich Schliemann, and it appeared in sites in southern Spain and Portugal. Its distribution is similar to that of ivory, so it is possible that amber from Sicily reached the Iberian Peninsula through contacts with North Africa. After a decline in the consumption and trade of amb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refuge Castle
A refuge castleCreighton, Oliver (2015). ''Early European Castles''. Bloomsbury. or refuge fort (german: Fliehburg, also ''Fluchtburg'', ''Volksburg'', ''Bauernburg'' or ''Vryburg'') is a castle-like defensive location, usually surrounded by ramparts, that is not permanently occupied but acts as a temporary retreat for the local population when threatened by war or attack. In former times such sites were also described as giant castles (German: ''Hünenburgen'') because their origin was ascribed to giants. History In Europe a multitude of large protohistoric sites surrounded by earthworks has been uncovered by archaeological excavations, many over 100 metres in diameter, that are understood to be refuge castles. Amongst ancient historical references to them are the refuge castles of the Gauls described by Caesar as ''oppida'', although they could also be permanent settlements. Similar ringwork (''Ringwall'') systems were built by the various Germanic and Slavic tribes, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hammaburg
Hamburg was founded in the 9th century as a mission settlement to convert the Saxons. Since the Middle Ages, it has been an important trading center in Europe. The convenient location of the port and its independence as a city and state for centuries strengthened this position. The city was a member of the medieval Hanseatic trading league and a free imperial city of the Holy Roman Empire. From 1815 until 1866 Hamburg was an independent and sovereign state of the German Confederation, then the North German Confederation (1866–71), the German Empire (1871–1918) and during the period of the Weimar Republic (1918–33). In Nazi Germany Hamburg was a city-state and a ''Gau'' from 1934 until 1945. After the Second World War Hamburg was in the British Zone of Occupation and became a state in the western part of Germany in the Federal Republic of Germany (Since 1949). Etymology According to Ptolemy, the settlement's first name was Treva. A fortress there was name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Hamburg
Hamburg was founded in the 9th century as a mission settlement to convert the Saxons. Since the Middle Ages, it has been an important trading center in Europe. The convenient location of the port and its independence as a city and state for centuries strengthened this position. The city was a member of the medieval Hanseatic trading league and a free imperial city of the Holy Roman Empire. From 1815 until 1866 Hamburg was an independent and sovereign state of the German Confederation, then the North German Confederation (1866–71), the German Empire (1871–1918) and during the period of the Weimar Republic (1918–33). In Nazi Germany Hamburg was a city-state and a ''Gau'' from 1934 until 1945. After the Second World War Hamburg was in the British Zone of Occupation and became a state in the western part of Germany in the Federal Republic of Germany (Since 1949). Etymology According to Ptolemy, the settlement's first name was Treva. A fortress the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altona_Hamburg_Harburg.png)