|
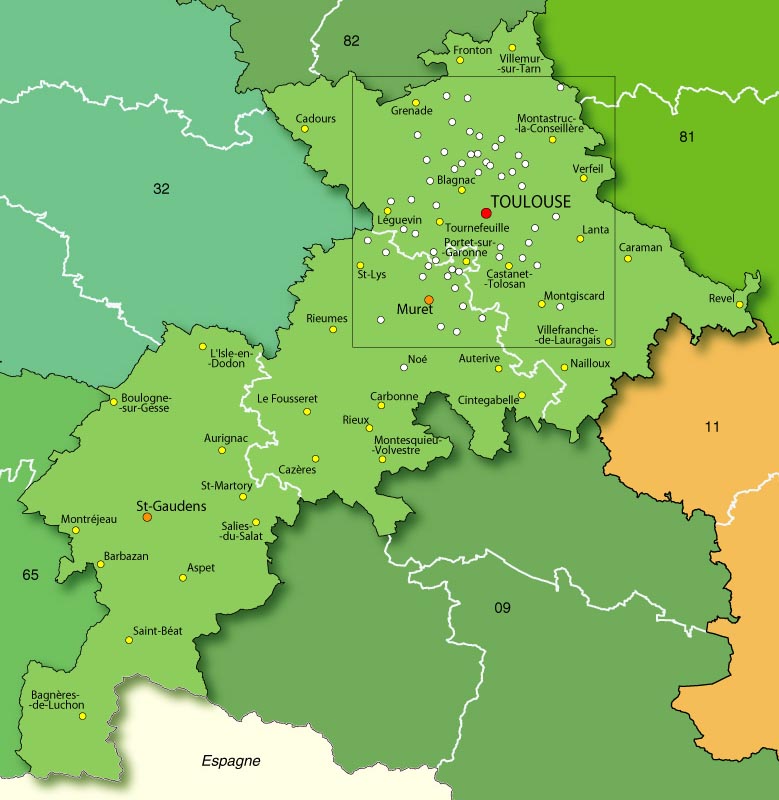
Grenade-sur-Garonne
Grenade (; Languedocien: ''Granada''), also referred to as Grenade-sur-Garonne, is a commune in the Haute-Garonne department in southwestern France. History The town is a bastide founded in the 1290s on the initiative of the Cistercian monks of the Abbey of Grandselve who had founded Beaumont-de-Lomagne ten years earlier. The city is the subject of a '' paréage'' agreement between the monks and the seneschal Eustache de Beaumarchais representing King Philip IV. The new bastides created at this time are baptized with the names of large influential cities of the time, from Spain or Italy , such as Fleurance (Florence), or Cologne. Grenada is therefore called so to show that it is destined to be an influential city in the South West of France. It has also been suggested that Granada comes from the Latin Granat - meaning grain - as the region was noted for its agriculture. Later, when the king had regained control of the different regions of the South-West, a “network” of basti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eustache De Beaumarchais
Eustache de Beaumarchais (''c''. 1235 – 23 August 1294) was a French baron and military leader who served as seneschal of the County of Poitou (1268–76) and the County of Toulouse (1272–94). He took part in the War of the Navarrería in 1276–77 and in the Aragonese Crusade in 1284–85. Eustache was probably born in the hamlet of Beaumarchais, now part of Othis, into a family of the petty nobility. He first entered royal service as guardian of the abbey of Aurillac. In 1257, Count Alphonse of Poitiers appointed him bailiff of the royal part of the Auvergne, which Alphonse held as an appanage. Eustache continued as bailiff down to 1266, when he was succeeded by Geoffroy de Montirel. In 1268, Alphonse, who was also Count of Toulouse, named him his seneschal in Poitou. Alphonse died in 1271 and his counties escheated to the crown, but Eustache continued in the seneschalate of Poitou until 1276. In 1272, Eustache was appointed royal seneschal in Toulouse, a post he held unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bastide
Bastides are fortified new towns built in medieval Languedoc, Gascony, Aquitaine, England and Wales during the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries, although some authorities count Mont-de-Marsan and Montauban, which was founded in 1144, as the first bastides.Bastide in the French Wikipedia, retrieved March 8, 2007. Some of the first bastides were built under Raymond VII of Toulouse to replace villages destroyed in the Albigensian Crusade. He encouraged the construction of others to colonize the wilderness, especially of southwest France. Almost 700 bastides were built between 1222 (Cordes-sur-Ciel, Tarn) and 1372 (La Bastide d'Anjou, Tarn). History were developed in number under the terms of the Treaty of Paris (1229), which permitted Raymond VII of Toulouse to build new towns in his shattered domains but not to fortify them. When the Capetian Alphonse of Poitiers inherited, under a marriage stipulated by the treaty, this " founder of unparalleled energy" consolidated his regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of France
The () is a level of administrative division in the French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipalities in the United States and Canada, ' in Germany, ' in Italy, or ' in Spain. The United Kingdom's equivalent are civil parishes, although some areas, particularly urban areas, are unparished. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the lack of administrative powers. Except for the municipal arrondi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languedocien Dialect
Languedocien (French name, ), Languedocian or Lengadocian (), is an Occitan dialect spoken in rural parts of southern France such as Languedoc, Rouergue, Quercy, Agenais and Southern Périgord. It is sometimes also called Languedocien-Guyennais. Due to its central position among the dialects of Occitan, it is often used as a basis for a Standard Occitan. About 10% of the population of Languedoc are fluent in the language (about 300,000), and another 20% (600,000) "have some understanding" of the language. All speak French as their first or second language. Geographic distribution Languedocien is spoken in certain parts of three French regions. * Occitanie: Aveyron, Lot, Tarn, Tarn-et-Garonne except Lomagne, Ariège (except a western part), Haute-Garonne (except the districts of Saint-Gaudens and Muret), Aude, Hérault, Lozère, western and northern parts of Gard and Fenouillèdes. * Nouvelle-Aquitaine: south of the Dordogne, east of the Gironde, north-eastern two-thirds of L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haute-Garonne
Haute-Garonne (; oc, Nauta Garona, ; en, Upper Garonne) is a department in the Occitanie region of Southwestern France. Named after the river Garonne, which flows through the department. Its prefecture and main city is Toulouse, the country's fourth-largest. In 2019, it had a population of 1,400,039.Populations légales 2019: 31 Haute-Garonne INSEE History Haute-Garonne is one of the original 83 departments created during the on 4 March 1790. It was created from part of the former provinces of an ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Departments Of France
In the administrative divisions of France, the department (french: département, ) is one of the three levels of government under the national level ("territorial collectivities"), between the administrative regions and the communes. Ninety-six departments are in metropolitan France, and five are overseas departments, which are also classified as overseas regions. Departments are further subdivided into 332 arrondissements, and these are divided into cantons. The last two levels of government have no autonomy; they are the basis of local organisation of police, fire departments and, sometimes, administration of elections. Each department is administered by an elected body called a departmental council ( ing. lur.. From 1800 to April 2015, these were called general councils ( ing. lur.. Each council has a president. Their main areas of responsibility include the management of a number of social and welfare allowances, of junior high school () buildings and technical staff, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its Metropolitan France, metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin (island), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbey Of Grandselve
The choir stall Grandselve Abbey (french: Abbaye de Notre-Dame de Grandselve) was a Cistercian monastery in south-west France, at Bouillac, Tarn-et-Garonne. It was one of the most important Cistercian abbeys in the south of France. History Grandselve was founded as a hermitage under the Benedictine rule in 1114 by Gerald of Sales, who placed it under the supervision of Cadouin Abbey. In 1117 Bishop Amelius Raymond du Puy of Toulouse recognized it as a monastery. He authorized the monks to build a church, gave them the lands, and required them to follow the rule as practiced at Cîteaux Abbey. Over time, the monks began to detach themselves from their connection to Cadouin, and in 1135 Bishop Amelius, at the request of Pope Innocent II, reminded them of their required obedience. Grandselve joined the Cistercian movement as a daughter house of Clairvaux Abbey in 1145. The church was dedicated in 1253. The land was cultivated, mills were established on the rivers and vineyards ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beaumont-de-Lomagne
Beaumont-de-Lomagne (; Languedocien: ''Bèumont de Lomanha'') is a commune in the Tarn-et-Garonne department in the Occitanie region in southern France. Geography The river Gimone runs through the town. History Beaumont-de-Lomagne, bastide, was founded in 1276 following the act of coregency between the abbey of Grandselve and King Philip III of France – the King was represented by his seneschal for the former County of Toulouse, Eustache de Beaumarchais. In 1278 the town was granted a very liberal charter of laws, by the standards of the period, defining the rights and duties of its inhabitants. In 1280, work commenced on a large church; its flat apse shows the influence of Cîteaux. The bell-tower, was made in the fifteenth century and resembles that of Saint-Sernin in Toulouse. Construction finished around 1430 and the Bishop of Montauban, driven out of his city by the English, made it his episcopal seat until 1432. The Market (place), market hall, in the centre of the to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paréage
In Medieval France a ''paréage'' or pariage was a feudal treaty recognising joint sovereignty over a territory by two rulers, who were on an equal footing, ''pari passu''; compare peerage, peer. On a familial scale, ''paréage'' could also refer to the equal division of lands and the titles they brought between sons of an inheritance. Such a power-sharing contract could be signed between two secular rulers or, most usually, by a secular and an ecclesiastic ruler, as in the case of the most famous, the Paréage of Andorra 1278, Act of paréage of 1278 that founded a legal basis for the Principality of Andorra, signed by the County of Foix, Count of Foix and Viscount of Castellbo and the Bishop of Urgell. The Count and the Bishop were to receive taxes in alternate years, to appoint local representatives to administer justice jointly, and should forbear to make war within Andorra, where each might levy soldiers, nevertheless. The wording of a ''paréage'', an exercise in defining r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip IV Of France
Philip IV (April–June 1268 – 29 November 1314), called Philip the Fair (french: Philippe le Bel), was King of France from 1285 to 1314. By virtue of his marriage with Joan I of Navarre, he was also King of Navarre as Philip I from 1284 to 1305, as well as Count of Champagne. Although Philip was known to be handsome, hence the epithet ''le Bel'', his rigid, autocratic, imposing, and inflexible personality gained him (from friend and foe alike) other nicknames, such as the Iron King (french: le Roi de fer, link=no). His fierce opponent Bernard Saisset, bishop of Pamiers, said of him: "He is neither man nor beast. He is a statue." Philip, seeking to reduce the wealth and power of the nobility and clergy, relied instead on skillful civil servants, such as Guillaume de Nogaret and Enguerrand de Marigny, to govern the kingdom. The king, who sought an uncontested monarchy, compelled his upstart vassals by wars and restricted their feudal privileges, paving the way for the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico anno 2013, datISTAT/ref> Florence was a centre of medieval European trade and finance and one of the wealthiest cities of that era. It is considered by many academics to have been the birthplace of the Renaissance, becoming a major artistic, cultural, commercial, political, economic and financial center. During this time, Florence rose to a position of enormous influence in Italy, Europe, and beyond. Its turbulent political history includes periods of rule by the powerful Medici family and numerous religious and republican revolutions. From 1865 to 1871 the city served as the capital of the Kingdom of Italy (established in 1861). The Florentine dialect forms the base of Standard Italian and it became the language of culture throughout Ital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |