|
Guo Wenjing
Guo Wenjing (born 1 February 1956, in Chongqing) is a Chinese composer and educator. Guo Wenjing is a contemporary Chinese composer. Unlike many Chinese composers who have studied and lived in other countries, he has only studied in Beijing. He has lived and worked in his home country for nearly his entire life with the exception of a short period of time living in New York. However, over the years he has had many works commissioned around the world. He and his music have appeared at the Beijing Music Festival, Edinburgh Festival, Hong Kong Arts Festival, Holland Music Festival, New York Lincoln Center Festival, Paris Autumn Festival, Perth International Arts Festival, Almeida Theatre (London), Frankfurt Opera (Germany), Konzerthaus Berlin (Germany), Kennedy Center (Washington), as well as Turin, Warsaw, etc. In addition, he is contracted by CASA RICORDI-BMG and the first composer to be contracted by People's Music Publishing House. His music has been given high praise both at hom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chongqing
Chongqing ( or ; ; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), Postal Romanization, alternately romanized as Chungking (), is a Direct-administered municipalities of China, municipality in Southwest China. The official abbreviation of the city, "" (), was approved by the State Council of the People's Republic of China, State Council on 18 April 1997. This abbreviation is derived from the old name of a part of the Jialing River that runs through Chongqing and feeds into the Yangtze River. Administratively, it is one of the four municipalities under the direct administration of the Government of China, central government of the People's Republic of China (the other three are Beijing, Shanghai, and Tianjin), and the only such municipality located deep inland. The municipality of Chongqing, roughly the size of Austria, includes the city of Chongqing as well as various discontiguous cities. Due to a classification technicality, Chongqing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Göteborg Symphony Orchestra
The Gothenburg Symphony Orchestra (GSO; sv, Göteborgs Symfoniker) is a Swedish symphony orchestra based in Gothenburg. The GSO is resident at the Gothenburg Concert Hall at Götaplatsen. The orchestra received the title of the National Orchestra of Sweden ( sv, Sveriges Nationalorkester) in 1997. Background and history The GSO was founded in 1905, with Heinrich Hammer as its first principal conductor. The composer Wilhelm Stenhammar was the orchestra's second principal conductor, from 1907 to 1922. In addition to Stenhammar conducting his own works, Jean Sibelius and Carl Nielsen made regular guest-conducting appearances with the GSO. The orchestra's fortunes waxed and waned in subsequent years, until the advent of Neeme Järvi as principal conductor, from 1982 to 2004. Although the GSO has a broad repertoire, it has a special affinity for the works of the Nordic Late Romantic composers, such as Jean Sibelius and Edvard Grieg. During Järvi's tenure as principal conduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Night Banquet
Night (also described as night time, unconventionally spelled as "nite") is the period of ambient darkness from sunset to sunrise during each 24-hour day, when the Sun is below the horizon. The exact time when night begins and ends depends on the location and varies throughout the year, based on factors such as season and latitude. The word can be used in a different sense as the time between bedtime and morning. In common communication, the word ''night'' is used as a farewell ("good night", sometimes shortened to "night"), mainly when someone is going to sleep or leaving. Astronomical night is the period between astronomical dusk and astronomical dawn when the Sun is between 18 and 90 degrees below the horizon and does not illuminate the sky. As seen from latitudes between about 48.56° and 65.73° north or south of the Equator, complete darkness does not occur around the summer solstice because, although the Sun sets, it is never more than 18° below the horizon at lower cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poet Li Bai
''Poet Li Bai'' (Chinese: 《诗人李白》) is a Chinese-language chamber opera by Guo Wenjing to a libretto by Diana Liao (廖端丽) and Xu Ying (徐瑛) on the subject of the poet Li Bai. It was premiered, with subtitles, 7 July 2007 at the Central City Opera House, Central City, Colorado, directed by Lin Zhaohua, conducted by Ed Spanjaard Eduard Philip Spanjaard (born 22 December 1948), known professionally as Ed Spanjaard, is a Dutch conductor and pianist. Early life Spanjaard was born in 1948 in Haarlem. His father was a psychiatrist and amateur pianist, and his mother a fl ..., and produced by Martha Liao. Subsequently, the opera was performed in Beijing and Hong Kong References {{reflist Chinese western-style operas Operas 2007 operas Chamber operas Operas by Guo Wenjing Li Bai Operas set in China Tang dynasty in fiction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolf Cub Village
''Wolf Cub Village'' (Chinese ''Diary of a Madman'') is a 1994 Chinese-language chamber opera in four scenes by Guo Wenjing to a libretto by Zeng Li after Lu Xun Zhou Shuren (25 September 1881 – 19 October 1936), better known by his pen name Lu Xun (or Lu Sun; ; Wade–Giles: Lu Hsün), was a Chinese writer, essayist, poet, and literary critic. He was a leading figure of modern Chinese literature. W ...'s story " Diary of a Madman".The Oxford Dictionary of Musical Works - Page 181 Alison Latham - 2004 "Wolf Cub Village. Chamber opera in four scenes by Guo Wenjing to a libretto by Zeng Li and the composer after Lu Xun's story Kuangren riji ('Diary of a Madman', 1918) (Beijing, 1994)." References {{Lu Xun Chinese western-style operas 1994 operas Operas Operas by Guo Wenjing Operas set in China Chamber operas Operas based on literature Adaptations of works by Lu Xun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sichuan Opera
Sichuan opera (; Sichuanese Pinyin: Cuan1ju4; ) is a type of Chinese opera originating in China's Sichuan province around 1700. Today's Sichuan opera is a relatively recent synthesis of 5 historic melodic styles. Regionally Chengdu remains to be the main home of Sichuan opera, while other influential locales include Chongqing, Guizhou, Yunnan, Hubei and Taiwan. History Initially there were 5 distinct opera styles.Stanton, Sarah. Banham, Martin. 996(1996). The Cambridge Paperback Guide to Theatre. Cambridge press publishing. The history of each style varies greatly. At least one of the Chinese operatic styles began as early as the Three Kingdoms period with some form of ''Canjun opera''. During the Tang dynasty, a band of five came about in Chengdu. In the Song dynasty, the opera developed into ''zaju''. In the Ming dynasty, artists performed the skill in Jinling (modern-day Nanjing). During the reign of Yongzheng and Qianlong emperor in the Qing dynasty, in the Huabu areas, Kun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peking Opera
Peking opera, or Beijing opera (), is the most dominant form of Chinese opera, which combines music, vocal performance, mime, dance and acrobatics. It arose in Beijing in the mid-Qing dynasty (1644–1912) and became fully developed and recognized by the mid-19th century. The form was extremely popular in the Qing court and has come to be regarded as one of the cultural treasures of China. Major performance troupes are based in Beijing, Tianjin and Shanghai. The art form is also preserved in Taiwan, where it is also known as (). It has also spread to other regions such as the United States and Japan. Peking opera features four main role types, '' sheng'' (gentlemen), ''dan'' (women), '' jing'' (rough men), and '' chou'' (clowns). Performing troupes often have several of each variety, as well as numerous secondary and tertiary performers. With their elaborate and colorful costumes, performers are the only focal points on Peking opera's characteristically sparse stage. They use the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Tang
Southern Tang () was a state in Southern China that existed during Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period, which proclaimed itself to be the successor of the former Tang dynasty. The capital was located at Nanjing in present-day Jiangsu Province. At its territorial peak in 951, the Southern Tang controlled the whole of modern Jiangxi, and portions of Anhui, Fujian, Hubei, Hunan, and Jiangsu provinces. The Southern Tang was founded by Li Bian in 937, when he overthrew emperor Yang Pu of Wu. He largely maintained peaceable relations with neighboring states. His son Li Jing did not follow this foreign policy, conquering the Min Kingdom in 945 and Chu in 951. The Later Zhou dynasty invaded the Southern Tang domain in 956 and defeated them by 958. Li Jing was forced to become a vassal of emperor Chai Rong, cede all territory north of the Yangtze River, and relinquish his title of emperor. In 960 the Southern Tang became vassals of the newly established Song dynasty. After Empero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Xizai
Han Xizai () (902 – August 31, 970''Spring and Autumn Annals of the Ten Kingdoms''vol. 28Academia Sinica Chinese-Western Calendar Converter ), Shuyan (叔言), was an official of the and dynasties during the of China, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zou Jingzhi
Zou Jingzhi (邹静之, 1952) is a Chinese playwright. He has written the librettos for two Chinese-language western-style operas by woman composer Lei Lei: Xi Shi (opera) based on the story of Xi Shi, and ''The Chinese Orphan'' (2011) based on the story The Orphan of Zhao. The premiere of both operas was at Beijing's NCPA. Filmography * '' Riding Alone for Thousands of Miles'' (2005) (screenplay) * ''The 601st Phone Call'' (2006) (writer) * ''My Kingdom'' (2011) (screenplay) * '' The Grandmaster'' (2013) (screenplay) * '' Coming Home'' (2014) (screenplay) * ''Xuanzang Xuanzang (, ; 602–664), born Chen Hui / Chen Yi (), also known as Hiuen Tsang, was a 7th-century Chinese Buddhist monk, scholar, traveler, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making contributions to Chinese Buddhism, the travelogue of ...'' (2015) (screenplay) References External links * {{DEFAULTSORT:Zou, Jingzhi Chinese dramatists and playwrights 1952 births Living people 20th-century C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diary Of A Madman (Lu Xun)
"Diary of a Madman", also translated as "A Madman's Diary" () is a short story by the Chinese writer Lu Xun, published in 1918. It was the first and most influential work written in vernacular Chinese in republican era China, and would become a cornerstone of the New Culture Movement. Lu Xun's stories often critiqued early 20th century Chinese society, and "Diary of a Madman" established a new language and revolutionary figure of Chinese literature, an attempt to challenge conventional thinking and traditional understanding. The diary form and the idea of the madman who sees reality more clearly than those around him were inspired by Nikolai Gogol's short story " Diary of a Madman". Lu Xun's "madman" sees "cannibalism" both in his family and the village around him, and he then finds cannibalism in the Confucian classics which had long been credited with a humanistic concern for the mutual obligations of society, and thus used to justify the superiority of Confucian civilizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
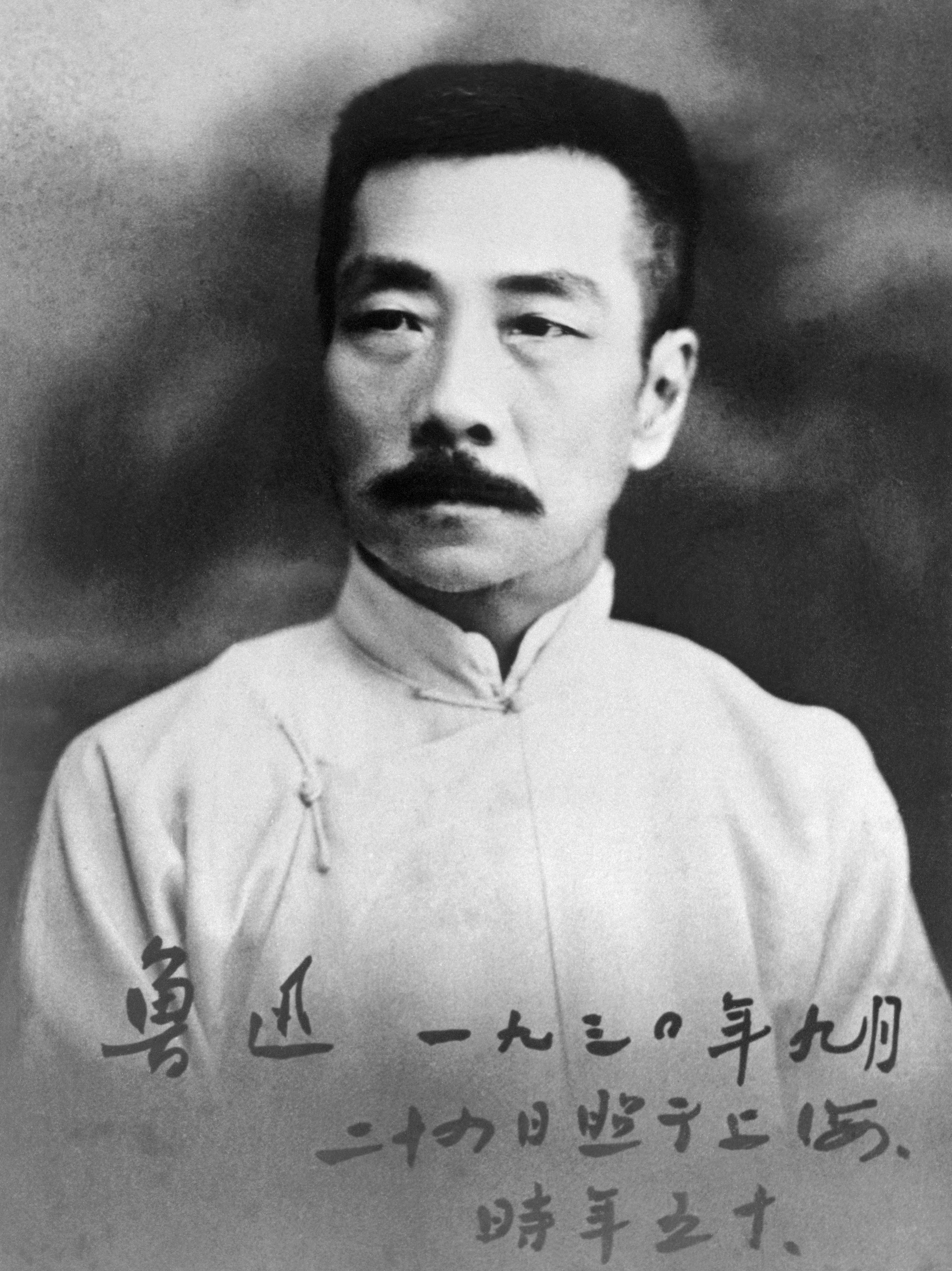
Lu Xun
Zhou Shuren (25 September 1881 – 19 October 1936), better known by his pen name Lu Xun (or Lu Sun; ; Wade–Giles: Lu Hsün), was a Chinese writer, essayist, poet, and literary critic. He was a leading figure of modern Chinese literature. Writing in vernacular Chinese and classical Chinese, he was a short story writer, editor, translator, literary critic, essayist, poet, and designer. In the 1930s, he became the titular head of the League of Left-Wing Writers in Shanghai during republican era China (1912-1949). Lu Xun was born into a family of landlords and government officials in Shaoxing, Zhejiang; the family's financial resources declined over the course of his youth. Lu aspired to take the imperial examinations, but due to his family's relative poverty he was forced to attend government-funded schools teaching "Western education". Upon graduation, Lu went to medical school in Japan but later dropped out. He became interested in studying literature but was eventually f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.jpg)