|
GyÃķnk
GyÃķnk (german: Jink) is a village in Tolna County, Hungary. History GyÃķnk was mentioned for the first time in 1280, but the neighborhood (and GyÃķnk) was already a populated area by then. The village was inhabited by Turks for some time, and by the time of the RÃĄkÃģczi it was depopulated. In the early 18th century Hungarian and German families arrived in the village. The school was founded in 1806. In 1882, the Budapest-PÃĐcs-DombÃģvÃĄr-rail line, which passes through the Kapos Valley connected the village. In 1891, there were 3,371 German and Hungarian inhabitants. In 1947, a Czechoslovak-Hungarian population exchange saw 9 Highland Hungarian families (55 people) resettled in the upland village of Martos. Until the end of World War II, the majority of the inhabitants were Danube Swabians (Schwowe), their ancestors came from Swabia and Franconia. Around 1790, Catholic German families from GyÃķnk settled in Illocska. Mostly of the former German Settlers was expelled to Allied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tolna County
Tolna ( hu, Tolna megye, ; german: Komitat Tolnau) is an administrative county (Comitatus (Kingdom of Hungary), comitatus or megye) in present Hungary as it was of the former Kingdom of Hungary. It lies in central Hungary, on the west bank of the river Danube. It shares borders with the Hungarian counties Somogy County, Somogy, FejÃĐr, BÃĄcs-Kiskun, and Baranya (county), Baranya. The capital of Tolna county is SzekszÃĄrd. Its area is 3703 km2. History Tolna (in Latin: ''comitatus Tolnensis'') was also the name of a historic administrative county (Comitatus (Kingdom of Hungary), comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory, which was about the same as that of present Tolna county, is now in central Hungary. The capital of the county was SzekszÃĄrd. Demographics In 2015, it had a population of 225,936 and the population density was . Ethnicity Besides the Hungarian majority, the main minorities are the Germans (approx. 10,000) and Roma (8,500). Total population ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bar-le-Duc
Bar-le-Duc (), formerly known as Bar, is a commune in the Meuse dÃĐpartement, of which it is the capital. The department is in Grand Est in northeastern France. The lower, more modern and busier part of the town extends along a narrow valley, shut in by wooded or vine-clad hills, and is traversed throughout its length by the Ornain, which is crossed by several bridges. It is limited towards the north-east by the MarneâRhine Canal, on the south-west by a small arm of the Ornain, called the ''Canal des Usines'', on the left bank of which the upper town (''Ville Haute'') is situated. The highly rarefied Bar-le-duc jelly, also known as Lorraine jelly, is a spreadable preparation of white currant or red currant fruit preserves, hailing from this town. First referenced in the historical record in 1344, it is also colloquially referred to as "Bar caviar". History Bar-le-Duc was at one time the seat of the county, from 1354 the Duchy of Bar. Though probably of ancient origin, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Griesheim (Hesse)
Griesheim () is a town in the Darmstadt-Dieburg district in Hesse, Germany. It is situated west of Darmstadt. History The area of Griesheim has been inhabited since around 4500 BCE yet it was first mentioned in 1165 CE. Wine was an important source of income in Griesheim in earlier times. The Thirty Year War hit Griesheim hard. The surviving inhabitants fled behind the walls of the Darmstadt, where many of them died of the plague. By the end of the war in 1648 only about 370 were left, who set out to rebuild the community. The late 18th, early 19th Century a major industry was the production and trade of fir tree seeds. The city also became a center of woodwork-craft. The Protestant Reformation was introduced to the town in 1529. In 1874 in the southwest part of Griesheim an artillery range opened. In 1908 August Euler opened one of the first airfields in Germany. Griesheim was occupied by France from 1918 to 1930. During World War II, 65% of its buildings were destroyed, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darmstadt
Darmstadt () is a city in the States of Germany, state of Hesse in Germany, located in the southern part of the Frankfurt Rhine Main Area, Rhine-Main-Area (Frankfurt Metropolitan Region). Darmstadt has around 160,000 inhabitants, making it the fourth largest city in the state of Hesse after Frankfurt am Main, Wiesbaden, and Kassel. Darmstadt holds the official title "City of Science" (german: link=no, Wissenschaftsstadt) as it is a major centre of scientific institutions, universities, and high-technology companies. The European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT) and the European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) are located in Darmstadt, as well as Gesellschaft fÞr Schwerionenforschung, GSI Centre for Heavy Ion Research, where several chemical elements such as bohrium (1981), meitnerium (1982), hassium (1984), darmstadtium (1994), roentgenium (1994), and copernicium (1996) were discovered. The existence of the following elements were also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illocska
Illocska, (german: Illutsch), ( sr, ÐÐŧÐūŅаŅ, IloÄac) is a village in Baranya county, Hungary. Residents are Magyars, with a minority of Serbs and Danube Swabians. Until the end of World War II, the majority of the inhabitants were Roman Catholic Danube Swabians (Schwowe), their ancestors once came in 1790 from NagyszÃĐkely and GyÃķnk villages to Illocska. Most of the former German settlers were expelled to allied-occupied Germany and allied-occupied Austria in 1946â1948, as a result of the Potsdam Agreement. Only a few Germans of Hungary live there, the majority today are the descendants of Hungarians from the CzechoslovakâHungarian population exchange The CzechoslovakâHungarian population exchange was the exchange of inhabitants between Czechoslovakia and Hungary after World War II. Between 45,000 and 120,000 Hungarians were forcibly transferred from Czechoslovakia to Hungary, and their propert .... They got the houses of the former Danube Swabians Inhabitants. Refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countries Of The World
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, 2 United Nations General Assembly observers#Present non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (2 states, both in associated state, free association with New Zealand). Compi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franconia
Franconia (german: Franken, ; Franconian dialect: ''Franggn'' ; bar, Frankn) is a region of Germany, characterised by its culture and Franconian dialect (German: ''FrÃĪnkisch''). The three administrative regions of Lower, Middle and Upper Franconia (largest cities, respectively: WÞrzburg, Nuremberg and Bamberg) in the State of Bavaria are part of the cultural region of Franconia, as are the adjacent Franconian-speaking South Thuringia, south of the Rennsteig ridge (largest city: Suhl), Heilbronn-Franconia (largest city: SchwÃĪbisch Hall) in the state of Baden-WÞrttemberg, and small parts of the state of Hesse. Those parts of the Vogtland lying in the state of Saxony (largest city: Plauen) are sometimes regarded as Franconian as well, because the Vogtlandian dialects are mostly East Franconian. The inhabitants of Saxon Vogtland, however, mostly do not consider themselves as Franconian. On the other hand, the inhabitants of the Hessian-speaking parts of Lower Franconia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twin Towns And Sister Cities
A sister city or a twin town relationship is a form of legal or social agreement between two geographically and politically distinct localities for the purpose of promoting cultural and commercial ties. While there are early examples of international links between municipalities akin to what are known as sister cities or twin towns today dating back to the 9th century, the modern concept was first established and adopted worldwide during World War II. Origins of the modern concept The modern concept of town twinning has its roots in the Second World War. More specifically, it was inspired by the bombing of Coventry on 14 November 1940, known as the Coventry Blitz. First conceived by the then Mayor of Coventry, Alfred Robert Grindlay, culminating in his renowned telegram to the people of Stalingrad (now Volgograd) in 1942, the idea emerged as a way of establishing solidarity links between cities in allied countries that went through similar devastating events. The comradeship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CzechoslovakâHungarian Population Exchange
The CzechoslovakâHungarian population exchange was the exchange of inhabitants between Czechoslovakia and Hungary after World War II. Between 45,000 and 120,000 Hungarians were forcibly transferred from Czechoslovakia to Hungary, and their properties confiscated, while around 72,000 Slovaks voluntarily transferred from Hungary to Czechoslovakia. Post-war Czechoslovakia In 1945, at the end of World War II, Czechoslovakia was recreated and Czechoslovak politicians aimed to completely remove the German and Hungarian minorities from their territory through ethnic cleansing.Ethnic cleansing is a term that has come to be used broadly to describe all activities designed to force the removal of specific ethnicities from specific territories.() Both minorities were considered collectively as " war criminals", based on the actions of some individuals, such as Konrad Henlein, and the participation of their countries in the dismemberment of Czechoslovakia through the Munich Agreement and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germans Of Hungary
German Hungarians (german: Ungarndeutsche, hu, magyarorszÃĄgi nÃĐmetek) are the German-speaking minority of Hungary, sometimes called Danube Swabians (German: ''Donauschwaben'', Hungarian: ''dunai svÃĄbok''), many of whom call themselves "Shwoveh". There are 131,951 German speakers in Hungary (according to the 2011 census). Danube Swabian is a collective term for a number of German ethnic groups who lived in the former Kingdom of Hungary, including the Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia and Vojvodina. Hungarian Germans refers to the descendants of Danube Swabians who immigrated to the Carpathian Basin and surrounding regions, and who are now minorities in those areas. Many Hungarian Germans were expelled from the region between 1946 and 1948, and many now live in Germany or Austria, but also in Australia, Brazil, the United States, and Canada. However, many are still dispersed within present-day Hungary. History The migration of Germanic-speaking peoples into Hungary began in app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
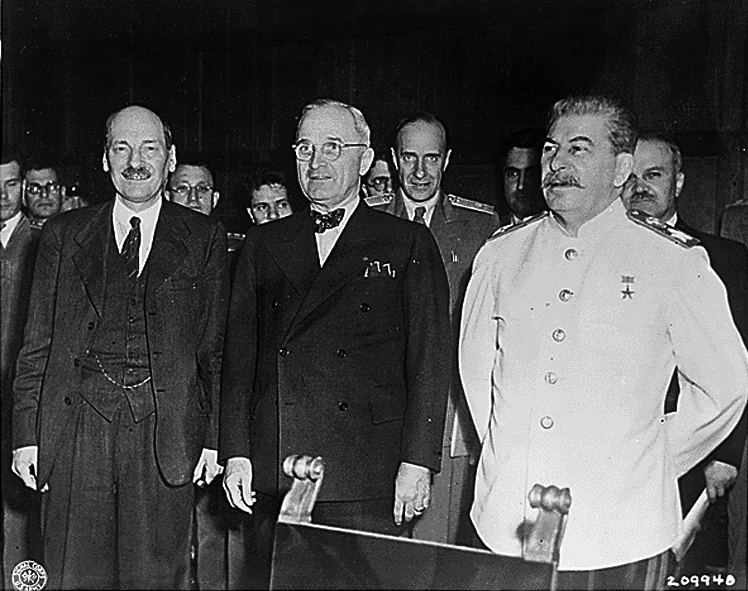
Potsdam Agreement
The Potsdam Agreement (german: Potsdamer Abkommen) was the agreement between three of the Allies of World War II: the United Kingdom, the United States, and the Soviet Union on 1 August 1945. A product of the Potsdam Conference, it concerned the military occupation and reconstruction of Germany, its border, and the entire European Theatre of War territory. It also addressed Germany's demilitarisation, reparations, the prosecution of war criminals and the Flight and expulsion of Germans (1944â1950), mass expulsion of ethnic Germans from various parts of Europe. Executed as a communiquÃĐ, the agreement was not a peace treaty according to international law, although it created accomplished facts. It was superseded by the Treaty on the Final Settlement with Respect to Germany signed on 12 September 1990. As De Gaulle had not been invited to the Conference, the French resisted implementing the Potsdam Agreements within their occupation zone. In particular, the French refused to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allied-occupied Austria
The Allied occupation of Austria started on 8 May 1945 with the fall of Nazi Germany and ended with the Austrian State Treaty on 27 July 1955. After the in 1938, Austria had generally been recognized as part of Nazi Germany. In 1943, however, the Allies agreed in the Declaration of Moscow that Austria would instead be regarded as the first victim of Nazi aggression, and treated as a liberated and independent country after the war. In the immediate aftermath of World War II, Austria was divided into four zones and jointly occupied by the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union, the United States, and France. Vienna was similarly subdivided, but the central district was collectively administered by the Allied Control Council. Whereas Germany was divided into East and West Germany in 1949, Austria remained under joint occupation of the Western Allies and the Soviet Union until 1955; its status became a controversial subject in the Cold War until the warming of relations known as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)


