|
Gottfried Heinrich Graf Zu Pappenheim
Gottfried Heinrich Graf zu Pappenheim (29 May 1594 – 17 November 1632) was a field marshal of the Holy Roman Empire in the Thirty Years' War. A supporter of the Catholic League, he was mortally wounded during the Battle of Lützen fighting the Protestant forces under Swedish king Gustavus Adolphus. Biography Pappenheim was born in the little town of Treuchtlingen, a secondary seat of his family, the ruling Lords of Pappenheim on the Altmühl in Bavaria, a free lordship of the empire ''(see: Pappenheim (state))'', from which the ancient family to which he belonged derived its name. He was the second son of Veit zu Pappenheim, Lord of Treuchtlingen and Schwindegg, and his second wife Maria Salome von Preysing-Kopfsburg. He was educated at Altdorf and Tübingen, and subsequently traveled in southern and central Europe, mastering the various languages, and seeking knightly adventures. His stay in these countries led him eventually to adopt the Roman Catholic faith in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pappenheim
Pappenheim is a town in the Weißenburg-Gunzenhausen district, in Bavaria, Germany. It is situated on the river Altmühl, 11 km south of Weißenburg in Bayern. History Historically, Pappenheim was a statelet within Holy Roman Empire. It was German mediatization, mediatised to Bavaria in 1806. Counts of Pappenheim settled at the territory, particularly Gottfried Heinrich Graf zu Pappenheim. Sites * Galluskirche * Neues Schloss Pappenheim (built by Leo von Klenze, Klenze after the mediatisation of the Pappenheim state. Not open to the public) * Altes Schloss Notable people The architect and professor Eduard Mezger (1807–1894) was born in Pappenheim. Else Pappenheim (1911-2009) and her father Martin Pappenheim (1881-1943), both were famous psychoanalysts. References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Altdorf
The University of Altdorf () was a university in Altdorf bei Nürnberg, a small town outside the Free Imperial City of Nuremberg. It was founded in 1578 and received university privileges in 1622 and was closed in 1809 by Maximilian I Joseph of Bavaria. History In the period 1614–1617 Altdorf was briefly the centre of Socinianism in Germany. Encouraged by the connections of German Antitrinitarians to the Racovian Academy in Poland, German and Polish Socinians attempted to establish in Altdorf a similar Academy. Among the notable Socinian students was the 26-year-old Samuel Przypkowski. He was admitted as student on March 22, 1614, three weeks after Thomas Seget, but was expelled from Altdorf in 1616''The Polish Review'', Volume 11, 1966, p. 33. "Crypto-Socinianism" was widely suspected among the student body. In January 1617 the syndicus Jacob Weigel brought two students Joachim Peuschel and Johann Vogel back to Altdorf and the college made them give a public recantation. This re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peasants' War In Upper Austria
The Peasants' War in Upper Austria (german: Oberösterreichischer Bauernkrieg) was a rebellion led by farmers in 1626 whose goal was to free Upper Austria from Bavarian rule. The motive (found in the of 1625) was an escalation of the Bavarian Electorate's attempt to press the country into the Catholic faith at the time of the Thirty Years' War. History In the beginning of the Thirty Years' War, Upper Austria was pledged to the Bavarian Electorate by the House of Habsburg. The new ruler assumed ''cuius regio, eius religio'' (the religion of the ruler dictated the religion of the ruled) and tried to convert the lands to the Catholic faith. In May 1625, the Protestant priest of the Frankenburg am Hausruck parish was replaced by a Catholic priest sent from Bavaria. After an armed uprising, the new priest was forced to flee from the castle. However, the men feared the reaction from Bavaria and surrendered three days later. Adam von Herberstorff, the Bavarian steward of Upper Austri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximilian I, Elector Of Bavaria
Maximilian I (17 April 157327 September 1651), occasionally called the Great, a member of the House of Wittelsbach, ruled as Duke of Bavaria from 1597. His reign was marked by the Thirty Years' War during which he obtained the title of a Prince-elector of the Holy Roman Empire at the 1623 Diet of Regensburg. Maximilian was a capable monarch who, by overcoming the feudal rights of the local estates (''Landstände''), laid the foundations for absolutist rule in Bavaria. A devout Catholic, he was one of the leading proponents of the Counter-Reformation and founder of the Catholic League of Imperial Princes. In the Thirty Years' War, he was able to conquer the Upper Palatinate region, as well as the Electoral Palatinate affiliated with the electoral dignity of his Wittelsbach cousin, the "Winter King" Frederick V. The 1648 Peace of Westphalia affirmed his possession of Upper Palatinate and the hereditary electoral title, though it returned Electoral Palatinate to Frederick's heir a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Of Garda
Lake Garda ( it, Lago di Garda or ; lmo, label=Eastern Lombard, Lach de Garda; vec, Ƚago de Garda; la, Benacus; grc, Βήνακος) is the largest lake in Italy. It is a popular holiday location in northern Italy, about halfway between Brescia and Verona, and between Venice and Milan on the edge of the Dolomites. Glaciers formed this alpine region at the end of the last ice age. The lake and its shoreline are divided between the provinces of Brescia (to the south-west), Verona (south-east) and Trentino (north). Etymology In Roman times the lake was known as ''Benacus'' and by some it was revered as god Benacus, the personification of the lake, sometimes associated with the cult of Neptune. Today it is better known as Lake Garda, a toponym of Germanic origin attested since the Middle Ages and deriving from that of the homonymous town on the Veronese shore of the lake, which, together with another famous locality of the lake, Gardone Riviera, and others less known – s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riva Del Garda
Riva del Garda (''Rìva'' in local dialect) is a town and ''comune'' in the northern Italian province of Trento of the Trentino Alto Adige region. It is also known simply as ''Riva'' and is located at the northern tip of Lake Garda. History Riva del Garda belonged to the Republic of Venice, the Bishopric of Trent, the Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy and later (1815–1918) to the Austro-Hungarian Empire (when it was known as ). During the Third Italian War of Independence, Riva del Garda was an important supply base for the Austrian navy and was the only town on the lake captured by Italian forces. In 1918, after the end of World War I, Riva del Garda, with the rest of the Trentino, became part of the Kingdom of Italy. Riva was the terminus for the long Mori–Arco–Riva railway line, opened in 1891. However, the railway line closed in 1936 and the railway terminus has been converted into a restaurant. Austrian dictator Kurt Schuschnigg was born in the town in 1897 and was of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grisons
The Grisons () or Graubünden,Names include: *german: (Kanton) Graubünden ; * Romansh: ** rm, label= Sursilvan, (Cantun) Grischun ** rm, label=Vallader, (Chantun) Grischun ** rm, label= Puter, (Chantun) Grischun ** rm, label=Surmiran, (Cantun) Grischun ** rm, label= Sutsilvan, (Cantùn) Grischùn ** rm, label=Rumantsch Grischun, (Chantun) Grischun; * it, (Cantone dei) Grigioni ; *french: (Canton des) Grisons . See also other names. more formally the Canton of the Grisons or the Canton of Graubünden, is one of the twenty-six cantons of Switzerland. It has eleven regions, and its capital is Chur. The German name of the canton, , translates as the "Grey Leagues", referring to the canton's origin in three local alliances, the Three Leagues. The other native names also refer to the Grey League: in Sutsilvan, in the other forms of Romansh, and in Italian. ''" Rhaetia"'' is the Latin name for the area. The Alpine ibex is the canton's heraldic symbol. The largest and easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lombardy
Lombardy ( it, Lombardia, Lombard language, Lombard: ''Lombardia'' or ''Lumbardia' '') is an administrative regions of Italy, region of Italy that covers ; it is located in the northern-central part of the country and has a population of about 10 million people, constituting more than one-sixth of Italy's population. Over a fifth of the Italian gross domestic product (GDP) is produced in the region. The Lombardy region is located between the Alps mountain range and tributaries of the Po river, and includes Milan, the largest metropolitan area in the country, and among the largest in the European Union (EU). Of the fifty-eight UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Italy, eleven are in Lombardy. Virgil, Pliny the Elder, Ambrose, Gerolamo Cardano, Caravaggio, Claudio Monteverdi, Antonio Stradivari, Cesare Beccaria, Alessandro Volta and Alessandro Manzoni; and popes Pope John XXIII, John XXIII and Pope Paul VI, Paul VI originated in the area of modern-day Lombardy region. Etymology The name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuirassiers
Cuirassiers (; ) were cavalry equipped with a cuirass, sword, and pistols. Cuirassiers first appeared in mid-to-late 16th century Europe as a result of armoured cavalry, such as men-at-arms and demi-lancers, discarding their lances and adopting the use of pistols as their primary weapon. In the later part of the 17th century the cuirassier lost his limb armour and subsequently wore only the cuirass (breastplate and backplate), and sometimes a helmet. By this time, the sword or sabre had become his primary weapon, with pistols relegated to a secondary function. Cuirassiers achieved increased prominence during the Napoleonic Wars and were last fielded in the opening stages of World War I (1914-1918). A number of countries continue to use cuirassiers as ceremonial troops. The French term ''cuirassier'' means "one with a cuirass" ( fr , cuirasse), the breastplate armour which they wore. 16th and 17th centuries The first cuirassiers were similar in appearance to the fully a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst, Graf Von Mansfeld
Peter Ernst, Graf von Mansfeld (german: Peter Ernst Graf von Mansfeld; c. 158029 November 1626), or simply Ernst von Mansfeld, was a German military commander who, despite being a Catholic, fought for the Protestants during the early years of the Thirty Years' War. He was one of the leading mercenary generals of the war. Biography Mansfeld was an illegitimate son of Count Peter Ernst von Mansfeld (1517–1604), a member of the comital House of Mansfeld and royal Spanish stadtholder. He was raised in the Catholic faith at his father's palace in Luxembourg. He gained his earliest military experiences during the Long War in Hungary, where his elder half-brother Charles (1543–1595), also a soldier of renown, held a high command in the imperial army. While his brother succumbed to an epidemic within short time, young Ernst stayed at the theatre of war for several years. In the War of the Jülich Succession he served under Archduke Leopold V of Austria, until that prince's ingra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 million people. The city has a temperate oceanic climate, with relatively warm summers and chilly winters. Prague is a political, cultural, and economic hub of central Europe, with a rich history and Romanesque, Gothic, Renaissance and Baroque architectures. It was the capital of the Kingdom of Bohemia and residence of several Holy Roman Emperors, most notably Charles IV (r. 1346–1378). It was an important city to the Habsburg monarchy and Austro-Hungarian Empire. The city played major roles in the Bohemian and the Protestant Reformations, the Thirty Years' War and in 20th-century history as the capital of Czechoslovakia between the World Wars and the post-war Communist era. Prague is home to a number of well-known cultural attractions, many of which survived the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
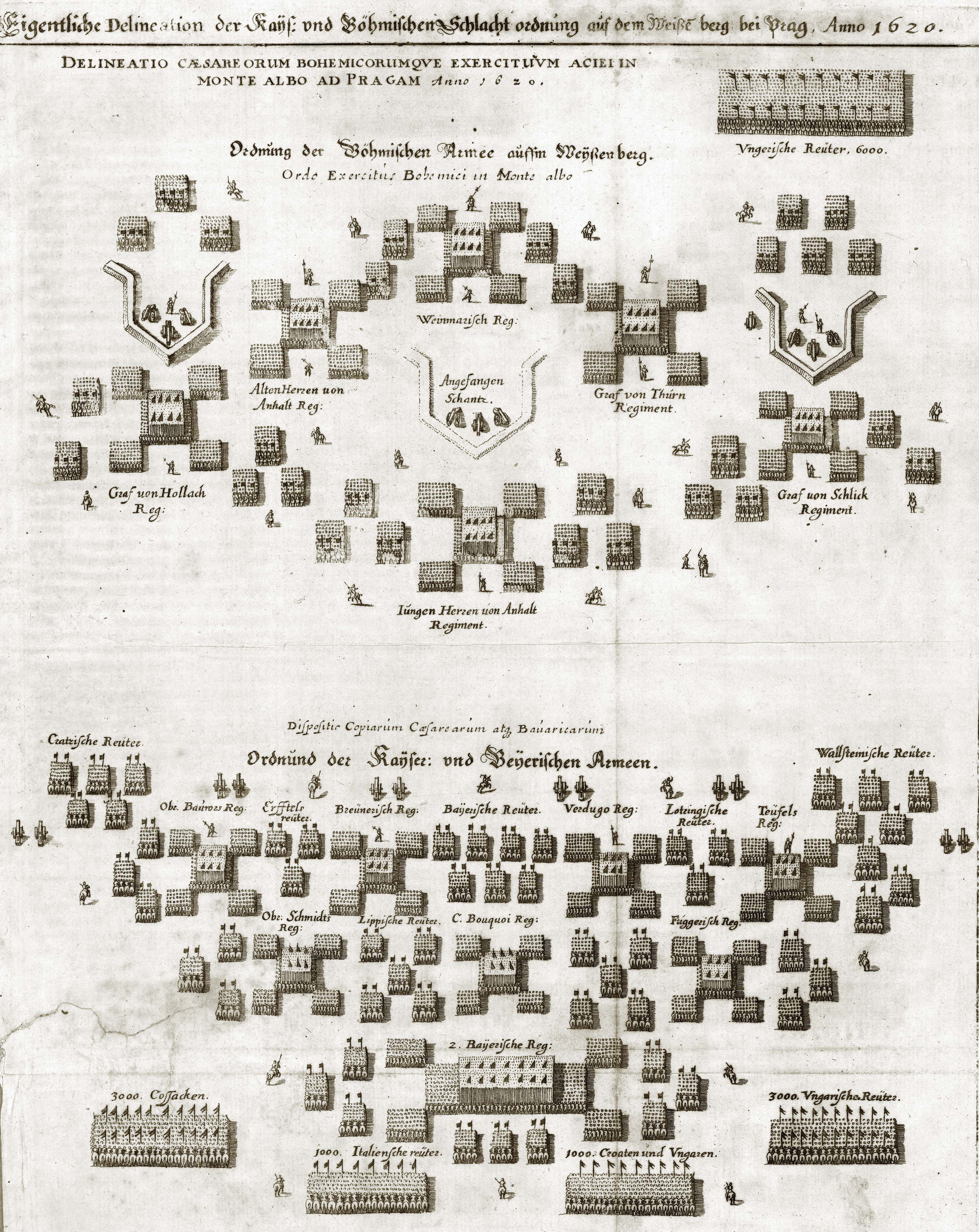
Battle Of The White Mountain
), near Prague, Bohemian Confederation(present-day Czech Republic) , coordinates = , territory = , result = Imperial-Spanish victory , status = , combatants_header = , combatant1 = Catholic League , combatant2 = Bohemian Confederation Electoral Palatinate , commander1 = , commander2 = , strength1 = 23,00012 guns , strength2 = 21,00010 guns , casualties1 = 650 killed and wounded , casualties2 = 2,800 killed and wounded , map_type = Czech Republic Prague#Czech Republic , map_mark = Battle icon (crossed swords).svg , map_relief = , map_size = 300px , map_marksize = 30 , map_caption = , map_label = White Mountain The Battle of White Mountain ( cz, Bitva na Bílé hoře; german: Schlacht am Weißen Berg) was an important battle in the early stages of the Thirty Years' War. It led to the defeat of the Bohemian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_-_Bavarian_State_Painting_Collections.jpg)