|
Gravedigging
A gravedigger is a cemetery worker who is responsible for digging a grave prior to a funeral service. Description If the grave is in a cemetery on the property of a church or other religious organization (part of, or called, a churchyard), gravediggers may be members of the decedent's family or volunteer parishioners. Digging graves has also been one of the traditional duties of a church's sexton. In municipal and privately owned cemeteries, gravediggers may be low-paid, unskilled and temporary labourers, or they may be well-paid, trained and professional careerists, as their duties may include landscaping tasks and courteous interactions with mourners and other visitors. In some countries, gravedigging may be done by landscaping workers for the local council or local authority. A gravedigger implements a variety of tools to accomplish his primary task. A template, in the form of a wooden frame built to prescribed specifications, is often placed on the ground over the intend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasnetsov Grave Digger
Vasnetsov (russian: Васнецов) may refer to: * Apollinary Vasnetsov (1856–1933), Russian painter * Viktor Vasnetsov Viktor Mikhaylovich Vasnetsov (russian: Ви́ктор Миха́йлович Васнецо́в; May 15 ( N.S.), 1848 – July 23, 1926) was a Russian artist who specialized in mythological and historical subjects. He is considered the co-founde ... (1848–1926), Russian painter {{surname, Vasnetsov Russian-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headstone
A headstone, tombstone, or gravestone is a stele or marker, usually stone, that is placed over a grave. It is traditional for burials in the Christian, Jewish, and Muslim religions, among others. In most cases, it has the deceased's name, date of birth, and date of death inscribed on it, along with a personal message, or prayer, but may contain pieces of funerary art, especially details in stone relief. In many parts of Europe, insetting a photograph of the deceased in a frame is very common. Use The stele (plural stelae), as it is called in an archaeological context, is one of the oldest forms of funerary art. Originally, a tombstone was the stone lid of a stone coffin, or the coffin itself, and a gravestone was the stone slab that was laid over a grave. Now, all three terms are also used for markers placed at the head of the grave. Some graves in the 18th century also contained footstones to demarcate the foot end of the grave. This sometimes developed into full kerb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardinal (Catholicism)
A cardinal ( la, Sanctae Romanae Ecclesiae cardinalis, literally 'cardinal of the Holy Roman Church') is a senior member of the clergy of the Catholic Church. Cardinals are created by the ruling pope and typically hold the title for life. Collectively, they constitute the College of Cardinals. Their most solemn responsibility is to elect a new pope in a conclave, almost always from among themselves (with a few historical exceptions), when the Holy See is vacant. During the period between a pope's death or resignation and the election of his successor, the day-to-day governance of the Holy See is in the hands of the College of Cardinals. The right to participate in a conclave is limited to cardinals who have not reached the age of 80 years by the day the vacancy occurs. In addition, cardinals collectively participate in papal consistories (which generally take place annually), in which matters of importance to the Church are considered and new cardinals may be created. Cardina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subdeacon
Subdeacon (or sub-deacon) is a minor order or ministry for men in various branches of Christianity. The subdeacon has a specific liturgical role and is placed between the acolyte (or reader) and the deacon in the order of precedence. Subdeacons in the Eastern Orthodox Church A subdeacon or hypodeacon is the highest of the minor orders of clergy in the Eastern Orthodox Church. This order is higher than the reader and lower than the deacon. Canonical discipline Like the reader, the clerical street-dress of the subdeacon is the cassock, which is usually black but only need be so if he is a monk. This is symbolic of his suppression of his own tastes, will, and desires, and his canonical obedience to God, his bishop, and the liturgical and canonical norms of the Church. As a concession in countries where Eastern Orthodoxy is little known, many only wear the cassock when attending liturgies or when moving about the faithful on church business. In some jurisdictions in the United Stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is called episcopacy. Organizationally, several Christian denominations utilize ecclesiastical structures that call for the position of bishops, while other denominations have dispensed with this office, seeing it as a symbol of power. Bishops have also exercised political authority. Traditionally, bishops claim apostolic succession, a direct historical lineage dating back to the original Twelve Apostles or Saint Paul. The bishops are by doctrine understood as those who possess the full priesthood given by Jesus Christ, and therefore may ordain other clergy, including other bishops. A person ordained as a deacon, priest (i.e. presbyter), and then bishop is understood to hold the fullness of the ministerial priesthood, given responsibility b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persecution Of Diocletian
The Diocletianic or Great Persecution was the last and most severe persecution of Christians in the Roman Empire. In 303, the Roman emperor, emperors Diocletian, Maximian, Galerius, and Constantius Chlorus, Constantius issued a series of edicts rescinding Christians' legal rights and demanding that they comply with traditional religious practices. Later edicts targeted the clergy and demanded universal sacrifice, ordering all inhabitants to sacrifice to the gods. The persecution varied in intensity across the empire—weakest in Gaul and Roman Britain, Britain, where only the first edict was applied, and strongest in the Eastern provinces. Persecutory laws were nullified by different emperors (Galerius with the Edict of Serdica in 311) at different times, but Constantine the Great, Constantine and Licinius' Edict of Milan in 313 has traditionally marked the end of the persecution. Christians had been subject to intermittent local discrimination in the empire, but emperors prio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
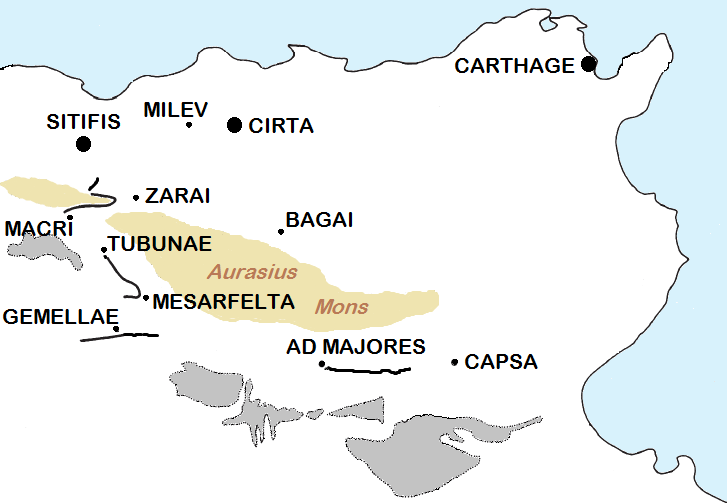
Cirta
Cirta, also known by various other names in antiquity, was the ancient Berber and Roman settlement which later became Constantine, Algeria. Cirta was the capital city of the Berber kingdom of Numidia; its strategically important port city was Russicada. Although Numidia was a key ally of the ancient Roman Republic during the Punic Wars (264–146BC), Cirta was subject to Roman invasions during the 2nd and 1st centuriesBC. Eventually it fell under Roman dominion during the time of Julius Caesar. Cirta was then repopulated with Roman colonists by Caesar and Augustus and was surrounded by the autonomous territory of a " Confederation of four free Roman cities" (with Chullu, Russicada, and Milevum), ruled initially by Publius Sittius. The city was destroyed in the beginning of the 4thcentury and was rebuilt by the Roman emperor Constantine the Great, who gave his name to the newly constructed city, Constantine. The Vandals damaged Cirta, but emperor reconquered and improved th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clergy
Clergy are formal leaders within established religions. Their roles and functions vary in different religious traditions, but usually involve presiding over specific rituals and teaching their religion's doctrines and practices. Some of the terms used for individual clergy are clergyman, clergywoman, clergyperson, churchman, and cleric, while clerk in holy orders has a long history but is rarely used. In Christianity, the specific names and roles of the clergy vary by denomination and there is a wide range of formal and informal clergy positions, including deacons, elders, priests, bishops, preachers, pastors, presbyters, ministers, and the pope. In Islam, a religious leader is often known formally or informally as an imam, caliph, qadi, mufti, mullah, muezzin, or ayatollah. In the Jewish tradition, a religious leader is often a rabbi (teacher) or hazzan (cantor). Etymology The word ''cleric'' comes from the ecclesiastical Latin ''Clericus'', for those belonging ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Era
The terms (AD) and before Christ (BC) are used to label or number years in the Julian and Gregorian calendars. The term is Medieval Latin and means 'in the year of the Lord', but is often presented using "our Lord" instead of "the Lord", taken from the full original phrase "''anno Domini nostri Jesu Christi''", which translates to 'in the year of our Lord Jesus Christ'. The form "BC" is specific to English and equivalent abbreviations are used in other languages: the Latin form is but is rarely seen. This calendar era is based on the traditionally reckoned year of the conception or birth of Jesus, ''AD'' counting years from the start of this epoch and ''BC'' denoting years before the start of the era. There is no year zero in this scheme; thus ''the year AD 1 immediately follows the year 1 BC''. This dating system was devised in 525 by Dionysius Exiguus, but was not widely used until the 9th century. Traditionally, English follows Latin usage by placing the "AD" abbr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catacombs
Catacombs are man-made subterranean passageways for religious practice. Any chamber used as a burial place is a catacomb, although the word is most commonly associated with the Roman Empire. Etymology and history The first place to be referred to as ''catacombs'' was the system of underground tombs between the 2nd and 3rd milestones of the Appian Way in Rome, where the bodies of the apostles Peter and Paul, among others, were said to have been buried. The name of that place in Late Latin was L.L. fem. nom. pl. n. ''catacumbas'' (sing. ''catacumba'') a word of obscure origin, possibly deriving from a proper name or a derivation of the Latin phrase ''catatumbas'', "among the tombs". The word referred originally only to the Roman catacombs, but was extended by 1836 to refer to any subterranean receptacle of the dead, as in the 18th-century Paris catacombs. The ancient Christians carved the first catacombs from soft tufa rock. (ref)" (World Book Encyclopedia, page 296) All Roman ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_-_Foto_G._Dall'Orto_28-5-2006.jpg)