|
Gustav Scanzoni Von Lichtenfels
Gustav Leofried Ignaz Scanzoni von Lichtenfels was a German General of the Artillery of World War I. He is known for conducting the Attack at Fromelles but was relieved before the war concluded. Family Gustav was born as the son of the professor of obstetrics at the University of Würzburg, Friedrich Wilhelm Scanzoni von Lichtenfels and his wife Auguste (née Höniger) (1826-1891). His father was elevated to the hereditary Bavarian nobility on June 19, 1863 by King Maximilian II of Bavaria as "Scanzoni von Lichtenfels". Gustav later married Emilie Lederer (b. 1858) on March 4, 1882 in Würzburg. They'd have one son, Albert Scanzoni von Lichtenfels (1885-1960) who was a painter and writer. Initial Military Career After attending the , Scanzoni von Lichtenfels enlisted in the on October 1, 1875 as a '. He was promoted to second lieutenant by the end of November 1877 and served as adjutant to the cavalry detachment from November 1881 to October 1885. Scanzoni then graduated fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Würzburg
Würzburg (; Main-Franconian: ) is a city in the region of Franconia in the north of the German state of Bavaria. Würzburg is the administrative seat of the ''Regierungsbezirk'' Lower Franconia. It spans the banks of the Main River. Würzburg is situated approximately east-southeast of Frankfurt am Main and approximately west-northwest of Nuremberg (). The population (as of 2019) is approximately 130,000 residents. The administration of the ''Landkreis Würzburg'' ( district of Würzburg) is also located in the town. The regional dialect is East Franconian. History Early and medieval history A Bronze Age (Urnfield culture) refuge castle, the Celtic Segodunum,Koch, John T. (2020)CELTO-GERMANIC Later Prehistory and Post-Proto-Indo-European vocabulary in the North and West p. 131 and later a Roman fort, stood on the hill known as the Leistenberg, the site of the present Fortress Marienberg. The former Celtic territory was settled by the Alamanni in the 4th or 5th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justus Perthes (publishing Company)
''Justus Perthes Publishers'' (german: Justus Perthes Verlag) was established in 1785 in Gotha, Germany. Justus Perthes was primarily a publisher of geographic atlases and wall maps. He published ''Petermanns Geographische Mitteilungen'' and also the Almanach de Gotha (''Gothaischer Hofkalender''). In 2016 the publisher was discontinued. Almanacs From 1778 Johann Georg Justus Perthes worked as a bookseller in Gotha, where he founded the publishing firm 'Justus Perthes' in September 1785, when he got a fifteen-year lease for the Almanach de Gotha. This almanac was published since 1763 by Carl Wilhelm Ettinger, Gotha, and was the French version of the ''Almanach de Gotha''. Only after the second 15-year lease contract in 1816 he was allowed to publish the almanac with the imprint of his own publishing house. The publication of the almanac as a Justus Perthes publication ceased in 1944. In later years another set of almanacs was published in the German language: ''Gothaisches genea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
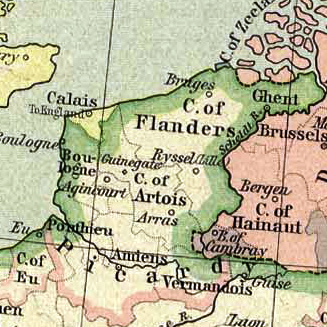
Artois
Artois ( ; ; nl, Artesië; English adjective: ''Artesian'') is a region of northern France. Its territory covers an area of about 4,000 km2 and it has a population of about one million. Its principal cities are Arras (Dutch: ''Atrecht''), Saint-Omer, Lens, and Béthune. It is the eponym for the term '' artesian''. Location Artois occupies the interior of the Pas-de-Calais ''département'',"Artois" in ''The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th ed., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 607. the western part of which constitutes the former Boulonnais. Artois roughly corresponds to the arrondissements of Arras, Béthune, Saint Omer, and Lens, and the eastern part of the arrondissement of Montreuil. It occupies the western end of the coalfield which stretches eastward through the neighbouring Nord ''département'' and across central Belgium. History Originally a feudal county itself, Artois was annexed by the county of Flanders. It came to France in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, language, politics, and history, and sometimes involving neighbouring countries. The demonym associated with Flanders is Fleming, while the corresponding adjective is Flemish. The official capital of Flanders is the City of Brussels, although the Brussels-Capital Region that includes it has an independent regional government. The powers of the government of Flanders consist, among others, of economic affairs in the Flemish Region and the community aspects of Flanders life in Brussels, such as Flemish culture and education. Geographically, Flanders is mainly flat, and has a small section of coast on the North Sea. It borders the French department of Nord to the south-west near the coast, the Dutch provinces of Zeeland, North Brabant an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
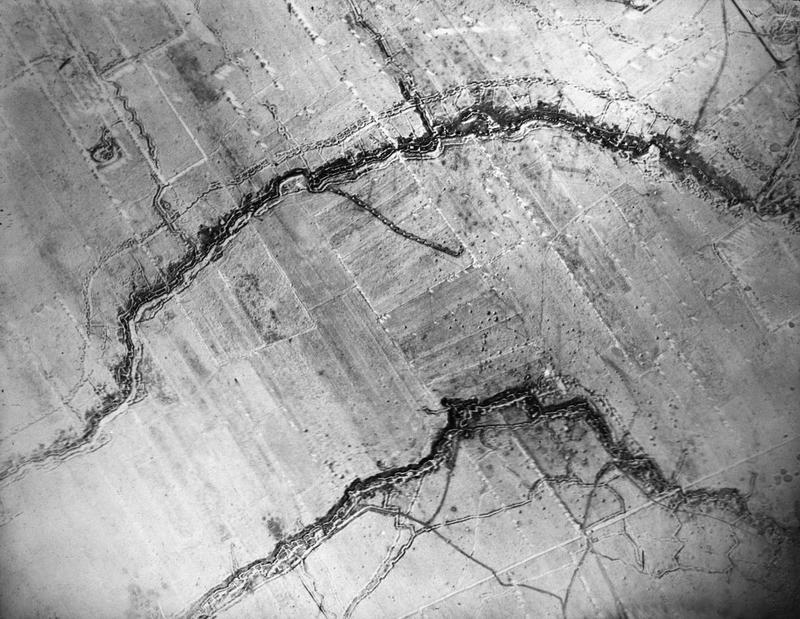
Trench Warfare
Trench warfare is a type of land warfare using occupied lines largely comprising military trenches, in which troops are well-protected from the enemy's small arms fire and are substantially sheltered from artillery. Trench warfare became archetypically associated with World War I (1914–1918), when the Race to the Sea rapidly expanded trench use on the Western Front starting in September 1914.. Trench warfare proliferated when a revolution in firepower was not matched by similar advances in mobility, resulting in a grueling form of warfare in which the defender held the advantage. On the Western Front in 1914–1918, both sides constructed elaborate trench, underground, and dugout systems opposing each other along a front, protected from assault by barbed wire. The area between opposing trench lines (known as " no man's land") was fully exposed to artillery fire from both sides. Attacks, even if successful, often sustained severe casualties. The development of armoured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Front (World War I)
The Western Front was one of the main theatres of war during the First World War. Following the outbreak of war in August 1914, the German Army opened the Western Front by invading Luxembourg and Belgium, then gaining military control of important industrial regions in France. The German advance was halted with the Battle of the Marne. Following the Race to the Sea, both sides dug in along a meandering line of fortified trenches, stretching from the North Sea to the Swiss frontier with France, which changed little except during early 1917 and in 1918. Between 1915 and 1917 there were several offensives along this front. The attacks employed massive artillery bombardments and massed infantry advances. Entrenchments, machine gun emplacements, barbed wire and artillery repeatedly inflicted severe casualties during attacks and counter-attacks and no significant advances were made. Among the most costly of these offensives were the Battle of Verdun, in 1916, with a combined 700,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th Reserve Division (German Empire)
The 6th Reserve Division (''6. Reserve-Division'') was a unit of the German Army, in World War I. The division was formed on mobilization of the German Army in August 1914. The division was disbanded in September 1918. The division was a reserve division of the III Reserve Corps and was raised primarily in the Prussian Province of Brandenburg. Combat chronicle The 6th Reserve Division began the war on the Western Front. It fought in the opening campaigns against the Belgian Army and the British Expeditionary Force, including the Battle of Mons, and participated in the Siege of Antwerp. It was in the Yser region during the Race to the Sea The Race to the Sea (; , ) took place from about 1914 during the First World War, after the Battle of the Frontiers () and the German advance into France. The invasion had been stopped at the First Battle of the Marne and was followed by the .... In December 1914, the division was transferred to the Eastern Front. In 1915, it fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Entry Into World War I
Germany entered into World War I on August 1, 1914, when it declared war on Russia. In accordance with its war plan, it ignored Russia and moved first against France–declaring war on August 3 and sending its main armies through Belgium to capture Paris from the north. The German invasion of Belgium caused Britain to declare war on Germany on August 4. Most of the main parties were now at war. In October 1914, Turkey joined the war on Germany's side, becoming part of the Central Powers. Italy, which was allied with Germany and Austria-Hungary before World War I, was neutral in 1914 before switching to the Allied side in May 1915. Historians have vigorously debated Germany's role. One line of interpretation, promoted by German historian Fritz Fischer in the 1960s, argues that Germany had long desired to dominate Europe politically and economically, and seized the opportunity that unexpectedly opened in July 1914, making Germany guilty of starting the war. At the opposite end of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Merit Order (Bavaria)
The Bavarian Military Merit Order (german: Militär-Verdienstorden) was established on 19 July 1866 by King Ludwig II of Bavaria. It was the kingdom's main decoration for bravery and military merit for officers and higher-ranking officials. Civilians acting in support of the army were also made eligible for the decoration. The Military Merit Order ranked below the Military Order of Max Joseph (''Militär-Max-Joseph-Orden''), which was Bavaria's highest military honor for officers (and conferred a patent of non-hereditary nobility on officers who were not already nobles). Description and Wear The design of the order was a Maltese cross of blue enamel with a center medallion. Between the arms of most classes (and all classes after 1905) were golden flames (silver flames for the 4th Class after the 1905 revisions of the order). The obverse of the center medallion had a gold crowned "L" cipher (for the founder King Ludwig II) on the black-enameled center and the word "MERENTI" on a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Regent Luitpold
''Leopold Charles Joseph William Louis'' , image_size = , image = Luitpold Wittelsbach cropped.jpg , succession = Prince Regent of Bavaria , reign = 10 June 1886 – 12 December 1912 , reign-type = Tenure , regent = Ludwig IIOtto , reg-type = Monarch , successor = Prince Ludwig , spouse = Archduchess Auguste Ferdinande of Austria , issue = , house = Wittelsbach , father = Ludwig I of Bavaria , mother = Therese of Saxe-Hildburghausen , birth_date = , birth_place = Würzburg , death_date = , death_place = Munich, Kingdom of Bavaria , burial_place = Theatinerkirche, Munich, Bavaria Luitpold Karl Joseph Wilhelm Ludwig, Prince Regent of Bavaria (12 March 1821 – 12 December 1912), was the ''de facto'' ruler of Bavaria from 1886 to 1912, due to the incapacity of his nephews, King Ludwig II for three days and King Otto for 26 years. He was the oldest regent of any country unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generalleutnant
is the Germanic variant of lieutenant general, used in some German speaking countries. Austria Generalleutnant is the second highest general officer rank in the Austrian Armed Forces (''Bundesheer''), roughly equivalent to the NATO rank of OF-8. Belgium Germany ''Generalleutnant'', short ''GenLt'', ('lieutenant general') is the second highest general officer rank in the German Army (''Heer'') and the German Air Force (''Luftwaffe''). This three-star rank in other countries is lieutenant general. Rank in modern Germany The rank is rated OF-8 in NATO, and is grade B9 in the pay rules of the Federal Ministry of Defence. It is equivalent to ''Vizeadmiral'' in the German Navy (''Marine''), or to Generaloberstabsarzt, and Admiraloberstabsarzt in the '' Zentraler Sanitätsdienst der Bundeswehr''. On the shoulder straps (Heer, Luftwaffe) there are three golden pips (stars) in golden oak leaves. History German armies and air forces until 1945 =Generalleutnant of the Wehrm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generalmajor
is the Germanic variant of major general, used in a number of Central and Northern European countries. Austria Belgium Denmark is the second lowest general officer rank in the Royal Danish Army and Royal Danish Air Force. As a two-star rank it is the equivalent to the rank of counter admiral in the Royal Danish Navy. The rank is rated OF-7 within NATO. It has the grade of M404 within the Ministry of Defence's pay structure. The rank of major general is reserved for the Chief of the army and air force. History On 25 May 1671, the ranks were codified, by King Christian V, with the publication of the Danish order of precedence. Here generals of the branch were placed below Lieutenant field marshal ( da, Feltmarskal Lieutenant), and above the noble rank of Count and the military rank of Lieutenant general. As part of the Army Reform of 1867, the ranks of Major, Lieutenant colonel were removed and only a single "General" rank was kept. After the 1880 reform, the gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.gif)