Southern India on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
South India, also known as Dakshina Bharata or Peninsular India, consists of the peninsular southern part of  The majority of the people in South India speak at least one of the four major
The majority of the people in South India speak at least one of the four major
 South India is also known as Peninsular India, and has been known by several other names too. The term "Deccan", referring to the area covered by the
South India is also known as Peninsular India, and has been known by several other names too. The term "Deccan", referring to the area covered by the



 After the
After the

 South India is a
South India is a  The Deccan plateau is the elevated region bound by the mountain ranges. The plateau rises to in the north and to more than in the south, forming a raised triangle within the downward-pointing triangle of the
The Deccan plateau is the elevated region bound by the mountain ranges. The plateau rises to in the north and to more than in the south, forming a raised triangle within the downward-pointing triangle of the
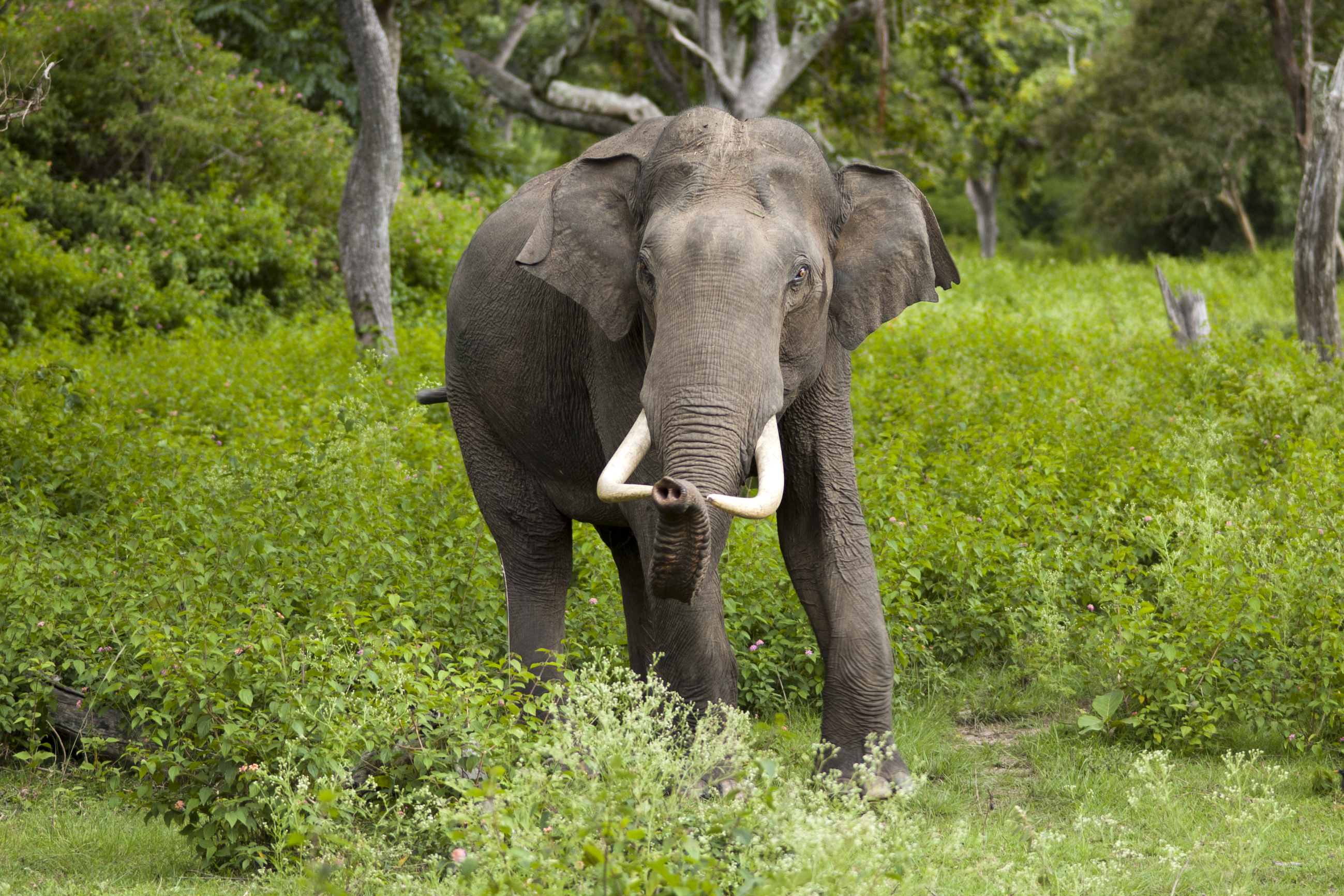 There is a wide diversity of plants and animals in South India, resulting from its varied climates and geography.
There is a wide diversity of plants and animals in South India, resulting from its varied climates and geography.


 Restricted international airport
Restricted international airport

 The Kerala backwaters are a network of interconnected canals, rivers, lakes, and inlets, a labyrinthine system formed by more than 900 km of waterways. In the midst of this landscape, there are a number of towns and cities, which serve as the starting and endpoints of transportation services and backwater cruises. Vizhinjam International Seaport also called The Port of Trivandrum is a mother port under construction on the Arabian Sea at Vizhinjam in Trivandrum, India. Once completed, it is estimated that this port will handle over 40% of India's transshipments, thereby reducing the country's reliance on ports at Dubai, Colombo, and Singapore.
The Eastern Naval Command and Southern Naval Command of the Indian Navy are headquartered at Visakhapatnam Port, Visakhapatnam and Cochin Port, Kochi, respectively. In the region, the Indian Navy has its major operational bases at Visakhapatnam, Chennai, Kochi, Karwar, and Kavaratti.
The Kerala backwaters are a network of interconnected canals, rivers, lakes, and inlets, a labyrinthine system formed by more than 900 km of waterways. In the midst of this landscape, there are a number of towns and cities, which serve as the starting and endpoints of transportation services and backwater cruises. Vizhinjam International Seaport also called The Port of Trivandrum is a mother port under construction on the Arabian Sea at Vizhinjam in Trivandrum, India. Once completed, it is estimated that this port will handle over 40% of India's transshipments, thereby reducing the country's reliance on ports at Dubai, Colombo, and Singapore.
The Eastern Naval Command and Southern Naval Command of the Indian Navy are headquartered at Visakhapatnam Port, Visakhapatnam and Cochin Port, Kochi, respectively. In the region, the Indian Navy has its major operational bases at Visakhapatnam, Chennai, Kochi, Karwar, and Kavaratti.
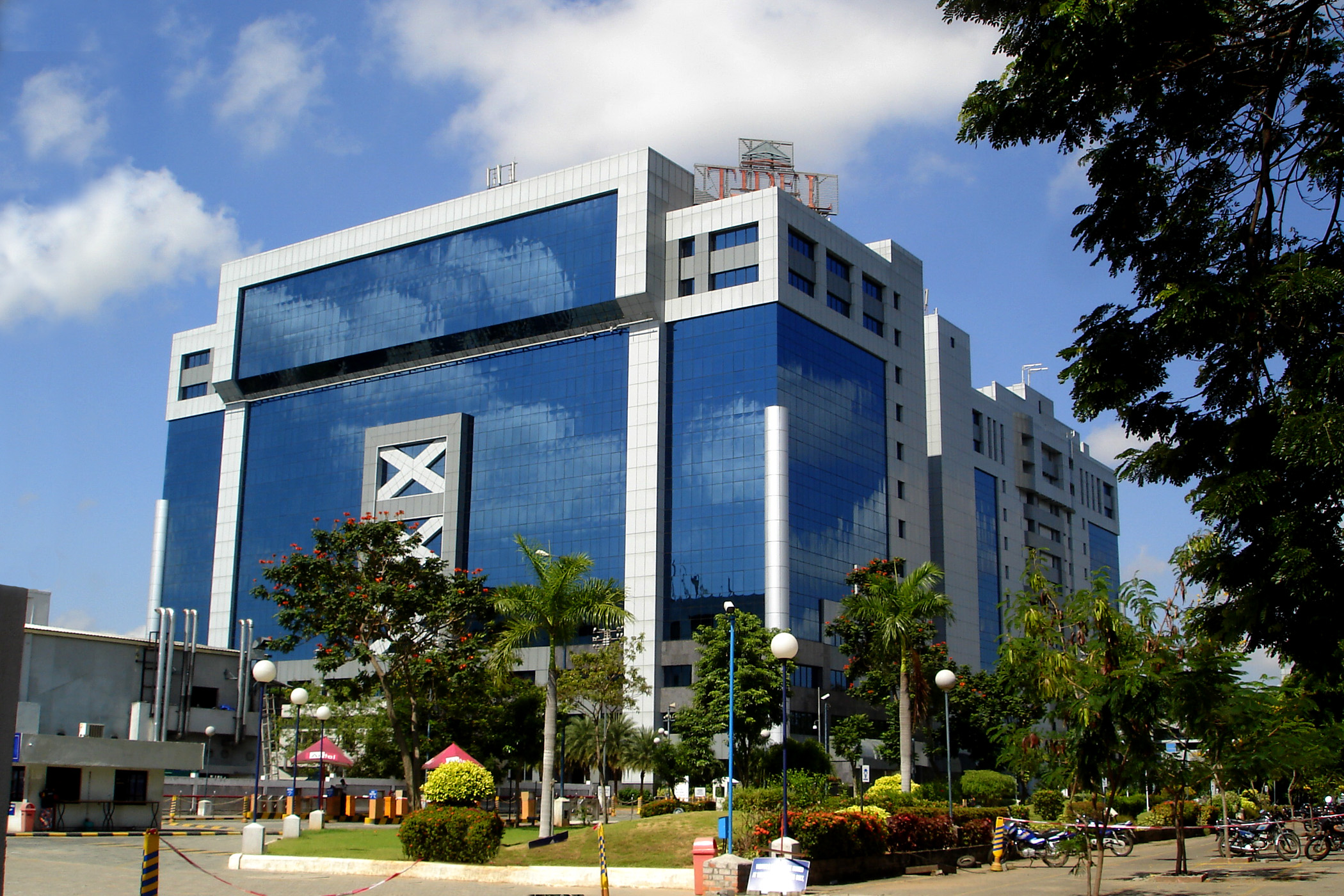

 After independence, the economy of South India conformed to a socialism, socialist framework, with strict governmental control over private sector participation, foreign trade, and foreign direct investment. From 1960 to 1990, the South Indian economies experienced mixed economic growth. In the 1960s, Kerala achieved above-average growth while Andhra Pradesh's economy declined. Kerala experienced an economic decline in the 1970s while the economies of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Andhra Pradesh consistently exceeded national average growth rates, due to Economic reforms in India, reform-oriented economic policies. As of March 2015, there are 109 operational Special Economic Zones in South India, which is about 60% of the country's total. As of 2019–20, the total gross domestic product of the region is ₹67 trillion (US$946 billion).
After independence, the economy of South India conformed to a socialism, socialist framework, with strict governmental control over private sector participation, foreign trade, and foreign direct investment. From 1960 to 1990, the South Indian economies experienced mixed economic growth. In the 1960s, Kerala achieved above-average growth while Andhra Pradesh's economy declined. Kerala experienced an economic decline in the 1970s while the economies of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Andhra Pradesh consistently exceeded national average growth rates, due to Economic reforms in India, reform-oriented economic policies. As of March 2015, there are 109 operational Special Economic Zones in South India, which is about 60% of the country's total. As of 2019–20, the total gross domestic product of the region is ₹67 trillion (US$946 billion).  Over 48% of South India's population is engaged in agriculture, which is largely dependent on seasonal monsoons. Frequent droughts have left farmers debt-ridden, forcing them to sell their livestock and sometimes to commit suicide. Some of the main crops cultivated in South India include Paddy field, paddy, sorghum, pearl millet, pulses, Finger millet, ragi, sugarcane, mangoes, chile pepper, chilli, and cotton. The staple food is rice; the delta regions of Godavari,
Over 48% of South India's population is engaged in agriculture, which is largely dependent on seasonal monsoons. Frequent droughts have left farmers debt-ridden, forcing them to sell their livestock and sometimes to commit suicide. Some of the main crops cultivated in South India include Paddy field, paddy, sorghum, pearl millet, pulses, Finger millet, ragi, sugarcane, mangoes, chile pepper, chilli, and cotton. The staple food is rice; the delta regions of Godavari,
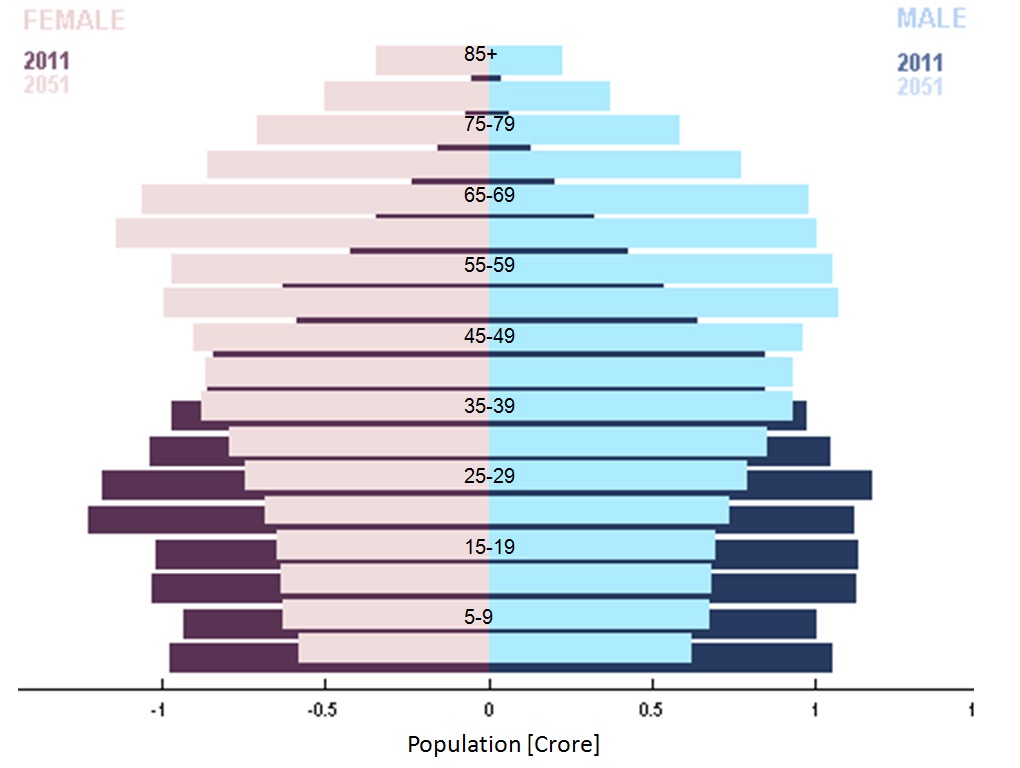 As per the 2011 census of India, the estimated population of South India was 252 million, around one fifth of the total population of the country. The region's total fertility rate (TFR) was less than the Sub-replacement fertility, population replacement level of 2.1 for all states, with Kerala and Tamil Nadu having the lowest TFRs in India at 1.7. As a result, from 1981 to 2011 the proportion of the population of South India to India's total population has declined. The population density of the region is approximately 463 per square kilometer. Scheduled Castes and Tribes form 18% of the population of the region. Agriculture is the major employer in the region, with 47.5% of the population being involved in agrarian activities. About 60% of the population lives in permanent housing structures. 67.8% of South India has access to tap water, with wells and springs being major sources of water supply.
After experiencing fluctuations in the decades immediately after the independence of India, the economies of South Indian states have, over the past three decades, registered growth higher than the national average. While South Indian states have improved in some of the
As per the 2011 census of India, the estimated population of South India was 252 million, around one fifth of the total population of the country. The region's total fertility rate (TFR) was less than the Sub-replacement fertility, population replacement level of 2.1 for all states, with Kerala and Tamil Nadu having the lowest TFRs in India at 1.7. As a result, from 1981 to 2011 the proportion of the population of South India to India's total population has declined. The population density of the region is approximately 463 per square kilometer. Scheduled Castes and Tribes form 18% of the population of the region. Agriculture is the major employer in the region, with 47.5% of the population being involved in agrarian activities. About 60% of the population lives in permanent housing structures. 67.8% of South India has access to tap water, with wells and springs being major sources of water supply.
After experiencing fluctuations in the decades immediately after the independence of India, the economies of South Indian states have, over the past three decades, registered growth higher than the national average. While South Indian states have improved in some of the
 The largest linguistic group in South India is the Dravidian family of languages, of approximately 73 languages. The major languages spoken include
The largest linguistic group in South India is the Dravidian family of languages, of approximately 73 languages. The major languages spoken include
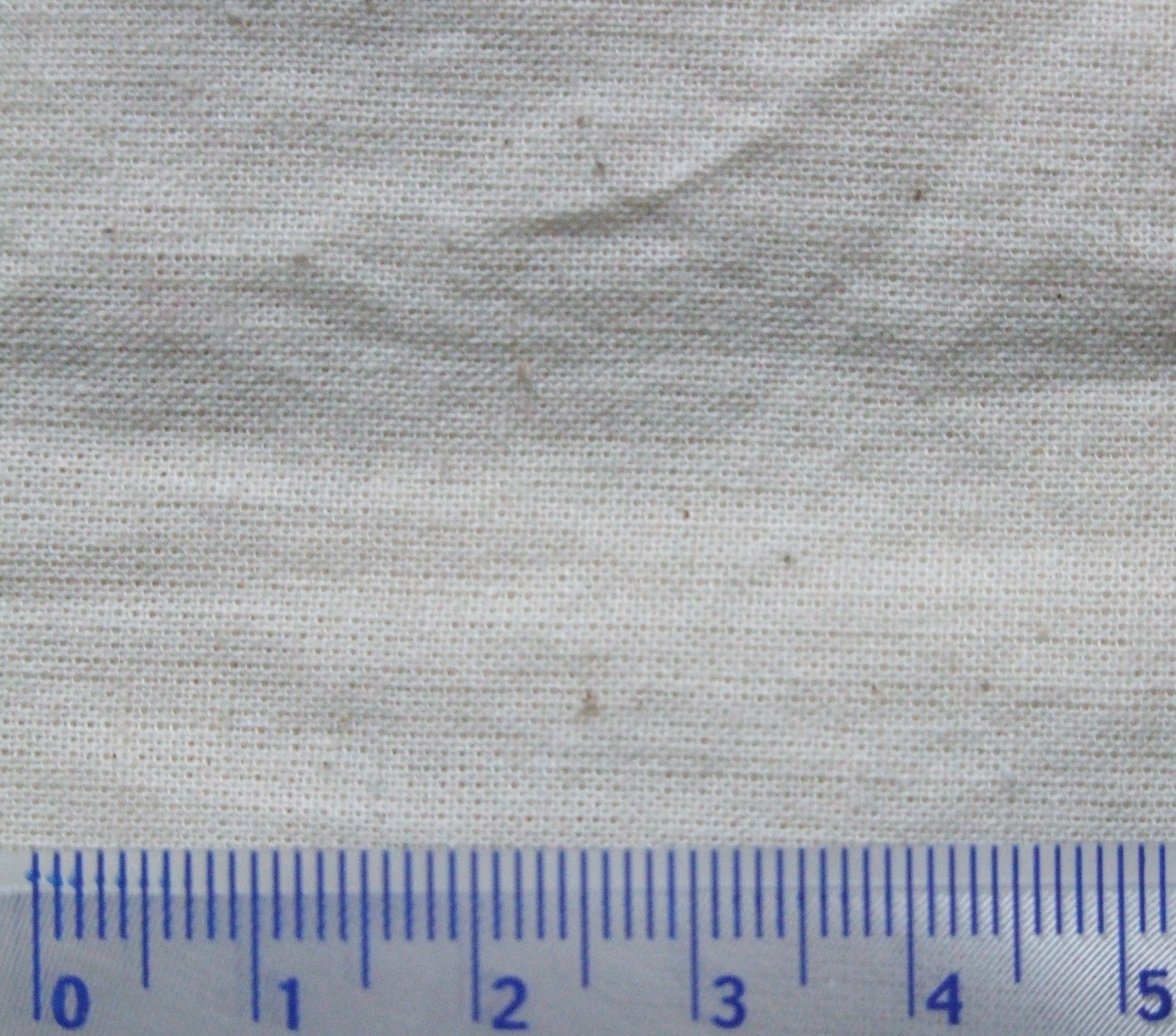 Calico, a plain weave, plain-woven textile made from unbleached, and often not fully processed, cotton, was originated at Kozhikode, Calicut (Kozhikode), from which the name of the textile came, in South India, now
Calico, a plain weave, plain-woven textile made from unbleached, and often not fully processed, cotton, was originated at Kozhikode, Calicut (Kozhikode), from which the name of the textile came, in South India, now
 Rice is the diet staple, while fish is an integral component of coastal South Indian meals. Coconut and spices are used extensively in South Indian cuisine. The region has a rich cuisine involving both traditional non-vegetarian and vegetarian dishes comprising rice, legumes, and lentils. Its distinct aroma and flavour is achieved by the blending of flavourings and spices, including Curry tree, curry leaves, mustard seeds, coriander, ginger, garlic, chili powder, chili, black pepper, pepper, cinnamon, cloves, green cardamom, cumin, nutmeg, coconut, and rosewater.
The traditional way of eating a meal involves being seated on the floor, having the food served on a banana leaf, and using clean fingers of the right hand to take the food into the mouth. After the meal, the fingers are washed; the easily degradable banana leaf is discarded or becomes fodder for cattle. Eating on banana leaves is a custom thousands of years old, imparts a unique flavor to the food, and is considered healthy.
''Idli'', ''Dosa (food), dosa'', ''uthappam'', ''Pesarattu'', ''appam'', ''Pongal (dish), pongal'', and ''paniyaram'' are popular breakfast dishes in Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, and Kerala. Rice is served with ''Sambar (dish), sambar'', ''Rasam (dish), rasam'', and ''poriyal'' for lunch. Telugu cuisine, Andhra cuisine is characterised by Pickling, pickles and spicy curry, curries. Famous dishes are ''Pesarattu'', ''Ulava charu'', ''Bobbatlu'', ''Pootharekulu'', and ''Gongura''. Chettinad cuisine is famous for its non-vegetarian items, and Hyderabadi cuisine is popular for its ''Hyderabadi biryani, biryani''. ''Neer dosa'', ''Chitranna'', ''Ragi mudde'', ''Maddur vada'', ''Mysore pak'', ''Obbattu'', ''Bisi Bele Bath'', ''Mangalore buns'', ''Kesari bat'', ''Akki rotti'' and ''Dharwad pedha'' are famous cuisines of Karnataka. Udupi cuisine, Udupi Cuisine, which originates from Udupi located in the Coastal Kanara region of Karnataka is famous for its vegetarian dishes.
Rice is the diet staple, while fish is an integral component of coastal South Indian meals. Coconut and spices are used extensively in South Indian cuisine. The region has a rich cuisine involving both traditional non-vegetarian and vegetarian dishes comprising rice, legumes, and lentils. Its distinct aroma and flavour is achieved by the blending of flavourings and spices, including Curry tree, curry leaves, mustard seeds, coriander, ginger, garlic, chili powder, chili, black pepper, pepper, cinnamon, cloves, green cardamom, cumin, nutmeg, coconut, and rosewater.
The traditional way of eating a meal involves being seated on the floor, having the food served on a banana leaf, and using clean fingers of the right hand to take the food into the mouth. After the meal, the fingers are washed; the easily degradable banana leaf is discarded or becomes fodder for cattle. Eating on banana leaves is a custom thousands of years old, imparts a unique flavor to the food, and is considered healthy.
''Idli'', ''Dosa (food), dosa'', ''uthappam'', ''Pesarattu'', ''appam'', ''Pongal (dish), pongal'', and ''paniyaram'' are popular breakfast dishes in Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, and Kerala. Rice is served with ''Sambar (dish), sambar'', ''Rasam (dish), rasam'', and ''poriyal'' for lunch. Telugu cuisine, Andhra cuisine is characterised by Pickling, pickles and spicy curry, curries. Famous dishes are ''Pesarattu'', ''Ulava charu'', ''Bobbatlu'', ''Pootharekulu'', and ''Gongura''. Chettinad cuisine is famous for its non-vegetarian items, and Hyderabadi cuisine is popular for its ''Hyderabadi biryani, biryani''. ''Neer dosa'', ''Chitranna'', ''Ragi mudde'', ''Maddur vada'', ''Mysore pak'', ''Obbattu'', ''Bisi Bele Bath'', ''Mangalore buns'', ''Kesari bat'', ''Akki rotti'' and ''Dharwad pedha'' are famous cuisines of Karnataka. Udupi cuisine, Udupi Cuisine, which originates from Udupi located in the Coastal Kanara region of Karnataka is famous for its vegetarian dishes.
 Coconut is native to Southern India and spread to Europe, Arabia, and Persia through the southwestern
Coconut is native to Southern India and spread to Europe, Arabia, and Persia through the southwestern
/ref> with Egyptian and Arab traders being particularly active. The Thalassery cuisine, a style of cuisine originated in the Malabar District, Northern Kerala over centuries, makes use of such spices.
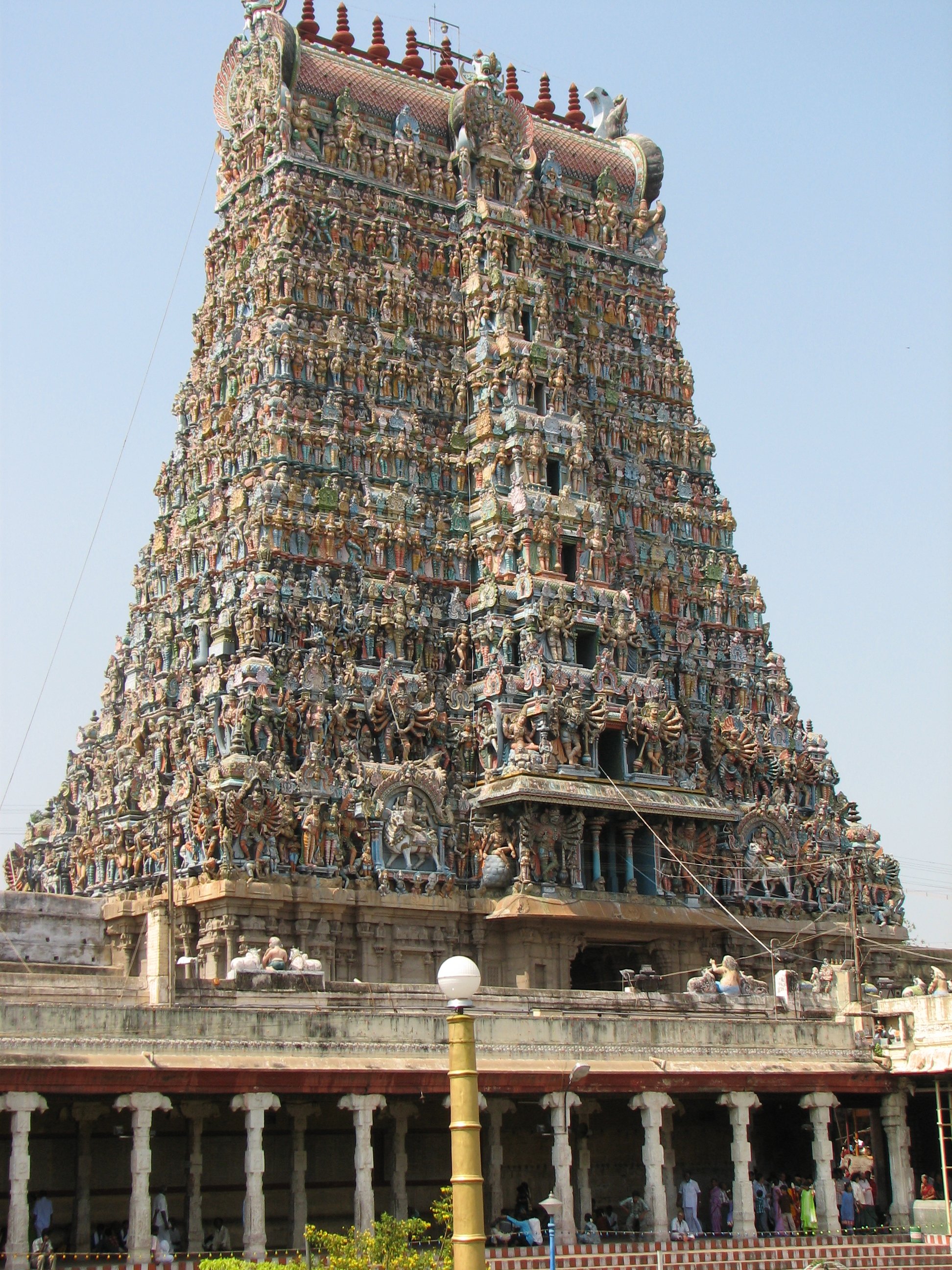 South India has an independent literary tradition dating back over 2500 years. The first known literature of South India is the poetic Sangam literature, which was written in
South India has an independent literary tradition dating back over 2500 years. The first known literature of South India is the poetic Sangam literature, which was written in
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
. It encompasses the Indian states
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, with a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions.
History
Pre-indepen ...
of Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
, Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a state in the southwestern region of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act. Originally known as Mysore State , it was renamed ''Karnat ...
, Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South ...
, Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a States and union territories of India, state in southern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, tenth largest Indian state by area and the List of states and union territories of India ...
, and Telangana
Telangana (; , ) is a States and union territories of India, state in India situated on the south-central stretch of the Indian subcontinent, Indian peninsula on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the List of states and union territories of India b ...
, as well as the union territories of Lakshadweep
Lakshadweep (), also known as Laccadives (), is a union territory of India. It is an archipelago of 36 islands in the Arabian sea, located off the Malabar Coast.
The name ''Lakshadweep'' means "one lakh islands" in Sanskrit, though the Lac ...
and Puducherry Puducherry or Pondicherry may refer to:
* Puducherry (union territory), a union territory of India
** Pondicherry, capital of the union territory of Puducherry
** Puducherry district, a district of the union territory of Puducherry
** Puducherry t ...
, comprising 19.31% of India's area () and 20% of India's population. Covering the southern part of the peninsula
A peninsula (; ) is a landform that extends from a mainland and is surrounded by water on most, but not all of its borders. A peninsula is also sometimes defined as a piece of land bordered by water on three of its sides. Peninsulas exist on all ...
r Deccan Plateau
The large Deccan Plateau in southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bounded by the ...
, South India is bounded by the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line between ...
in the east, the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel ...
in the west and the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by th ...
in the south. The geography of the region is diverse with two mountain ranges – the Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and Eastern Ghats
The Eastern Ghats are a discontinuous range of mountains along India's eastern coast. The Eastern Ghats pass through Odisha, Andhra Pradesh to Tamil Nadu in the south passing some parts of Karnataka as well as Telangana. They are eroded and cut ...
– bordering the plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; ), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides ha ...
heartland. The Godavari
The Godavari ( IAST: ''Godāvarī'' �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga river and drains into the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakesh ...
, Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is one ...
, Kaveri
The Kaveri (also known as Cauvery, the anglicized name) is one of the major Indian rivers flowing through the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. The Kaveri river rises at Talakaveri in the Brahmagiri range in the Western Ghats, Kodagu dis ...
, Tungabhadra, Periyar
Erode Venkatappa Ramasamy (17 September 1879 – 24 December 1973), revered as Periyar or Thanthai Periyar, was an Indian social activist and politician who started the Self-Respect Movement and Dravidar Kazhagam. He is known as the ' ...
, Bharathappuzha
Bharathappuzha ("River of Bhārata"), also known as the Nila or Ponnani River, is a river in India in the state of Kerala. With a length of 209 km, it is the second longest river that flows through Kerala after the Periyar. It flows throu ...
, Pamba, Thamirabarani
The Thamirabarani or Tamraparni or Porunai is a perennial river that originates from the Agastyarkoodam peak of Pothigai hills of the Western Ghats, above Papanasam in the Ambasamudram taluk. It flows through Tirunelveli and Thoothukudi di ...
, Palar
Palar is a river of southern India. It rises in the Nandi Hills in Chikkaballapura district of Karnataka state, and flows in Karnataka, in Andhra Pradesh and in Tamil Nadu before reaching its confluence into the Bay of Bengal at Vayalur ab ...
, and Vaigai
The Vaigai is a river in the Tamil Nadu state of southern India; it passes through the towns of Theni, Dindigul and Madurai. It originates in Varusanadu Hills, the Periyar Plateau of the Western Ghats range, and flows northeast through the ...
rivers are important perennial
A perennial plant or simply perennial is a plant that lives more than two years. The term ('' per-'' + '' -ennial'', "through the years") is often used to differentiate a plant from shorter-lived annuals and biennials. The term is also wide ...
rivers.
Dravidian languages
The Dravidian languages (or sometimes Dravidic) are a family of languages spoken by 250 million people, mainly in southern India, north-east Sri Lanka, and south-west Pakistan. Since the colonial era, there have been small but significant ...
: Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
* Tamils, an ethnic group native to India and some other parts of Asia
**Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka also called ilankai tamils
**Tamil Malaysians, Tamil people native to Malaysia
* Tamil language, nativ ...
, Telugu
Telugu may refer to:
* Telugu language, a major Dravidian language of India
*Telugu people, an ethno-linguistic group of India
* Telugu script, used to write the Telugu language
** Telugu (Unicode block), a block of Telugu characters in Unicode
S ...
, Malayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of 22 scheduled languages of India. Malayalam was des ...
and Kannada
Kannada (; ಕನ್ನಡ, ), originally romanised Canarese, is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by the people of Karnataka in southwestern India, with minorities in all neighbouring states. It has around 47 million native s ...
(all 4 of which are among the 6 Classical Languages of India
Languages spoken in India belong to several language families, the major ones being the Indo-European languages spoken by 78.05% of Indians and the Dravidian languages spoken by 19.64% of Indians, both families together are sometimes known ...
). Some states and union territories also recognize a minority language, such as Deccani Urdu
Deccani (also known as Deccani Urdu and Deccani Hindi). https://knowledgehubadda.blogspot.com/2022/02/blog-post_74.html? m=1 or Dakni, Dakhni, Dakhini, Dakkhani and Dakkani (, ''dekanī'' or , ''dakhanī''), is a variety of Hindustani spoken ...
in Telangana
Telangana (; , ) is a States and union territories of India, state in India situated on the south-central stretch of the Indian subcontinent, Indian peninsula on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the List of states and union territories of India b ...
, and Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
* Tamils, an ethnic group native to India and some other parts of Asia
**Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka also called ilankai tamils
**Tamil Malaysians, Tamil people native to Malaysia
* Tamil language, nativ ...
and French in Puducherry. Besides these languages, English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
is used by both the central and state governments for official communications and is used on all public signboards.
During its history
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the History of writing#Inventions of writing, invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbr ...
, a number of dynastic kingdoms ruled over parts of South India, and the Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent
The Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent mainly took place from the 13th to 17th centuries. Earlier Muslim conquests include the invasions into what is now modern-day Pakistan and the Umayyad campaigns in India in eighth century and res ...
across southern and southeastern
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each se ...
Asia affected the history and culture in those regions. Major dynasties established in South India include the Cheras, Cholas
The Chola dynasty was a Tamil thalassocratic empire of southern India and one of the longest-ruling dynasties in the history of the world. The earliest datable references to the Chola are from inscriptions dated to the 3rd century BCE d ...
, Pandyas, Pallavas
The Pallava dynasty existed from 275 CE to 897 CE, ruling a significant portion of South India, the Deccan, also known as Tondaimandalam. The dynasty rose to prominence after the downfall of the Satavahanas, Satavahana dynasty, with whom they ...
, Satavahanas
The Satavahanas (''Sādavāhana'' or ''Sātavāhana'', International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: ), also referred to as the Andhras in the Puranas, were an ancient Indian dynasty based in the Deccan Plateau, Deccan region. Mos ...
, Chalukyas
The Chalukya dynasty () was a Classical Indian dynasty that ruled large parts of southern and central India between the 6th and the 12th centuries. During this period, they ruled as three related yet individual dynasties. The earliest dynas ...
, Rashtrakutas
Rashtrakuta (IAST: ') (r. 753-982 CE) was a royal Indian dynasty ruling large parts of the Indian subcontinent between the sixth and 10th centuries. The earliest known Rashtrakuta inscription is a 7th-century copper plate grant detailing their ...
, Bahmani
The Bahmani Sultanate, or Deccan, was a Persianate Sunni Muslim Indian Kingdom located in the Deccan region. It was the first independent Muslim kingdom of the Deccan,
, Deccan Sultanates
The Deccan sultanates were five Islamic late-medieval Indian kingdoms—on the Deccan Plateau between the Krishna River and the Vindhya Range—that were ruled by Muslim dynasties: namely Ahmadnagar, Berar, Bidar, Bijapur, and Golconda. Th ...
, Cochin
Kochi (), also known as Cochin ( ) ( the official name until 1996) is a major port city on the Malabar Coast of India bordering the Laccadive Sea, which is a part of the Arabian Sea. It is part of the district of Ernakulam in the state of K ...
, Kakatiyas, Kadambas, Hoysalas
The Hoysala Empire was a Kannadiga power originating from the Indian subcontinent that ruled most of what is now Karnataka between the 10th and the 14th centuries. The capital of the Hoysalas was initially located at Belur, but was later moved ...
, Zamorin
The Samoothiri (Anglicised as Zamorin; Malayalam: , Arabic: ''Sāmuri'', Portuguese: ''Samorim'', Dutch: ''Samorijn'', Chinese: ''Shamitihsi''Ma Huan's Ying-yai Sheng-lan: 'The Overall Survey of the Ocean's Shores' 433 Translated and Edited by ...
, Vijayanagara
Vijayanagara () was the capital city of the historic Vijayanagara Empire. Located on the banks of the Tungabhadra River, it spread over a large area and included the modern era Group of Monuments at Hampi site in Vijayanagara district, Bellary ...
, Maratha
The Marathi people (Marathi: मराठी लोक) or Marathis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are indigenous to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed as a M ...
, Travancore
The Kingdom of Travancore ( /ˈtrævənkɔːr/), also known as the Kingdom of Thiruvithamkoor, was an Indian kingdom from c. 1729 until 1949. It was ruled by the Travancore Royal Family from Padmanabhapuram, and later Thiruvananthapuram. At ...
, Arakkal, and Mysore
Mysore (), officially Mysuru (), is a city in the southern part of the state of Karnataka, India. Mysore city is geographically located between 12° 18′ 26″ north latitude and 76° 38′ 59″ east longitude. It is located at an altitude of ...
. Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, Saint Thomas Christian
The Saint Thomas Christians, also called Syrian Christians of India, ''Marthoma Suriyani Nasrani'', ''Malankara Nasrani'', or ''Nasrani Mappila'', are an ethno-religious community of Indian Christians in the state of Kerala (Malabar region), ...
s, Mappila Muslims
Mappila Muslim, often shortened to Mappila, formerly anglicized as Moplah/Mopla and historically known as Jonaka/Chonaka Mappila or Moors Mopulars/Mouros da Terra and Mouros Malabares, in general, is a member of the Muslim community of same n ...
, and Europeans
Europeans are the focus of European ethnology, the field of anthropology related to the various ethnic groups that reside in the states of Europe. Groups may be defined by common genetic ancestry, common language, or both. Pan and Pfeil (2004) ...
entered India through the southwestern Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is the southwestern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing m ...
of Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South ...
. Parts of South India were colonized under Portuguese India
The State of India ( pt, Estado da Índia), also referred as the Portuguese State of India (''Estado Português da Índia'', EPI) or simply Portuguese India (), was a state of the Portuguese Empire founded six years after the discovery of a se ...
, French India
French India, formally the ( en, French Settlements in India), was a French colony comprising five geographically separated enclaves on the Indian Subcontinent that had initially been factories of the French East India Company. They were ''de ...
and the British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was himsel ...
. The Hyderabad State
Hyderabad State () was a princely state located in the south-central Deccan region of India with its capital at the city of Hyderabad. It is now divided into the present-day state of Telangana, the Kalyana-Karnataka region of Karnataka, and t ...
ruled by the Nizam
The Nizams were the rulers of Hyderabad from the 18th through the 20th century. Nizam of Hyderabad (Niẓām ul-Mulk, also known as Asaf Jah) was the title of the monarch of the Hyderabad State ( divided between the state of Telangana, Mar ...
s was the last princely state of India.
South India witnessed sustained growth in per-capita income and population, structural changes in the economy, an increased pace of technological innovation. After experiencing fluctuations in the decades immediately after Indian independence, the economies of South Indian states have registered a higher-than-national-average growth over the past three decades. South India has the largest gross domestic product compared to other regions in India. The South Indian states lead in some socio-economic
Socioeconomics (also known as social economics) is the social science that studies how economic activity affects and is shaped by social processes. In general it analyzes how modern societies progress, stagnate, or regress because of their local ...
metrics of India. The HDI
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, wh ...
in the southern states is high and the economy has undergone growth at a faster rate than in most northern states. Literacy rates
This is a list of countries by literacy rate.
The global literacy rate for all people aged 15 and above is 86.3%. The global literacy rate for all males is 90.0%, and the rate for all females is 82.7%. The rate varies throughout the world, with ...
in the southern states is higher than the national average, with approximately 81% of the population capable of reading and writing. The fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that would be born to a woman over her lifetime if:
# she were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through her lifetime
# she were t ...
in South India is 1.9, the lowest of all regions in India.
Etymology
 South India is also known as Peninsular India, and has been known by several other names too. The term "Deccan", referring to the area covered by the
South India is also known as Peninsular India, and has been known by several other names too. The term "Deccan", referring to the area covered by the Deccan Plateau
The large Deccan Plateau in southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bounded by the ...
that covers most of peninsular India excluding the coastal areas, is an anglicised form of the Prakrit
The Prakrits (; sa, prākṛta; psu, 𑀧𑀸𑀉𑀤, ; pka, ) are a group of vernacular Middle Indo-Aryan languages that were used in the Indian subcontinent from around the 3rd century BCE to the 8th century CE. The term Prakrit is usu ...
word ''dakkhin'' derived from the Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
word ''dakshina'' meaning south. ''Carnatic'', derived from ''"Karnād"'' or ''"Karunād"'' meaning ''high country'', has also been associated with South India.
History
Historical references
Historical South India has been referred to asDeccan
The large Deccan Plateau in South India, southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bou ...
, a prakrit
The Prakrits (; sa, prākṛta; psu, 𑀧𑀸𑀉𑀤, ; pka, ) are a group of vernacular Middle Indo-Aryan languages that were used in the Indian subcontinent from around the 3rd century BCE to the 8th century CE. The term Prakrit is usu ...
ic derivative of an ancient term 'Dakshin' or Dakshinapatha. The term had geographical as well as the geopolitical meaning and was mentioned as early as Panini (500 BCE).
Ancient and Medieval era

Carbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was dev ...
shows that ash mounds associated with Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
cultures in South India date back to 8000 BCE. Artifacts such as ground stone axes and minor copper objects have been found in the Odisha region. Towards the beginning of 1000 BCE, iron technology spread through the region; however, there does not appear to be a fully developed Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
preceding the Iron Age in South India. The region was in the middle of a trade route that extended from Muziris
Muziris ( grc, Μουζιρίς, Old Malayalam: ''Muciri'' or ''Muciripattanam'' possibly identical with the medieval ''Muyirikode'') was an ancient harbour and an urban centre on the Malabar Coast. Muziris found mention in the ''Periplus of ...
to Arikamedu linking the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the e ...
to East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea and ...
. Trade with Phoenicians
Phoenicia () was an ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient thalassocracy, thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-st ...
, Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
, Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
, Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Wester ...
, Syrians
Syrians ( ar, سُورِيُّون, ''Sūriyyīn'') are an Eastern Mediterranean ethnic group indigenous to the Levant. They share common Levantine Semitic roots. The cultural and linguistic heritage of the Syrian people is a blend of both indi ...
, Jew
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""Th ...
s, and Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
began during the Sangam period
The Sangam period or age (, ), particularly referring to the third Sangam period, is the period of the history of ancient Tamil Nadu, Kerala and parts of Sri Lanka (then known as Tamilakam) spanning from c. 6th century BCE to c. 3rd century CE. ...
(c. 3rd century BCE to c. 4th century CE). The region was part of the ancient Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and reli ...
connecting the East
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fa ...
with the West
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sunset, Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic languages, German ...
.
Several dynasties – such as the Cheras of Karuvur
Karur () is a city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. Karur is the administrative headquarters of Karur district. It is located on the banks of River Amaravathi, Kaveri and Noyyal.
Karur is well known for the export of Home Textile products to ...
, the Pandyas of Madurai
Madurai ( , also , ) is a major city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is the cultural capital of Tamil Nadu and the administrative headquarters of Madurai District. As of the 2011 census, it was the third largest Urban agglomeration in ...
, the Cholas
The Chola dynasty was a Tamil thalassocratic empire of southern India and one of the longest-ruling dynasties in the history of the world. The earliest datable references to the Chola are from inscriptions dated to the 3rd century BCE d ...
of Thanjavur
Thanjavur (), also Tanjore, Pletcher 2010, p. 195 is a city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. Thanjavur is the 11th biggest city in Tamil Nadu. Thanjavur is an important center of South Indian religion, art, and architecture. Most of the Gr ...
, the Zamorin
The Samoothiri (Anglicised as Zamorin; Malayalam: , Arabic: ''Sāmuri'', Portuguese: ''Samorim'', Dutch: ''Samorijn'', Chinese: ''Shamitihsi''Ma Huan's Ying-yai Sheng-lan: 'The Overall Survey of the Ocean's Shores' 433 Translated and Edited by ...
s of Kozhikode
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second la ...
, the Travancore royal family of Thiruvananthapuram
Thiruvananthapuram (; ), also known by its former name Trivandrum (), is the capital of the Indian state of Kerala. It is the most populous city in Kerala with a population of 957,730 as of 2011. The encompassing urban agglomeration populati ...
, the Kingdom of Cochin
The Kingdom of Cochin, named after its capital in the city of Kochi (Cochin), was a kingdom in the central part of present-day Kerala state. It commenced at the early part of the 12th century and continued to rule until 1949, when monarchy w ...
, the Mushikas
Mushika dynasty, also spelled Mushaka, was a minor dynastic power that held sway over the region in and around Mount Ezhi (Ezhimala) in present-day North Malabar, Kerala, India. The country of the Mushikas, ruled by an ancient lineage of the Heh ...
of Kannur
Kannur (), formerly known in English as Cannanore, is a city and a municipal corporation in the state of Kerala, India. It is the administrative headquarters of the Kannur district and situated north of the major port city and commercial hu ...
, the Satavahanas
The Satavahanas (''Sādavāhana'' or ''Sātavāhana'', International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: ), also referred to as the Andhras in the Puranas, were an ancient Indian dynasty based in the Deccan Plateau, Deccan region. Mos ...
of Amaravati
Amaravati () is the capital of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is located on the banks of the river Krishna in Guntur district.
The Prime Minister of India, Narendra Modi laid the foundation stone at a ceremonial event in Uddandar ...
, the Pallavas
The Pallava dynasty existed from 275 CE to 897 CE, ruling a significant portion of South India, the Deccan, also known as Tondaimandalam. The dynasty rose to prominence after the downfall of the Satavahanas, Satavahana dynasty, with whom they ...
of Kanchi
Kanchipuram ('; ) also known as ''Conjeevaram,'' is a city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu in the Tondaimandalam region, from Chennaithe capital of Tamil Nadu. Known as the ''City of Thousand Temples'', Kanchipuram is known for its temple ...
, the Kadambas of Banavasi
Banavasi is an ancient temple town located near Sirsi in Karnataka. Banavasi was the ancient capital of the Kannada empire Kadamba that ruled all of modern-day Karnataka state. They were the first native empire to bring Kannada and Karnataka t ...
, the Western Gangas
Western Ganga was an important ruling dynasty of ancient Karnataka in India which lasted from about 350 to 1000 CE. They are known as "Western Gangas" to distinguish them from the Eastern Gangas who in later centuries ruled over Kalinga (mo ...
of Kolar
Kolar or Kolara is a city in the Indian state of Karnataka. It is the headquarters of Kolar district. The city is known for its milk production and gold mines. It is also known for Someshwara temple and Kolaramma temple.
History
The Weste ...
, the Rashtrakuta
Rashtrakuta (IAST: ') (r. 753-982 CE) was a royal Indian dynasty ruling large parts of the Indian subcontinent between the sixth and 10th centuries. The earliest known Rashtrakuta inscription is a 7th-century copper plate grant detailing their ...
s of Manyakheta
Malkhed originally known as Manyakheta (IAST: Mānyakheṭa, Prakrit: "Mannakheḍa"), and also known as Malkhed,Village code= 311400 Malkhed (J), Gulbarga, Karnataka is a town in Karnataka, India. It is located on the banks of Kagina river i ...
, the Chalukyas
The Chalukya dynasty () was a Classical Indian dynasty that ruled large parts of southern and central India between the 6th and the 12th centuries. During this period, they ruled as three related yet individual dynasties. The earliest dynas ...
of Badami
Badami, formerly known as Vatapi, is a town and headquarters of a taluk by the same name, in the Bagalkot district of Karnataka, India. It was the regal capital of the Badami Chalukyas from CE 540 to 757. It is famous for its rock cut monumen ...
, the Hoysalas
The Hoysala Empire was a Kannadiga power originating from the Indian subcontinent that ruled most of what is now Karnataka between the 10th and the 14th centuries. The capital of the Hoysalas was initially located at Belur, but was later moved ...
of Belur
Belur may refer to:
Places
* Belur, Karnataka, a town in Karnataka, India
** Belur temple (Chennakeshava temple), Belur
* Belur, Tamil Nadu, a town in Salem district, Tamil Nadu, India
* Belur, West Bengal, a neighbourhood of Howrah, India
** Be ...
, and the Kakatiyas of Orugallu
Warangal () is a city in the Indian state of Telangana and the district headquarters of Warangal district. It is the second largest city in Telangana with a population of 704,570 per 2011 Census of India, and spreading over an .
Warangal ser ...
– ruled over the region from the 6th century BCE to the 14th century CE. The Vijayanagara Empire
The Vijayanagara Empire, also called the Karnata Kingdom, was a Hinduism, Hindu empire based in the region of South India, which consisted the modern states of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Goa and some parts of Telangana an ...
, founded in the 14th century CE. was the last Indian dynasty to rule over the region. After repeated invasions from the Sultanate of Delhi
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206–1526).
and the fall of Vijayanagara empire in 1646, the region was ruled by Deccan Sultanates
The Deccan sultanates were five Islamic late-medieval Indian kingdoms—on the Deccan Plateau between the Krishna River and the Vindhya Range—that were ruled by Muslim dynasties: namely Ahmadnagar, Berar, Bidar, Bijapur, and Golconda. Th ...
, the Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern Indian confederation that came to dominate much of the Indian subcontinent in the 18th century. Maratha rule formally began in 1674 with the coronation of Shi ...
, and polygars
Palaiyakkarars, or Poligar, (as the British referred to them) in Tamil Nadu refers to the holder of a small kingdom as a feudatory to a greater sovereign. Under this system, ''palayam'' was given for valuable military services rendered by any in ...
and Nayak governors of the Vijayanagara empire who declared their independence.
Colonial era
The Europeans arrived in the 15th century; and by the middle of the 18th century, the French and theBritish
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
were involved in a protracted struggle for military control over South India. After the defeat of Tipu Sultan
Tipu Sultan (born Sultan Fateh Ali Sahab Tipu, 1 December 1751 – 4 May 1799), also known as the Tiger of Mysore, was the ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore based in South India. He was a pioneer of rocket artillery.Dalrymple, p. 243 He int ...
in the Fourth Anglo-Mysore War
The Fourth Anglo-Mysore War was a conflict in South India between the Kingdom of Mysore against the British East India Company and the Hyderabad Deccan in 1798–99.
This was the final conflict of the four Anglo-Mysore Wars. The British captured ...
in 1799 and the end of the Vellore Mutiny
The Vellore mutiny, or Vellore Revolution, occurred on 10 July 1806 and was the first instance of a large-scale and violent mutiny by Indian sepoys against the East India Company, predating the Indian Rebellion of 1857 by half a century. The re ...
in 1806, the British consolidated their power over much of present-day South India, with the exception of French Pondichéry. The British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
took control of the region from the British East India Company in 1857. During the British colonial rule, the region was divided into the Madras Presidency
The Madras Presidency, or the Presidency of Fort St. George, also known as Madras Province, was an administrative subdivision (presidency) of British India. At its greatest extent, the presidency included most of southern India, including the ...
, Hyderabad State
Hyderabad State () was a princely state located in the south-central Deccan region of India with its capital at the city of Hyderabad. It is now divided into the present-day state of Telangana, the Kalyana-Karnataka region of Karnataka, and t ...
, Mysore
Mysore (), officially Mysuru (), is a city in the southern part of the state of Karnataka, India. Mysore city is geographically located between 12° 18′ 26″ north latitude and 76° 38′ 59″ east longitude. It is located at an altitude of ...
, Travancore
The Kingdom of Travancore ( /ˈtrævənkɔːr/), also known as the Kingdom of Thiruvithamkoor, was an Indian kingdom from c. 1729 until 1949. It was ruled by the Travancore Royal Family from Padmanabhapuram, and later Thiruvananthapuram. At ...
, Kochi
Kochi (), also known as Cochin ( ) ( the official name until 1996) is a major port city on the Malabar Coast of India bordering the Laccadive Sea, which is a part of the Arabian Sea. It is part of the district of Ernakulam in the state of K ...
, Jeypore, and a number of other minor princely state
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Raj, British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, ...
s. The region played a major role in the Indian independence movement
The Indian independence movement was a series of historic events with the ultimate aim of ending British Raj, British rule in India. It lasted from 1857 to 1947.
The first nationalistic revolutionary movement for Indian independence emerged ...
: of the 72 delegates who participated in the first session of the Indian National Congress
The Indian National Congress (INC), colloquially the Congress Party but often simply the Congress, is a political party in India with widespread roots. Founded in 1885, it was the first modern nationalist movement to emerge in the British Em ...
at Bombay in December 1885, 22 hailed from South India.
Post-independence
independence of India
The Indian independence movement was a series of historic events with the ultimate aim of ending British Raj, British rule in India. It lasted from 1857 to 1947.
The first nationalistic revolutionary movement for Indian independence emerged ...
in 1947, the region was organised into four states: Madras State
Madras State was a state of India during the mid-20th century. At the time of its formation in 1950, it included the whole of present-day Tamil Nadu (except Kanyakumari district), Coastal Andhra, Rayalaseema, the Malabar region of North and c ...
, Mysore State
Mysore State, colloquially Old Mysore, was a state within the Dominion of India and the later Republic of India from 1947 until 1956. The state was formed by renaming the Kingdom of Mysore, and Bangalore replaced Mysore as the state's capital. ...
, Hyderabad State
Hyderabad State () was a princely state located in the south-central Deccan region of India with its capital at the city of Hyderabad. It is now divided into the present-day state of Telangana, the Kalyana-Karnataka region of Karnataka, and t ...
and Travancore–Cochin
Travancore–Cochin, or Thiru–Kochi, was a short-lived state of India (1949–1956). It was originally called United State of Travancore and Cochin following the merger of two former kingdoms, Travancore and Cochin on 1 July 1949. Its origina ...
. The States Reorganisation Act
The States Reorganisation act, 1956 was a major reform of the boundaries of India's States and territories of India, states and territories, organising them along linguistic lines.
Although additional changes to India's state boundaries have b ...
of 1956 reorganized the states on linguistic lines, resulting in the creation of the new states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu. As a result of this Act, Madras State retained its name and Kanyakumari district
Kanniyakumari district is one of the 38 districts in Tamil Nadu state and the southernmost district in mainland India. It stands second in terms of population density among the districts of Tamil Nadu. It is also the richest district in Tamil Nad ...
was added to it from the state of Travancore-Cochin. The state was subsequently renamed Tamil Nadu in 1968. Andhra Pradesh was created through the merger of Andhra State
Andhra State (IAST: ; ) was a Administrative divisions of India#States and union territories, state in India created in 1953 from the Telugu language, Telugu-speaking northern List of districts in India, districts of Madras State. The state was ...
with the Telugu-speaking districts of Hyderabad State in 1956. The Marathi
Marathi may refer to:
*Marathi people, an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group of Maharashtra, India
*Marathi language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Marathi people
*Palaiosouda, also known as Marathi, a small island in Greece
See also
*
* ...
-speaking Marathwada
Marathwada () is a proposed state and geographical region of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It was formed during the Nizam's rule and was part of the then Hyderabad State. The region coincides with the Aurangabad division of Maharashtra. ...
region of Hyderabad State
Hyderabad State () was a princely state located in the south-central Deccan region of India with its capital at the city of Hyderabad. It is now divided into the present-day state of Telangana, the Kalyana-Karnataka region of Karnataka, and t ...
was transferred to Bombay State
Bombay State was a large Indian state created at the time of India's Independence, with other regions being added to it in the succeeding years. Bombay Presidency (roughly equating to the present-day Indian state of Maharashtra, excluding Sou ...
and ceased to be a part of South India. Kerala emerged from the merger of Malabar district
Malabar District, also known as Malayalam District, was an administrative district on the southwestern Malabar Coast of Bombay Presidency (1792-1800) and Madras Presidency (1800-1947) in British India, and independent India's Madras State (19 ...
and the Kasaragod taluk
Kasaragod or Casrod a taluk which along with Hosdurg taluk, Manjeshwaram Taluk and Vellarikundu taluk constitute the Kasaragod district, Kerala, India. Its educational center is Vidyanagar. The major areas include Kasaragod municipality, Chemnad, ...
of South Canara
South Canara was a district of the Madras Presidency of British India, located at . It comprised the towns of Kassergode and Udipi and adjacent villages, with the capital in Mangalore city. South Canara was one of the most heterogeneous areas o ...
districts of Madras State with Travancore–Cochin. Mysore State
Mysore State, colloquially Old Mysore, was a state within the Dominion of India and the later Republic of India from 1947 until 1956. The state was formed by renaming the Kingdom of Mysore, and Bangalore replaced Mysore as the state's capital. ...
was re-organised with the addition of the districts of Bellary
Bellary, officially Ballari, in the eponymous Bellary district, is a city in the state of Karnataka, India.
History
Bellary was a part of Rayalaseema (Ceded Districts) which was part of Madras Presidency till 1 November 1956.
The Ball ...
and South Canara (excluding Kasaragod ''taluk'') and the Kollegal taluk of Coimbatore district
Coimbatore district is one of the 38 districts in the state of Tamil Nadu in India. Coimbatore is the administrative headquarters of the district. It is one of the most industrialized districts and a major textile, industrial, commercial, educ ...
from Madras State; the districts of Belgaum
Belgaum (ISO 15919, ISO: ''Bēḷagāma''; also Belgaon and officially known as Belagavi) is a city in the Indian state of Karnataka located in its northern part along the Western Ghats. It is the administrative headquarters of the eponymous ...
, Bijapur
Bijapur, officially known as Vijayapura, is the district headquarters of Bijapur district of the Karnataka state of India. It is also the headquarters for Bijapur Taluk. Bijapur city is well known for its historical monuments of architectural ...
, North Canara
Uttara Kannada is a district in the Indian state of Karnataka. Uttara Kannada District is a major coastal district of Karnataka, and currently holding the title of the largest district in Karnataka. It is bordered by the state of Goa and Bela ...
, and Dharwad
Dharwad (), also known as Dharwar, is a city located in the north western part of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is the headquarters of the Dharwad district of Karnataka and forms a contiguous urban area with the city of Hubballi. It was merge ...
from Bombay State
Bombay State was a large Indian state created at the time of India's Independence, with other regions being added to it in the succeeding years. Bombay Presidency (roughly equating to the present-day Indian state of Maharashtra, excluding Sou ...
; the Kannada-majority districts of Bidar
Bidar (/ biːd̪ər/) is a city in the north-eastern part of Karnataka state in India. It is the headquarters of Bidar district, which borders Maharashtra and Telangana. It is a rapidly urbanising city in the wider ''Bidar Metropolitan area ...
, Raichur
Raichur (formerly Raichore) is a city and municipality in the district of Raichur in the Indian state of Karnataka. Raichur, located between Krishna and Tungabhadra rivers, is the headquarters of Raichur district. It is located 409 km fr ...
, and Gulbarga
Kalaburagi, formerly known as Gulbarga, is a city in the Indian state of Karnataka. It is the administrative headquarters of the Kalaburagi district and is the largest city in the region of North Karnataka (Kalyana-Karnataka). Kalaburagi is 6 ...
from the Hyderabad State; and the province of Coorg
Kodagu (also known by its former name Coorg) is an administrative district in the Karnataka state of India. Before 1956, it was an administratively separate Coorg State, at which point it was merged into an enlarged Mysore State.
It occupies ...
. Mysore State was renamed as Karnataka in 1973. The Union territory of Puducherry was created in 1954, comprising the previous French enclaves of Pondichérry, Karaikal
Karaikal ( /kʌdɛkʌl/, french: Karikal /kaʁikal/) is a town of the Indian Union Territory of Puducherry. Karaikal was sold to the French by the Rajah of Thanjavur and became a French Colony in 1739. The French held control, with occasi ...
, Yanam
Yanam (Telugu: ''యానాం'') is a town located in the Yanam district in Puducherry. It has a population of 35,000 and is entirely surrounded by Andhra Pradesh. It was formerly a French colony for nearly 200 years, and, though united wi ...
, and Mahé. The Laccadive Islands
The Laccadive or Cannanore Islands are one of the three island subgroups in the Union Territory of Lakshadweep, India. It is the central subgroup of the Lakshadweep, separated from the Amindivi Islands subgroup roughly by the 11th parallel ...
, which were divided between South Canara and the Malabar districts of Madras State, were united and organised into the union territory of Lakshadweep
Lakshadweep (), also known as Laccadives (), is a union territory of India. It is an archipelago of 36 islands in the Arabian sea, located off the Malabar Coast.
The name ''Lakshadweep'' means "one lakh islands" in Sanskrit, though the Lac ...
. Goa
Goa () is a state on the southwestern coast of India within the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan highlands by the Western Ghats. It is located between the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north and Karnataka to the ...
was created as a union territory by taking military actions against the Portuguese by the government of India, later it has been declared as a state due to its drastic growth. Telangana was created on 2 June 2014 by bifurcating Andhra Pradesh; and it comprises ten districts of the erstwhile state of Andhra Pradesh.
Geography

 South India is a
South India is a peninsula
A peninsula (; ) is a landform that extends from a mainland and is surrounded by water on most, but not all of its borders. A peninsula is also sometimes defined as a piece of land bordered by water on three of its sides. Peninsulas exist on all ...
in the shape of an inverted triangle bound by the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel ...
on the west, by the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line between ...
on the east and the Vindhya
The Vindhya Range (also known as Vindhyachal) () is a complex, discontinuous chain of mountain ridges, hill ranges, highlands and plateau escarpments in west-central India.
Technically, the Vindhyas do not form a single mountain range in the ...
and Satpura
The Satpura Range is a range of hills in central India. The range rises in eastern Gujarat running east through the border of Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh and ends in Chhattisgarh. The range parallels the Vindhya Range to the north, and th ...
ranges on the north. The Narmada river flows westwards in the depression between the Vindhya and Satpura ranges, which define the northern spur of the Deccan plateau
The large Deccan Plateau in southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bounded by the ...
. The Western Ghats run parallel to the Arabian Sea along the western coast and the narrow strip of land between the mountains and the sea forms the Konkan
The Konkan ( kok, कोंकण) or Kokan () is a stretch of land by the western coast of India, running from Damaon in the north to Karwar in the south; with the Arabian Sea to the west and the Deccan plateau in the east. The hinterland ...
region. The Western Ghats continue south until Kanyakumari
Kanniyakumari (; , referring to Devi Kanya Kumari), also known as Cape Comorin, is a city in Kanniyakumari district in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. It is the southern tip of the Indian subcontinent and the southernmost city in mainland Ind ...
. The Eastern Ghats
The Eastern Ghats are a discontinuous range of mountains along India's eastern coast. The Eastern Ghats pass through Odisha, Andhra Pradesh to Tamil Nadu in the south passing some parts of Karnataka as well as Telangana. They are eroded and cut ...
run parallel to the Bay of Bengal along the eastern coast and the strip of land between them forms the Coromandel
Coromandel may refer to:
Places India
*Coromandel Coast, India
**Presidency of Coromandel and Bengal Settlements
** Dutch Coromandel
*Coromandel, KGF, Karnataka, India
New Zealand
*Coromandel, New Zealand, a town on the Coromandel Peninsula
*Coro ...
region. Both mountain ranges meet at the Nilgiri mountains. The Nilgiris run in a crescent approximately along the borders of Tamil Nadu with northern Kerala and Karnataka, encompassing the Palakkad
Palakkad (), formerly known as Palghat, historically known as Palakkattussery is a city and municipality in the Indian state of Kerala. It is the administrative headquarters of the Palakkad District. Palakkad is most densely populated municipal ...
and Wayanad
Wayanad () is a district in the north-east of Indian state Kerala with administrative headquarters at the municipality of Kalpetta. It is the only plateau in Kerala. The Wayanad Plateau forms a continuation of the Mysore Plateau, the southern ...
hills and the Sathyamangalam
Sathyamangalam (also known as Sathy) is a town and municipality in Erode district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. 8 th century Town. It lies on the banks of the River Bhavani, a tributary of the River Cauvery in the foothills of the ...
ranges, extending to the relatively low-lying hills of the Eastern Ghats on the western portion of the Tamil Nadu–Andhra Pradesh border, forming the Tirupati
Tirupati () is a city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is the administrative headquarters of the Tirupati district. The city is home to the important Hindu shrine of Tirumala Venkateswara Temple and other historic temples and is refe ...
and Annamalai hills
Arunachala ( IAST: , 'Red Mountain') is a hill in Tiruvannamalai, Tamil Nadu, and one of the five main Shaiva holy places in South India. The Arunachalesvara Temple to Shiva is located at the base of the hill. The hill is also known by the na ...
.
The low-lying coral
Corals are marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and sec ...
islands of Lakshadweep
Lakshadweep (), also known as Laccadives (), is a union territory of India. It is an archipelago of 36 islands in the Arabian sea, located off the Malabar Coast.
The name ''Lakshadweep'' means "one lakh islands" in Sanskrit, though the Lac ...
are situated off the southwestern coast of India. The Andaman and Nicobar islands lie far off the eastern coast. The Palk Strait
The Palk Strait ( ta, பாக்கு நீரிணை ''Pākku Nīriṇai'', si, පෝක් සමුද්ර සන්ධිය ''Pok Samudra Sandhiya'') is a strait between the Tamil Nadu state of India and the Jaffna Distric ...
and the chain of low sandbars and islands known as Rama's Bridge
Adam's Bridge, '; ta, ஆதாம் பாலம் ' also known as Rama's Bridge or ''Rama Setu'', '; ta, ராமர் பாலம் '; sa, रामसेतु ' is a chain of natural limestone shoals, between Pamban Island, a ...
separate the region from Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
, which lies off the southeastern coast. The southernmost tip of mainland India is at Kanyakumari
Kanniyakumari (; , referring to Devi Kanya Kumari), also known as Cape Comorin, is a city in Kanniyakumari district in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. It is the southern tip of the Indian subcontinent and the southernmost city in mainland Ind ...
where the Indian Ocean meets the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea.
 The Deccan plateau is the elevated region bound by the mountain ranges. The plateau rises to in the north and to more than in the south, forming a raised triangle within the downward-pointing triangle of the
The Deccan plateau is the elevated region bound by the mountain ranges. The plateau rises to in the north and to more than in the south, forming a raised triangle within the downward-pointing triangle of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
's coastline. It also slopes gently from West to East resulting in major rivers arising in the Western Ghats and flowing east into the Bay of Bengal. The volcanic basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
beds of the Deccan were laid down in the massive Deccan Traps
The Deccan Traps is a large igneous province of west-central India (17–24°N, 73–74°E). It is one of the largest volcanic features on Earth, taking the form of a large shield volcano. It consists of numerous layers of solidified flood ...
eruption, which occurred towards the end of the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
period, between 67 and 66 million years ago. Layer after layer was formed by the volcanic activity that lasted 30,000 years; and when the volcanoes became extinct, they left a region of highlands with typically vast stretches of flat areas on top like a table. The plateau is watered by the east-flowing Godavari
The Godavari ( IAST: ''Godāvarī'' �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga river and drains into the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakesh ...
, Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is one ...
, Kaveri
The Kaveri (also known as Cauvery, the anglicized name) is one of the major Indian rivers flowing through the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. The Kaveri river rises at Talakaveri in the Brahmagiri range in the Western Ghats, Kodagu dis ...
, and Vaigai
The Vaigai is a river in the Tamil Nadu state of southern India; it passes through the towns of Theni, Dindigul and Madurai. It originates in Varusanadu Hills, the Periyar Plateau of the Western Ghats range, and flows northeast through the ...
rivers. The major tributaries include the Pennar
Penna (also known as Pinakini, Pennar, Penner, Penneru (Telugu), Pennai (Tamil)) is a river of southern India. This is a unique river in world where after originating from Nandi hills, it flows as two different streams, one in North and South ...
, Tungabhadra, Bhavani
Bhavānī (also known as Bhāvya, Tulajā, Turajā, Tvarita, Aṃbā, Jagadambā and Aṃbē) is manifestation of Adi Shakti (Durga). Bhavani translates to "giver of life", meaning the power of nature or the source of creative energy. She is co ...
, and Thamirabarani
The Thamirabarani or Tamraparni or Porunai is a perennial river that originates from the Agastyarkoodam peak of Pothigai hills of the Western Ghats, above Papanasam in the Ambasamudram taluk. It flows through Tirunelveli and Thoothukudi di ...
rivers.
Climate
The region has atropical climate
Tropical climate is the first of the five major climate groups in the Köppen climate classification identified with the letter A. Tropical climates are defined by a monthly average temperature of 18 °C (64.4 °F) or higher in the cool ...
and depends on monsoons for rainfall. According to the Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
, it has a non-arid
A region is arid when it severely lacks available water, to the extent of hindering or preventing the growth and development of plant and animal life. Regions with arid climates tend to lack vegetation and are called xeric or desertic. Most ar ...
climate with minimum mean temperatures of . The most humid is the tropical monsoon climate
An area of tropical monsoon climate (occasionally known as a sub-equatorial, tropical wet climate or a tropical monsoon and trade-wind littoral climate) is a tropical climate sub-type that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification category ...
characterized by moderate to high year-round temperatures and seasonally heavy rainfall above per year. The tropical climate is experienced in a strip of south-western lowlands abutting the Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is the southwestern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing m ...
, the Western Ghats; the islands of Lakshadweep and Andaman and Nicobar are also subject to this climate.
A tropical wet and dry climate
Tropical savanna climate or tropical wet and dry climate is a tropical climate sub-type that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification categories ''Aw'' (for a dry winter) and ''As'' (for a dry summer). The driest month has less than of p ...
, drier than areas with a tropical monsoon climate, prevails over most of the inland peninsular region except for a semi-arid rain shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.
Evaporated moisture from water bodies (such as oceans and large lakes) is carrie ...
east of the Western Ghats. Winter and early summer are long dry periods with temperatures averaging above ; summer is exceedingly hot with temperatures in low-lying areas exceeding ; and the rainy season lasts from June to September, with annual rainfall averaging between across the region. Once the dry northeast monsoon begins in September, most precipitation in India falls in Tamil Nadu, leaving other states comparatively dry. A hot semi-arid climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-ar ...
predominates in the land east of the Western Ghats and the Cardamom Hills
The Cardamom Hills or Yela Mala are mountain range of southern India and part of the southern Western Ghats located in Idukki district, Kerala, India. Their name comes from the cardamom spice grown in much of the hills' cool elevation, wh ...
. The region – which includes Karnataka, inland Tamil Nadu and western Andhra Pradesh – gets between of rainfall annually, with hot summers and dry winters with temperatures around . The months between March and May are hot and dry, with mean monthly temperatures hovering around , with precipitation. Without artificial irrigation, this region is not suitable for agriculture.
The southwest monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscill ...
from June to September accounts for most of the rainfall in the region. The Arabian Sea branch of the southwest monsoon hits the Western Ghats along the coastal state of Kerala and moves northward along the Konkan coast
The Konkan ( kok, कोंकण) or Kokan () is a stretch of land by the western coast of India, running from Damaon in the north to Karwar in the south; with the Arabian Sea to the west and the Deccan plateau in the east. The hinterland ...
, with precipitation on coastal areas west of the Western Ghats. The lofty Western Ghats prevent the winds from reaching the Deccan Plateau; hence, the leeward region (the region deprived of winds) receives very little rainfall. The Bay of Bengal branch of the southwest monsoon heads toward northeast India, picking up moisture from the Bay of Bengal. The Coramandel coast
The Coromandel Coast is the southeastern coastal region of the Indian subcontinent, bounded by the Utkal Plains to the north, the Bay of Bengal to the east, the Kaveri delta to the south, and the Eastern Ghats to the west, extending over an ...
does not receive much rainfall from the southwest monsoon, due to the shape of the land. Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a States and union territories of India, state in southern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, tenth largest Indian state by area and the List of states and union territories of India ...
and southeast Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
receive rains from the northeast monsoon. The northeast monsoon takes place from November to early March, when the surface high-pressure system
A high-pressure area, high, or anticyclone, is an area near the surface of a planet where the atmospheric pressure is greater than the pressure in the surrounding regions. Highs are middle-scale meteorological features that result from interpl ...
is strongest. The North Indian Ocean tropical cyclone
In the Indian Ocean north of the equator, tropical cyclones can form throughout the year on either side of India, although most frequently between April and June, and between October and December.
Sub-basins
The North Indian Ocean is the lea ...
s occur throughout the year in the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea, bringing devastating winds and heavy rainfall.
Flora and fauna
 There is a wide diversity of plants and animals in South India, resulting from its varied climates and geography.
There is a wide diversity of plants and animals in South India, resulting from its varied climates and geography. Deciduous forests
In the fields of horticulture and Botany, the term ''deciduous'' () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, afte ...
are found along the Western Ghats while tropical dry forests
The tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forest is a habitat type defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature and is located at tropical and subtropical latitudes. Though these forests occur in climates that are warm year-round, and may receive ...
and scrub lands are common in the interior Deccan plateau. The southern Western Ghats have rain forests located at high altitudes called the South Western Ghats montane rain forests
The South Western Ghats montane rain forests is an ecoregion in South India, covering the southern portion of the Western Ghats in Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu at elevations from . Annual rainfall in this ecoregion exceeds .
Setting
The e ...
, and the Malabar Coast moist forests
The Malabar Coast moist forests are a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of southwestern India.
Geography
The ecoregion lies along India's Konkan and Malabar coasts, in a narrow strip between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats range, ...
are found on the coastal plains. The Western Ghats is one of the eight hottest biodiversity hotspot
A biodiversity hotspot is a biogeographic region with significant levels of biodiversity that is threatened by human habitation. Norman Myers wrote about the concept in two articles in ''The Environmentalist'' in 1988 and 1990, after which the co ...
s in the world and a UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
.
Important ecological regions of South India are the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve
The Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve is a biosphere reserve in the Nilgiri mountains of the Western Ghats in South India. It is the largest protected forest area in India, spreading across Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Kerala. It includes the protected ar ...
– located at the conjunction of Karnataka, Kerala and, Tamil Nadu in the Nilgiri Hills
The Nilgiri Mountains form part of the Western Ghats in northwestern Tamil Nadu, Southern Karnataka, and eastern Kerala in India. They are located at the trijunction of three states and connect the Western Ghats with the Eastern Ghats. At le ...
– and the Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve
The Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve is a biosphere reserve in India established in 2001, located in the southernmost end of the Western Ghats and includes of which 1828 km2 is in Kerala and 1672.36 km2 is in Tamil Nadu. It encompasses ...
- located at the conjunction of Kerala and, Tamil Nadu in the Agastya Mala
Agastyaarkoodam is one of the peaks in the Western Ghats of Tirunelveli District of Tamil Nadu, India. This peak is a part of the Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve which lies on the border between the Indian states of Tamil Nadu, Tirunelveli ...
hills - and the Cardamom Hills
The Cardamom Hills or Yela Mala are mountain range of southern India and part of the southern Western Ghats located in Idukki district, Kerala, India. Their name comes from the cardamom spice grown in much of the hills' cool elevation, wh ...
of Western Ghats. Bird sanctuaries – including Thattekad, Kadalundi
Kadalundi is a village in Kozhikode district, Kerala, India. It is a coastal village close to the Arabian Sea. Kadalundi is famous for its bird sanctuary, which is home to various migratory birds during certain seasons and has been recently decla ...
, Vedanthangal
Vedanthangal Bird Sanctuary is a protected area located in the Madurantakam taluk of the Chengalpattu District in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. The sanctuary is about from Chennai on National Highway 45 ( H45. It is easily reachable fro ...
, Ranganathittu
Ranganathittu Bird Sanctuary (also known as ''Pakshi Kashi of Karnataka''), is a bird sanctuary in the Mandya District of the state of Karnataka in India. It is the largest bird sanctuary in the state, in area, and comprises six islets on the b ...
, Kumarakom
Kumarakom is a popular tourism destination located near the city of Kottayam (), in Kerala, India, famous for its backwater tourism. It is set in the backdrop of the Vembanad Lake, the largest lake in the state of Kerala.
History
Kuma ...
, Neelapattu, and Pulicat
Pulicat or Pazhaverkadu is a historic seashore town in Chennai Metropolitan Area at Thiruvallur District, of Tamil Nadu state, India. It is about north of Chennai and from Elavur, on the southern periphery of the Pulicat Lake. Pulicat lake i ...
– are home to numerous migratory and local birds. Lakshadweep
Lakshadweep (), also known as Laccadives (), is a union territory of India. It is an archipelago of 36 islands in the Arabian sea, located off the Malabar Coast.
The name ''Lakshadweep'' means "one lakh islands" in Sanskrit, though the Lac ...
has been declared a bird sanctuary by the Wildlife Institute of India
The Wildlife Institute of India (WII) is an autonomous natural resource service institution established in 1982 under the Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate change, Government of India.
WII carries out wildlife research in areas of stu ...
. Other protected ecological sites include the mangrove forests of Pichavaram
Pichavaram is a village near Chidambaram in Cuddalore District, Tamil Nadu, India. It is located between the Vellar estuary in the north and Coleroon estuary in the south. The Vellar-Coleroon estuarine complex forms the Killai backwater and the ...
, and the backwaters of Pulicat lake, in Tamil Nadu; and Vembanad
Vembanad is the longest lake in India, as well as the largest lake in the state of Kerala. The lake has an area of 230 square kilometers and a maximum length of 96.5 km. Spanning several districts in the state of Kerala, it is known as Ve ...
, Ashtamudi, Paravur, and Kayamkulam
Kayamkulam is a town and municipality in the ''Onattukara'' region of Alappuzha district in Kerala. It is the second biggest town in Alappuzha district. It is located on the western coast of India, and was an ancient maritime trading center. O ...
lakes in Kerala. The Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve
The Gulf of Mannar Marine National Park is a protected area of India consisting of 21 small islands (islets) and adjacent coral reefs in the Gulf of Mannar in the Indian Ocean. It lies 1 to 10 km away from the east coast of Tamil Nadu, Indi ...
covers an area of 10,500 km2 of ocean, islands and the adjoining coastline including coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
Co ...
s, salt marsh
A salt marsh or saltmarsh, also known as a coastal salt marsh or a tidal marsh, is a coastal ecosystem in the upper coastal intertidal zone between land and open saltwater or brackish water that is regularly flooded by the tides. It is dominated ...
es and mangroves. It is home to endangered
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching and inva ...
aquatic species, including dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal within the infraorder Cetacea. Dolphin species belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontoporiidae (the ...
s, dugong
The dugong (; ''Dugong dugon'') is a marine mammal. It is one of four living species of the order Sirenia, which also includes three species of manatees. It is the only living representative of the once-diverse family Dugongidae; its closest m ...
s, whale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully aquatic placental marine mammals. As an informal and colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea, i.e. all cetaceans apart from dolphins and ...
s and Holothuroidea, sea cucumbers.
South India is home to one of the largest populations of endangered Bengal tigers and Indian elephants in India, being home to one-third of the tiger population and more than half of the elephant population, with 14 Project Tiger Tiger reserves of India, reserves and 11 Project Elephant reserves. Elephant populations are found in eight fragmented sites in the region: in northern Karnataka, along the Western Ghats, in Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary, Bhadra–Malnad, in Brahmagiri (hill), Brahmagiri–Nilgiri Mountains, Nilgiris–Eastern Ghats
The Eastern Ghats are a discontinuous range of mountains along India's eastern coast. The Eastern Ghats pass through Odisha, Andhra Pradesh to Tamil Nadu in the south passing some parts of Karnataka as well as Telangana. They are eroded and cut ...
, in Nilambur–Silent Valley National Park, Silent Valley–Coimbatore, in Anamalai–Parambikulam, in Periyar National Park, Periyar–Srivilliputhur, and in Agasthyamalai Other threatened and endangered species found in the region include the grizzled giant squirrel, grey slender loris, sloth bear, Nilgiri tahr, Nilgiri langur, lion-tailed macaque, and the Indian leopard.
Transport
Road
South India has an extensive road network with of National Highway (India), National Highways and of State Highway (India), State Highways. The Golden Quadrilateral connects Chennai with Mumbai via Bangalore, and with Kolkata via Visakhapatnam. Bus services are provided by state-run transport corporations, namely the Andhra Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation, Tamil Nadu State Transport Corporation, Karnataka State Road Transport Corporation, Telangana State Road Transport Corporation, Kerala State Road Transport Corporation, and Puducherry Road Transport Corporation.Rail
The South Indian Railway Company, Great Southern of India Railway Company was founded in England in 1853 and registered in 1859. Construction of track in the Madras Presidency began in 1859 and the link from Tiruchirappalli, Trichinopoly to Nagapattinam, Negapatam and a link from Tirur to the Beypore, Port of Beypore atKozhikode
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second la ...
on the Malabar District, Malabar Coast, which eventually got expanded into the Mangalore-Chennai line via Palakkad Gap were opened in 1861. The Carnatic Railway Company was founded in 1864 and opened a Madras–Arakkonam–Kancheepuram, Conjeevaram–Katpadi junction line in 1865. These two companies subsequently merged in 1874 to form the South Indian Railway Company. In 1880, the Great Indian Peninsula Railway, established by the British India, British, built a railway network radiating from Madras. In 1879, the Madras Railway constructed a line from Royapuram to Bangalore; and the Maharaja of Mysore established the Mysore State Railway to build an extension from Bangalore to Mysore. In order to get access to the west coast, Malabar region of the country through Port of Quilon, Maharajah Uthram Thirunal Marthanda Varma, Uthram Thirunal of Travancore
The Kingdom of Travancore ( /ˈtrævənkɔːr/), also known as the Kingdom of Thiruvithamkoor, was an Indian kingdom from c. 1729 until 1949. It was ruled by the Travancore Royal Family from Padmanabhapuram, and later Thiruvananthapuram. At ...
built the Kollam–Sengottai branch line, Quilon-Madras rail line jointly with the South Indian Railway Company and the Madras Presidency
The Madras Presidency, or the Presidency of Fort St. George, also known as Madras Province, was an administrative subdivision (presidency) of British India. At its greatest extent, the presidency included most of southern India, including the ...
. The Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway was founded on 1 January 1908 by merging the Madras Railway and the Southern Mahratta Railway.
On 14 April 1951, the Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway, the South Indian Railway, and the Mysore State Railway were merged to form the Southern Railway (India), Southern Railway, in the Southern Railway zone, first zone of Indian Railways. The South Central Railway zone, South Central zone was created on 2 October 1966 as the ninth zone of Indian Railways and the South Western Railway zone, South Western zone was created on 1 April 2003. Most of the region is covered by the three zones, with small portions of the coasts covered by East Coast Railway zone, East Coast Railway and Konkan Railway, In 2019, the Government of India announced the formation of the South Coast Railway zone in the southeast, with headquarters at Visakhapatnam.
Rapid transit, Metro rail is operated by Namma Metro in Bangalore, Chennai Metro in Chennai, Kochi Metro in Kochi and Hyderabad Metro in Hyderabad. Chennai MRTS provides suburban rail services in Chennai and was the first elevated railway line in India. Hyderabad Hyderabad Multi-Modal Transport System, MMTS provides the suburban rail services in the city of Hyderabad.
The Nilgiri Mountain Railway is a UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
.
Air
Quilon Aerodrome at Kollam, was established under the kingdom ofTravancore
The Kingdom of Travancore ( /ˈtrævənkɔːr/), also known as the Kingdom of Thiruvithamkoor, was an Indian kingdom from c. 1729 until 1949. It was ruled by the Travancore Royal Family from Padmanabhapuram, and later Thiruvananthapuram. At ...
in 1920, but it was closed in 1932. In March 1930, a discussion initiated by pilot G. Vlasto led to the founding of the Madras Flying Club, which became a pioneer in pilot training in South India. On 15 October 1932, Indian aviator J. R. D. Tata flew a De Havilland Puss Moth, Puss Moth aircraft carrying mail from Karachi airport, Karachi to Juhu aerodrome, Bombay; and the aircraft continued to Madras, piloted by Neville Vincent, a former Royal Air Force pilot and friend of Tata. Kannur
Kannur (), formerly known in English as Cannanore, is a city and a municipal corporation in the state of Kerala, India. It is the administrative headquarters of the Kannur district and situated north of the major port city and commercial hu ...
had an airstrip used for commercial aviation as early as 1935 when Tata Group, Tata airlines operated weekly flights between Mumbai and Thiruvananthapuram
Thiruvananthapuram (; ), also known by its former name Trivandrum (), is the capital of the Indian state of Kerala. It is the most populous city in Kerala with a population of 957,730 as of 2011. The encompassing urban agglomeration populati ...
– stopping at Goa
Goa () is a state on the southwestern coast of India within the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan highlands by the Western Ghats. It is located between the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north and Karnataka to the ...
and Kannur. Chennai International Airport and Trivandrum International Airport, both inaugurated in 1932 and now managed by the Airport Authority of India, are among the oldest existing airports in South India.
There are 11 international airports, 2 customs airports, 15 domestic airports, and 11 air bases in South India. Kempegowda International Airport, Bengaluru, Chennai International Airport, Chennai, Rajiv Gandhi International Airport, Hyderabad, and Cochin International Airport, Kochi international airports are amongst the 10 busiest in the country. Chennai International Airport serves as the Southern Regional Headquarters of the Airports Authority of India, the Southern Region comprising the states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, and the union territories of Puducherry and Lakshadweep.
The Southern Air Command, Indian Air Force, Southern Air Command of the Indian Air Force is headquartered at Thiruvananthapuram
Thiruvananthapuram (; ), also known by its former name Trivandrum (), is the capital of the Indian state of Kerala. It is the most populous city in Kerala with a population of 957,730 as of 2011. The encompassing urban agglomeration populati ...
, and the Training Command, Indian Air Force, Training Command is headquartered at Bangalore, Bengaluru. The Air Force operates eleven air bases in Southern India including two in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. In the region, the Indian Navy operates airbases at INS Garuda, Kochi, INS Rajali, Arakkonam, INS Parundu, Uchipuli, INS Dega, Vizag, INS Baaz, Campbell Bay, and INS Kohassa, Diglipur.

 Restricted international airport
Restricted international airport
Water
A total of 89 ports are situated along the southern seacoast: Andaman and Nicobar (23), Kerala (17), Tamil Nadu (15), Andhra Pradesh (12), Karanataka(10), Lakshadweep (10), Pondicherry (2). Major ports include those at Visakhapatnam Port, Visakhapatnam, Chennai Port, Chennai, New Mangalore Port, Mangalore, Tuticorin Port, Tuticorin, Ennore Port, Ennore, Kakinada Port, Kakinada, and Cochin Port Trust, Kochi. The Kerala backwaters are a network of interconnected canals, rivers, lakes, and inlets, a labyrinthine system formed by more than 900 km of waterways. In the midst of this landscape, there are a number of towns and cities, which serve as the starting and endpoints of transportation services and backwater cruises. Vizhinjam International Seaport also called The Port of Trivandrum is a mother port under construction on the Arabian Sea at Vizhinjam in Trivandrum, India. Once completed, it is estimated that this port will handle over 40% of India's transshipments, thereby reducing the country's reliance on ports at Dubai, Colombo, and Singapore.
The Eastern Naval Command and Southern Naval Command of the Indian Navy are headquartered at Visakhapatnam Port, Visakhapatnam and Cochin Port, Kochi, respectively. In the region, the Indian Navy has its major operational bases at Visakhapatnam, Chennai, Kochi, Karwar, and Kavaratti.
The Kerala backwaters are a network of interconnected canals, rivers, lakes, and inlets, a labyrinthine system formed by more than 900 km of waterways. In the midst of this landscape, there are a number of towns and cities, which serve as the starting and endpoints of transportation services and backwater cruises. Vizhinjam International Seaport also called The Port of Trivandrum is a mother port under construction on the Arabian Sea at Vizhinjam in Trivandrum, India. Once completed, it is estimated that this port will handle over 40% of India's transshipments, thereby reducing the country's reliance on ports at Dubai, Colombo, and Singapore.
The Eastern Naval Command and Southern Naval Command of the Indian Navy are headquartered at Visakhapatnam Port, Visakhapatnam and Cochin Port, Kochi, respectively. In the region, the Indian Navy has its major operational bases at Visakhapatnam, Chennai, Kochi, Karwar, and Kavaratti.
Economy


 After independence, the economy of South India conformed to a socialism, socialist framework, with strict governmental control over private sector participation, foreign trade, and foreign direct investment. From 1960 to 1990, the South Indian economies experienced mixed economic growth. In the 1960s, Kerala achieved above-average growth while Andhra Pradesh's economy declined. Kerala experienced an economic decline in the 1970s while the economies of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Andhra Pradesh consistently exceeded national average growth rates, due to Economic reforms in India, reform-oriented economic policies. As of March 2015, there are 109 operational Special Economic Zones in South India, which is about 60% of the country's total. As of 2019–20, the total gross domestic product of the region is ₹67 trillion (US$946 billion).
After independence, the economy of South India conformed to a socialism, socialist framework, with strict governmental control over private sector participation, foreign trade, and foreign direct investment. From 1960 to 1990, the South Indian economies experienced mixed economic growth. In the 1960s, Kerala achieved above-average growth while Andhra Pradesh's economy declined. Kerala experienced an economic decline in the 1970s while the economies of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Andhra Pradesh consistently exceeded national average growth rates, due to Economic reforms in India, reform-oriented economic policies. As of March 2015, there are 109 operational Special Economic Zones in South India, which is about 60% of the country's total. As of 2019–20, the total gross domestic product of the region is ₹67 trillion (US$946 billion). Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a States and union territories of India, state in southern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, tenth largest Indian state by area and the List of states and union territories of India ...
has the List of Indian states by GDP, second-highest GDP and is the second-most industrialised state in the country after Maharashtra. With the presence of two major ports, an international airport, and a converging road and rail networks, Chennai is referred to as the "Gateway of South India."
 Over 48% of South India's population is engaged in agriculture, which is largely dependent on seasonal monsoons. Frequent droughts have left farmers debt-ridden, forcing them to sell their livestock and sometimes to commit suicide. Some of the main crops cultivated in South India include Paddy field, paddy, sorghum, pearl millet, pulses, Finger millet, ragi, sugarcane, mangoes, chile pepper, chilli, and cotton. The staple food is rice; the delta regions of Godavari,
Over 48% of South India's population is engaged in agriculture, which is largely dependent on seasonal monsoons. Frequent droughts have left farmers debt-ridden, forcing them to sell their livestock and sometimes to commit suicide. Some of the main crops cultivated in South India include Paddy field, paddy, sorghum, pearl millet, pulses, Finger millet, ragi, sugarcane, mangoes, chile pepper, chilli, and cotton. The staple food is rice; the delta regions of Godavari, Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is one ...
, and Kaveri River, Kaveri are among the top rice producing areas in the country. Areca nut, coffee, tea, turmeric and other spices, and rubber are cultivated in the hills, the region accounting for 92% of the total coffee production in India. Other major agricultural products include poultry and silk.
South India's urban centres are significant contributors to the Indian and global economy. According to the Globalization and World Cities Research Network, Bengaluru, Chennai, and Hyderabad are the South Indian cities most integrated with the global economy. Bengaluru is classified as an Global city, alpha world city, while Chennai and Hyderabad are beta world cities.
Bengaluru, Chennai, Hyderabad, Coimbatore, Visakhapatnam, and Thiruvananthapuram are amongst the major information technology (IT) hubs of India, with Bengaluru known as the Silicon Valley of India.
*
*
* The presence of these hubs has spurred economic growth and attracted foreign investments and job seekers from other parts of the country. Software exports from South India grossed over in fiscal 2005–06.
Salem Steel Plant (SSP), a unit of Steel Authority of India, Steel Authority of India Limited (SAIL), is a Steel mill, steel plant involved in the production of stainless steel. It is located along the Salem, Tamil Nadu, Salem — Bangalore National Highway 44 (India), National Highway 44 in the foothills of Kanjamalai in Salem district, Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a States and union territories of India, state in southern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, tenth largest Indian state by area and the List of states and union territories of India ...
, India. The plant has an installed capacity of 70,000 tonnes per annum in its cold rolling mill and 3,64,000 tonnes per annum in the hot rolling mill. It also has the country's first stainless steel blanking facility.
Chennai, known as the "Detroit of Asia", accounts for about 35% of India's overall automotive components and automobile output. Coimbatore supplies two-thirds of India's requirements of motors and pumps, and is one of the largest exporters of wet grinders and Automobile, auto components, as well as jewellery. Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
is emerging as another automobile manufacturing hub.
Another major industry is textiles with the region being home to nearly 60% of the fiber textile mills in India.
Tourism in India, Tourism contributes significantly to the GDP of the region, with three states – Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, and Telangana – among the top 10 states for tourist arrivals, accounting for more than 50% of domestic tourist visits.
Demographics
 As per the 2011 census of India, the estimated population of South India was 252 million, around one fifth of the total population of the country. The region's total fertility rate (TFR) was less than the Sub-replacement fertility, population replacement level of 2.1 for all states, with Kerala and Tamil Nadu having the lowest TFRs in India at 1.7. As a result, from 1981 to 2011 the proportion of the population of South India to India's total population has declined. The population density of the region is approximately 463 per square kilometer. Scheduled Castes and Tribes form 18% of the population of the region. Agriculture is the major employer in the region, with 47.5% of the population being involved in agrarian activities. About 60% of the population lives in permanent housing structures. 67.8% of South India has access to tap water, with wells and springs being major sources of water supply.
After experiencing fluctuations in the decades immediately after the independence of India, the economies of South Indian states have, over the past three decades, registered growth higher than the national average. While South Indian states have improved in some of the
As per the 2011 census of India, the estimated population of South India was 252 million, around one fifth of the total population of the country. The region's total fertility rate (TFR) was less than the Sub-replacement fertility, population replacement level of 2.1 for all states, with Kerala and Tamil Nadu having the lowest TFRs in India at 1.7. As a result, from 1981 to 2011 the proportion of the population of South India to India's total population has declined. The population density of the region is approximately 463 per square kilometer. Scheduled Castes and Tribes form 18% of the population of the region. Agriculture is the major employer in the region, with 47.5% of the population being involved in agrarian activities. About 60% of the population lives in permanent housing structures. 67.8% of South India has access to tap water, with wells and springs being major sources of water supply.
After experiencing fluctuations in the decades immediately after the independence of India, the economies of South Indian states have, over the past three decades, registered growth higher than the national average. While South Indian states have improved in some of the socio-economic
Socioeconomics (also known as social economics) is the social science that studies how economic activity affects and is shaped by social processes. In general it analyzes how modern societies progress, stagnate, or regress because of their local ...
metrics, poverty continues to affect the region as it does the rest of the country, although it has considerably decreased over the years. Based on the 2011 census, the HDI
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, wh ...
in the southern states is high, and the economy has grown at a faster rate than those of most northern states.
As per the 2011 census, the average literacy rate in South India is approximately 80%, considerably higher than the Indian national average of 74%, with Kerala having the highest literacy rate of 93.91%. South India has the highest human sex ratio, sex ratio with Kerala and Tamil Nadu being the top two states. The South Indian states rank amongst the top 10 in Indian states ranked by economic freedom, economic freedom, List of Indian states by life expectancy at birth, life expectancy, Indian states ranking by drinking water, access to drinking water, Indian states ranking by families owning house, house ownership, and Indian states ranking by television ownership, TV ownership. The Poverty in India, poverty rate is at 19% while that in the other Indian states is at 38%. The per capita income is , which is more than double of the other Indian states (). Of the three demographically related targets of the Millennium Development Goals set by the United Nations and expected to be achieved by 2015, Kerala and Tamil Nadu achieved the goals related to improvement of maternal health and of reducing infant mortality and child mortality by 2009.
Languages
 The largest linguistic group in South India is the Dravidian family of languages, of approximately 73 languages. The major languages spoken include
The largest linguistic group in South India is the Dravidian family of languages, of approximately 73 languages. The major languages spoken include Telugu
Telugu may refer to:
* Telugu language, a major Dravidian language of India
*Telugu people, an ethno-linguistic group of India
* Telugu script, used to write the Telugu language
** Telugu (Unicode block), a block of Telugu characters in Unicode
S ...
, Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
* Tamils, an ethnic group native to India and some other parts of Asia
**Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka also called ilankai tamils
**Tamil Malaysians, Tamil people native to Malaysia
* Tamil language, nativ ...
, Kannada
Kannada (; ಕನ್ನಡ, ), originally romanised Canarese, is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by the people of Karnataka in southwestern India, with minorities in all neighbouring states. It has around 47 million native s ...
, and Malayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of 22 scheduled languages of India. Malayalam was des ...
. Tulu language, Tulu is spoken by about 1.5 million people in coastal Kerala and Karnataka; Konkani language, Konkani, an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language, is spoken by around 0.8 million people in the Konkan coast (Canara) and Kerala; Kodava language, Kodava Takk is spoken by more than half a million people in Kodagu, Mysore, and Bangalore. English is also widely spoken in urban areas of South India. Deccani Urdu
Deccani (also known as Deccani Urdu and Deccani Hindi). https://knowledgehubadda.blogspot.com/2022/02/blog-post_74.html? m=1 or Dakni, Dakhni, Dakhini, Dakkhani and Dakkani (, ''dekanī'' or , ''dakhanī''), is a variety of Hindustani spoken ...
is spoken by around 12 million Indian Muslims, Muslims in southern India. Telugu, Tamil, Kannada, Malayalam, Konkani, and Deccani Urdu are listed among the 22 official languages of India as per the Official Languages Act (1963). Tamil was the first language to be granted Classical language in India, classical language status by the Government of India in 2004. Other major languages declared classical are Kannada (in 2008), Telugu
Telugu may refer to:
* Telugu language, a major Dravidian language of India
*Telugu people, an ethno-linguistic group of India
* Telugu script, used to write the Telugu language
** Telugu (Unicode block), a block of Telugu characters in Unicode
S ...
(in 2008), and Malayalam (in 2013) These four languages have literary outputs larger than other literary languages of India.
Religion
Evidence of prehistoric religion in South India comes from scattered Mesolithic rock paintings depicting dances and rituals, such as the Kupgal petroglyphs of eastern Karnataka, at South Asian Stone Age, Stone Age sites. Hinduism is the major religion today in South India, with about 84% of the population adhering to it, which is often regarded as the oldest religion in the world, tracing its roots to prehistoric times in India. Its spiritual traditions include both the Shaivism, Shaivite and Vaishnavism, Vaishnavite branches of Hinduism, although Buddhist and Jainism, Jain philosophies were influential several centuries earlier. Ayyavazhi has spread significantly across the southern parts of South India. Shaiva Siddhanta philosophy is prominent among many communities. Shaivism developed as an amalgam of pre-Vedic religions and traditions derived from the southern Tamils, Tamil Dravidian Shaiva Siddhanta traditions and philosophies, which were assimilated in the non-Vedic Shiva-tradition. The religious history of South India is influenced by Hinduism quite notably during the medieval century. The twelve Azhwars, Alvars (saint-poets of Vaishnavite tradition) and sixty-three Nayanars (saint poets of Shaivite tradition) are regarded as exponents of the ''bhakti'' tradition of Hinduism in South India. Most of them came from the Tamil region and the last of them lived in the 9th century CE. About 11% of the population follow Islam, which was introduced to South India in the early 7th century by Arab traders on the Malabar Coast, and spread during the rule of the Deccan Sultanates, from the 17th to 18th centuries. Muslims of Arab descent in Kerala are called Jonaka Mappila. About 4% follow Christianity. According to tradition, Christianity was introduced to South India by Thomas the Apostle, who visited Muziris in Kerala in 52 CE and proselytized natives, who are called Saint Thomas Christians, Nazrani Mappila. Kerala is also home to one of the oldest Jewish communities in the world, who are supposed to have arrived on the Malabar coast during the reign of Biblical account of King Solomon, King Solomon.Administration
South India consists of the five southern Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu, as well as the union territories of Puducherry, and Lakshadweep. Puducherry and the five states each have an elected state government, while Lakshadweep is Government of India, centrally administered by the president of India. Each state is headed by a Governor (India), Governor who is appointed by the President of India and who names the leader of the state legislature's ruling party or coalition government, coalition as chief minister, who is the head of the state government. Each state or territory is further divided into Districts of India, districts, which are further subdivided into revenue divisions and ''taluk''s / ''Mandal''s or ''tehsil''s. Local bodies govern respective cities, towns, and villages, along with an elected mayor, municipality, municipal chairman, or panchayat, panchayat chairman, respectively.States
* Andhra Pradesh was divided into two states, Telangana and a residual Andhra Pradesh on 2 June 2014. Hyderabad, India, Hyderabad, located entirely within the borders of Telangana, is to serve as joint capital for both states for a period of time not exceeding ten years.Union territories
Legislative representation
South India elects 132 Member of Parliament (India), members to the Lok Sabha, accounting for roughly one-fourth of the total strength. The region is allocated 58 seats in the Rajya Sabha, out of the total of 245. The Legislative Assembly, state legislatures of Tamil Nadu, Kerala and Puducherry are unicameral legislature, unicameral, while Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, and Telangana have bicameral legislature, bicameral legislatures. States with bicameral legislatures have an upper house (Legislative Council) with members not more than one-third the size of the Assembly. State legislatures elect members for terms of five years. Governors may suspend or dissolve assemblies and can administer when no party is able to form a government.Politics
Politics in South India is characterized by a mix of regional and national political parties. The Justice Party (India), Justice Party and Swaraj Party were the two major parties in the erstwhile Madras Presidency. The Justice Party eventually lost the 1937 Madras Presidency legislative assembly election, 1937 elections to the Indian National Congress, and Chakravarti Rajagopalachari became the Chief Minister of the Madras Presidency. During the 1920s and 1930s, the Self-Respect Movement, spearheaded by Theagaroya Chetty and E. V. Ramaswamy (commonly known as Periyar), emerged in the Madras Presidency. In 1944, Periyar transformed the party into a social organisation, renaming the party Dravidar Kazhagam, and withdrew from electoral politics. The initial aim was the secession of Dravida Nadu from the rest of India upon Indian independence. After independence, C. N. Annadurai, a follower of Periyar, formed the Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam (DMK) in 1948. The Anti-Hindi agitations of Tamil Nadu led to the rise of Dravidian parties that formed Tamil Nadu's first government, in 1967. In 1972, a split in the DMK resulted in the formation of the All India Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam (AIADMK) led by M. G. Ramachandran. Dravidian parties continue to dominate Tamil Nadu electoral politics, the national parties usually aligning as junior partners to the major Dravidian parties, AIADMK and DMK. Indian National Congress dominated the political scene in Tamil Nadu in the 1950s and 1960s under the leadership of K. Kamaraj, who led the party after the death of Jawaharlal Nehru and ensured the selection of Prime Ministers Lal Bahadur Shastri and Indira Gandhi. Congress continues to be a major party in Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, and Kerala. The party ruled with minimal opposition for 30 years in Andhra Pradesh, before the formation of the Telugu Desam Party by Nandamuri Taraka Rama Rao in 1982. Two prominent coalitions in Kerala are the United Democratic Front (India), United Democratic Front, led by the Indian National Congress, and the Left Democratic Front (Kerala), Left Democratic Front, led by the Communist Party of India (Marxist). For the past fifty years, these two coalitions have been alternately in power; and E. M. S. Namboodiripad, the first elected chief minister of Kerala in 1957, is credited as the leader of the first democratically elected communist government in the world. The Bharatiya Janata Party and Janata Dal (Secular) are significant parties in Karnataka. C. Rajagopalachari, the first Indian Governor General of India post independence, was from South India. The region has produced six Indian presidents, namely, Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan, V. V. Giri, Neelam Sanjiva Reddy, R. Venkataraman, K. R. Narayanan, and APJ Abdul Kalam. Prime Minister of India, Prime ministers P. V. Narasimha Rao and H. D. Deve Gowda were from the region.Culture and heritage
Clothing
South Indian women traditionally wear a ''sari'', a garment that consists of a drape varying from to in length and to in breadth that is typically wrapped around the waist, with one end draped over the shoulder, baring the midriff, as according to Indian philosophy, the navel is considered as the source of life and creativity. Ancient Tamil poetry, such as the ''Silappadhikaram'', describes women in exquisite drapery or sari. Madisar is a typical style worn by Brahmin women from Tamil Nadu. Women wear colourful silk sarees on special occasions such as marriages. The men wear a ''dhoti'', a long, white rectangular piece of non-stitched cloth often bordered in brightly coloured stripes. It is usually wrapped around the waist and the legs and knotted at the waist. A colourful ''lungi'' with typical batik patterns is the most common form of male attire in the countryside. People in urban areas generally wear tailored clothing, and western dress is popular. Western-style school uniforms are worn by both boys and girls in schools, even in rural areas.Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South ...
, during the 11th century, where the cloth was known as ''Chaliyan''. The raw fabric was dyed and printed in bright hues, and Chintz, calico prints later became popular in the Europe.
Cuisine
 Coconut is native to Southern India and spread to Europe, Arabia, and Persia through the southwestern
Coconut is native to Southern India and spread to Europe, Arabia, and Persia through the southwestern Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is the southwestern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing m ...
of South India over the centuries. Coconut of Indian origin was brought to the Americas by Portuguese merchants. Black pepper is also native to the Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is the southwestern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing m ...
of India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, and the Malabar pepper is extensively cultivated there. During classical era, Phoenicians
Phoenicia () was an ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient thalassocracy, thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-st ...
, Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
, Egyptians, Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
, and Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
were attracted by the spices including Cinnamon and Black pepper from the ancient port of Muziris
Muziris ( grc, Μουζιρίς, Old Malayalam: ''Muciri'' or ''Muciripattanam'' possibly identical with the medieval ''Muyirikode'') was an ancient harbour and an urban centre on the Malabar Coast. Muziris found mention in the ''Periplus of ...
in the Malabar coast, southwestern coast of India.
During Middle Ages prior to the Age of Discovery which began with the end of the 15th century CE, the kingdom of Kozhikode, Calicut (Kozhikode) on Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is the southwestern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing m ...
was the centre of Indian black pepper, pepper exports to the Red Sea and Europe at this time''Foundations of the Portuguese empire, hi lo millo1415–1580'' Bailey Wallys Diffie p.234''ff'/ref> with Egyptian and Arab traders being particularly active. The Thalassery cuisine, a style of cuisine originated in the Malabar District, Northern Kerala over centuries, makes use of such spices.
Music and dance
The traditional music of South India is known as Carnatic music, which includes rhythmic and structured music by composers such as Purandara Dasa, Kanaka Dasa, Tyagayya, Annamacharya, Bhadrachala Ramadasu, Baktha Ramadasu, Muthuswami Dikshitar, Shyama Shastri, Kshetrayya, Mysore Vasudevachar, and Swathi Thirunal. The main instrument that is used in South Indian Hindu temples is the ''nadaswaram'', a reed instrument that is often accompanied by the thavil, a type of drum instrument. South India is home to several distinct dance forms such as Bharata Natyam, Bharatanatyam, Kuchipudi, Andhra Natyam, Kathakali, Kerala Natanam, Koodiyattam, Margamkali, Mohiniaattam, Oppana, Ottamthullal, Theyyam, Vilasini Natyam, and Yakshagana. The dance, clothing, and sculptures of South India exemplify the beauty of the body and motherhood.Cinema
Films done in regional languages are prevalent in Cinema of South India, South India, with several regional cinemas being recognized: Kannada cinema (Karnataka), Malayalam cinema (Kerala), Tamil cinema (Tamil Nadu), and Telugu cinema (Andhra Pradesh and Telangana). The first silent film in South India, ''Keechaka Vadham'', was made by R. Nataraja Mudaliar in 1916. Mudaliar also established Madras's first film studio. The first Tamil talkie, ''Kalidas (film), Kalidas'', was released on 31 October 1931, barely seven months after India's first talking picture, ''Alam Ara''. Swamikannu Vincent built the first cinema studio of South India, at Coimbatore, introducing the "tent cinema", which he first established in Madras and which was known as "Edison's Grand Cinemamegaphone". Filmmakers K Balachandar, Balu Mahendra, Bharathiraaja, and Mani Ratnam in Tamil cinema; Adoor Gopalakrishnan, Shaji N. Karun, John Abraham (director), John Abraham, and G. Aravindan in Malayalam cinema; Girish Kasaravalli , Girish Karnad and P. Sheshadri in Kannada cinema; and K. N. T. Sastry and B. Narsing Rao in Telugu cinema produced realistic cinema in parallel with each other throughout the 1970s. South Indian cinema has also Tamil cinema and Dravidian politics, had an influence on politics of Tamil Nadu. Prominent film personalities such as C N Annadurai, M G Ramachandran, M Karunanidhi, N. T. Rama Rao, and Jayalalithaa have become chief ministers of South Indian states. As of 2014, South Indian film industries contribute to 53% of the total films produced in India.Literature
 South India has an independent literary tradition dating back over 2500 years. The first known literature of South India is the poetic Sangam literature, which was written in
South India has an independent literary tradition dating back over 2500 years. The first known literature of South India is the poetic Sangam literature, which was written in Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
* Tamils, an ethnic group native to India and some other parts of Asia
**Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka also called ilankai tamils
**Tamil Malaysians, Tamil people native to Malaysia
* Tamil language, nativ ...
2500 to 2100 years ago. Tamil literature was composed in three successive poetic assemblies known as Tamil Sangams, the earliest of which, according to ancient tradition, were held on a now vanished Kumari Kandam, continent far to the south of India. This Tamil literature includes the oldest grammatical treatise, ''Tholkappiyam'', and the epics ''Silappatikaram'' and ''Manimekalai''. References to Kannada literature appear from the fourth century CE. Telugu literature inscriptions. Poets such as Annamacharya made many contributions to this literature. A distinct Malayalam literature came about in the 13th century.
Architecture
South India has two distinct styles of rock architecture, the ''Dravidian architecture, Dravidian'' style of Tamil Nadu and the ''Vesara'' style of Karnataka. ''Koil'', Hindu temple architecture, Hindu temples of the Dravidian style, consist of porches or ''mantapas'' preceding the door leading to the sanctum. Monumental, ornate gate-pyramids, or ''gopurams'' – each topped by a ''kalasam'', or stone finial – are the principal features in the quadrangular enclosures that surround the more notable temples along with pillared halls. A South Indian temple typically has a Temple tank, water reservoir called the ''Kalyani'' or ''Pushkarni''. The origins of the ''gopuram'' can be traced back to early structures of the Pallavas. Under the Pandya rulers in the twelfth century, gateways had become the dominant feature of a temple's outer appearance, eventually overshadowing the inner sanctuary which became obscured from view by the ''gopuram''s colossal size. The Architecture of Kerala is a unique architecture that emerged in the Malabar Coast, southwestern part of India, which is in its striking contrast to Dravidian architecture, which is normally practised in other parts of South India. It has been performed/followed according to Indian Vedic architectural science (''Vastu Shastra'').Notes
References
External links
{{Authority control South India, Peninsulas of India Regions of India South Asia Landforms of Andhra Pradesh Landforms of Kerala Landforms of Karnataka Landforms of Tamil Nadu Landforms of Telangana Landforms of Lakshadweep Landforms of Puducherry