|
Guadalcanal, Seville
Guadalcanal () is a village in the province of Seville, in the autonomous community of Andalusia, Spain. The name was given to the island of Guadalcanal in the Solomon Islands in 1568. The name was chosen by Pedro de Ortega Valencia who had been born in the village. He was a subordinate of Spanish explorer and navigator Álvaro de Mendaña de Neira. Location and population In 2006 there were 2,970 inhabitants. It has an area of 275 square kilometres and a population density of 10,6 people per square-km. It is at an altitude of 662 metres, in a valley between the Sierra del Agua and the Sierra del Viento, in the region of the Sierra Norte of Seville. Guadalcanal is 80 kilometres north of Seville, it depends to the judicial party of Cazalla de la Sierra. Etymology The name, etymologically, comes from the Arabic phrase ''wādī al-qanāl'', meaning 'river of the stalls' or 'valley of stalls', referring to the refreshment stalls set up there during the Muslim rule in Andal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate. The term ''municipality'' may also mean the governing body of a given municipality. A municipality is a general-purpose administrative subdivision, as opposed to a special-purpose district. The term is derived from French and Latin . The English word ''municipality'' derives from the Latin social contract (derived from a word meaning "duty holders"), referring to the Latin communities that supplied Rome with troops in exchange for their own incorporation into the Roman state (granting Roman citizenship to the inhabitants) while permitting the communities to retain their own local governments (a limited autonomy). A municipality can be any political jurisdiction, from a sovereign state such as the Principality of Monaco, to a small village such as West Hampton Dunes, New York. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seville
Seville (; es, Sevilla, ) is the capital and largest city of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula. Seville has a municipal population of about 685,000 , and a metropolitan population of about 1.5 million, making it the largest city in Andalusia, the fourth-largest city in Spain and the 26th most populous municipality in the European Union. Its old town, with an area of , contains three UNESCO World Heritage Sites: the Alcázar palace complex, the Cathedral and the General Archive of the Indies. The Seville harbour, located about from the Atlantic Ocean, is the only river port in Spain. The capital of Andalusia features hot temperatures in the summer, with daily maximums routinely above in July and August. Seville was founded as the Roman city of . Known as ''Ishbiliyah'' after the Islamic conquest in 711, Seville became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolt Of The Comuneros
The Revolt of the Comuneros ( es, Guerra de las Comunidades de Castilla, "War of the Communities of Castile") was an uprising by citizens of Castile against the rule of Charles I and his administration between 1520 and 1521. At its height, the rebels controlled the heart of Castile, ruling the cities of Valladolid, Tordesillas, and Toledo. The revolt occurred in the wake of political instability in the Crown of Castile after the death of Queen Isabella I in 1504. Isabella's daughter Joanna succeeded to the throne. Due to Joanna's mental instability, Castile was ruled by the nobles and her father, King Ferdinand II of Aragon, as a regent, while Joanna was confined. After Ferdinand's death in 1516, Joanna's sixteen-year-old son Charles was proclaimed her co-monarch of both Castile and Aragon; while Joanna also succeeded as Queen of Aragon, during her co-regency with her own son, she remained confined. Charles had been raised in the Netherlands with little knowledge of Castili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extremadura
Extremadura (; ext, Estremaúra; pt, Estremadura; Fala: ''Extremaúra'') is an autonomous community of Spain. Its capital city is Mérida, and its largest city is Badajoz. Located in the central-western part of the Iberian Peninsula, it is crossed from east to west by the Tagus and Guadiana rivers. The autonomous community is formed by the two largest provinces of Spain: Cáceres and Badajoz. Extremadura is bordered by Portugal to the west and by the autonomous communities of Castile and León (north), Castilla–La Mancha (east) and Andalusia (south). It is an important area for wildlife, particularly with the major reserve at Monfragüe, which was designated a National Park in 2007, and the International Tagus River Natural Park (''Parque Natural Tajo Internacional''). The regional executive body, led by the President of Extremadura, is called Junta de Extremadura. The Day of Extremadura is celebrated on 8 September. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of León
The Kingdom of León; es, Reino de León; gl, Reino de León; pt, Reino de Leão; la, Regnum Legionense; mwl, Reino de Lhion was an independent kingdom situated in the northwest region of the Iberian Peninsula. It was founded in 910 when the Christian princes of Asturias along the northern coast of the peninsula shifted their capital from Oviedo to the city of León. The kings of León fought civil wars, wars against neighbouring kingdoms, and campaigns to repel invasions by both the Moors and the Vikings, all in order to protect their kingdom's changing fortunes. García is the first of the kings described by the charters as reigning in León. It is generally assumed that the old Asturian kingdom was divided among the three sons of Alfonso III of Asturias: García (León), Ordoño ( Galicia) and Fruela (Asturias), as all three participated in the deposition of their father. When García died in 914, León went to Ordoño, who now ruled both León and Galicia as Ordo� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moors
The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages. Moors are not a distinct or self-defined people. The 1911 ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' observed that the term had "no real ethnological value." Europeans of the Middle Ages and the early modern period variously applied the name to Arabs and North African Berbers, as well as Muslim Europeans. The term has also been used in Europe in a broader, somewhat derogatory sense to refer to Muslims in general,Menocal, María Rosa (2002). ''Ornament of the World: How Muslims, Jews and Christians Created a Culture of Tolerance in Medieval Spain''. Little, Brown, & Co. , p. 241 especially those of Arab or Berber descent, whether living in Spain or North Africa. During the colonial era, the Portuguese introduced the names " Ceylon Moors" and "Indian Moors" in South Asia and Sri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of Santiago
The Order of Santiago (; es, Orden de Santiago ), is a religious and military order founded in the 12th century. It owes its name to the Patron Saint of Spain, "Santiago" ( St. James the Greater). Its initial objective was to protect the pilgrims on the Way of St. James, to defend Christendom and to remove the Muslim Moors from the Iberian Peninsula. Entrance was not however restricted to nobility of Spain exclusively, and many members have been prominent Catholic Europeans in general. The Order's insignia is particularly recognisable and abundant in Western art. After the death of the Grand Master Alonso de Cárdenas in 1493, the Catholic Monarchs incorporated the Order into the Spanish Crown. Pope Adrian VI forever united the office of grandmaster of Santiago to the crown in 1523. The First Republic suppressed the Order in 1873 and, although it was re-established in the Restoration, it was reduced to a nobiliary institute of honorable character. It was ruled by a Superior C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ermita De San Benito
Ermita is a district in Manila, Philippines. Located at the central part of the city, the district is a significant center of finance, education, culture, and commerce. Ermita serves as the civic center of the city, bearing the seat of city government and a large portion of the area's employment, business, and entertainment activities. Private and government offices, museums, and universities thrive in Ermita. It is also home to famous tourist attractions and landmarks, notably the Rizal Park, the premier national park of the Philippines. Originally, Ermita and its neighboring district Malate were posh neighborhoods for Manila's high society during the early 20th century where large, grandiose mansions once stood. Ermita and its surroundings were heavily bombed and flattened during the Second World War after it became a battleground during the Manila Massacre. After the war, Ermita and its twin district, Malate, had undergone commercialization resulting in a shift from being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iberians
The Iberians ( la, Hibērī, from el, Ἴβηρες, ''Iberes'') were an ancient people settled in the eastern and southern coasts of the Iberian peninsula, at least from the 6th century BC. They are described in Greek and Roman sources (among others, by Hecataeus of Miletus, Avienius, Herodotus and Strabo). Roman sources also use the term ''Hispani'' to refer to the Iberians. The term ''Iberian'', as used by the ancient authors, had two distinct meanings. One, more general, referred to all the populations of the Iberian peninsula without regard to ethnic differences ( Pre-Indo-European, Celts and non-Celtic Indo-Europeans). The other, more restricted ethnic sense and the one dealt with in this article, refers to the people living in the eastern and southern coasts of the Iberian Peninsula, which by the 6th century BC had absorbed cultural influences from the Phoenicians and the Greeks. This pre-Indo-European cultural group spoke the Iberian language from the 7th to the 1s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus DIN 31635, translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label=Berber languages, Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the Muslim-ruled area of the Iberian Peninsula. The term is used by modern historians for the former Islamic states in modern Spain and Portugal. At its greatest geographical extent, it occupied most of the peninsula and a part of present-day southern France, Septimania (8th century). For nearly a hundred years, from the 9th century to the 10th, al-Andalus extended its presence from Fraxinetum into the Alps with a series of organized raids and chronic banditry. The name describes the different Arab and Muslim states that controlled these territories at various times between 711 and 1492. These boundaries changed constantly as the Christian Reconquista progressed,"Para los autores árabes medievales, el término Al-And ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
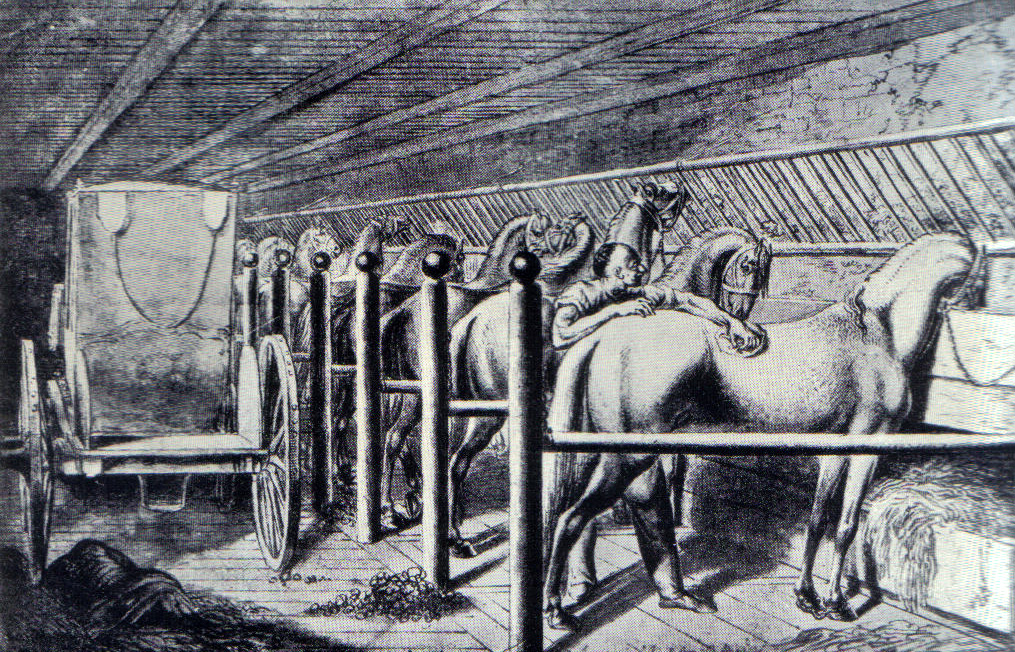
Animal Stall
An animal stall is an enclosure housing one or a few animals. Stalls for animals can often be found wherever animals are kept: a horse stable is often a purpose-built and permanent structure. A farmer's barn may be subdivided into animal stalls or pens for cows and other livestock. Tie stalls are a type of stall where animals are tethered at the neck to their stall. It is mostly used in the dairy industry, although horses might also be stalled in tie stalls (often referred to as stands or straight stalls). Typical the barn has two rows of stalls, where the cow is tied up for resting, feeding, milking and watering. This type of housing is used in both regular and organic farming. Horse care In horse care, the standard dimensions for a "loose box" (UK) or "box stall" (US) vary from to , depending on local cultural traditions, the breed of horse, gender, and any special needs. Mares with foals often are kept in double stalls. Stallions, kept alone with less access to turnout, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wadi
Wadi ( ar, وَادِي, wādī), alternatively ''wād'' ( ar, وَاد), North African Arabic Oued, is the Arabic term traditionally referring to a valley. In some instances, it may refer to a wet (ephemeral) riverbed that contains water only when heavy rain occurs. Etymology The term ' is very widely found in Arabic toponyms. Some Spanish toponyms are derived from Andalusian Arabic where ' was used to mean a permanent river, for example: Guadalcanal from ''wādī al-qanāl'' ( ar, وَادِي الْقَنَال, "river of refreshment stalls"), Guadalajara from ''wādī al-ḥijārah'' ( ar, وَادِي الْحِجَارَة, "river of stones"), or Guadalquivir, from ''al-wādī al-kabīr'' ( ar, اَلْوَادِي الْكَبِير, "the great river"). General morphology and processes Wadis are located on gently sloping, nearly flat parts of deserts; commonly they begin on the distal portions of alluvial fans and extend to inland sabkhas or dry lakes. In basin and r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |