|
Großhansdorf
Großhansdorf is a municipality in the district of Stormarn, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is situated approximately 3 km east of Ahrensburg, and 25 km northeast of Hamburg. History Großhansdorf was first mentioned in 1274 in a deed of Hamburg's St. Catherine's Church congregation, to which Großhansdorf was affiliated at that time. In 1435 the city of Hamburg acquired Großhansdorf and administered it as part of its forest villages domain (Walddörfer), consisting of a series of Hamburgian exclaves surrounded by then else Holstein territories. In 1642 the erection of a water mill is recorded, which operated until the 19th century. Since 1701 Großhansdorf was the seat of a ''forest rider'' (german: Waldreiter), an official of Hamburg's police administration, which is recalled in today's coat-of-arms of Großhansdorf. Hamburg then formed a free imperial city within the Holy Roman Empire. By 1806 the rotation of arable fields among the resident farming families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Großhansdorf (Hamburg U-Bahn Station)
Großhansdorf is a municipality in the district of Stormarn, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is situated approximately 3 km east of Ahrensburg, and 25 km northeast of Hamburg. History Großhansdorf was first mentioned in 1274 in a deed of Hamburg's St. Catherine's Church congregation, to which Großhansdorf was affiliated at that time. In 1435 the city of Hamburg acquired Großhansdorf and administered it as part of its forest villages domain (Walddörfer), consisting of a series of Hamburgian exclaves surrounded by then else Holstein territories. In 1642 the erection of a water mill is recorded, which operated until the 19th century. Since 1701 Großhansdorf was the seat of a ''forest rider'' (german: Waldreiter), an official of Hamburg's police administration, which is recalled in today's coat-of-arms of Großhansdorf. Hamburg then formed a free imperial city within the Holy Roman Empire. By 1806 the rotation of arable fields among the resident farming families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamburg U-Bahn
The Hamburg U-Bahn is a rapid transit system serving the cities of Hamburg, Norderstedt and Ahrensburg in Germany. Although referred to by the term U-Bahn (the "U" commonly being understood as standing for "underground"), most of the system's track length is above ground. The network is interconnected with the city's S-Bahn system, which also has underground sections. It is operated by Hamburger Hochbahn within the Hamburger Verkehrsverbund (HVV). It was opened in February 1912, and comprises four lines serving 93 stations, with a route length of in 2019. History In 1906 the Senate of Hamburg awarded a contract for the Elevated and Underground Railway to Siemens & Halske and AEG of Berlin. The first stretch was completed on 7 October 1906. This was followed in 1911 with the founding of the ''Hamburger Hochbahn Aktiengesellschaft'' (HHA). Thus Hamburg became the third German city (after Berlin, 1902 and Schöneberg, 1910) to have a U-Bahn (then known as the Elevated and Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiekut (Hamburg U-Bahn Station)
Kiekut is a station on the Großhansdorf branch of Hamburg U-Bahn line U1. The station was opened in June 1922, and is located in the Hamburg suburb of Großhansdorf, Germany. History The railway station was built according to a design by Eugen Göbel around 1915. When the station was built, the area around it was very sparsely populated, so only the most necessary parts were built, such as the platform, stairway, and bridge to the street. No station building was built. When the tracks at the station were electrified, the westbound track was taken out and since hasn't been replaced. The track was electrified in 1921, but trains did not stop here until 1922. In 1954 and 1994, the entrance to the station was redesigned. Services Kiekut is served by Hamburg U-Bahn The Hamburg U-Bahn is a rapid transit system serving the cities of Hamburg, Norderstedt and Ahrensburg in Germany. Although referred to by the term U-Bahn (the "U" commonly being understood as standing for "undergro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schmalenbeck (Hamburg U-Bahn Station)
Schmalenbeck is a station on the Großhansdorf branch of Hamburg U-Bahn line U1, located in the town of Großhansdorf. History The station was built following schematics by Eugen Göbel in 1914 and was opened in 1921. The second track at the station was added a year later, in 1922. Services Schmalenbeck is served by Hamburg U-Bahn The Hamburg U-Bahn is a rapid transit system serving the cities of Hamburg, Norderstedt and Ahrensburg in Germany. Although referred to by the term U-Bahn (the "U" commonly being understood as standing for "underground"), most of the system's ... line U1. References {{Hamburg rail, lineU1=yes U1 (Hamburg U-Bahn) stations Hamburg U-Bahn stations in Schleswig-Holstein Buildings and structures in Stormarn (district) Transport infrastructure completed in 1914 Railway stations in Germany opened in 1921 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stormarn (district)
Stormarn () is a district in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is bounded by (from the north and clockwise) the districts of Segeberg and Ostholstein, the city of Lübeck, the district of Lauenburg, and the city-state of Hamburg. History In medieval times the name Stormarn was applied to a larger area, of which the present-day district is only the eastern half. It was the home of the Saxon tribe the Sturmarii. Stormarn became a part of Holstein in the 12th century. When Schleswig-Holstein became a province of Prussia in 1867, the Prussian administration established the district of Stormarn, with Wandsbek as its capital. In 1937 the southwestern part of the district was incorporated into Hamburg, and the district lost half of its population. Since Wandsbek was now a borough of Hamburg, the capital was moved to Bad Oldesloe after the war. In 1970 Stormarn again lost a substantial portion of its territory, when the city of Norderstedt was founded in order to become a part of the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Schleswig-Holstein
The Province of Schleswig-Holstein (german: Provinz Schleswig-Holstein ) was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia (subsequently the Free State of Prussia after 1918) from 1868 to 1946. History It was created from the Duchies of Schleswig and Holstein, which had been conquered by Prussia and the Austrian Empire from Denmark in the Second War of Schleswig in 1864. Following the Austro-Prussian War in 1866, which ended in Austrian defeat, Schleswig and Holstein were annexed by decree of the King of Prussia on 12 January 1867. The province was created in 1868, and it incorporated the Duchy of Lauenburg from 1876 onward. Following the defeat of Imperial Germany in World War I, the Allied powers organised two plebiscites in Northern and Central Schleswig on 10 February and 14 March 1920, respectively. In Northern Schleswig, 75% voted for reunification with Denmark and 25% for staying with Germany. In Central Schleswig, the situation was reversed, with 80% voting for Germany and 20% f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City State
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as Rome, Athens, Sparta, Carthage, and the Italian city-states during the Middle Ages and Renaissance, such as Florence, Venice, Genoa and Milan. With the rise of nation states worldwide, only a few modern sovereign city-states exist, with some disagreement as to which qualify; Monaco, Singapore and Vatican City are most commonly accepted as such. Singapore is the clearest example, with full self-governance, its own currency, a robust military and a population of 5.5 million. Several non-sovereign cities enjoy a high degree of autonomy and are sometimes considered city-states. Hong Kong, Macau, and members of the United Arab Emirates—most notably Dubai and Abu Dhabi—are often cited as such. Historical background Ancient and medieva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Hamburg Act
The Greater Hamburg Act (german: Groß-Hamburg-Gesetz), in full the Law Regarding Greater Hamburg and Other Territorial Readjustments (german: Gesetz über Groß-Hamburg und andere Gebietsbereinigungen), was passed by the government of Nazi Germany on 26 January 1937, and mandated the exchange of territories between Hamburg and the Free State of Prussia. It became effective on 1 April 1937.With the exception of paragraph 2 (unifying Hamburg to a single ''Gemeinde'') which according to paragraph 15 had to be put into effect separately at a date determined by the minister of the interior no later than 1 April 1938, and with the exception of paragraph 10, which became effective immediately Greater Hamburg Hamburg lost most of its exclaves, including Geesthacht and Cuxhaven. In return, Hamburg was enlarged by including formerly Prussian towns like Altona, Wandsbek, and Harburg-Wilhelmsburg as well as a number of villages. Altona and Wandsbek had been part of the Prussian province ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free And Hanseatic City Of Hamburg
(male), (female) en, Hamburger(s), Hamburgian(s) , timezone1 = Central (CET) , utc_offset1 = +1 , timezone1_DST = Central (CEST) , utc_offset1_DST = +2 , postal_code_type = Postal code(s) , postal_code = 20001–21149, 22001–22769 , area_code_type = Area code(s) , area_code = 040 , registration_plate = , blank_name_sec1 = GRP (nominal) , blank_info_sec1 = €123 billion (2019) , blank1_name_sec1 = GRP per capita , blank1_info_sec1 = €67,000 (2019) , blank1_name_sec2 = HDI (2018) , blank1_info_sec2 = 0.976 · 1st of 16 , iso_code = DE-HH , blank_name_sec2 = NUTS Region , blank_info_sec2 = DE6 , website = , footnotes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Confederation
The German Confederation (german: Deutscher Bund, ) was an association of 39 predominantly German-speaking sovereign states in Central Europe. It was created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 as a replacement of the former Holy Roman Empire, which had been dissolved in 1806. The Confederation had only one organ, the Federal Convention (also Federal Assembly or Confederate Diet). The Convention consisted of the representatives of the member states. The most important issues had to be decided on unanimously. The Convention was presided over by the representative of Austria. This was a formality, however, the Confederation did not have a head of state, since it was not a state. The Confederation, on the one hand, was a strong alliance between its member states because federal law was superior to state law (the decisions of the Federal Convention were binding for the member states). Additionally, the Confederation had been established for eternity and was impossible to dissolve (l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
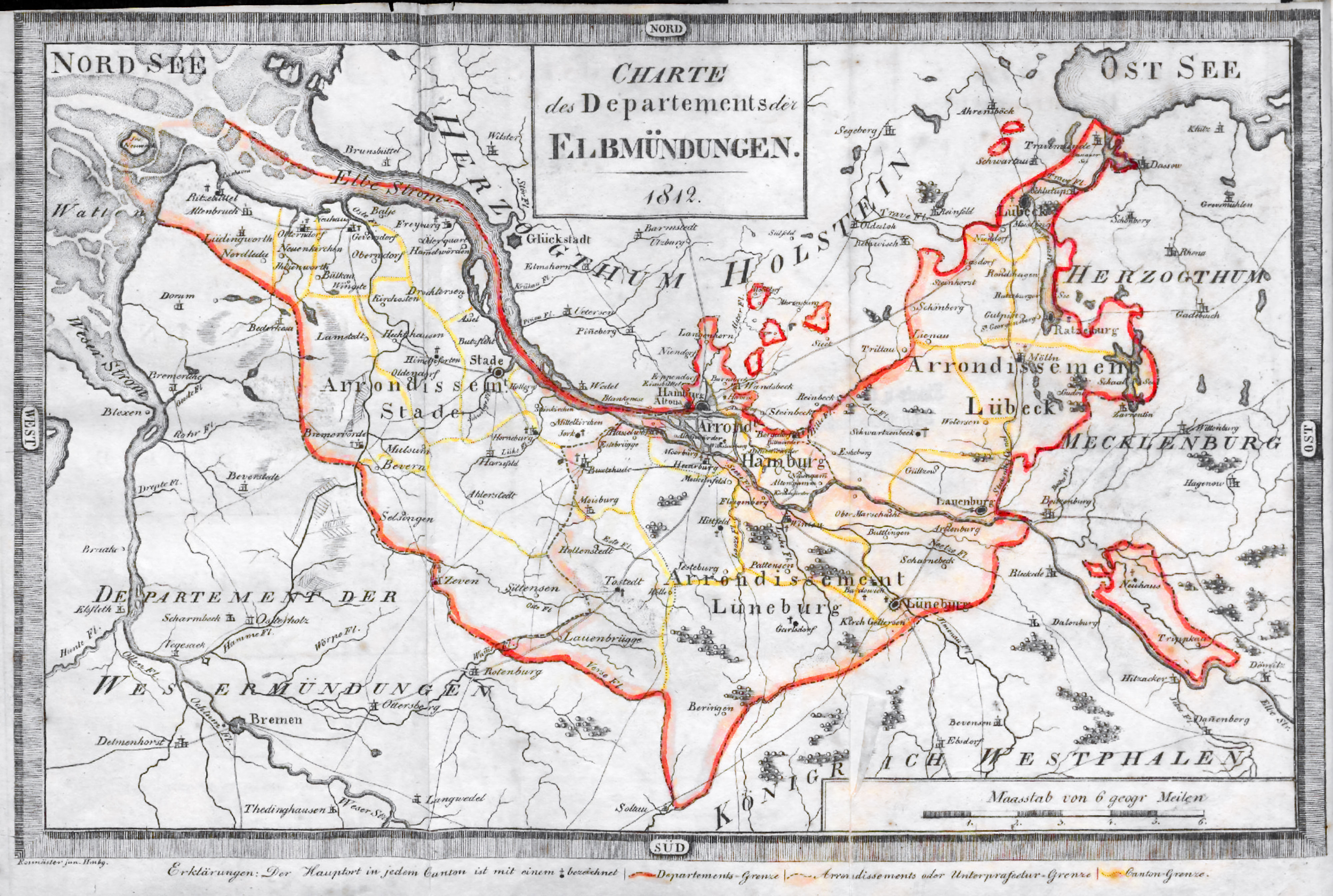
Bouches-de-l'Elbe
Bouches-de-l'Elbe (; "Mouths of the Elbe", ) was a departments of France, department of the First French Empire in present-day Germany that survived for three years. It was named after the mouth of the river Elbe. It was formed in 1811, when the region, originally belonging partially to Bremen-Verden (which in 1807 had been intermittently incorporated into the Kingdom of Westphalia), to Hamburg, Free City of Lübeck, Lübeck and Saxe-Lauenburg, was annexed by France. Its territory is part of the present-day German states of Lower Saxony, Schleswig-Holstein and Hamburg. Its capital was Hamburg. The department was subdivided into four arrondissements and the following canton (subnational entity), cantons (situation in 1812, French translated names where applicable):Almanach Impérial an bissextil MDCCCXII p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Schleswig. Its capital city is Kiel; other notable cities are Lübeck and Flensburg. The region is called ''Slesvig-Holsten'' in Danish and pronounced . The Low German name is ''Sleswig-Holsteen'', and the North Frisian name is ''Slaswik-Holstiinj''. In more dated English, it is also known as ''Sleswick-Holsatia''. Historically, the name can also refer to a larger region, containing both present-day Schleswig-Holstein and the former South Jutland County (Northern Schleswig; now part of the Region of Southern Denmark) in Denmark. It covers an area of , making it the 5th smallest German federal state by area (including the city-states). Schleswig was under Danish control during the Viking Age, but in the 12th century it escaped full control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |