|
Halikarnassos
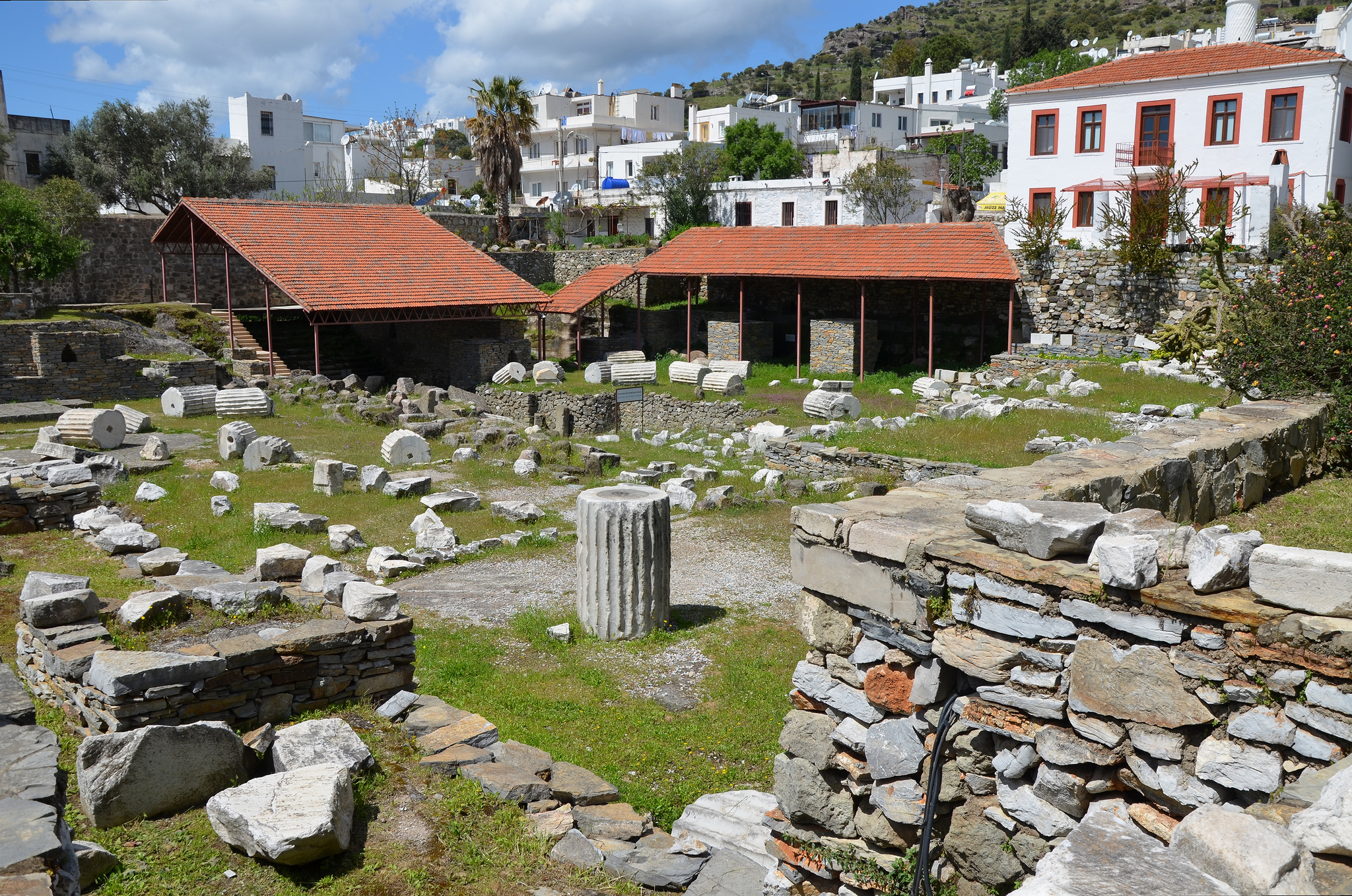
Halicarnassus (; grc, Ἁλικαρνᾱσσός ''Halikarnāssós'' or ''Alikarnāssós''; tr, Halikarnas; Carian: 𐊠𐊣𐊫𐊰 𐊴𐊠𐊥𐊵𐊫𐊰 ''alos k̂arnos'') was an ancient Greek city in Caria, in Anatolia. It was located in southwest Caria, on an advantageous site on the Gulf of Gökova, which is now in Bodrum, Turkey.} The city was famous for the Mausoleum of Halicarnassus, also known simply as the Tomb of Mausolus, whose name provided the origin of the word " mausoleum". The mausoleum, built from 353 to 350 BC, ranked as one of the seven wonders of the ancient world. Halicarnassus' history was special on two interlinked issues. Halicarnassus retained a monarchical system of government at a time when most other Greek city states had long since rid themselves of their kings. And secondly, while their Ionian neighbours rebelled against Persian rule, Halicarnassus remained loyal to the Persians and formed part of the Persian Empire until Alexander the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mausoleum At Halicarnassus
The Mausoleum at Halicarnassus or Tomb of Mausolus ( grc, ОњО±П…ПѓП‰О»Оµбї–ОїОЅ П„бї†П‚ бј‰О»О№ОєО±ПЃОЅО±ПѓПѓОїбї¦; tr, Halikarnas Mozolesi) was a tomb built between 353 and 350 BC in Halicarnassus (present Bodrum, Turkey) for Mausolus, an Anatolian from Caria and a satrap in the Achaemenid Empire, and his sister-wife Artemisia II of Caria. The structure was designed by the Greek architects Satyros and Pythius of Priene. Its elevated tomb structure is derived from the tombs of neighbouring Lycia, a territory Mausolus had invaded and annexed c. 360 BC, such as the Nereid Monument. The Mausoleum was approximately in height, and the four sides were adorned with sculptural reliefs, each created by one of four Greek sculptors: Leochares, Bryaxis, Scopas of Paros, and Timotheus. The mausoleum was considered to be such an aesthetic triumph that Antipater of Sidon identified it as one of his Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. It was destroyed by successive earthquakes from the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mausoleum Of Halicarnassus
The Mausoleum at Halicarnassus or Tomb of Mausolus ( grc, ОњО±П…ПѓП‰О»Оµбї–ОїОЅ П„бї†П‚ бј‰О»О№ОєО±ПЃОЅО±ПѓПѓОїбї¦; tr, Halikarnas Mozolesi) was a tomb built between 353 and 350 BC in Halicarnassus (present Bodrum, Turkey) for Mausolus, an Anatolian from Caria and a satrap in the Achaemenid Empire, and his sister-wife Artemisia II of Caria. The structure was designed by the Greek architects Satyros and Pythius of Priene. Its elevated tomb structure is derived from the tombs of neighbouring Lycia, a territory Mausolus had invaded and annexed c. 360 BC, such as the Nereid Monument. The Mausoleum was approximately in height, and the four sides were adorned with sculptural reliefs, each created by one of four Greek sculptors: Leochares, Bryaxis, Scopas of Paros, and Timotheus. The mausoleum was considered to be such an aesthetic triumph that Antipater of Sidon identified it as one of his Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. It was destroyed by successive earthquakes from the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mausolus
Mausolus ( grc, ОњО±ПЌПѓП‰О»ОїП‚ or , xcr, ђЉЄрђЉ ђЉІрђЉёрђЉ«рђЉ¦ ''MauЕ›oО»'') was a ruler of Caria (377–353 BCE) and a satrap of the Achaemenid Empire. He enjoyed the status of king or dynast by virtue of the powerful position created by his father Hecatomnus ( xcr, рђЉґрђЉрђЉЄрђЉірђЉ« ), who had succeeded the assassinated Persian Satrap Tissaphernes as the first satrap of Caria and founded the hereditary Hecatomnid dynasty. Alongside Caria, Mausolus also ruled Lycia and parts of Ionia and the Dodecanese islands. He is best known for the monumental shrine, the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus, erected and named for him by order of his widow (who was also his sister) Artemisia. Name Mausolus' name is only known directly in Greek ( grc, ОњО±ПЌПѓП‰О»ОїП‚ or ). It is clearly of Carian origin, though, and would have been written as *рђЉЄрђЉ рђЉІрђЉёрђЉ«рђЉ¦ (''*MauЕ›oО»'') or similar. This is a compound name perhaps meaning "much blessed". The first part, ''*Ma-'', may mean "much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
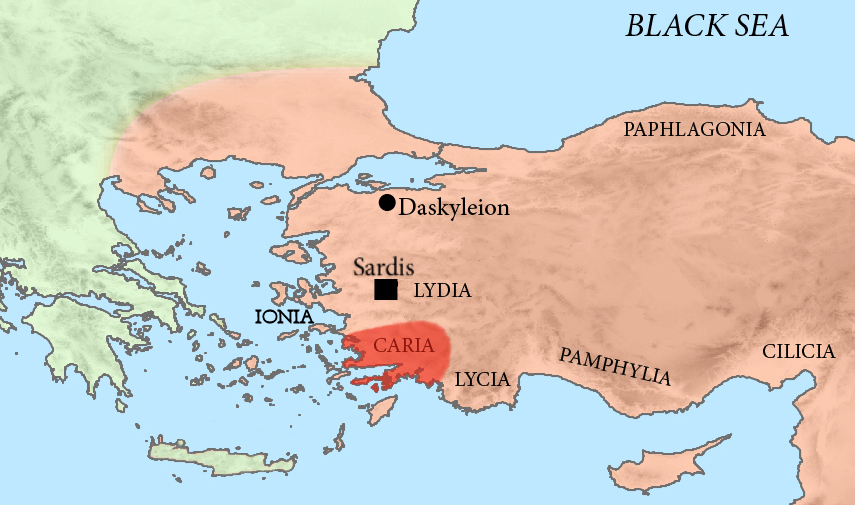
Caria
Caria (; from Greek: ОљО±ПЃОЇО±, ''Karia''; tr, Karya) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid-Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Ionians, Ionian and Dorians, Dorian Greeks colonized the west of it and joined the Carian population in forming Greek-dominated states there. Carians were described by Herodotus as being of Minoan civilization, Minoan descent,''The Histories'', Book I Section 171. while he reports that the Carians themselves maintained that they were Anatolian mainlanders intensely engaged in seafaring and were akin to the Mysians and the Lydians. The Carians spoke Carian language, Carian, a native Anatolian language closely related to Luwian language, Luwian. Also closely associated with the Carians were the Leleges, which could be an earlier name for Carians. Municipalities of Caria Cramer's detailed catalog of Carian towns in classical Greece is based entirely on ancient sources. The multiple names of towns and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorians
The Dorians (; el, О”П‰ПЃО№Оµбї–П‚, ''DЕЌrieГ®s'', singular , ''DЕЌrieГєs'') were one of the four major ethnic groups into which the Hellenes (or Greeks) of Classical Greece divided themselves (along with the Aeolians, Achaeans, and Ionians). They are almost always referred to as just "the Dorians", as they are called in the earliest literary mention of them in the ''Odyssey'', where they already can be found inhabiting the island of Crete. They were diverse in way of life and social organization, varying from the populous trade center of the city of Corinth, known for its ornate style in art and architecture, to the isolationist, military state of Sparta. And yet, all Hellenes knew which localities were Dorian, and which were not. Dorian states at war could more likely, but not always, count on the assistance of other Dorian states. Dorians were distinguished by the Doric Greek dialect and by characteristic social and historical traditions. In the 5th century BC, Dorians an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leleges
The Leleges (; grc-gre, О›ОО»ОµОіОµП‚) were an aboriginal people of the Aegean region, before the Greeks arrived. They were distinct from another pre-Hellenic people of the region, the Pelasgians. The exact areas to which they were native are uncertain, since they were apparently pre-literate and the only references to them are in ancient Greek sources. These references are casual and (it is alleged) sometimes fictitious. Likewise, little is known about the language of the ''Leleges''. Many Greek authors link the Leleges to the Carians of south-west Anatolia. Homer names the Leleges among the Trojan allies alongside the Carians, Pelasgians, Paeonians and Gaucones. Etymology It is thought that the name ''Leleges'' is an exonym, in a long-extinct language, rather than an endonym (or autonym). That is, during the Bronze Age the word ''lulahi'' apparently meaning "strangers" was used in the Luwian language and in other Anatolian languages. For example, in a Hittite cuneiform insc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knights Of Rhodes
The Order of Knights of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem ( la, Ordo Fratrum Hospitalis Sancti Ioannis Hierosolymitani), commonly known as the Knights Hospitaller (), was a medieval and early modern Catholic military order. It was headquartered in the Kingdom of Jerusalem until 1291, on the island of Rhodes from 1310 until 1522, in Malta from 1530 until 1798 and at Saint Petersburg from 1799 until 1801. Today several organizations continue the Hospitaller tradition, specifically the mutually recognized orders of St. John, which are the Sovereign Military Order of Malta, the Most Venerable Order of the Hospital of Saint John, theВ Bailiwick of Brandenburg of the Chivalric Order of Saint John, theВ Order of Saint John in the Netherlands, and theВ Order of Saint John in Sweden. The Hospitallers arose in the early 12th century, during the time of the Cluniac movement (a Benedictine Reform movement). Early in the 11th century, merchants from Amalfi founded a hospital in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmacis (Caria)
Salmacis or Salmakis ( grc, ОЈО±О»ОјО±ОєОЇП‚) was a town of ancient Caria. While the famed fountain appears in Strabo, the town is only mentioned in inscriptions. It was a ''polis'' (city-state) and a member of the Delian League The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Pl .... Its site is unlocated. References Populated places in ancient Caria Former populated places in Turkey Greek city-states Members of the Delian League Lost ancient cities and towns {{AncientCaria-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-Greek Substrate
The Pre-Greek substrate (or Pre-Greek substratum) consists of the unknown pre-Indo-European language(s) spoken in prehistoric Greece before the coming of the Proto-Greek language in the Greek peninsula during the Bronze Age. It is possible that Greek acquired approximately one thousand words and proper names from such a language or group of languages, because some of its vocabulary cannot be satisfactorily explained as deriving from Proto-Greek and a Proto-Indo-European reconstruction is almost certainly impossible for such terms. Introduction Linguistic situation Based upon toponymic and lexical evidence, it is generally assumed that one or several languages were once spoken in both the Greek peninsula and western Asia Minor before Mycenaean Greek and the attested Anatolian languages ( Hittite and Luwian) became predominant in the region. Various explanations for this phenomenon have been given by scholars. One substrate language, whose influence is observable on Ancient Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carians
The Carians (; grc, Ољбѕ¶ПЃОµП‚, ''Kares'', plural of , ''Kar'') were the ancient inhabitants of Caria in southwest Anatolia. Historical accounts Karkisa It is not clear when the Carians enter into history. The definition is dependent on corresponding Caria and the Carians to the "Karkiya" or "Karkisa" mentioned in the Hittites, Hittite records. Bronze Age Karkisa are first mentioned as having aided the Assuwa League against the Hittite King Tudhaliya I. Later in 1323 BC, King Arnuwandas II was able to write to Karkiya for them to provide asylum for the deposed Manapa-Tarhunta of "the land of the Seha River", one of the principalities within the Luwians, Luwian Arzawa complex in western Anatolia. This they did, allowing Manapa-Tarhunta to take back his kingdom. In 1274 BC, Karkisa are also mentioned among those who fought on the History of the Hittites, Hittite Empire side against the Egyptians in the Battle of Kadesh. Taken as a whole, Hittite records seem to point at a Luw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Halicarnassus
The siege of Halicarnassus was fought between Alexander the Great and the Achaemenid Persian Empire in 334 BC. Alexander, who had no navy, was constantly being threatened by the Persian navy. It continuously attempted to provoke an engagement with Alexander, who would not oblige them. Eventually, the Persian fleet sailed to Halicarnassus, in order to establish a new defense. Ada of Caria, the former queen of Halicarnassus, had been driven from her throne by her younger brother Pixodarus of Caria. When Pixodarus died, Persian King Darius had appointed Orontobates satrap of Caria, which included Halicarnassus in its jurisdiction. On the arrival of Alexander in 334 BC, Ada, who was in possession of the fortress of Alinda, surrendered the fortress to him. Orontobates and Memnon of Rhodes entrenched themselves in Halicarnassus. Alexander had sent spies to meet with dissidents inside the city, who had promised to open the gates and allow Alexander to enter. When his spies arrived, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parnassus
Mount Parnassus (; el, О О±ПЃОЅО±ПѓПѓПЊП‚, ''ParnassГіs'') is a mountain range of central Greece that is and historically has been especially valuable to the Greek nation and the earlier Greek city-states for many reasons. In peace, it offers scenic views of the countryside, being a major international recreational site, with views of montane landscapes. Economically its rolling foothills and valleys host extensive groves of olive, a cash crop marketed world-wide since prehistory. The mountain is also the location of historical, archaeological, and other cultural sites, such as Delphi perched on the southern slopes of the mountain in a rift valley north of the Gulf of Corinth. Parnassus is laced with trails for hiking in the three warm seasons. In the winter the entire range is open to skiing, especially from the resorts of Arachova. Its melting snows are a source of municipal water to the surrounding communities. The mountain is composed of limestone, but also contains bauxit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |