|
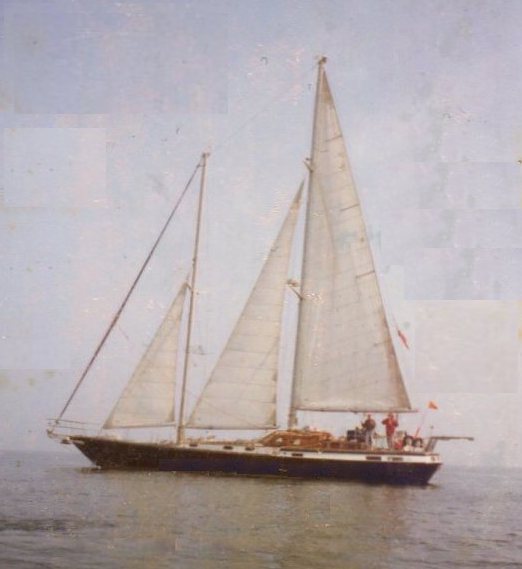
Cutter (boat)
A cutter is a type of watercraft. The term has several meanings. It can apply to the rig (or sailplan) of a sailing vessel (but with regional differences in definition), to a governmental enforcement agency vessel (such as a coast guard or border force cutter), to a type of ship's boat which can be used under sail or oars, or, historically, to a type of fast-sailing vessel introduced in the 18th century, some of which were used as small warships. As a sailing rig, a cutter is a single-masted boat, with two or more headsails. On the eastern side of the Atlantic, the two headsails on a single mast is the fullest extent of the modern definition. In U.S. waters, a greater level of complexity applies, with the placement of the mast and the rigging details of the bowsprit taken into account so a boat with two headsails may be classed as a sloop. Government agencies use the term "cutter" for vessels employed in patrolling their territorial waters and other enforcement activities. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beam (nautical)
The beam of a ship is its width at its widest point. The maximum beam (BMAX) is the distance between planes passing through the outer extremities of the ship, beam of the hull (BH) only includes permanently fixed parts of the hull, and beam at waterline (BWL) is the maximum width where the hull intersects the surface of the water. Generally speaking, the wider the beam of a ship (or boat), the more initial stability it has, at the expense of secondary stability in the event of a capsize, where more energy is required to right the vessel from its inverted position. A ship that heels on her ''beam ends'' has her deck beams nearly vertical. Typical values Typical length-to-beam ratios ( aspect ratios) for small sailboats are from 2:1 (dinghies to trailerable sailboats around ) to 5:1 (racing sailboats over ). Large ships have widely varying beam ratios, some as large as 20:1. Rowing shells designed for flatwater racing may have length to beam ratios as high as 30:1, while a cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaching (sailing)
A point of sail is a sailing craft's direction of travel under sail in relation to the true wind direction over the surface. The principal points of sail roughly correspond to 45° segments of a circle, starting with 0° directly into the wind. For many sailing craft 45° on either side of the wind is a ''no-go'' zone, where a sail is unable to mobilize power from the wind. Sailing on a course as close to the wind as possible—approximately 45°—is termed ''beating'', a point of sail when the sails are ''close-hauled''. At 90° off the wind, a craft is on a ''beam reach''. The point of sail between beating and a beam reach is called a ''close reach''. At 135° off the wind, a craft is on a ''broad reach''. At 180° off the wind (sailing in the same direction as the wind), a craft is ''running downwind''. A given point of sail (beating, close reach, beam reach, broad reach, and running downwind) is defined in reference to the true wind—the wind felt by a stationary observe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
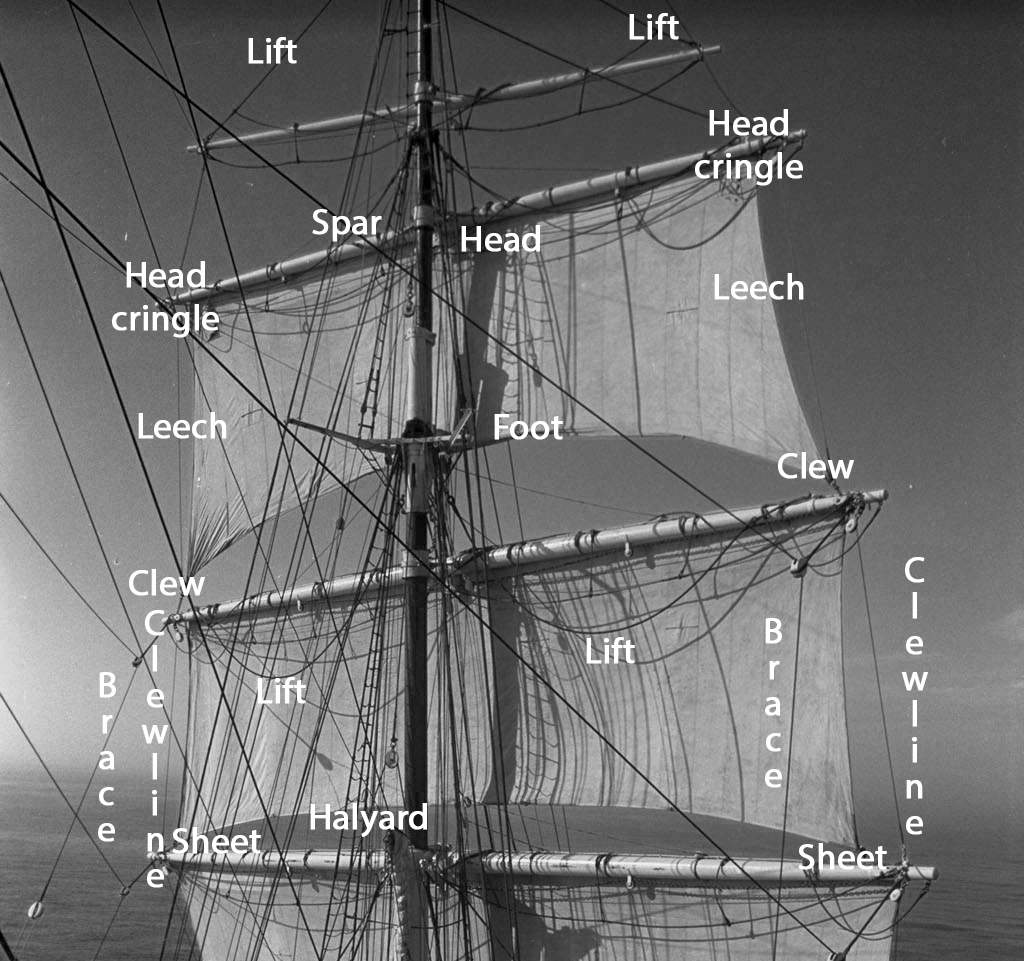
Studding Sail
A studding sail, or stun'sl (pronounced stuns'l ) is an extra sail on a square rigged vessel for use in fair weather. It is set outside the square sails, using stun'sl booms which run out along the yards. They came into use some time in the middle of the 17th century and by the beginning of the 19th century were usual on all square rigged sailing vessels. They started to become less common in the last quarter of the 19th century, as the economies of smaller crews and avoidance of damage to the ship's gear became more important than a fast voyage. History The origins of studding sails are relatively uncertain. The earliest reference is in 1655, but precise information on how these early examples were rigged is unknown. It is not until 1790 that this is available. Some changes in the detail of design and usage occurred over succeeding years. All ordinary working square-rigged vessels were usually fitted out to set stun'sls by the start of the 19th century. This started to change ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ringtail (sail)
A ringtail a sail which is set abaft (behind) a fore-and-aft sail to increase the total sail area of a sailing vessel in light winds. It may be three or four-sided. Description A ringtail sail may be quadrilateral or triangular in shape. Quadrilateral The older and more common type is a quadrilateral sail set on spars which extend the gaff and boom of a gaff sail Gaff rig is a sailing rig (configuration of sails, mast and stays) in which the sail is four-cornered, fore-and-aft rigged, controlled at its peak and, usually, its entire head by a spar (pole) called the ''gaff''. Because of the size and sha .... The effect is as if the gaff sail were larger in size, with the extra sail cloth of the ringtail continuing the plane in which the gaff sail is set. Triangular The triangular ringtail is set both above and behind a triangular working sail on the mizzen mast, providing extra sail area with minimal crew input, typically on late 19th-century schooners on the America ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flying Jib
A jib is a triangular sail that sets ahead of the foremast of a sailing vessel. Its tack is fixed to the bowsprit, to the bows, or to the deck between the bowsprit and the foremost mast. Jibs and spinnakers are the two main types of headsails on a modern boat. Modern yachts and small craft Boats may be sailed using a jib alone, but more commonly jibs make a minor direct contribution to propulsion compared to a main sail. Generally, a jib's most crucial function is as an airfoil, increasing performance and overall stability by reducing turbulence on the main sail's leeward side. On boats with only one jib, it is common for the clew of the jib to be abaft the mast, meaning the jib and mainsail overlap. An overlapping jib is called a ''genoa jib'' or simply a genoa (see illustration). These are efficiently used when reaching more broadly than a close reach. Alternatively, a boat may carry smaller jibs, to compensate aerodynamics when the main sail is reefed; these more rugged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bowsprit
The bowsprit of a sailing vessel is a spar extending forward from the vessel's prow. The bowsprit is typically held down by a bobstay that counteracts the forces from the forestays. The word ''bowsprit'' is thought to originate from the Middle Low German word ''bōchsprēt'' – ''bōch'' meaning "bow" and ''sprēt'' meaning "pole". It is sometimes used to hold up the figurehead In politics, a figurehead is a person who ''de jure'' (in name or by law) appears to hold an important and often supremely powerful title or office, yet ''de facto'' (in reality) exercises little to no actual power. This usually means that they .... References References * {{Sailing ship elements Sailboat components ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forestay
On a sailing vessel, a forestay, sometimes just called a stay, is a piece of standing rigging which keeps a mast from falling backwards. It is attached either at the very top of the mast, or in fractional rigs between about 1/8 and 1/4 from the top of the mast. The other end of the forestay is attached to the bow of the boat. Often a sail is attached to the forestay. This sail may be a jib or a genoa. In a cutter rig, the jib or jibs are flown from stays in front of the forestay, perhaps going from the masthead to a bowsprit. The sail on the forestay is then referred to as the staysail or stays'l. A forestay might be made from stainless steel wire on a modern yacht, solid stainless steel rod, carbon rod, or ultra high molecular weight polyethylene (such as Spectra or Dyneema) on a high-performance racing boat, and galvanised wire or natural fibers on an older cutter or square-rigged ship. See also * Backstay * Shroud (sailing) On a sailing boat, the shrouds are pieces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staysail
A staysail ("stays'l") is a fore-and-aft rigged sail whose Sail components#Edges, luff can be affixed to a stays (nautical), stay running forward (and most often but not always downwards) from a mast (sailing), mast to the deck (ship), deck, the bowsprit, or to another mast. Description Most staysails are triangular; however, some are four-cornered, notably some fisherman's staysails. Triangular staysails set forward of the foremost mast are called jibs, headsails, or foresails. The innermost such sail on a Cutter (ship), cutter, schooner, and many other rigs having two or more foresails is referred to simply as ''the staysail'', while the others are referred to as jibs, flying jibs, etc. Types of staysail include the tallboy staysail (a narrow staysail carried between the spinnaker and the mainsail on racing yachts), the Genoa (sail), genoa staysail (a larger one carried inside the spinnaker when broad reaching), and the bigboy staysail (another name for the shooter or bloo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roach (sail)
Sail components include the features that define a sail's shape and function, plus its constituent parts from which it is manufactured. A sail may be classified in a variety of ways, including by its orientation to the vessel (e.g. ''fore-and-aft'') and its shape, (e.g. ''(a)symmetrical'', ''triangular'', ''quadrilateral'', etc.). Sails are typically constructed out of flexible material that is shaped by various means, while in use, to offer an appropriate airfoil, according to the strength and apparent direction of the wind. A variety of features and fittings allow the sail to be attached to lines and spars. Whereas conventional sails form an airfoil with one layer of fabric, wingsails comprise a structure that has material on both sides to form an airfoil—much like a wing placed vertically on the vessel—and are beyond the scope of this article. Classifications Sails may be classified as either ''triangular'', which describes sails that either come to one point of suspens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topgallant Sail
On a square rigged sailing vessel, a topgallant sail (topgallant alone pronounced "t'gallant", topgallant sail pronounced "t'garns'l",C.S. Forester, ''Beat to Quarters'', Chapter VI. is the square-rigged sail or sails immediately above the topsail or topsails. It is also known as a gallant or garrant sail. Later full-rigged ships split the topsail (and often the topgallant sail) for easier handling. They thus set two topsails (and possibly two topgallant sails) per mast. The lower topgallant sail is immediately above the upper topsail. The upper or only topgallant sail is set from the top of the topgallant mast, if there is a lower topgallant it is set from midway down the topgallant mast. A staysail A staysail ("stays'l") is a fore-and-aft rigged sail whose Sail components#Edges, luff can be affixed to a stays (nautical), stay running forward (and most often but not always downwards) from a mast (sailing), mast to the deck (ship), deck, the b ... set on a stay running forward a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topsail
A topsail ("tops'l") is a sail set above another sail; on square-rigged vessels further sails may be set above topsails. Square rig On a square rigged vessel, a topsail is a typically trapezoidal shaped sail rigged above the course sail and below the topgallant sail where carried ,on any mast (i.e., a fully rigged ship would have a foremast topsail, a mainmast topsail, and a mizzen topsail). A full rigged ship will have either single or double (i.e, "split" upper and lower) topsails on all masts, the single or lower topsail being the second sail above the deck and the upper topsail where so rigged being the third. Although described as a "square" sail, a topsail on a full rigged ship refers not to the sail's shape but to it and its yard being rigged square (i.e., at a right angle) to the vessel's keel rather than in line with it (in which case it would be called a fore-and-aft rig or a fore-and-aft rigged sail) ; a square rigged topsail is nearly always trapezoidal in shape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.jpg)


