|
HTTP Live Streaming
HTTP Live Streaming (also known as HLS) is an HTTP-based adaptive bitrate streaming communications protocol developed by Apple Inc. and released in 2009. Support for the protocol is widespread in media players, web browsers, mobile devices, and streaming media servers. As of 2019, an annual video industry survey has consistently found it to be the most popular streaming format. HLS resembles MPEG-DASH in that it works by breaking the overall stream into a sequence of small HTTP-based file downloads, each downloading one short chunk of an overall potentially unbounded transport stream. A list of available streams, encoded at different bit rates, is sent to the client using an extended M3U playlist. Based on standard HTTP transactions, HTTP Live Streaming can traverse any firewall or proxy server that lets through standard HTTP traffic, unlike UDP-based protocols such as RTP. This also allows content to be offered from conventional HTTP servers and delivered over widely available ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OBS Studio
OBS Studio (also Open Broadcaster Software or OBS, for short) is a free, open-source, and cross-platform screencasting and streaming app. It is available for Windows, macOS, Linux distributions, and BSD The Berkeley Software Distribution or Berkeley Standard Distribution (BSD) is a discontinued operating system based on Research Unix, developed and distributed by the Computer Systems Research Group (CSRG) at the University of California, Berk .... The OBS Project raises funds on the platforms Open Collective and Patreon. Overview OBS Studio is a free and open-source app for screencasting and live streaming. Written in C (programming language), C/C++ and built with Qt (software), Qt, OBS Studio provides real-time capture, scene composition, recording, encoding, and broadcasting via Real Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP), HTTP_Live_Streaming, HLS, SRT or Reliable_Internet_Stream_Transport, RIST. It can stream videos to any RTMP-supporting destination, including YouTube, Tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Engineering Task Force
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) is a standards organization for the Internet and is responsible for the technical standards that make up the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP). It has no formal membership roster or requirements and all its participants are volunteers. Their work is usually funded by employers or other sponsors. The IETF was initially supported by the federal government of the United States but since 1993 has operated under the auspices of the Internet Society, an international non-profit organization. Organization The IETF is organized into a large number of working groups and birds of a feather informal discussion groups, each dealing with a specific topic. The IETF operates in a bottom-up task creation mode, largely driven by these working groups. Each working group has an appointed chairperson (or sometimes several co-chairs); a charter that describes its focus; and what it is expected to produce, and when. It is open to all who want to particip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Web Server
A web server is computer software and underlying hardware that accepts requests via HTTP (the network protocol created to distribute web content) or its secure variant HTTPS. A user agent, commonly a web browser or web crawler, initiates communication by making a request for a web page or other resource using HTTP, and the server responds with the content of that resource or an error message. A web server can also accept and store resources sent from the user agent if configured to do so. The hardware used to run a web server can vary according to the volume of requests that it needs to handle. At the low end of the range are embedded systems, such as a router that runs a small web server as its configuration interface. A high-traffic Internet website might handle requests with hundreds of servers that run on racks of high-speed computers. A resource sent from a web server can be a preexisting file (static content) available to the web server, or it can be generated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adobe Flash Media Server
Adobe Media Server (AMS) is a proprietary data and media Server (computing), server from Adobe Systems (originally a Macromedia product). This server works with the Flash Player and HTML5 Run-time system, runtime to create media driven, multiuser RIAs (Rich Internet application, Rich Internet Applications). The server uses ActionScript 1, an ECMAScript based scripting language, for server-side logic. Prior to version 2, it was known as Flash Communication Server. Prior to version 5, it was known as Flash Media Server. In February 2019, Adobe Systems Incorporated granteVeriskope Incrights to further develop, resell, and extend distribution of the software product. History On March 16, 2002, Macromedia released Flash Player 6. This version included all the functionality for a yet to be released server called Flash Communication Server MX. Version 1.0 was released on 9 July 2002 and included all the basic features that make up the product, including the NetConnection, SharedObj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCTE-35
SCTE-35 (ANSI/SCTE 35 2013) is a joint ANSI/ Society of Cable and Telecommunications Engineers standard that describes the inline insertion of cue tones in mpeg-ts streams. The full standard name is "Digital Program Insertion Cueing Message for Cable." History SCTE-35 was originally used in the US to signal a local ad insertion opportunity in the transport streams, and in Europe to insert local TV programs (e.g. local news transmissions). It is now used to signal all kinds of program and ad events in linear transport streams and in newer ABR delivery formats such as HLS and DASH. Work on splicing GOP compressed video streams was started by SMPTE ST 312M Television - Splice Points for MPEG-2 Transport Streams. This standard had some basic signaling and details on how to perform seamless and near seamless splicing of compressed streams. Although it mainly worked on constant bit rate streams, and in the cable industry the digital feeds were moving to a statistical multiplex. A company ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MPEG-DASH
Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (DASH), also known as MPEG-DASH, is an adaptive bitrate streaming technique that enables high quality streaming of media content over the Internet delivered from conventional HTTP web servers. Similar to Apple's HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) solution, MPEG-DASH works by breaking the content into a sequence of small segments, which are served over HTTP. An early HTTP web server based streaming system called SProxy was developed and deployed in the Hewlett Packard Laboratories in 2006. It showed how to use HTTP range requests to break the content into small segments. SProxy shows the effectiveness of segment based streaming, gaining best Internet penetration due to the wide deployment of firewalls, and reducing the unnecessary traffic transmission if a user chooses to terminate the streaming session earlier before reaching the end. Each segment contains a short interval of playback time of content that is potentially many hours in duration, such as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Encoding
In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compression reduces bits by identifying and eliminating statistical redundancy. No information is lost in lossless compression. Lossy compression reduces bits by removing unnecessary or less important information. Typically, a device that performs data compression is referred to as an encoder, and one that performs the reversal of the process (decompression) as a decoder. The process of reducing the size of a data file is often referred to as data compression. In the context of data transmission, it is called source coding; encoding done at the source of the data before it is stored or transmitted. Source coding should not be confused with channel coding, for error detection and correction or line coding, the means for mapping data onto a signal. Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
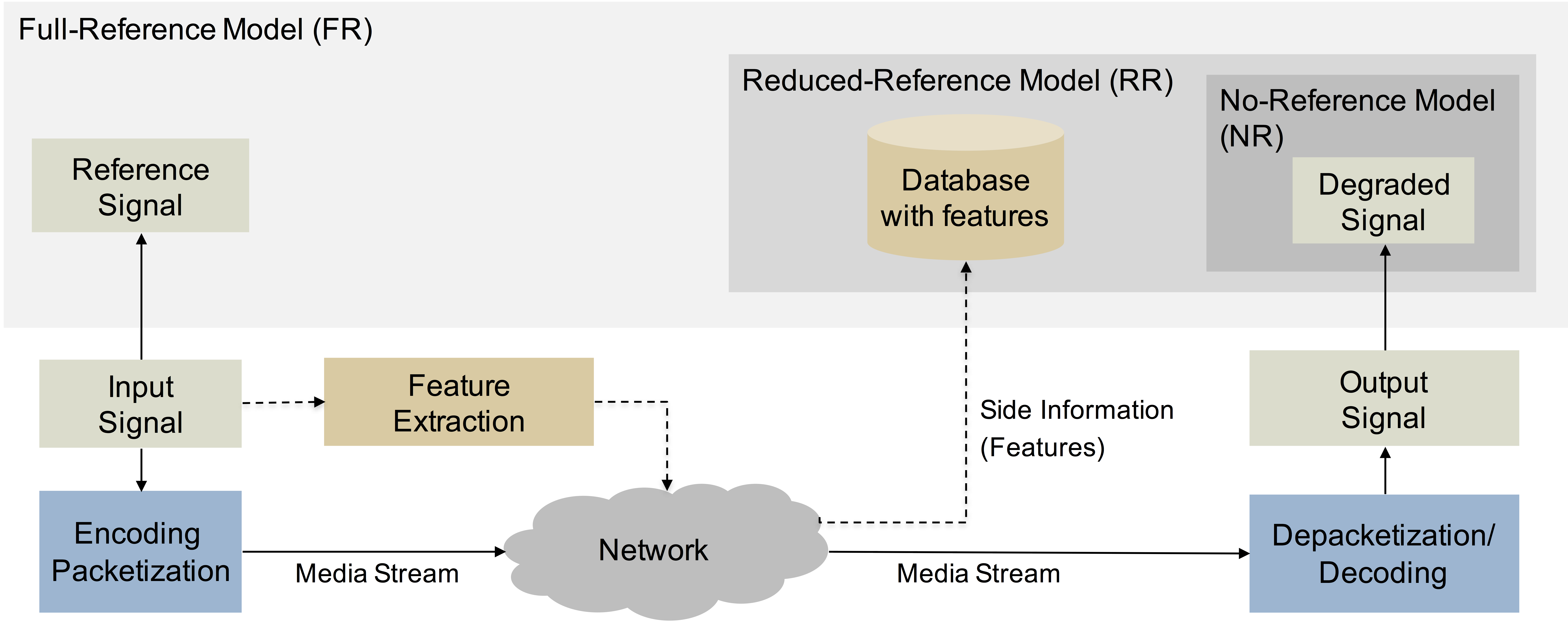
Video Quality
Video quality is a characteristic of a video passed through a video transmission or processing system that describes perceived video degradation (typically, compared to the original video). Video processing systems may introduce some amount of distortion or artifacts in the video signal that negatively impacts the user's perception of a system. For many stakeholders in video production and distribution, assurance of video quality is an important task. Video quality evaluation is performed to describe the quality of a set of video sequences under study. Video quality can be evaluated objectively (by mathematical models) or subjectively (by asking users for their rating). Also, the quality of a system can be determined offline (i.e., in a laboratory setting for developing new codecs or services), or in-service (to monitor and ensure a certain level of quality). From analog to digital video Since the world's first video sequence was recorded and transmitted, many video processing sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streaming Media
Streaming media is multimedia that is delivered and consumed in a continuous manner from a source, with little or no intermediate storage in network elements. ''Streaming'' refers to the delivery method of content, rather than the content itself. Distinguishing delivery method from the media applies specifically to telecommunications networks, as most of the traditional media delivery systems are either inherently ''streaming'' (e.g. radio, television) or inherently ''non-streaming'' (e.g. books, videotape, audio CDs). There are challenges with streaming content on the Internet. For example, users whose Internet connection lacks sufficient bandwidth may experience stops, lags, or poor buffering of the content, and users lacking compatible hardware or software systems may be unable to stream certain content. With the use of buffering of the content for just a few seconds in advance of playback, the quality can be much improved. Livestreaming is the real-time delivery of co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MPEG Transport Stream
MPEG transport stream (MPEG-TS, MTS) or simply transport stream (TS) is a standard digital container format for transmission and storage of audio, video, and Program and System Information Protocol (PSIP) data. It is used in broadcast systems such as DVB, ATSC and IPTV. Transport stream specifies a container format encapsulating packetized elementary streams, with error correction and synchronization pattern features for maintaining transmission integrity when the communication channel carrying the stream is degraded. Transport streams differ from the similarly-named MPEG program stream in several important ways: program streams are designed for reasonably reliable media, such as discs (like DVDs), while transport streams are designed for less reliable transmission, namely terrestrial or satellite broadcast. Further, a transport stream may carry multiple programs. Transport stream is specified in '' MPEG-2 Part 1, Systems'', formally known as ''ISO/IEC standard 13818- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolby Digital Plus
Dolby Digital Plus, also known as Enhanced AC-3 (and commonly abbreviated as DDP, DD+, E-AC-3 or EC-3) is a data compression, digital audio compression scheme developed by Dolby Labs for transport and storage of multi-channel digital audio. It is a successor to Dolby Digital (AC-3), also developed by Dolby, and has a number of improvements including support for a wider range of data rates (32 kbit/s to 6144 kbit/s), increased channel count and multi-program support (via substreams), and additional tools (algorithms) for representing compressed data and counteracting artifacts. While Dolby Digital (AC-3) supports up to five full-bandwidth audio channels at a maximum bitrate of 640 kbit/s, E-AC-3 supports up to 15 full-bandwidth audio channels at a maximum bitrate of 6.144 Megabits per second, Mbit/s. The full set of technical specifications for E-AC-3 (and AC-3) are standardized and published in Annex E of ATSC A/52:2012, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolby AC-3
Dolby Digital, originally synonymous with Dolby AC-3, is the name for what has now become a family of audio compression technologies developed by Dolby Laboratories. Formerly named Dolby Stereo Digital until 1995, the audio compression is lossy (except for Dolby TrueHD), based on the modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT) algorithm. The first use of Dolby Digital was to provide digital sound in cinemas from 35 mm film prints; today, it is also used for applications such as TV broadcast, radio broadcast via satellite, digital video streaming, DVDs, Blu-ray discs and game consoles. The main basis of the Dolby AC-3 multi-channel audio coding standard is the modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT), a lossy audio compression algorithm. It is a modification of the discrete cosine transform (DCT) algorithm, which was first proposed by Nasir Ahmed in 1972 and was originally intended for image compression. The DCT was adapted into the modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |