|
HMS Seaflower (1782)
Four vessels of the Royal Navy have been named HMS ''Seaflower'': * was a 16-gun brig-sloop purchased in April 1782 that the , under Jean Dornal de Guy, captured near Bencoolen on 29 September 1808. * HMS ''Seaflower'' was a 16-gun brig-sloop listed in 1809, and sold on 1 September 1814. * was a 4 gun cutter launched at Portsmouth Dockyard His Majesty's Naval Base, Portsmouth (HMNB Portsmouth) is one of three operating bases in the United Kingdom for the Royal Navy (the others being HMNB Clyde and HMNB Devonport). Portsmouth Naval Base is part of the city of Portsmouth; it is l ... on 20 May 1830 and broken up at Charlton, scrapping completed on 8 October 1866. * was an 8 gun training brig, launched at Pembroke Dockyard on 25 February 1873. Converted to a floating workship in January 1904, the ship was sold at Charlton on 7 April 1908. References * {{DEFAULTSORT:Seaflower, Hms Royal Navy ship names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority globally. Owing to this historical prominence, it is common, even among non-Britons, to ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sloop-of-war
In the 18th century and most of the 19th, a sloop-of-war in the Royal Navy was a warship with a single gun deck that carried up to eighteen guns. The rating system covered all vessels with 20 guns and above; thus, the term ''sloop-of-war'' encompassed all the unrated combat vessels, including the very small gun-brigs and cutters. In technical terms, even the more specialised bomb vessels and fireships were classed as sloops-of-war, and in practice these were employed in the sloop role when not carrying out their specialised functions. In World War I and World War II, the Royal Navy reused the term "sloop" for specialised convoy-defence vessels, including the of World War I and the highly successful of World War II, with anti-aircraft and anti-submarine capability. They performed similar duties to the American destroyer escort class ships, and also performed similar duties to the smaller corvettes of the Royal Navy. Rigging A sloop-of-war was quite different from a civilian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Dornal De Guy
Jean Dornal de GuyThe name is sometimes written "Dornaldegu/ref> (13 October 1771 in Urrugne – 10 May 1855 in Saint Jean de Luz) was a French naval officer. Career In 1803, Commander Dornal de Guy was serving in the flotilla at the Camp de Boulogne. On 7 August, a British brig and a cutter anchored off Boulogne; and the next day, Dornal de Guy received the order from Bruix to attack the ships with five boats. Due to the tides, he couldn't set sail until 3:00 a.m. the next day. The British put to sail and exchanged gun fire with the boats, before retreating. In 1805, de Guy captained the frigate ''Félicité'', in the Brest squadron. In 1806, he ferried troops, weapons and ammunitions from Brest to San Domingo, where he arrived in time to take part in the Battle of San Domingo. ''Félicité'' was among the three French ships that survived the battle, and she returned to Lorient on 26 March 1806.Fonds marine In 1807, Dornal de Guy was appointed captain of the ''Manche'' at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
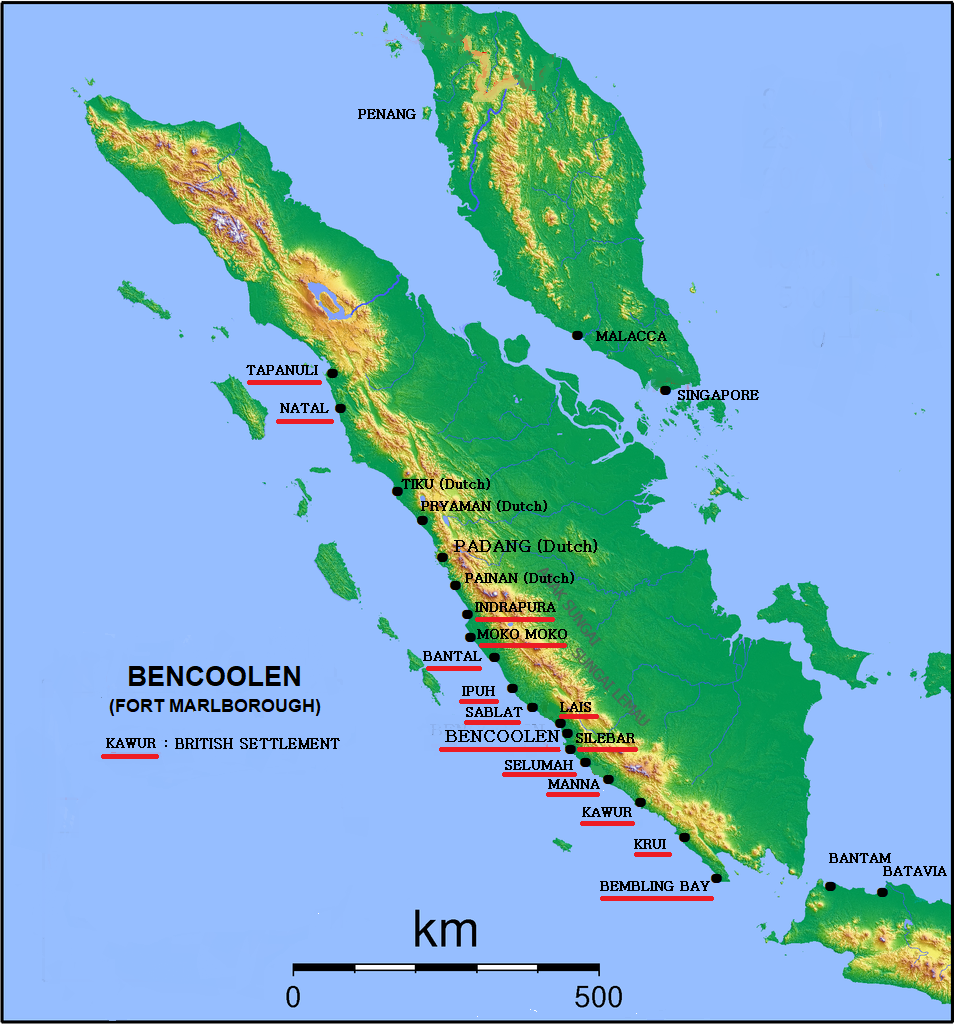
Bencoolen Presidency
British Bencoolen was a possession of the British East India Company (EIC) extending about 300 miles along the southwestern coast of Sumatra and centered on the area of what is now Bengkulu City. The EIC established a presence there in 1685, and in 1714 the EIC built Fort Marlborough there. A local datoo allowed EIC to build the fort in order to protect the settlement from the Dutch. Establishment and early development ''It was a fatall and never enough to be repented errour of our President and Council of Fort St. George adrasto break all our orders for a settlement at Pryaman upon a caprice of their owne to send our ships, spend our strength, our money and soe many men's lives upon settlement at such an unhealthful place as Bencoolen, because they hear there was more pepper there.'' In 1683, following the forcible closing of their factory at Bantam in Java and under the likelihood of being turned out at any moment from Dutch-ruled Malacca, the Directors of the East India C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cutter (boat)
A cutter is a type of watercraft. The term has several meanings. It can apply to the rig (or sailplan) of a sailing vessel (but with regional differences in definition), to a governmental enforcement agency vessel (such as a coast guard or border force cutter), to a type of ship's boat which can be used under sail or oars, or, historically, to a type of fast-sailing vessel introduced in the 18th century, some of which were used as small warships. As a sailing rig, a cutter is a single-masted boat, with two or more headsails. On the eastern side of the Atlantic, the two headsails on a single mast is the fullest extent of the modern definition. In U.S. waters, a greater level of complexity applies, with the placement of the mast and the rigging details of the bowsprit taken into account so a boat with two headsails may be classed as a sloop. Government agencies use the term "cutter" for vessels employed in patrolling their territorial waters and other enforcement activities. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portsmouth Dockyard
His Majesty's Naval Base, Portsmouth (HMNB Portsmouth) is one of three operating bases in the United Kingdom for the Royal Navy (the others being HMNB Clyde and HMNB Devonport). Portsmouth Naval Base is part of the city of Portsmouth; it is located on the eastern shore of Portsmouth Harbour, north of the Solent and the Isle of Wight. Until the early 1970s, it was officially known as Portsmouth Royal Dockyard (or HM Dockyard, Portsmouth); thereafter the term 'Naval Base' gained currency, acknowledging a greater focus on personnel and support elements alongside the traditional emphasis on building, repairing and maintaining ships. In 1984 Portsmouth's Royal Dockyard function was downgraded and it was formally renamed the 'Fleet Maintenance and Repair Organisation' (FMRO). The FMRO was privatized in 1998, and for a time (from 2002 to 2014), shipbuilding, in the form of block construction, returned. Around 2000, the designation HMS ''Nelson'' (which until then had been specific to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlton, London
Charlton is an area of southeast London, England, in the Royal Borough of Greenwich. It is east of Greenwich and west of Woolwich, on the south bank of the River Thames, southeast of Charing Cross. An ancient parish in the county of Kent, it became part of the metropolitan area of London in 1855 and is home to Charlton Athletic F.C. and Charlton House. History Toponymy Charlton is recorded in the 1086 Domesday Book as ''Cerletone''. It is formed from Old English ' ceorl' and 'tūn' and means 'farmstead of the freemen or peasants'. It is a common English placename and the parish was also known as Charlton next Woolwich to distinguish it from Charlton by Dover. During the 19th century the riverside portion of the area became known as New Charlton. Middle Ages Charlton is assessed in the Domesday Book of 1086 at one "sulung", which is commonly held to have been the equivalent of two hides. In 1086 it was in the fee of Gundulf, bishop of Rochester, but in 1066 it had been he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pembroke Dockyard
Pembroke Dockyard, originally called Pater Yard, is a former Royal Navy Dockyard in Pembroke Dock, Pembrokeshire, Wales. History It was founded in 1814, although not formally authorized until the Prince Regent signed the necessary Order in Council on 31 October 1815, and was known as ''Pater Yard'' until 1817. The Mayor of Pembroke had requested the change "in deference to the town of Pembroke some distant". The site selected for the dockyard was greenfield land and the closest accommodations were in Pembroke. Office space was provided by the old frigate after she was beached. The Royal Marine garrison was housed in the hulked 74-gun ship, , after she was run aground in 1832. Many of the workmen commuted by boat from nearby communities until Pembroke Dock town was built up. In 1860 the dockyard's policing was transferred to the new No. 4 Division of the Metropolitan Police, which remained in that role until the 1920s. After the end of the First World War, the dockyard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)