|
Gregory Tifernas
Gregory Tifernas ( el, Γρηγόριος Τιφέρνας; it, Gregorio Tifernate; Cortona, 1414 – Venice, 1462) was a Greek Renaissance humanist from the Italian city of Città di Castello ('' Tifernum'' in Latin, whence his surname). Biography He studied the Greek Classics under Manuel Chrysoloras and was the first teacher of Greek in France at the University of Paris. It appears that he only stayed a short time in Paris but it proved long enough to train several students who would carry on his work. Works * ''Physica Theophrasti e greco in latinam ab Gregorio Tifernio'' – Latin translation of Theophrastus' ''Physica''R. W. Sharples, Theophrastus of Eresus: Sources for His Life, Writings, Thought, and Influence, p.100,BRILL, See also * French humanism *Greek scholars in the Renaissance The migration waves of Byzantine Greek scholars and émigrés in the period following the end of the Byzantine Empire in 1453 is considered by many scholars key to the revival o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cortona
Cortona (, ) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Arezzo, in Tuscany, Italy. It is the main cultural and artistic centre of the Val di Chiana after Arezzo. Toponymy Cortona is derived from Latin Cortōna, and from Etruscan 𐌂𐌖𐌓𐌕𐌖𐌍 (curtun). This may be related to Indo-European *ghortos meaning "enclosed place" and consequently walled city like Latin hortus, German Garten, Italian orto, English yard, and Slavic grad. The name may also be linked to the Phrygian town of Gordium in Anatolia, although the founding myth for the latter is that it was named after founder, King Gordias. However, the Etruscan language is probably a pre-Indo-European language, and therefore if it was named by the Etruscans, an Indo-European etymology is uncertain. The Umbrian language, by contrast, is an Italic language, so if it was named by them, a link to Indo-European roots would be more likely. George Dennis suggests that it was known by many names "Corytus, Croton, Croto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge Modern History
''The Cambridge Modern History'' is a comprehensive modern history of the world, beginning with the 15th century Age of Discovery, published by the Cambridge University Press in England and also in the United States. The first series, planned by Lord Acton and edited by him with Stanley Mordaunt Leathes, Sir Adolphus William Ward and G. W. Prothero, was launched in 1902 and totalled fourteen volumes, the last of them being an historical atlas which appeared in 1912. The period covered was from 1450 to 1910. Each volume includes an extensive bibliography. A second series, with entirely new editors and contributors, ''The New Cambridge Modern History'', appeared in fourteen volumes between 1957 and 1979, again concluding with an atlas. It covered the world from 1450 to 1945. Planning and publishing The original ''Cambridge Modern History'' was planned by Lord Acton, who during 1899 and 1900 gave much of his time to coordinating the project, intended to be a monument of objecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Renaissance Humanists
Greek may refer to: Greece Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe: *Greeks, an ethnic group. *Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family. **Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all known varieties of Greek. **Mycenaean Greek, most ancient attested form of the language (16th to 11th centuries BC). **Ancient Greek, forms of the language used c. 1000–330 BC. **Koine Greek, common form of Greek spoken and written during Classical antiquity. **Medieval Greek or Byzantine Language, language used between the Middle Ages and the Ottoman conquest of Constantinople. **Modern Greek, varieties spoken in the modern era (from 1453 AD). *Greek alphabet, script used to write the Greek language. *Greek Orthodox Church, several Churches of the Eastern Orthodox Church. *Ancient Greece, the ancient civilization before the end of Antiquity. * Old Greek, the language as spoken from Late Antiquity to around 1500 AD. Other uses * ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
15th-century Byzantine People
The 15th century was the century which spans the Julian dates from 1 January 1401 ( MCDI) to 31 December 1500 ( MD). In Europe, the 15th century includes parts of the Late Middle Ages, the Early Renaissance, and the early modern period. Many technological, social and cultural developments of the 15th century can in retrospect be seen as heralding the " European miracle" of the following centuries. The architectural perspective, and the modern fields which are known today as banking and accounting were founded in Italy. The Hundred Years' War ended with a decisive French victory over the English in the Battle of Castillon. Financial troubles in England following the conflict resulted in the Wars of the Roses, a series of dynastic wars for the throne of England. The conflicts ended with the defeat of Richard III by Henry VII at the Battle of Bosworth Field, establishing the Tudor dynasty in the later part of the century. Constantinople, known as the capital of the world an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
14th-century Byzantine People
As a means of recording the passage of time, the 14th century was a century lasting from 1 January 1301 ( MCCCI), to 31 December 1400 ( MCD). It is estimated that the century witnessed the death of more than 45 million lives from political and natural disasters in both Europe and the Mongol Empire. West Africa experienced economic growth and prosperity. In Europe, the Black Death claimed 25 million lives wiping out one third of the European population while the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of France fought in the protracted Hundred Years' War after the death of Charles IV, King of France led to a claim to the French throne by Edward III, King of England. This period is considered the height of chivalry and marks the beginning of strong separate identities for both England and France as well as the foundation of the Italian Renaissance and Ottoman Empire. In Asia, Tamerlane (Timur), established the Timurid Empire, history's third largest empire to have been ever establish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Scholars In The Renaissance
The migration waves of Byzantine Greek scholars and émigrés in the period following the end of the Byzantine Empire in 1453 is considered by many scholars key to the revival of Greek studies that led to the development of the Renaissance humanism and science. These émigrés brought to Western Europe the relatively well-preserved remnants and accumulated knowledge of their own (Greek) civilization, which had mostly not survived the Early Middle Ages in the West. The ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' claims: "Many modern scholars also agree that the exodus of Greeks to Italy as a result of this event marked the end of the Middle Ages and the beginning of the Renaissance", although few scholars date the start of the Italian Renaissance this late. History The main role of Byzantine scholars within Renaissance humanism was the teaching of the Greek language to their western counterparts in universities or privately together with the spread of ancient texts. Their forerunners were Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Humanism
Humanism in France found its way from Italy, but did not become a distinct movement until the 16th century was well on its way. History On the completion of the Hundred Years' War between France and England, the intellectual currents of Renaissance humanism began to start. In 1464, Raoul Lefèvre composed for the Duke of Burgundy a history of Troy. At that time the French still regarded themselves as descendants of Hector. If we except the University of Paris, none of the French universities took part in the movement. Individual writers and printing-presses at Paris, Lyon, Rouen and other cities became its centres and sources. Guillaume Fichet and Robert Gaguin are usually looked upon as the first French Humanists. Fichet introduced "the eloquence of Rome" at Paris and set up a press at the Sorbonne. He corresponded with Bessarion and had in his library volumes of Petrarch, Guarino of Verona and other Italians. Gaguin copied and corrected Suetonius in 1468 and other Latin author ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
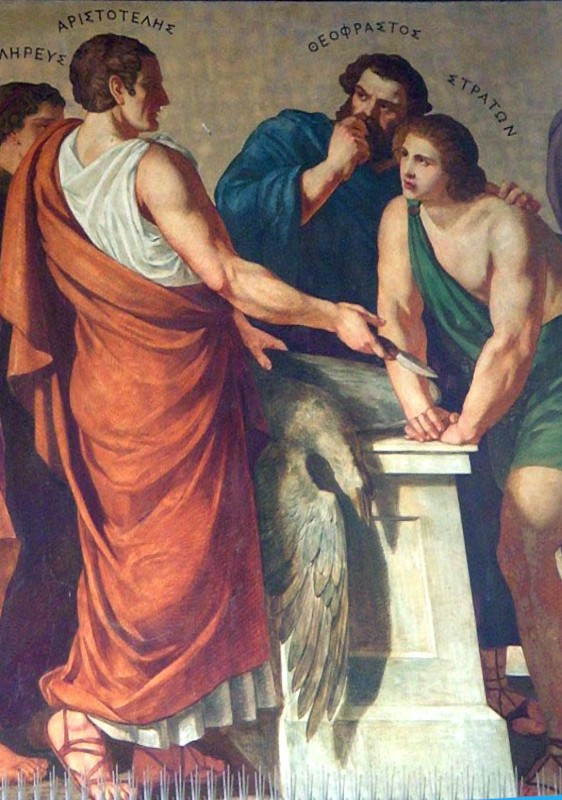
Theophrastus
Theophrastus (; grc-gre, Θεόφραστος ; c. 371c. 287 BC), a Greek philosopher and the successor to Aristotle in the Peripatetic school. He was a native of Eresos in Lesbos.Gavin Hardy and Laurence Totelin, ''Ancient Botany'', Routledge, 2015, p. 8. His given name was Tyrtamus (); his nickname (or 'godly phrased') was given by Aristotle, his teacher, for his "divine style of expression". He came to Athens at a young age and initially studied in Plato's school. After Plato's death, he attached himself to Aristotle who took to Theophrastus in his writings. When Aristotle fled Athens, Theophrastus took over as head of the Lyceum. Theophrastus presided over the Peripatetic school for thirty-six years, during which time the school flourished greatly. He is often considered the father of botany for his works on plants. After his death, the Athenians honoured him with a public funeral. His successor as head of the school was Strato of Lampsacus. The interests of Theophr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Claverhouse Jebb
Sir Richard Claverhouse Jebb (27 August 1841 – 9 December 1905) was a British classical scholar. Life Jebb was born in Dundee, Scotland. His father Robert was a well-known Irish barrister; his mother was Emily Harriet Horsley, daughter of the Reverend Heneage Horsley, Dean of Brechin. His grandfather Richard Jebb was a judge of the Court of King's Bench (Ireland). His sister was the social reformer Eglantyne Louisa Jebb, founder of the Home Arts and Industries Association; his niece, Eglantyne's daughter Eglantyne Jebb, co-founded the Save the Children Fund and wrote the Declaration of the Rights of the Child. He was educated at St Columba's College, Dublin 1853–55 then Charterhouse School 1855–1858. He then studied Classics at Trinity College, Cambridge. He was a Member of the Cambridge Apostles, the intellectual secret society, from 1859. He won the Porson and Craven scholarships, was senior classic in 1862, and became fellow and tutor of his college in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The islands are in the shallow Venetian Lagoon, an enclosed bay lying between the mouths of the Po and the Piave rivers (more exactly between the Brenta and the Sile). In 2020, around 258,685 people resided in greater Venice or the ''Comune di Venezia'', of whom around 55,000 live in the historical island city of Venice (''centro storico'') and the rest on the mainland (''terraferma''). Together with the cities of Padua and Treviso, Venice is included in the Padua-Treviso-Venice Metropolitan Area (PATREVE), which is considered a statistical metropolitan area, with a total population of 2.6 million. The name is derived from the ancient Veneti people who inhabited the region by the 10th century BC. The city was historica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Paris
The University of Paris (french: link=no, Université de Paris), Metonymy, metonymically known as the Sorbonne (), was the leading university in Paris, France, active from 1150 to 1970, with the exception between 1793 and 1806 under the French Revolution. Emerging around 1150 as a corporation associated with the cathedral school of Notre Dame de Paris, it was considered the List of medieval universities, second-oldest university in Europe.Charles Homer Haskins, Haskins, C. H.: ''The Rise of Universities'', Henry Holt and Company, 1923, p. 292. Officially chartered in 1200 by King Philip II of France and recognised in 1215 by Pope Innocent III, it was later often nicknamed after its theological College of Sorbonne, in turn founded by Robert de Sorbon and chartered by List of French monarchs, French King Louis IX, Saint Louis around 1257. Internationally highly reputed for its academic performance in the humanities ever since the Middle Ages – notably in theology and philosophy – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manuel Chrysoloras
Manuel (or Emmanuel) Chrysoloras ( el, Μανουὴλ Χρυσολωρᾶς; c. 1350 – 15 April 1415) was a Byzantine Greek classical scholar, humanist, philosopher, professor, and translator of ancient Greek texts during the Renaissance. Serving as the ambassador for the Byzantine emperor Manuel II Palaiologos in medieval Italy, he became a renowned teacher of Greek literature and history in the republics of Florence and Venice, and today he's widely regarded as a pioneer in the introduction of ancient Greek literature to Western Europe during the Late Middle Ages. Biography Chrysoloras was born in Constantinople, at the time capital of the Byzantine Empire, to a distinguished Greek Orthodox family. In 1390, he led an embassy sent to the Republic of Venice by the Byzantine emperor Manuel II Palaiologos to ask the aid of the Christian princes of Medieval Europe against the invasions of the Byzantine Empire by the Muslim Ottoman Turks. Roberto de' Rossi of Florence met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)

