|
HMS Calcutta (1795)
HMS ''Calcutta'' was the East Indiaman ''Warley'', converted to a Royal Navy 56-gun fourth rate. This ship of the line served for a time as an armed transport. She also transported convicts to Australia in a voyage that became a circumnavigation of the world. The French 74-gun captured ''Calcutta'' in 1805. In 1809, after she ran aground during the Battle of the Basque Roads and her crew had abandoned her, a British boarding party burned her. East Indiaman The East Indiaman ''Warley'' was built at John Perry's Blackwall Yard in 1788, the first vessel of the name that Perry built for the East India Company. She made two trading voyages to the Far East for the East India Company. ''Warley''s captain for her two voyages was Henry Wilson. He received a letter of marque on 7 September 1793.Letter of Marqu – accessed 15 May 2011. First EIC voyage (1789–90) Captain Henry Wilson sailed from Falmouth on 8 March 1789, bound for Chennai, Madras and China. ''Warley'' reached Madra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Ship Régulus (1805)
''Régulus'' was a 74-gun List of ships of the line of France, ship of the line of the French Navy. From 25 May 1801, her armament was upgraded to between 80 and 86 guns. During the Atlantic campaign of 1806, she was the flagship of Jean-Marthe-Adrien L'Hermite, L'Hermite's squadron (also comprising frigates and and corvette ) during L'Hermite's expedition. She patrolled from the Gulf of Guinea to Brazil and the Caribbean. On 6 January 1806 the French squadron captured the 16-gun sloop-of-war . The squadron also captured about 20 merchantman, notably including the ships and ''Plowers'' (). In 1808, ''Régulus'' was in station with the Brest squadron. In 1809, she was transferred to Rochefort. She famously took part in the Battle of the Basque Roads from 11 April 1809, under Captain Jean Jacques Étienne Lucas, Lucas, where she ran aground between Les Palles and Fouras. For 17 days, the stranded ship repelled assaults by the British, before refloating and returning to Roch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huangpu District, Guangzhou
, alternately romanized as Whampoa, is one of 11 urban districts of the prefecture-level city of Guangzhou, the capital of Guangdong Province, China. Despite its name, it does not include Huangpu Island (now Pazhou) or its famous anchorage. Huangpu absorbed Guangzhou's former Luogang District in 2014. The district has been awarded the status of "Happiest District of China" in 2020. History During the Canton trade, Changzhou was known as "Dane's Island" and used by Danish crews for repairs and burials. It lay on the eastern side of the Huangpu or "Whampoa" anchorage, named for Huangpu Island (now Pazhou in Haizhu District). The Whampoa Military Academy was founded on Changzhou in 1924. Huangpu district played an important role in China's economic development. Originally called "Guangzhou Development District", it was one of the first economic and technological development districts in China. On 12 February 2014, Luogang District was dissolved by China's central gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menorca
Menorca or Minorca (from la, Insula Minor, , smaller island, later ''Minorica'') is one of the Balearic Islands located in the Mediterranean Sea belonging to Spain. Its name derives from its size, contrasting it with nearby Majorca. Its capital is Mahón ( ca, Maó), situated on the island's eastern end, although Menorca is not a province and forms a political union with the other islands in the archipelago. Ciutadella and Mahon are the main ports and largest towns. The port of Mahon is the second biggest natural port in the world. Menorca has a population of approximately 93,397 (at 1 January 2019). It is located 39°47' to 40°00'N, 3°52' to 4°24'E. Its highest point, called El Toro (from Catalan "''turó''" meaning ''hill''), is above sea level. History The island is known for its collection of megalithic stone monuments: ''navetes'', ''taules'' and ''talaiots'', which indicate very early prehistoric human activity. Some of the earliest culture on Menorca was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport Board (Royal Navy)
The Transport Board was the British Royal Navy organisation responsible for the transport of supplies and military. It is also referred to as the Board of Transport and Transport Office. History It existed between 1690 and 1724, and again between 1794 and 1817 and was initially a subsidiary board of the Navy Board. In 1818 its functions were merged into the Board of Admiralty. It originated in the need to transport the British Army to Ireland in 1689 to meet the Jacobite invasion of Ireland. The responsibility for the transportation was given to a board, later named the Commission for Transportation. In time the commission assumed responsibility for transportation to all areas, not just Ireland. In 1724 the commission was disbanded and other Admiralty boards and several departments of the War Office assumed its functions. This arrangement did not work well. 1794 to 1817 The division of responsibilities and abuses that followed led to the creation of another Transport Board i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Bligh
Vice-Admiral William Bligh (9 September 1754 – 7 December 1817) was an officer of the Royal Navy and a colonial administrator. The mutiny on the HMS ''Bounty'' occurred in 1789 when the ship was under his command; after being set adrift in ''Bounty''s launch by the mutineers, Bligh and his loyal men all reached Timor alive, after a journey of . Bligh's logbooks documenting the mutiny were inscribed on the UNESCO Australian Memory of the World register on 26 February 2021. Seventeen years after the ''Bounty'' mutiny, on 13 August 1806, he was appointed Governor of New South Wales in Australia, with orders to clean up the corrupt rum trade of the New South Wales Corps. His actions directed against the trade resulted in the so-called Rum Rebellion, during which Bligh was placed under arrest on 26 January 1808 by the New South Wales Corps and deposed from his command, an act which the British Foreign Office later declared to be illegal. He died in London on 7 December 1817. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
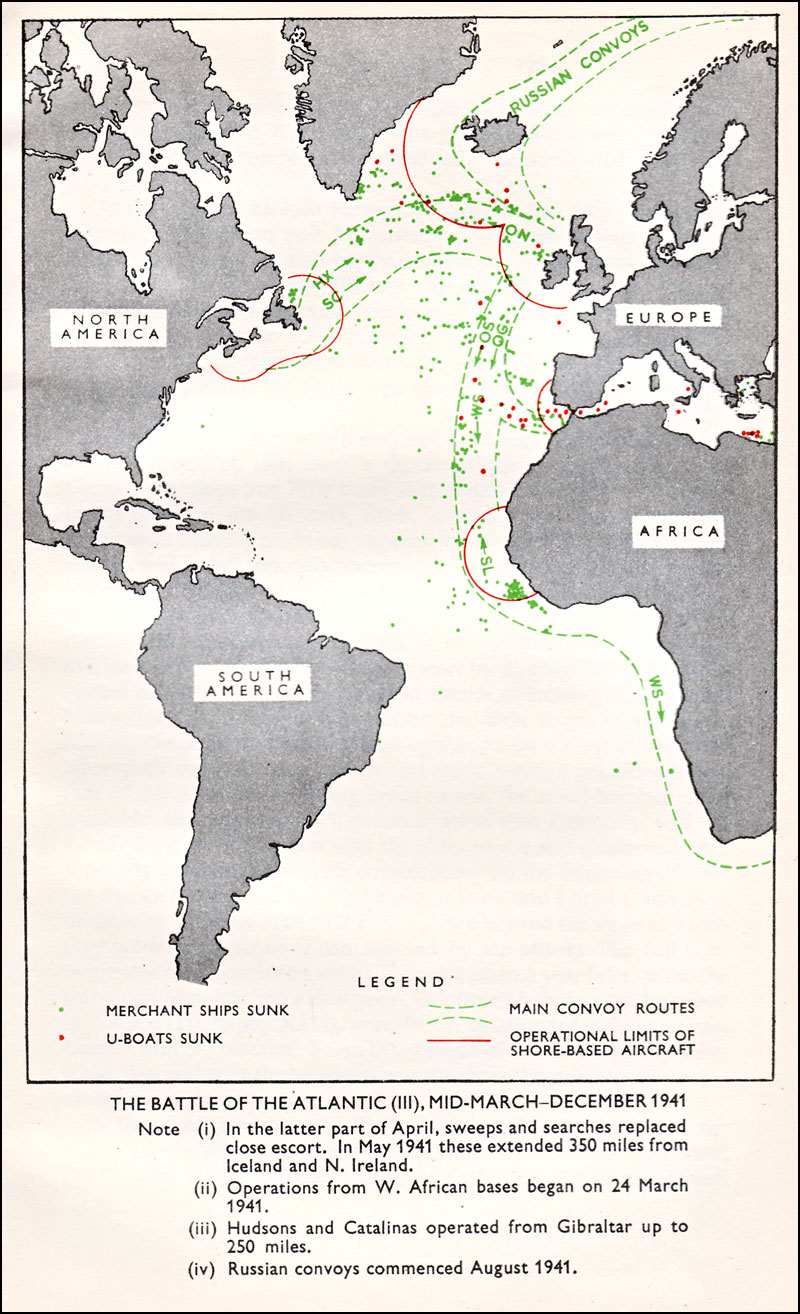
Convoy
A convoy is a group of vehicles, typically motor vehicles or ships, traveling together for mutual support and protection. Often, a convoy is organized with armed defensive support and can help maintain cohesion within a unit. It may also be used in a non-military sense, for example when driving through remote areas. Naval convoys Age of Sail Naval convoys have been in use for centuries, with examples of merchant ships traveling under naval protection dating to the 12th century. The use of organized naval convoys dates from when ships began to be separated into specialist classes and national navies were established. By the French Revolutionary Wars of the late 18th century, effective naval convoy tactics had been developed to ward off pirates and privateers. Some convoys contained several hundred merchant ships. The most enduring system of convoys were the Spanish treasure fleets, that sailed from the 1520s until 1790. When merchant ships sailed independently, a privateer cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Macartney, 1st Earl Macartney
:''George Macartney should not be confused with Sir George Macartney, a later British statesman.'' George McCartney, 1st Earl McCartney (14 May 1737 – 31 May 1806), also spelt Macartney, was an Anglo-Irish statesman, colonial administrator and diplomat who served as the governor of Grenada, Madras and the British-occupied Cape Colony. He is often remembered for his observation following Britain's victory in the Seven Years' War and subsequent territorial expansion at the Treaty of Paris that Britain now controlled " a vast Empire, on which the sun never sets". Early years He was born in 1737 as the only son of George McCartney, High Sheriff of Antrim and Elizabeth Winder. Macartney descended from a Scottish branch of the McCartney family whose ancestors originated in Ireland and were granted land in Scotland for serving under Edward Bruce, Robert the Bruce's brother. The Macartneys of Auchenleck, Kirkcudbrightshire settled in Lissanoure County Antrim, Ireland, where he w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Abergavenny (1795)
HMS ''Abergavenny'' was originally ''Earl of Abergavenny'', an East Indiaman sailing for the British East India Company (EIC). As an East Indiaman she made two trips to China between 1790 and 1794. The Royal Navy bought her in 1795, converted her to a 56-gun fourth-rate ship of the line, and renamed her. One year later the East India Company built a new and much larger ship which was also named the ''Earl of Abergavenny'' and which sank off Weymouth Bay in 1805. HMS ''Abergavenny'' was sold for breaking in 1807. East India Company Captain John Wordsworth completed two return voyages to China and back between January 1790 and September 1794. On her first voyage ''Earl of Abergavenny'' departed the Downs on 30 January 1790, arriving Bombay, India on 5 June 1790. She left there on 8 August and arrived in Penang on 25 August. She reached Whampoa on 3 October. For her return she crossed the Second Bar on 4 February 1791 and reached St Helena on 17 August. She arrived back at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunda Strait
The Sunda Strait ( id, Selat Sunda) is the strait between the Indonesian islands of Java island, Java and Sumatra. It connects the Java Sea with the Indian Ocean. Etymology The strait takes its name from the Sunda Kingdom, which ruled the western portion of Java (an area covering the present day West Java, Jakarta, Banten, and some of western Central Java) from 669 to around 1579."Sunda Islands". Concise Dictionary of World Place-Names. John Everett-Heath. Oxford University Press 2005. Oxford Reference Online. Oxford University Press. The name also alludes to the Sundanese people native to West Java and Banten, as distinct from the Javanese people, who live mostly in Central and East Java. Geography Extending in a roughly southwest/northeast orientation, with a minimum width of at its northeastern end between Cape Tua on Sumatra and Cape Pujat on Java, the strait is part of the Java Sea. It is essentially triangular in shape, with two large bays on its northern side. It is al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prize (law)
In admiralty law prizes are equipment, vehicles, vessels, and cargo captured during armed conflict. The most common use of ''prize'' in this sense is the capture of an enemy ship and her cargo as a prize of war. In the past, the capturing force would commonly be allotted a share of the worth of the captured prize. Nations often granted letters of marque that would entitle private parties to capture enemy property, usually ships. Once the ship was secured on friendly territory, she would be made the subject of a prize case: an ''in rem'' proceeding in which the court determined the status of the condemned property and the manner in which the property was to be disposed of. History and sources of prize law In his book ''The Prize Game'', Donald Petrie writes, "at the outset, prize taking was all smash and grab, like breaking a jeweler's window, but by the fifteenth century a body of guiding rules, the maritime law of nations, had begun to evolve and achieve international recogn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sailing Frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied somewhat. The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuverability, intended to be used in scouting, escort and patrol roles. The term was applied loosely to ships varying greatly in design. In the second quarter of the 18th century, the 'true frigate' was developed in France. This type of vessel was characterised by possessing only one armed deck, with an unarmed deck below it used for berthing the crew. Late in the 19th century (British and French prototypes were constructed in 1858), armoured frigates were developed as powerful ironclad warships, the term frigate was used because of their single gun deck. Later developments in ironclad ships rendered the frigate designation obsolete and the term fell out of favour. During the Second World War the name 'frigate' was reintroduced to des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straits Of Malacca
The Strait of Malacca is a narrow stretch of water, 500 mi (800 km) long and from 40 to 155 mi (65–250 km) wide, between the Malay Peninsula (Peninsular Malaysia) to the northeast and the Indonesian island of Sumatra to the southwest, connecting the Andaman Sea (Indian Ocean) and the South China Sea (Pacific Ocean). As the main shipping channel between the Indian and Pacific oceans, it is one of the most important shipping lanes in the world. It is named after the Malacca Sultanate that ruled over the strait between 1400 and 1511, the center of administration of which was located in the modern-day state of Malacca, Malaysia. Extent The International Hydrographic Organization define the limits of the Strait of Malacca as follows: History Early traders from Arabia, Africa, Persia, and Southern India reached Kedah before arriving at Guangzhou. Kedah served as a western port on the Malay Peninsula. They traded glassware, camphor, cotton goods, brocades, ivory, sandalwood, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |