|
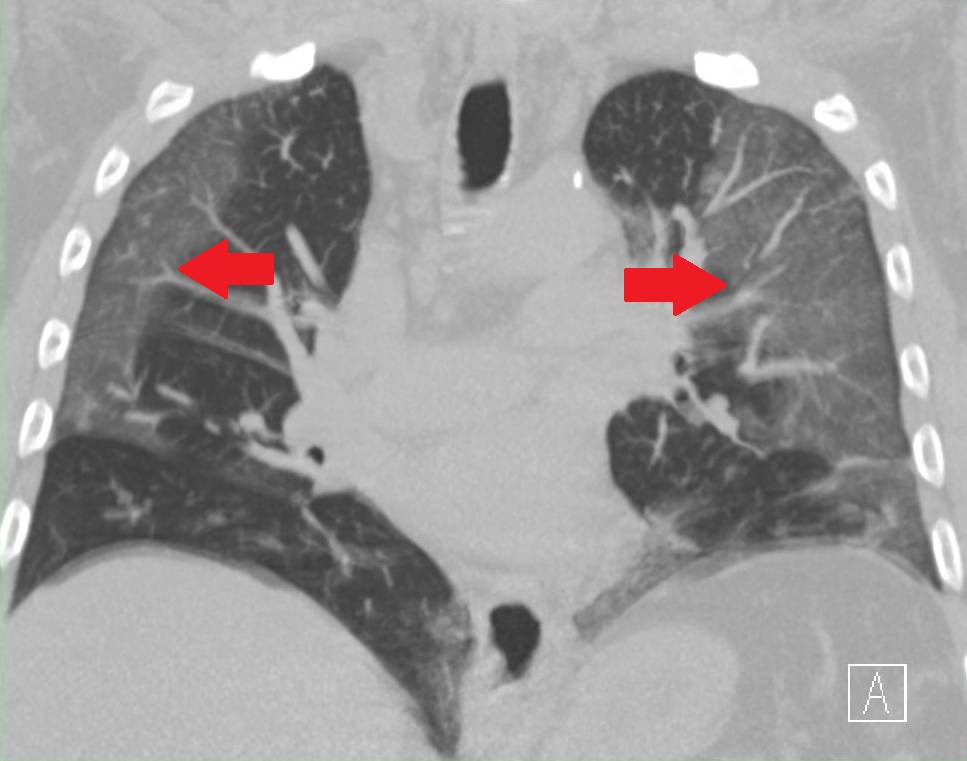
Ground-glass Opacity
Ground-glass opacity (GGO) is a finding seen on chest x-ray (radiograph) or computed tomography (CT) imaging of the lungs. It is typically defined as an area of hazy opacification (x-ray) or increased attenuation (CT) due to air displacement by fluid, airway collapse, fibrosis, or a neoplastic process. When a substance other than air fills an area of the lung it increases that area's density. On both x-ray and CT, this appears more grey or hazy as opposed to the normally dark-appearing lungs. Although it can sometimes be seen in normal lungs, common pathologic causes include infections, interstitial lung disease, and pulmonary edema. Definition In both CT and chest radiographs, normal lungs appear dark due to the relative lower density of air compared to the surrounding tissues. When air is replaced by another substance (e.g. fluid or fibrosis), the density of the area increases, causing the tissue to appear lighter or more grey. Ground-glass opacity is most often used to d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Hemorrhage
Pulmonary hemorrhage (or pulmonary haemorrhage) is an acute bleeding from the lung, from the upper respiratory tract and the trachea, and the pulmonary alveoli. When evident clinically, the condition is usually massive.Pulmonary Hemorrhage Intensive Care Nursery House Staff Manual. UCSF Children's Hospital at UCSF Medical Center. 2004:The Regents of the University of California. Retrieved 2008-10-28. The onset of pulmonary hemorrhage is characterized by a cough productive of blood ( |
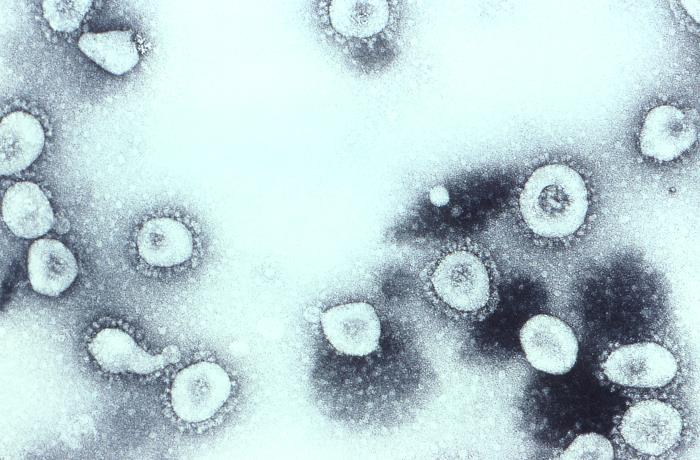
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome–related Coronavirus
''Middle East respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (''MERS-CoV''), or EMC/2012 ( HCoV-EMC/2012), is the virus that causes Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). It is a species of coronavirus which infects humans, bats, and camels. The infecting virus is an enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus which enters its host cell by binding to the DPP4 receptor. The species is a member of the genus '' Betacoronavirus'' and subgenus ''Merbecovirus''. Initially called simply novel coronavirus or nCoV, it was first reported in June 2012 after genome sequencing of a virus isolated from sputum samples from a person who fell ill in a 2012 outbreak of a new flu-like respiratory illness. By July 2015, MERS-CoV cases had been reported in over 21 countries, in Europe, North America and Asia as well as the Middle East. MERS-CoV is one of several viruses identified by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a likely cause of a future epidemic. They list it for urgent rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the common cold (which is also caused by other viruses, predominantly rhinoviruses), while more lethal varieties can cause SARS, MERS and COVID-19, which is causing the ongoing pandemic. In cows and pigs they cause diarrhea, while in mice they cause hepatitis and encephalomyelitis. Coronaviruses constitute the subfamily ''Orthocoronavirinae'', in the family '' Coronaviridae'', order ''Nidovirales'' and realm ''Riboviria''. They are enveloped viruses with a positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome and a nucleocapsid of helical symmetry. The genome size of coronaviruses ranges from approximately 26 to 32 kilobases, one of the largest among RNA viruses. They have characteristic club-shaped spikes that project from their surface, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenoviridae
Adenoviruses (members of the family ''Adenoviridae'') are medium-sized (90–100 nm), nonenveloped (without an outer lipid bilayer) viruses with an icosahedral nucleocapsid containing a double-stranded DNA genome. Their name derives from their initial isolation from human adenoids in 1953. They have a broad range of vertebrate hosts; in humans, more than 50 distinct adenoviral serotypes have been found to cause a wide range of illnesses, from mild respiratory infections in young children (known as the common cold) to life-threatening multi-organ disease in people with a weakened immune system. Virology Classification This family contains the following genera: * '' Atadenovirus'' * '' Aviadenovirus'' * '' Ichtadenovirus'' * '' Mastadenovirus'' (including all human adenoviruses) * '' Siadenovirus'' * '' Testadenovirus'' Diversity In humans, currently there are 88 human adenoviruses (HAdVs) in seven species (Human adenovirus A to G): * A: 12, 18, 31 * B: 3, 7, 11, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septic Embolism
A septic embolism is a type of embolism that is infected with bacteria, resulting in the formation of pus. These may become dangerous if dislodged from their original location. Like other emboli, a septic embolism may be fatal. One of the common microbes that can lead to widespread dissemination of septic emboli is ''Fusobacterium necrophorum'', a Gram negative anaerobic bacillus. Fusobacteriota are commensal organisms in the oral cavity. ''F. necrophorum'' and'' F. nucleatum'' are the most important among the non-spore forming anaerobic bacilli in causing human infections.'' F. necroporum'' may occasionally cause septicaemia with metastatic abscesses (Lemierre's syndrome). Pathogenesis Septic emboli most often originate from extrapulmonary locations which have been infected for a period of time. For example, a person's intravenous access site, which is used to insert intravenous drugs, may become infected. When present in great number, septic emboli can coalesce and mimick a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nocardia
''Nocardia'' is a genus of weakly staining Gram-positive, catalase-positive, rod-shaped bacteria. It forms partially acid-fast beaded branching filaments (acting as fungi, but being truly bacteria). It contains a total of 85 species. Some species are nonpathogenic, while others are responsible for nocardiosis. ''Nocardia'' species are found worldwide in soil rich in organic matter. In addition, they are oral microflora found in healthy gingiva, as well as periodontal pockets. Most ''Nocardia'' infections are acquired by inhalation of the bacteria or through traumatic introduction. Culture and staining ''Nocardia'' colonies have a variable appearance, but most species appear to have aerial hyphae when viewed with a dissecting microscope, particularly when they have been grown on nutritionally limiting media. ''Nocardia'' grow slowly on nonselective culture media, and are strict aerobes with the ability to grow in a wide temperature range. Some species are partially acid-f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycobacterium
''Mycobacterium'' is a genus of over 190 species in the phylum Actinomycetota, assigned its own family, Mycobacteriaceae. This genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis ('' M. tuberculosis'') and leprosy (''M. leprae'') in humans. The Greek prefix ''myco-'' means 'fungus', alluding to this genus' mold-like colony surfaces. Since this genus has cell walls with Gram-positive and Gram-negative features, acid-fast staining is used to emphasize their resistance to acids, compared to other cell types. Metabolism and Morphology Mycobacteria are aerobic with 0.2-0.6 µm wide and 1.0-10 µm long rod shapes. They are generally non-motile, except for the species '' Mycobacterium marinum'', which has been shown to be motile within macrophages. Mycobacteria possess capsules and most do not form endospores. ''M. marinum'' and perhaps ''M. bovis'' have been shown to sporulate; however, this has been contested by further research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legionella Pneumophila
''Legionella pneumophila'' is a thin, aerobic, pleomorphic, flagellated, non-spore-forming, Gram-negative bacterium of the genus '' Legionella''. ''L. pneumophila'' is the primary human pathogenic bacterium in this group and is the causative agent of Legionnaires' disease, also known as legionellosis. In nature, ''L. pneumophila'' infects freshwater and soil amoebae of the genera '' Acanthamoeba'' and '' Naegleria''. The mechanism of infection is similar in amoeba and human cells. Characterization ''L. pneumophila'' is a Gram-negative, non-encapsulated, aerobic bacillus with a single, polar flagellum often characterized as being a coccobacillus. It is aerobic and unable to hydrolyse gelatin or produce urease. It is also non- fermentative. ''L. pneumophila'' is neither pigmented nor does it autofluoresce. It is oxidase- and catalase-positive, and produces beta-lactamase. ''L. pneumophila'' colony morphology is gray-white with a textured, cut-glass appearance; it also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamydia Pneumoniae
''Chlamydia pneumoniae'' is a species of ''Chlamydia'', an obligate intracellular bacterium that infects humans and is a major cause of pneumonia. It was known as the Taiwan acute respiratory agent (TWAR) from the names of the two original isolates – Taiwan (TW-183) and an acute respiratory isolate designated AR-39. Briefly, it was known as ''Chlamydophila pneumoniae,'' and that name is used as an alternate in some sources. In some cases, to avoid confusion, both names are given. ''Chlamydia pneumoniae'' has a complex life cycle and must infect another cell to reproduce; thus, it is classified as an obligate intracellular pathogen. The full genome sequence for ''C. pneumoniae'' was published in 1999. It also infects and causes disease in koalas, emerald tree boas (''Corallus caninus''), iguanas, chameleons, frogs, and turtles. The first known case of infection with ''C. pneumoniae'' was a case of conjunctivitis in Taiwan in 1950. There are no known cases of ''C. pneumon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycoplasma Pneumoniae
''Mycoplasma pneumoniae'' is a very small bacterium in the class Mollicutes. It is a human pathogen that causes the disease mycoplasma pneumonia, a form of atypical bacterial pneumonia related to cold agglutinin disease. ''M. pneumoniae'' is characterized by the absence of a peptidoglycan cell wall and resulting resistance to many antibacterial agents. The persistence of ''M. pneumoniae'' infections even after treatment is associated with its ability to mimic host cell surface composition. Discovery and history In 1898, Nocard and Roux isolated an agent assumed to be the cause of cattle pneumonia and named it ''microbe de la peripneumonie'' Microorganisms from other sources, having properties similar to the pleuropneumonia organism (PPO) of cattle, soon came to be known as pleuropneumonia-like organisms (PPLO), but their true nature remained unknown. Many PPLO were later proven to be the cause of pneumonias and arthritis in several lower animals. In 1944, Monroe Eaton had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |