|
Haemosporidiasina
Haemosporidiasina (Haemosporidia) is a subclass of apicomplexans described by Jacques Euzéby in 1988.Euzéby, J. (1988) Comparative Medical Protozoology, Vol. 3: Apicomplexa, 2: Haemosporidioses, Part 1: Plasmodiids, Haemoproteids, "Piroplasms" (general characters) The taxon is very similar to Aconoidasida. Taxonomy Haemosporidiasina is divided into 2 orders: Order Chromatorida (with pigmented intraerythrocytic parasites) Suborder Laveraniina *Family Plasmodiidae ** Genus ''Bioccala'' Landau ''et al'' 1984 ** Genus '' Biguetiella'' Landau ''et al'' 1984 ** Genus ''Billbraya'' Paperna & Landau 1990 ** Genus '' Dionisia'' Landau ''et al'' 1980 ** Genus ''Hepatocystis'' Miller 1908 ** Genus '' Mesnilium'' Misra, Haldar & Chakravarty 1972 ** Genus ''Nycteria'' Garnham and Heisch 1953 ** Genus ''Plasmodium'' Marchiafava & Celli 1885 ** Genus ''Polychromophilus'' Landau ''et al'' 1984 ** Genus ''Rayella'' Dasgupta 1967 ** Genus ''Saurocytozoon'' Lainson & Shaw 1969 ** Genus ''Ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achromatorida
Achromatorida is an order (biology), order of non-pigmented intraerythrocytic parasitic alveolates belonging to the subclass Haemosporidiasina. The order was created by Jacques Euzéby in 1988. The taxonomy of these organisms has been one of some controversy. Weylon in 1926 grouped many of these genera into the genus ''Babesia'' - given what is now known about these genera this was probably an error. Agreement on the organisation of these genera probably cannot be regarded as being settled. Description These are minute rounded or pyriform parasites found within erythrocytes, or other circulating or endothelial cells of vertebrates. The parasites reproduce by Protozoal merogony, merogony without oocysts or spores. The apical complex has a polar ring and rhoptries. A conoid (organelle), conoid is lacking and most species lack the associated pellicular microtubules. Flagellae are lacking. The trophozoite stage is separated from erythrocyte by single membrane (in the other groups ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apicomplexa
The Apicomplexa (also called Apicomplexia) are a large phylum of parasitic alveolates. Most of them possess a unique form of organelle that comprises a type of non-photosynthetic plastid called an apicoplast, and an apical complex structure. The organelle is an adaptation that the apicomplexan applies in penetration of a host cell. The Apicomplexa are unicellular and spore-forming. All species are obligate endoparasites of animals, except '' Nephromyces'', a symbiont in marine animals, originally classified as a chytrid fungus. Motile structures such as flagella or pseudopods are present only in certain gamete stages. The Apicomplexa are a diverse group that includes organisms such as the coccidia, gregarines, piroplasms, haemogregarines, and plasmodia. Diseases caused by Apicomplexa include: * Babesiosis (''Babesia'') * Malaria (''Plasmodium'') * Cryptosporidiosis (''Cryptosporidium parvum'') * Cyclosporiasis (''Cyclospora cayetanensis'') * Cystoisosporiasis (''Cystoisosp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apicomplexa
The Apicomplexa (also called Apicomplexia) are a large phylum of parasitic alveolates. Most of them possess a unique form of organelle that comprises a type of non-photosynthetic plastid called an apicoplast, and an apical complex structure. The organelle is an adaptation that the apicomplexan applies in penetration of a host cell. The Apicomplexa are unicellular and spore-forming. All species are obligate endoparasites of animals, except '' Nephromyces'', a symbiont in marine animals, originally classified as a chytrid fungus. Motile structures such as flagella or pseudopods are present only in certain gamete stages. The Apicomplexa are a diverse group that includes organisms such as the coccidia, gregarines, piroplasms, haemogregarines, and plasmodia. Diseases caused by Apicomplexa include: * Babesiosis (''Babesia'') * Malaria (''Plasmodium'') * Cryptosporidiosis (''Cryptosporidium parvum'') * Cyclosporiasis (''Cyclospora cayetanensis'') * Cystoisosporiasis (''Cystoisosp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aconoidasida
The Aconoidasida are a class of apicomplexan parasites created by Mehlhorn ''et al'' in 1980. Description Organisms in this class bear a tip at one end of their outer membrane. This apical complex includes vesicles called rhoptries and micronemes, which open at the anterior of the cell. These secrete enzymes that allow the parasite to enter other cells. The tip is surrounded by a band of microtubules, called the polar ring. As the name indicates, Aconoidasida (from Greek: negative prefix ''a-'' = "lacking") lack a conoid (they do have one only during the ookinete stage) in contrast to the class Conoidasida which have one throughout their life cycle. See also *Haemosporidiasina Haemosporidiasina (Haemosporidia) is a subclass of apicomplexans described by Jacques Euzéby in 1988.Euzéby, J. (1988) Comparative Medical Protozoology, Vol. 3: Apicomplexa, 2: Haemosporidioses, Part 1: Plasmodiids, Haemoproteids, "Piroplasms" ... References Alveolata classes {{Api ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryota
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the Three-domain system, three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard (archaea), Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass (ecology), biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated phagotrophs. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haemoproteidae
The Haemoproteidae are a family of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa.Euzéby J (1988) Comparative Medical Protozoology, Vol. 3: Apicomplexa, 2: Haemosporidioses, Part 1: Plasmodiids, Haemoproteids, Piroplasms (general characters The species in this family produce pigment and do not have an asexual cycle in the blood. Taxonomy The genera in this family are: * Genus '' Johnsprentia'' Landau, Chavatte & Beveridge, 2012 * Genus '' Haemocystidium'' Castellani and Willey, 1904, emend. Telford, 1996 * Genus ''Haemoproteus ''Haemoproteus'' is a genus of alveolates that are parasitic in birds, reptiles and amphibians. Its name is derived from Greek: ''Haima'', "blood", and ''Proteus'', a sea god who had the power of assuming different shapes. The name ''Haemoprot ...'' Kruse, 1890 ** Subgenus ''Parahaemoproteus'' Bennett ''et al.'', 1965 ** Subgenus ''Haemoproteus'' * Genus '' Paleohaemoproteus'' Poinar and Telford, 2005 * Genus '' Sprattiella'' Landau ''et al.'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polychromophilus
The genus ''Polychromophilus'' consists of obligate intracellular eukaryotic Parasitism, parasites that infect bats from every continent except Antarctica. They are transmitted by bat flies, which act as an insect vector as well as the parasite’s site of Apicomplexan life cycle, sporogeny. ''Polychromophilus'' follows a fairly typical Haemosporida, Haemospororidian lifecycle, with gametocytes and gametes restricted to the bloodstream of the host and meronts infecting organs – most notably the lungs and the liver. The type species is ''Polychromophilus melanipherus'', and was described by Dionisi in 1898. Taxonomy ''Polychromophilus'' was first described by Dionisi in 1898, who also differentiated between the first two species, ''Polychromophilus murinus'' and ''Polychromophilus melanipherus''. Both of these original species were named after their primary hosts – ''Vespertilio murinus'' and ''Miniopterus schreibersi'' respectively. In 1906, Schingareff managed to observe and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rayella
''Rayella'' is a genus of parasitic alveolates belonging to the phylum Apicomplexia. Its vertebrate hosts are flying squirrels. The vectors are not presently known. Taxonomy This genus was described by Dasgupta in 1967. Hosts *''R. gigantica'' — spotted giant flying squirrel ('' Petaurista elegans caniceps'') *''R. hylopetei'' — particoloured flying squirrel ('' Hylopetes alboniger'') *''R. rayi'' — Himalaya The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 ...n flying squirrel ('' Petaurista magnificus'') Distribution All of the currently known species have been reported from Darjiling, India. References Apicomplexa genera Parasites of rodents Haemosporida {{Apicomplexa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saurocytozoon
''Saurocytozoon'' is a genus of parasitic alveolates. They infect reptiles and are thought to be transmitted by mosquitoes. Only two species have been described to date. Their relationship with the other members of this order is not presently clear. Description Members of this genus infect reptiles. They do not produce pigment nor do they undergo Protozoal merogony, merogony in the blood. Schizonts are found in the tissues. Gametocytes are found in the peripheral blood. They infect the leukocytes and cause gross distortion of the host cell. The gametocytes are large and round. Hosts Skinks (''Mabuya mabouya'') Tegu (''Tupinambis teguixin'') References Apicomplexa genera Parasites of lizards Parasites of Diptera Haemosporida {{Apicomplexa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
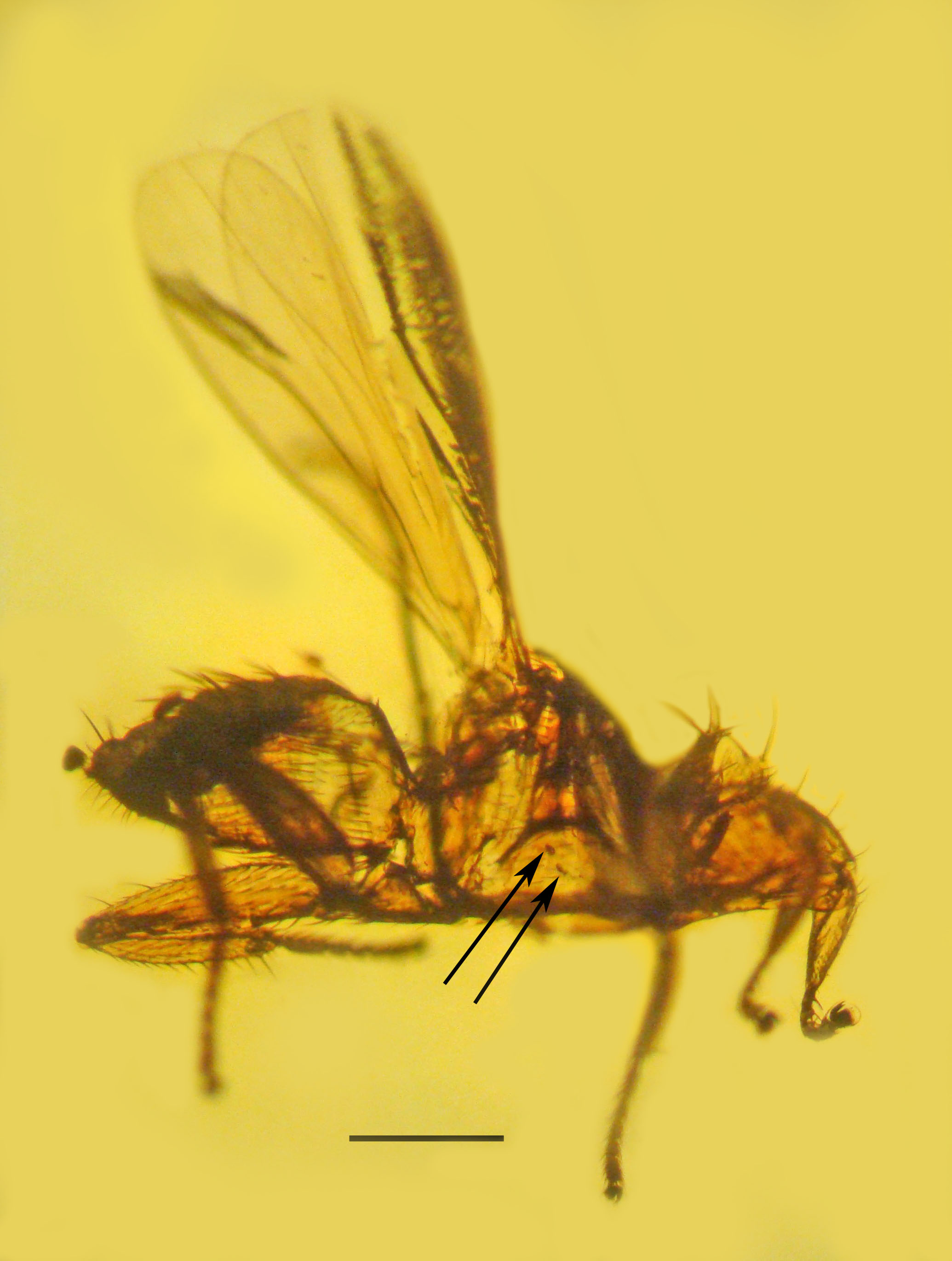
Vetufebrus
''Vetufebrus'' is an extinct genus of haemospororida in the family Plasmodiidae. At the time of its description the new genus comprised a single species ''Vetufebrus ovatus'' known from a single Miocene Dominican amber fossil found on Hispaniola. ''V. ovatus'' was vectored by ''Enischnomyia stegosoma'', the first fossil streblid bat fly described from a fossil, and the only member of the subfamily Nycterophiliinae described from Hispaniola. ''V. ovatus'' is the first instance of a Streblidae bat fly as a host for a malarial parasite. History and classification ''Vetufebrus ovatus'' was described based on a group of fossilized specimens which are preserved as in the host batfly, itself an Inclusion (mineral), inclusion in a transparent chunk of Dominican amber. The amber is fossil resin that was produced by the extinct ''Hymenaea protera'', which formerly grew on Hispaniola, across northern South America and up to southern Mexico. The amber dates from the Burdigalian stage (20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haemoproteus
''Haemoproteus'' is a genus of alveolates that are parasitic in birds, reptiles and amphibians. Its name is derived from Greek: ''Haima'', "blood", and ''Proteus'', a sea god who had the power of assuming different shapes. The name ''Haemoproteus'' was first used in the description of '' H. columbae'' in the blood of the pigeon ''Columba livia'' by Kruse in 1890. This was also the first description of this genus. Two other genera — '' Halteridium'' and '' Simondia'' — are now considered to be synonyms of ''Haemoproteus''. The protozoa are intracellular parasites that infect the erythrocytes. They are transmitted by blood sucking insects including mosquitoes, biting midges (''Culicoides''), louse flies (''Hippoboscidae'') and horse-flies (" tabanids", "tabanid flies"). Infection with this genus is sometimes known as pseudomalaria because of the parasites' similarities with ''Plasmodium'' species. Within the genus there are at least 173 species, 5 varieties and 1 subspecies. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |