|
Granuloma
A granuloma is an aggregation of macrophages that forms in response to chronic inflammation. This occurs when the immune system attempts to isolate foreign substances that it is otherwise unable to eliminate. Such substances include infectious organisms including bacteria and fungi, as well as other materials such as foreign objects, keratin, and suture fragments. Definition In pathology, a granuloma is an organized collection of macrophages. In medical practice, doctors occasionally use the term ''granuloma'' in its more literal meaning: "a small nodule". Since a small nodule can represent any tissue from a harmless nevus to a malignant tumor, this use of the term is not very specific. Examples of this use of the term ''granuloma'' are the lesions known as vocal cord granuloma (known as contact granuloma), pyogenic granuloma, and intubation granuloma, all of which are examples of granulation tissue, not granulomas. "Pulmonary hyalinizing granuloma" is a lesion characterized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
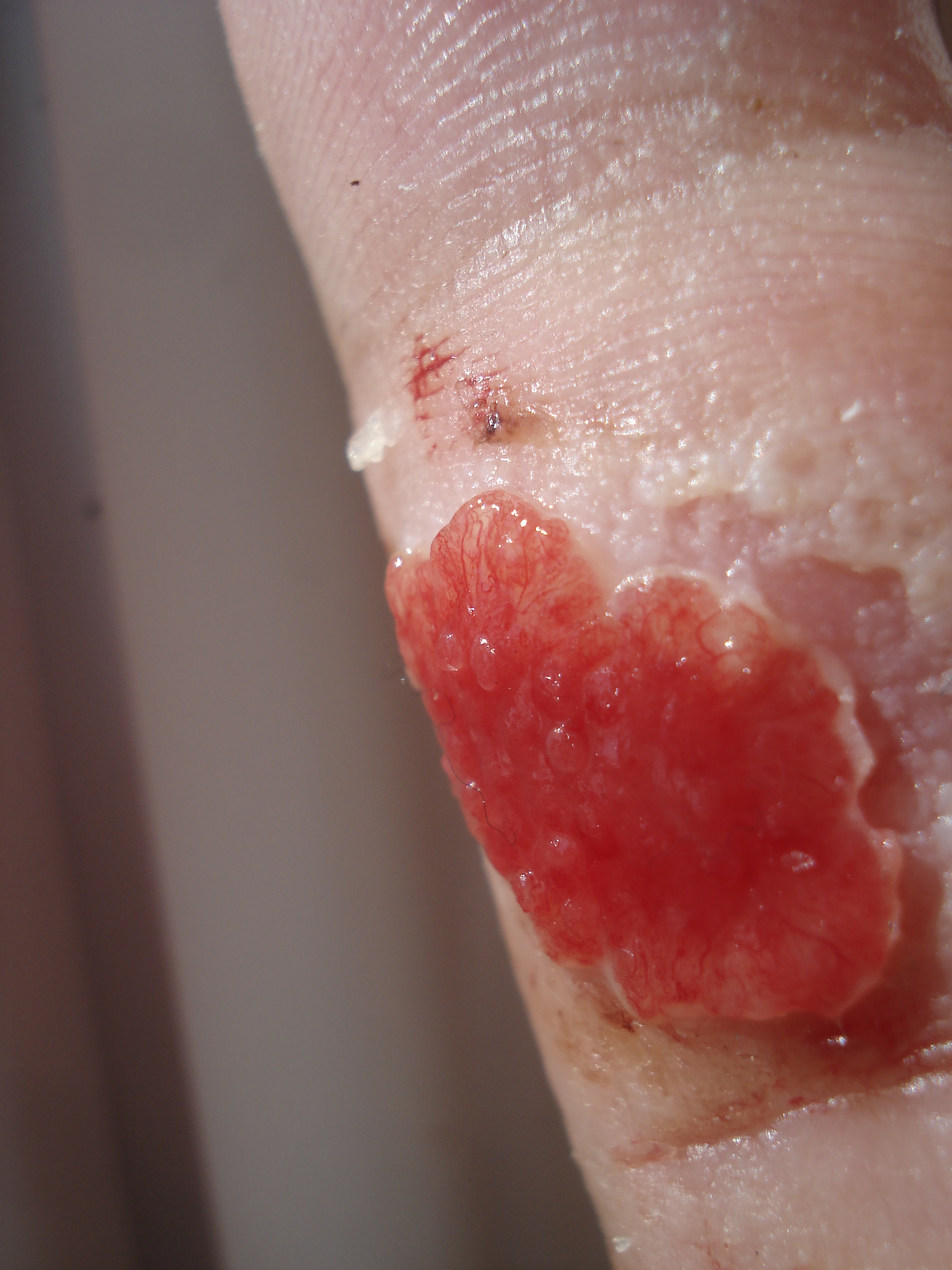
Pyogenic Granuloma
A pyogenic granuloma or lobular capillary hemangioma is a vascular tumor that occurs on both mucosa and skin, and appears as an overgrowth of tissue due to irritation, physical trauma, or hormonal factors. It is often found to involve the gums, skin, or nasal septum, and has also been found far from the head, such as in the thigh. Pyogenic granulomas may be seen at any age, and are more common in females than males. In pregnant women, lesions may occur in the first trimester with an increasing incidence until the seventh month, and are often seen on the gums. Signs and symptoms The appearance of pyogenic granuloma is usually a color ranging from red/pink to purple, grows rapidly, and can be smooth or mushroom-shaped. Younger lesions are more likely to be red because of their high number of blood vessels. Older lesions begin to change into a pink color. Size commonly ranges from a few millimeters to centimeters, though smaller or larger lesions may occur. A pyogenic granuloma can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histiocyte
A histiocyte is a vertebrate cell that is part of the mononuclear phagocyte system (also known as the reticuloendothelial system or lymphoreticular system). The mononuclear phagocytic system is part of the organism's immune system. The histiocyte is a tissue macrophage or a dendritic cell (histio, diminutive of histo, meaning ''tissue'', and cyte, meaning ''cell''). Part of their job is to clear out neutrophils once they've reached the end of their lifespan. Development Histiocytes are derived from the bone marrow by multiplication from a stem cell. The derived cells migrate from the bone marrow to the blood as monocytes. They circulate through the body and enter various organs, where they undergo differentiation into histiocytes, which are part of the mononuclear phagocytic system (MPS). However, the term ''histiocyte'' has been used for multiple purposes in the past, and some cells called "histocytes" do not appear to derive from monocytic-macrophage lines. The term Histioc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contact Granuloma
Contact granuloma is a condition that develops due to persistent tissue irritation in the posterior larynx. Granulation tissue, Benign granulomas, not to be confused with other types of granulomas, occur on the vocal process of the vocal folds, where the vocal ligament attaches. Signs and symptoms may include hoarseness of the voice, or a sensation of having a lump in the throat, but contact granulomas may also be without symptoms. There are two common causes associated with contact granulomas; the first common cause is sustained periods of increased pressure on the vocal folds, and is commonly seen in people who use their voice excessively, such as singers (John Mayer#Born and Raised, John Mayer, for example). Treatment typically includes voice therapy and changes to lifestyle factors. The second common cause of granulomas is Gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastroesophageal reflux and is controlled primarily through the use of anti-reflux medication. Other associated causes are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granulation Tissue
Granulation tissue is new connective tissue and microscopic blood vessels that form on the surfaces of a wound during the healing process. Granulation tissue typically grows from the base of a wound and is able to fill wounds of almost any size. Examples of granulation tissue can be seen in pyogenic granulomas and pulp polyps. Its histological appearance is characterized by proliferation of fibroblasts and new thin-walled, delicate capillaries (angiogenesis), infiltrated inflammatory cells in a loose extracellular matrix. Appearance During the migratory phase of wound healing, granulation tissue is: * light red or dark pink, being perfused with new capillary loops or "buds"; * soft to the touch; * moist; * bumpy (granular) in appearance, due to punctate hemorrhages; * pulsatile on palpation; * painless when healthy; Structure Granulation tissue is composed of tissue matrix supporting a variety of cell types, most of which can be associated with one of the following functions: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris, and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. The process is called phagocytosis, which acts to defend the host against infection and injury. These large phagocytes are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, and others), but all are part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense (innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adaptive immunity) by recruiting other immune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out necrotic cells and tissues damaged from the original insult and the inflammatory process, and initiate tissue repair. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and Functio laesa, loss of function (Latin ''calor'', ''dolor'', ''rubor'', ''tumor'', and ''functio laesa''). Inflammation is a generic response, and therefore it is considered as a mechanism of innate immune system, innate immunity, as compared to adaptive immune system, adaptive immunity, which is specific for each pathogen. Too little inflammation could lead to progressive tissue destruction by the harmful stimulus (e.g. b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nodule (medicine)
In medicine, nodules are small firm lumps, usually greater than 1 cm in diameter. If filled with fluid they are referred to as cysts. Smaller (less than 0.5 cm) raised soft tissue bumps may be termed papules. The evaluation of a skin nodule includes a description of its appearance, its location, how it feels to touch and any associated symptoms which may give clues to an underlying medical condition. Nodules in skin include dermatofibroma and pyogenic granuloma. Nodules may form on tendons and muscles in response to injury, and are frequently found on vocal cords. They may occur in organs such as the lung, or thyroid, or be a sign in other medical conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis. Characteristics Nodules are small firm lumps usually greater than 1 cm in diameter, found in skin and other organs. If filled with fluid they are usually softer and referred to as cysts. Smaller (less than 0.5 cm) raised soft tissue bumps may be termed papules. Evaluation The evaluation of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathology
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area which includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue, cell, and body fluid samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases (as in the statement "the many different forms of cancer have diverse pathologies", in which case a more proper choice of word would be " pathophysiologies"), and the affix ''pathy'' is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment (as in cardiomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathologist
Pathology is the study of the causal, causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area which includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue (biology), tissue, human cell, cell, and body fluid samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases (as in the statement "the many different forms of cancer have diverse pathologies", in which case a more proper choice of word would be "Pathophysiology, pathophysiologies"), and the affix ''pathy'' is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiologists
Radiology ( ) is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiation), but today it includes all imaging modalities, including those that use no electromagnetic radiation (such as ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging), as well as others that do, such as computed tomography (CT), fluoroscopy, and nuclear medicine including positron emission tomography (PET). Interventional radiology is the performance of usually minimally invasive medical procedures with the guidance of imaging technologies such as those mentioned above. The modern practice of radiology involves several different healthcare professions working as a team. The radiologist is a medical doctor who has completed the appropriate post-graduate training and interprets medical images, communicates these findings to other physicians by me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keloid
Keloid, also known as keloid disorder and keloidal scar, is the formation of a type of scar which, depending on its maturity, is composed mainly of either type III (early) or type I (late) collagen. It is a result of an overgrowth of granulation tissue (collagen type 3) at the site of a healed skin injury which is then slowly replaced by collagen type 1. Keloids are firm, rubbery lesions or shiny, fibrous nodules, and can vary from pink to the color of the person's skin or red to dark brown in color. A keloid scar is benign and not contagious, but sometimes accompanied by severe itchiness, pain, and changes in texture. In severe cases, it can affect movement of skin. In the United States keloid scars are seen 15 times more frequently in people of sub-Saharan African descent than in people of European descent. There is a higher tendency to develop a keloid among those with a family history of keloids and people between the ages of 10 and 30 years. Keloids should not be confused wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intubation
Intubation (sometimes entubation) is a medical procedure involving the insertion of a tube into the body. Patients are generally anesthetized beforehand. Examples include tracheal intubation, and the balloon tamponade with a Sengstaken-Blakemore tube (a tube into the gastrointestinal tract). Examples * Catheterization * Nasogastric intubation * Tracheal intubation Tracheal intubation, usually simply referred to as intubation, is the placement of a flexible plastic catheter, tube into the vertebrate trachea, trachea (windpipe) to maintain an open airway or to serve as a conduit through which to administer ce ... References Airway management Emergency medical procedures Medical equipment Routes of administration {{surgery-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)