|
Haidar Ali
Hyder Ali ( حیدر علی, ''Haidarālī''; 1720 – 7 December 1782) was the Sultan and ''de facto'' ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore in southern India. Born as Hyder Ali, he distinguished himself as a soldier, eventually drawing the attention of Mysore's rulers. Rising to the post of Dalavayi ( commander-in-chief) to Krishnaraja Wodeyar II, he came to dominate the titular monarch and the Mysore government. He became the de facto ruler of Mysore as Sarvadhikari (Chief Minister) by 1761. During intermittent conflicts against the East India Company during the First and Second Anglo–Mysore Wars, Hyder Ali was the military leader. Though illiterate, Hyder Ali concluded an alliance with the French, and used the services of French workmen in raising his artillery and arsenal. His rule of Mysore was characterised by frequent warfare with his neighbours and rebellion within his territories. This was not unusual for the time as much of the Indian subcontinent was then in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krishnaraja Wodeyar II
Krishnaraja Wadiyar II (1728 – 25 April 1766Hayavadana Rao, Conjeeveram. History of Mysore (1399-1799 A.D.): 1704-1766. India: Superintendent of the Government Press, 1946.), was the eighteenth Maharaja of Mysore, maharaja of the Kingdom of Mysore from 1734 to 1766. He ruled as monarch during his entire rule, first under the dalavayi, ''dalvoys'', and then, for the last five years, under Hyder Ali. Life On 8 October 1731, Krishnaraja Wadiyar II was adopted, like his predecessor, by Maharani Devajammani and Maharaja Dodda Krishnaraja Wodeyar I, Krishnaraja Wodeyar I, under the title ''Chikka Krishnaraja Wodeyar''. He was crowned at Mysore, on 15 June 1735. He reigned under the control of dalvoy Devarajaiya Urs, who was in charge of Mysore rule from 1724 to 1746. After the decline of the Devarajaiya's power and eventual death, Hyder Ali, another dalvoy, came to be considered the ''de facto'' supreme ruler of Mysore from 1761 until his death in 1782. He was a titular King. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sepoy
''Sepoy'' () was the Persian-derived designation originally given to a professional Indian infantryman, traditionally armed with a musket, in the armies of the Mughal Empire. In the 18th century, the French East India Company and its other European counterparts employed locally recruited soldiers within India, mainly consisting of infantry designated as "sepoys". The largest sepoy force, trained along European lines, served the British East India Company The term "sepoy" continues in use in the modern Indian, Pakistan and Nepalese armies, where it denotes the rank of private. Etymology In Persian (Aspa) means horse and Ispahai is also the word for cavalrymen. The term ''sepoy'' is derived from the Persian word () meaning the traditional "infantry soldier" in the Mughal Empire. In the Ottoman Empire the term was used to refer to cavalrymen. History The sepoys of the Mughal Empire were infantrymen usually armed with a musket and a talwar, although they some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalavayi
Dalavayi also spelled Dalwai, Dalavay and Dalvoy was meaning title of Chief in Commander or Commander in the military in South Indian dynasty. In Kingdom of Mysore, Hyder Ali and his eldest son Tipu Sultan were appointed to this position. The word Dalavayi is a Prakrit or vernacular form of the Sanskrit word (which literally means: leader or chief of the team or wing). In western India, especially Maharashtra and Goa the descendants of Dalavayis still use the title ''Dalvi'' (Devanagari Devanagari ( ; , , Sanskrit pronunciation: ), also called Nagari (),Kathleen Kuiper (2010), The Culture of India, New York: The Rosen Publishing Group, , page 83 is a left-to-right abugida (a type of segmental writing system), based on the ...: दळवी) as surname, which is modern form of the Prakrit word Dalavayi.{{cite book, last1=Bloch, first1=J., title=Formation of the Marathi Language, date=1970, publisher=Motilal Banarasidas Publishers, isbn=9788120823228, page=161 Referenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern India
South India, also known as Dakshina Bharata or Peninsular India, consists of the peninsular southern part of India. It encompasses the States and union territories of India, Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, as well as the union territory, union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry, comprising 19.31% of India's area () and 20% of India's population. Covering the southern part of the peninsular Deccan Plateau, South India is bounded by the Bay of Bengal in the east, the Arabian Sea in the west and the Indian Ocean in the south. The geography of the region is diverse with two mountain ranges – the Western Ghats, Western and Eastern Ghats – bordering the plateau heartland. The Godavari River, Godavari, Krishna River, Krishna, Kaveri, Tungabhadra River, Tungabhadra, Periyar River, Periyar, Bharathappuzha, Pamba River, Pamba, Thamirabarani River, Thamirabarani, Palar River, Palar, and Vaigai River, Va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
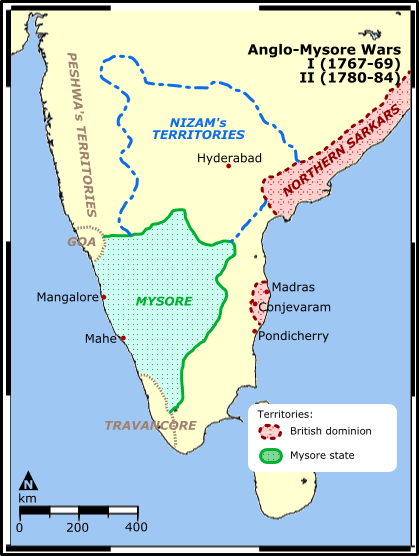
Second Anglo-Mysore War
The Second Anglo-Mysore War was a conflict between the Kingdom of Mysore and the British East India Company from 1780 to 1784. At the time, Mysore was a key French ally in India, and the conflict between Britain against the French and Dutch in the American Revolutionary War sparked Anglo-Mysorean hostilities in India. The great majority of soldiers on the company side were raised, trained, paid and commanded by the company, not the British government. However, the company's operations were also bolstered by Crown troops sent from Britain, and by troops from Hanover, which was also ruled by Britain's King George III. Following the British seizure of the French port of Mahé in 1779, Mysorean ruler Hyder Ali opened hostilities against the British in 1780, with significant success in early campaigns. As the war progressed, the British recovered some territorial losses. Both France and Britain sent troops and naval squadrons from Europe to assist in the war effort, which widened la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Anglo-Mysore War
The First Anglo-Mysore War (1766–1769) was a conflict in India between the Sultanate of Mysore and the East India Company. The war was instigated in part by the machinations of Asaf Jah II, the Nizam of Hyderabad, who sought to divert the company's resources from attempts to gain control over the Northern Circars. Background The eighteenth century was a period of great turmoil in Indian subcontinent. Although the century opened with much of the subcontinent under the control of the Mughal Empire, the death in 1707 of Emperor Aurangzeb resulted in the fracturing of the empire, and a struggle among viceroys and other local rulers for territory. In the 1740s and 1750s French and British colonial companies became more active in these local conflicts. By the Third Carnatic War (1757–1763) the British had gained somewhat solid footholds at Bombay, Madras, and Calcutta, and had also marginalised, although not eliminated, the influence of other colonial powers. Their eastern hol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mysorean Invasion Of Kerala
The Mysorean invasion of Malabar (1766 –1792) was the military invasion of the Malabar region of Kerala, including the territories of the Zamorin of Calicut, by the then-''de facto'' ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore, Hyder Ali. After the invasion, the Kingdom of Cochin to the south of Malabar became a tributary state of Mysore. The invasion of Malabar was motivated by a desire for access to the ports bordering the Indian Ocean. The Mysore invasion gave the East India Company the opportunity to tighten their grip on the ancient feudal principalities of Malabar and convert Travancore into only a protected ally. www.kerala.gov.in History By the late 18th century, the small kingdoms had been absorbed or subordinated by three large states: Travancore, Calicut (ruled by Zamorins), and the Kingdom of Cochin. The Kingdom of Mysore, ruled nominally by the Wodeyar family, rose to prominence in India after the decline of the Vijayanagara Empire and again after the Mughal Empire. In 1761 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mysore's Campaigns Against The States Of Malabar (1757)
The Mysore's campaigns against the states of Malabar was the result of the Calicut's attack on Palghat in 1756–1757. This comprised the attacks of the Zamorin of Calicut on the Kingdom of Palakkad, situated east to Calicut. It was a continuation of the attacks on the Kingdom of Valluvanad, the traditional rival of Calicut. In the one sided Valluvanad attacks the Zamorin had captured much of the land from Eranad to Nedunganad. So, this time Zamorin marched against Palakkad and easily occupied Nadvattom which tore the Kingdom of Palakkad right through the middle.Logan, William (2006). ''Malabar Manual'', Mathrubhumi Books, Calicut. . Komi Achan, the King of Palakkad, requested the faujdar of Dindigul, Hyder Ali to help him. Zamorin was fighting a war against Raja of Cochin at that time. Hyder Ali sent a massive force under his brother-in-law Makhdoom Ali and soon the allied forces swept through the Zamorin's territory and reached the sea coast. By these attacks, Hyder Ali als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754–1763), the Carnatic Wars and the Anglo-Spanish War (1762–1763). The opposing alliances were led by Great Britain and France respectively, both seeking to establish global pre-eminence at the expense of the other. Along with Spain, France fought Britain both in Europe and overseas with land-based armies and naval forces, while Britain's ally Prussia sought territorial expansion in Europe and consolidation of its power. Long-standing colonial rivalries pitting Britain against France and Spain in North America and the West Indies were fought on a grand scale with consequential results. Prussia sought greater influence in the German states, while Austria wanted to regain Silesia, captured by Prussia in the previous war, and to contain Pruss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnatic Wars
The Carnatic Wars were a series of military conflicts in the middle of the 18th century in India's coastal Carnatic region, a dependency of Hyderabad State, India. Three Carnatic Wars were fought between 1744 and 1763. The conflicts involved numerous nominally independent rulers and their vassals, struggles for succession and territory; and included a diplomatic and military struggle between the French East India Company and the British East India Company. They were mainly fought within the territories of Mughal India with the assistance of various fragmented polities loyal to the "Great Moghul". As a result of these military contests, the British East India Company established its dominance among the European trading companies within India. The French company was pushed to a corner and was confined primarily to Pondichéry. The East India Company's dominance eventually led to control by the British Company over most of India and eventually to the establishment of the British ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_from_Court_Game_of_Geography_MET_DP862917.jpg)