|
HMS Vulture (1744)
HMS ''Vulture'' was a 10-gun two-masted ''Hind''-class sloop of the Royal Navy, designed by Joseph Allin and built by John Greaves at Limehouse on the Thames River, England and launched on 4 May 1744, during the War of the Austrian Succession. Her name was often written as ''Vulter''. The ''Vulture'' set sail from Portsmouth as part of a joint Anglo-Dutch fleet under Vice Admiral Thomas Davers in September 1744. In the spring of 1746, the ''Vulture'' and the 14-gun sloop ''Shark'' engaged two superior French men of war. The ''Vulture'' broke off from the action to alert two nearby British cruisers. The arrival of these reinforcements caused the French ships to surrender. The sloop was part of a squadron that sailed from Britain in 1747 under Admirals Anson and Warren. On 3 June, the ''Vulture'' intercepted the lightly armed Cherbourg dogger privateer ''L'Huitre'' in the English Channel between the British coast and the Isle of Wight. The sloop captured the privateer intact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Ensign Of Great Britain (1707-1800)
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval warfare, naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral zone, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It includes anything conducted by surface Naval ship, ships, amphibious warfare, amphibious ships, submarines, and seaborne naval aviation, aviation, as well as ancillary support, communications, training, and other fields. The strategic offensive role of a navy is Power projection, projection of force into areas beyond a country's shores (for example, to protect Sea lane, sea-lanes, deter or confront piracy, ferry troops, or attack other navies, ports, or shore installations). The strategic defensive purpose of a navy is to frustrate seaborne projection-of-force by enemies. The strategic task of the navy also may incorporate nuclear deterrence by use of submarine-launched ballistic missiles. Naval operations can be broa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Shark
Thirteen ships of the Royal Navy have been named HMS ''Shark'' (or HMS ''Sharke'') after the shark: * was an 8-gun brigantine launched in 1691 and sold in 1698. * was a 14-gun sloop launched in 1699 and captured by French forces in 1703. * was a 14-gun sloop launched in 1711, rebuilt in 1722 and sold in 1732. * was a 14-gun sloop launched in 1732 and sold in 1755. * was a 16-gun sloop purchased on the stocks in 1775 and launched in 1776. She was converted to a fireship and renamed HMS ''Salamander'' in 1778, and was sold in 1783. She then became the mercantile ''Salamander'' and was seriatem a whaler, convict transport to Australia, whaler, and slaver. She is last listed in ''Lloyd's Register'' in 1811. * was a 16-gun sloop launched in 1779. She was used as a receiving ship on the Jamaica station from 1803 to 1816 and foundered in Port Royal harbor in 1818; her remains were sold a few months later. * was a 28-gun sixth rate bought in 1780 that foundered with the loss of her entir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Warships In The Age Of Sail
''British Warships in the Age of Sail'' is a series of four books by maritime historian Rif Winfield comprising a historical reference work providing details of all recorded ships that served or were intended to serve in the (British) Royal Navy from 1603 to 1863. Similar volumes dealing with other navies during the Age of Sail have followed from the same publisher. Scope The books draw data from Admiralty official records to give details on the location of construction, dates of construction (ordering, keel laying, launch, commissioning and completion of fitting-out), principal dimensions and tonnage, complement of men and armament, machinery (for steam vessels) and fate of every ship of the Royal Navy over the period. Designed dimensions and tonnage are given for every class of vessel planned and built for the Navy, but in addition the actual dimensions measured for each individual vessel completed to those designs are separately given; this treatment has also been applied to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isle Of Wight
The Isle of Wight ( ) is a county in the English Channel, off the coast of Hampshire, from which it is separated by the Solent. It is the largest and second-most populous island of England. Referred to as 'The Island' by residents, the Isle of Wight has resorts that have been popular holiday destinations since Victorian times. It is known for its mild climate, coastal scenery, and verdant landscape of fields, downland and chines. The island is historically part of Hampshire, and is designated a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve. The island has been home to the poets Algernon Charles Swinburne and Alfred, Lord Tennyson. Queen Victoria built her summer residence and final home, Osborne House at East Cowes, on the Isle. It has a maritime and industrial tradition of boat-building, sail-making, the manufacture of flying boats, hovercraft, and Britain's space rockets. The island hosts annual music festivals, including the Isle of Wight Festival, which in 1970 was the largest rock music ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kanaal, "The Channel"; german: Ärmelkanal, "Sleeve Channel" ( French: ''la Manche;'' also called the British Channel or simply the Channel) is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that separates Southern England from northern France. It links to the southern part of the North Sea by the Strait of Dover at its northeastern end. It is the busiest shipping area in the world. It is about long and varies in width from at its widest to at its narrowest in the Strait of Dover."English Channel". ''The Columbia Encyclopedia'', 2004. It is the smallest of the shallow seas around the continental shelf of Europe, covering an area of some . The Channel was a key factor in Britain becoming a naval superpower and has been utilised by Britain as a natural def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or delegated authority issued commissions, also referred to as a letter of marque, during wartime. The commission empowered the holder to carry on all forms of hostility permissible at sea by the usages of war. This included attacking foreign vessels and taking them as prizes, and taking prize crews as prisoners for exchange. Captured ships were subject to condemnation and sale under prize law, with the proceeds divided by percentage between the privateer's sponsors, shipowners, captains and crew. A percentage share usually went to the issuer of the commission (i.e. the sovereign). Privateering allowed sovereigns to raise revenue for war by mobilizing privately owned armed ships and sailors to supplement state power. For participants, privateerin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dogger (boat)
The dogger () was a form of fishing boat, described as early as the fourteenth century, that commonly operated in the North Sea. Early examples were single-masted: by the seventeenth century, two-masted doggers were common. They were largely used for fishing for cod by rod and line. Dutch boats were common in the North Sea, and the word ''dogger'' was given to the rich fishing grounds where they often fished, which became known as the Dogger Bank. The sea area in turn gave its name to the later design of boat that commonly fished that area, and so became associated with this specific design rather than the generic Dutch trawlers. Design The dogger was a development of the ketch. It was gaff-rigged on the main-mast, and carried a lug sail on the mizzen, with two jibs on a long bowsprit. The boats were generally short, wide-beamed and small, and were used for trawling or line fishing on the Dogger Bank. The name "dogger" was effectively synonymous with ketch from the early seventee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherbourg
Cherbourg (; , , ), nrf, Chèrbourg, ) is a former commune and subprefecture located at the northern end of the Cotentin peninsula in the northwestern French department of Manche. It was merged into the commune of Cherbourg-Octeville on 28 February 2000,Décret 23 February 2000 which was merged into the new commune of Cherbourg-en-Cotentin on 1 January 2016. Cherbourg is protected by Cherbourg Harbour, between and |
Peter Warren (Royal Navy Officer)
Vice-Admiral Sir Peter Warren, KB (10 March 1703 – 29 July 1752) was an Anglo-Irish naval officer and politician who sat in the British House of Commons representing the constituency of Westminster from 1747 to 1752. Warren is best known for his career in the Royal Navy, which he served in for thirty-six years and participated in numerous naval engagements, including most notably the capture of the French fortress of Louisbourg in 1745. Born in Ireland to an Irish Catholic family, Warren's parents raised him as a Protestant in order to allow him to pursue a career at sea. In 1716, Warren enlisted in the Royal Navy, largely spending the next decade serving off the West African coast or in the Caribbean, participating in anti-piracy operations and confrontations with Spanish coast guard vessels. Eleven years later in 1727, Warren was promoted to the rank of post-captain. From 1728 to 1745, Warren served almost continuously in the Americas. He commanded the '' Solebay'' off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Anson, 1st Baron Anson
Admiral of the Fleet George Anson, 1st Baron Anson, (23 April 1697 – 6 June 1762) was a Royal Navy officer. Anson served as a junior officer during the War of the Spanish Succession and then saw active service against Spain at the Battle of Cape Passaro during the War of the Quadruple Alliance. He then undertook a circumnavigation of the globe during the War of Jenkins' Ear. Anson commanded the fleet that defeated the French Admiral de la Jonquière at the First Battle of Cape Finisterre during the War of the Austrian Succession. Anson went on to be First Lord of the Admiralty during the Seven Years' War. Among his reforms were the removal of corrupt defence contractors, improved medical care, submitting a revision of the Articles of War to Parliament to tighten discipline throughout the Navy, uniforms for commissioned officers, the transfer of the Marines from Army to Navy authority, and a system for rating ships according to their number of guns. Family and early ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Davers
Vice-Admiral Thomas Davers (1689 – 16 September 1746) was a Royal Navy officer who served as Commander-in-Chief of the Jamaica Station. Naval career Born the third son of Sir Robert Davers, 2nd Baronet, Davers was promoted to post captain in January 1713 on appointment to the command of the sixth-rate HMS ''Seaford''. He transferred to the command of the sixth-rate HMS ''Solebay'' in August 1718, of the fifth-rate HMS ''Adventure'' in 1719 and of the fifth-rate HMS ''Dolphin'' in 1728. He went on to take the command of the third-rate HMS ''Grafton'' in March 1734, of the fourth-rate HMS ''Deptford'' in October 1734 and of the third-rate HMS ''Grafton'' again in October 1739. After that he took the command of the third-rate HMS ''Stirling Castle'' in May 1742 and of the second-rate HMS ''Duke'' in July 1743. Davers served as Commander-in-Chief of the Jamaica Station, with his flag in the third-rate HMS ''Cornwall'', from 1744 until he died of yellow fever in Jamaica o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
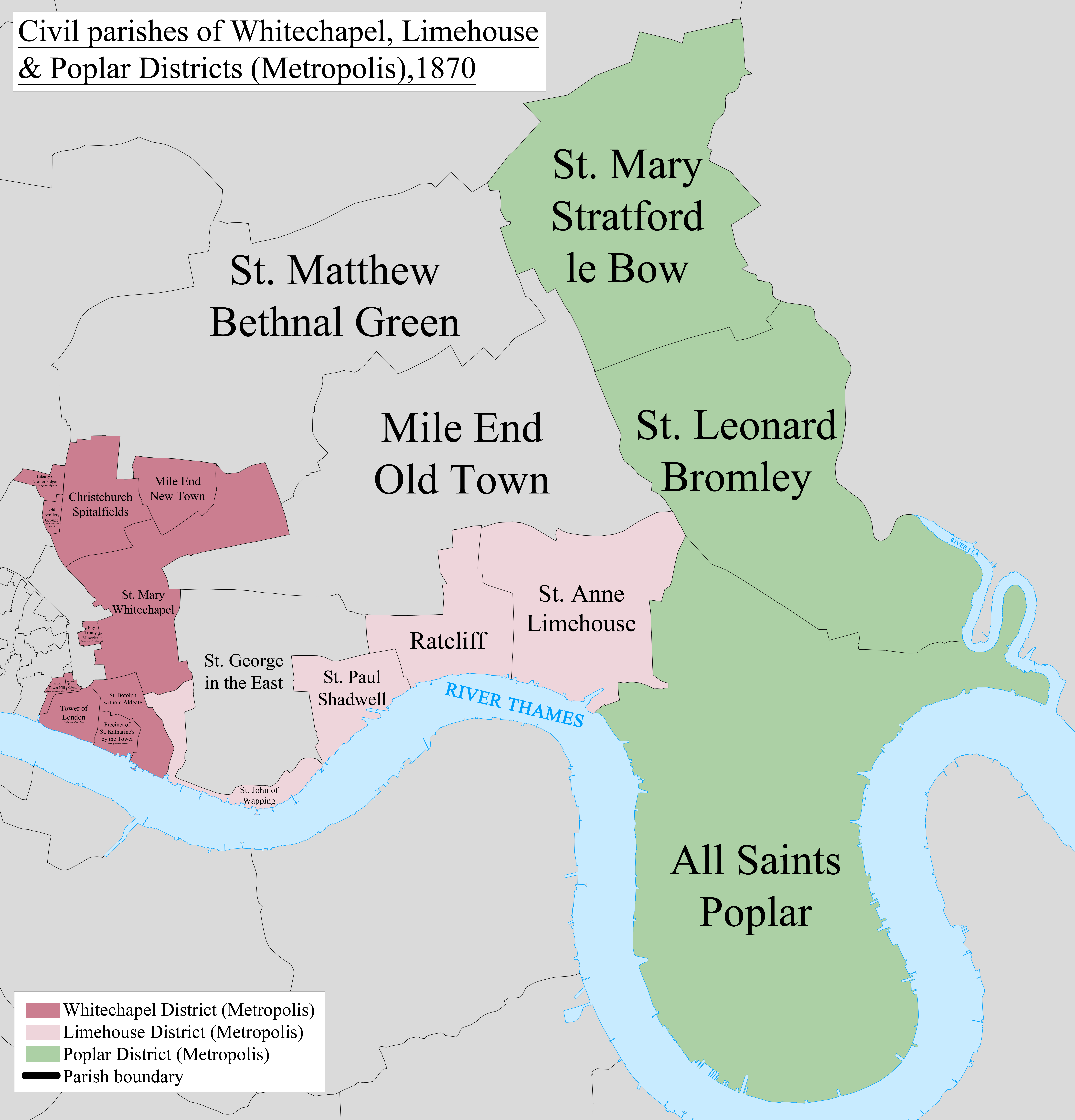
Limehouse
Limehouse is a district in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets in East London. It is east of Charing Cross, on the northern bank of the River Thames. Its proximity to the river has given it a strong maritime character, which it retains through its riverside public houses and steps, such as The Grapes and Limehouse Stairs. It is part of the traditional county of Middlesex. It became part of the ceremonial County of London following the passing of the Local Government Act 1888, and then part of Greater London in 1965. It is located between Stepney to the west and north, Mile End and Bow to the northwest, Poplar to the east, and Canary Wharf and Millwall to the south, and stretches from the end of Cable Street and Butcher Row in the west to Stainsby Road near Bartlett Park in the east, and from West India Dock (South Dock) and the River Thames in the south to Salmon Lane and Rhodeswell Road in the north. The area gives its name to Limehouse Reach, a section of the Thames wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)