|
Adobe Flash Media Server
Adobe Media Server (AMS) is a proprietary data and media Server (computing), server from Adobe Systems (originally a Macromedia product). This server works with the Flash Player and HTML5 Run-time system, runtime to create media driven, multiuser RIAs (Rich Internet application, Rich Internet Applications). The server uses ActionScript 1, an ECMAScript based scripting language, for server-side logic. Prior to version 2, it was known as Flash Communication Server. Prior to version 5, it was known as Flash Media Server. In February 2019, Adobe Systems Incorporated granteVeriskope Incrights to further develop, resell, and extend distribution of the software product. History On March 16, 2002, Macromedia released Flash Player 6. This version included all the functionality for a yet to be released server called Flash Communication Server MX. Version 1.0 was released on 9 July 2002 and included all the basic features that make up the product, including the NetConnection, SharedObj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adobe Systems
Adobe Inc. ( ), originally called Adobe Systems Incorporated, is an American multinational computer software company incorporated in Delaware and headquartered in San Jose, California. It has historically specialized in software for the creation and publication of a wide range of content, including graphics, photography, illustration, animation, multimedia/video, motion pictures, and print. Its flagship products include Adobe Photoshop image editing software; Adobe Illustrator vector-based illustration software; Adobe Acrobat Reader and the Portable Document Format (PDF); and a host of tools primarily for audio-visual content creation, editing and publishing. Adobe offered a bundled solution of its products named Adobe Creative Suite, which evolved into a subscription software as a service (SaaS) offering named Adobe Creative Cloud. The company also expanded into digital marketing software and in 2021 was considered one of the top global leaders in Customer Experience Manageme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorenson Codec
Sorenson Media was an American software company specializing in video encoding technology. Established in December 1995 as Sorenson Vision, the company developed technology which was licensed and ultimately acquired from Utah State University. The company first announced its codec (compression and decompression tool) at a developer’s preview at MacWorld Expo in January 1997. One of the company's best known products is the Sorenson Video codec licensed to Apple Inc. for their QuickTime 3.0 software. Since its release, Sorenson Media’s video encoding technology was used in Apple's trailer web site and video clips for film studios such as Disney, Lucasfilm, MGM, and Paramount, as well as Apple's iTunes music videos, before the switch to the industry standard H.264 format. The company was led by its chairman and founder James Lee Sorenson; its final president and CEO was Patrick Nola. The company filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in October 2018, and was acquired at auction by N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wowza Media Server
Wowza Streaming Engine (known as Wowza Media Server prior to version 4) is a unified streaming media server software developed by Wowza. The server is used for streaming of live and on-demand video, audio, and rich Internet applications over IP networks to desktop, laptop, and tablet computers, mobile devices, IPTV set-top boxes, internet-connected TV sets, game consoles, and other network-connected devices. The server is a Java application deployable on most operating systems. History Version 1.0.x was released on February 19, 2007.(Press Release) This version was originally offered as an alternative to the Adobe Flash Media Server, and supported streamed video, audio and RIA’s for the Flash Player client playback and interaction based on the Real Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP) using content encoded with Spark and VP6 codecs. The original product name was Wowza Media Server Pro. Version 1.5.x was released on May 15, 2008(Press Release) and added support for H.264 video a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WebORB Integration Server
WebORB is an integration server developed and maintained by Midnight Coders Incorporated. It is used in SOA/Rich Internet Application development projects to connect browser clients (Adobe Flex, Adobe Flash, AJAX, Java, .NET, Silverlight, JSON) and mobile clients ( Android, Windows Phone 7, BlackBerry PlayBook) with backend services (.NET, Java, PHP and Ruby on Rails) and databases (MySQL, Microsoft SQL Server, SQL Azure, PostgreSQL, ODBC and Oracle database). It combines technologies that provide developer productivity tools, AMF remoting, real time messaging, code-level security and real time streaming media. Midnight Coders positions WebORB as a full-featured platform that has been shown to reduce the complexity of multitier architecture integration, thus speeding the development process and time to market. (See Case Studies.http://www.themidnightcoders.com/company/case-studies.html) There are four WebORB versions - WebORB for .NET,http://www.themidnightcoders.com/products/w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red5 (media Server)
Red5 is a free software media streaming server implemented in Java, which provides services similar to those offered by the proprietary Adobe Flash Media Server and Wowza Streaming Engine including: * Streaming Video (FLV, F4V, MP4, 3GP) * Streaming Audio (MP3, F4A, M4A, AAC) * Recording Client Streams (FLV and AVC+AAC in FLV container) * Shared Objects * Live Stream Video Publishing (FLV, VP6) * Live Stream Audio Publishing (MP3, AAC) * Remoting (Action Message Format) * Protocols: RTMP, RTMPT, RTMPS, and RTMPE The project started in September 2005 and as of 2008 is now maintained at GitHub. Version 1.0 was released on December 3, 2012 and is available under the Apache License (version 2.0). History * Project Started September 2005 * Version 0.8.0 Released 4 June 2009 * Version 1.0.0 Released 3 December 2012 * Version 1.0.1 Released 15 January 2013 * Version 1.0.2 Released 13 July 2013 * Version 1.0.3 Released 5 August 2014 * Version 1.0.4 Released 26 December 2014 * Versi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helix Universal Server
The Helix Universal Media Server was a product developed by RealNetworks and originates from the first streaming media server originally developed by Progressive Networks in 1994. It supported a variety of streaming media delivery transports including MPEG-DASH (Standards based HTTP streaming) RTMP (flash), RTSP (standard), HTTP Live Streaming (HLS), Microsoft Silverlight and HTTP Progressive Download enabling mobile phone OS (Android, Blackberry, iOS, Symbian, Windows Mobile) and PC OS media client (Flash Media Player, QuickTime, RealPlayer, Windows Media Player) delivery. Helix Universal Media Server supported multiple streaming media codecs including H.264, MPEG-4, Flash Media, RealMedia, QuickTime, Windows Media and audio codecs including AAC/AAC+, MP4, MP3, WAV, RealAudio. It ingested encoder formats including RTP, MPEG2-TS, RTMP (Flash) and Windows Media Push/Pull MMS. Development of the product was discontinued in 2014, and licensing ended in October 2014. History 27 Jul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flash Video
Flash Video is a container file format used to deliver digital video content (e.g., TV shows, movies, etc.) over the Internet using Adobe Flash Player version 6 and newer. Flash Video content may also be embedded within SWF files. There are two different Flash Video file formats: FLV and F4V. The audio and video data within FLV files are encoded in the same way as SWF files. The F4V file format is based on the ISO base media file format, starting with Flash Player 9 update 3. Both formats are supported in Adobe Flash Player and developed by Adobe Systems. FLV was originally developed by Macromedia. In the early 2000s, Flash Video was the de facto standard for web-based streaming video (over RTMP). Users include Hulu, VEVO, Yahoo! Video, metacafe, Reuters.com, and many other news providers. Flash Video FLV files usually contain material encoded with codecs following the Sorenson Spark or VP6 video compression formats. public releases of Flash Player (collaboration between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action Message Format
Action Message Format (AMF) is a binary format used to serialize object graphs such as ActionScript objects and XML, or send messages between an Adobe Flash client and a remote service, usually a Flash Media Server or third party alternatives. The Actionscript 3 language provides classes for encoding and decoding from the AMF format. The format is often used in conjunction with Adobe's RTMP to establish connections and control commands for the delivery of streaming media. In this case, the AMF data is encapsulated in a ''chunk'' which has a header which defines things such as the message length and type (whether it is a "ping", "command" or media data). Format analysis AMF was introduced with Flash Player 6, and this version is referred to as AMF0. It was unchanged until the release of Flash Player 9 and ActionScript 3.0, when new data types and language features prompted an update, called AMF3. Flash Player 10 added vector and dictionary data types documented in a revised spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remote Procedure Call
In distributed computing, a remote procedure call (RPC) is when a computer program causes a procedure (subroutine) to execute in a different address space (commonly on another computer on a shared network), which is coded as if it were a normal (local) procedure call, without the programmer explicitly coding the details for the remote interaction. That is, the programmer writes essentially the same code whether the subroutine is local to the executing program, or remote. This is a form of client–server interaction (caller is client, executor is server), typically implemented via a request–response message-passing system. In the object-oriented programming paradigm, RPCs are represented by remote method invocation (RMI). The RPC model implies a level of location transparency, namely that calling procedures are largely the same whether they are local or remote, but usually, they are not identical, so local calls can be distinguished from remote calls. Remote calls are usually orde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
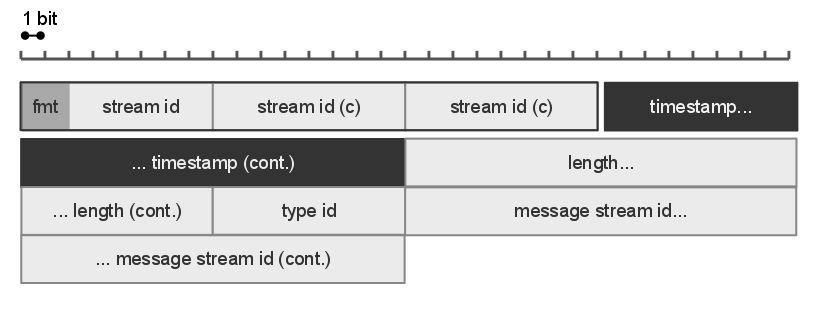
Real Time Messaging Protocol
Real-Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP) is a communication protocol for streaming audio, video, and data over the Internet. Originally developed as a proprietary protocol by Macromedia for streaming between Flash Player and the Flash Communication Server, Adobe (which acquired Macromedia) has released an incomplete version of the specification of the protocol for public use. The RTMP protocol has multiple variations: # RTMP proper, the "plain" protocol which works on top of Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and uses port number 1935 by default. # RTMPS, which is RTMP over a Transport Layer Security (TLS/SSL) connection. # RTMPE, which is RTMP encrypted using Adobe's own security mechanism. While the details of the implementation are proprietary, the mechanism uses industry standard cryptographic primitives. # RTMPT, which is encapsulated within HTTP requests to traverse firewalls. RTMPT is frequently found utilizing cleartext requests on TCP ports 80 and 443 to bypass most corpora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streaming Media
Streaming media is multimedia that is delivered and consumed in a continuous manner from a source, with little or no intermediate storage in network elements. ''Streaming'' refers to the delivery method of content, rather than the content itself. Distinguishing delivery method from the media applies specifically to telecommunications networks, as most of the traditional media delivery systems are either inherently ''streaming'' (e.g. radio, television) or inherently ''non-streaming'' (e.g. books, videotape, audio CDs). There are challenges with streaming content on the Internet. For example, users whose Internet connection lacks sufficient bandwidth may experience stops, lags, or poor buffering of the content, and users lacking compatible hardware or software systems may be unable to stream certain content. With the use of buffering of the content for just a few seconds in advance of playback, the quality can be much improved. Livestreaming is the real-time delivery of co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video On Demand
Video on demand (VOD) is a media distribution system that allows users to access videos without a traditional video playback device and the constraints of a typical static broadcasting schedule. In the 20th century, broadcasting in the form of over-the-air programming was the most common form of media distribution. As Internet and IPTV technologies continued to develop in the 1990s, consumers began to gravitate towards non-traditional modes of content consumption, which culminated in the arrival of VOD on televisions and personal computers. Unlike broadcast television, VOD systems initially required each user to have an Internet connection with considerable bandwidth to access each system's content. In 2000, the Fraunhofer Institute IIS developed the JPEG2000 codec, which enabled the distribution of movies via Digital Cinema Packages. This technology has since expanded its services from feature-film productions to include broadcast television programmes and has led to lower bandw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |