|
Gosslingiaceae
Gosslingiaceae is a family of extinct zosterophylls. The zosterophylls were among the first vascular plants in the fossil record, and are considered to share an ancestor with the living lycophytes. The family is variously placed in the order Sawdoniales or the order Gosslingiales Gosslingiales is an order of extinct zosterophylls. The zosterophylls were among the first vascular plants in the fossil record, and share an ancestor with the living lycophytes. The group has been divided up in various ways. Hao and Xue in 20 .... Genera Genera that have been placed in this family by Kenrick and Crane in 1997 and Hao and Xue in 2013 are shown in the table below. References Zosterophylls Prehistoric plant families {{paleobotany-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gosslingiales
Gosslingiales is an order of extinct zosterophylls. The zosterophylls were among the first vascular plants in the fossil record, and share an ancestor with the living lycophytes. The group has been divided up in various ways. Hao and Xue in 2013 used the presence or absence of terminal sporangia as a major dividing feature. The order Zosterophyllales was used for species with terminal as well as lateral sporangia, which were considered to have determinate growth, with their sporangia generally being arranged in spikes. The paraphyletic order Gosslingiales was used for species without terminal sporangia (i.e. with only lateral sporangia), which were considered to have indeterminate growth, with fertile branches generally circinate (initially curled up). Species assignable to the Gosslingiales made up about 9% of all confirmed species in the Early Devonian flora. Taxonomy Classification Hao and Xue consider the order Gosslingiales to be one of the two major divisions of the zost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sawdoniaceae
Sawdoniaceae is a family of extinct zosterophylls. The zosterophylls were among the first vascular plants in the fossil record, and are considered to share an ancestor with the living lycophytes. The family is recognized by some sources, and placed in the Sawdoniales The Sawdoniales are an order or plesion of extinct zosterophylls. The zosterophylls were among the first vascular plants in the fossil record, and share an ancestor with the living lycophytes. The group has been divided up in various ways. In t .... Other sources do not recognize the family, and place some of its members in the family Gosslingiaceae. Genera Genera that have been placed in this family by Kenrick and Crane in 1997 are shown in the table below, along with their treatment by Hao and Xue in 2013. References Zosterophylls Prehistoric plant families {{paleobotany-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
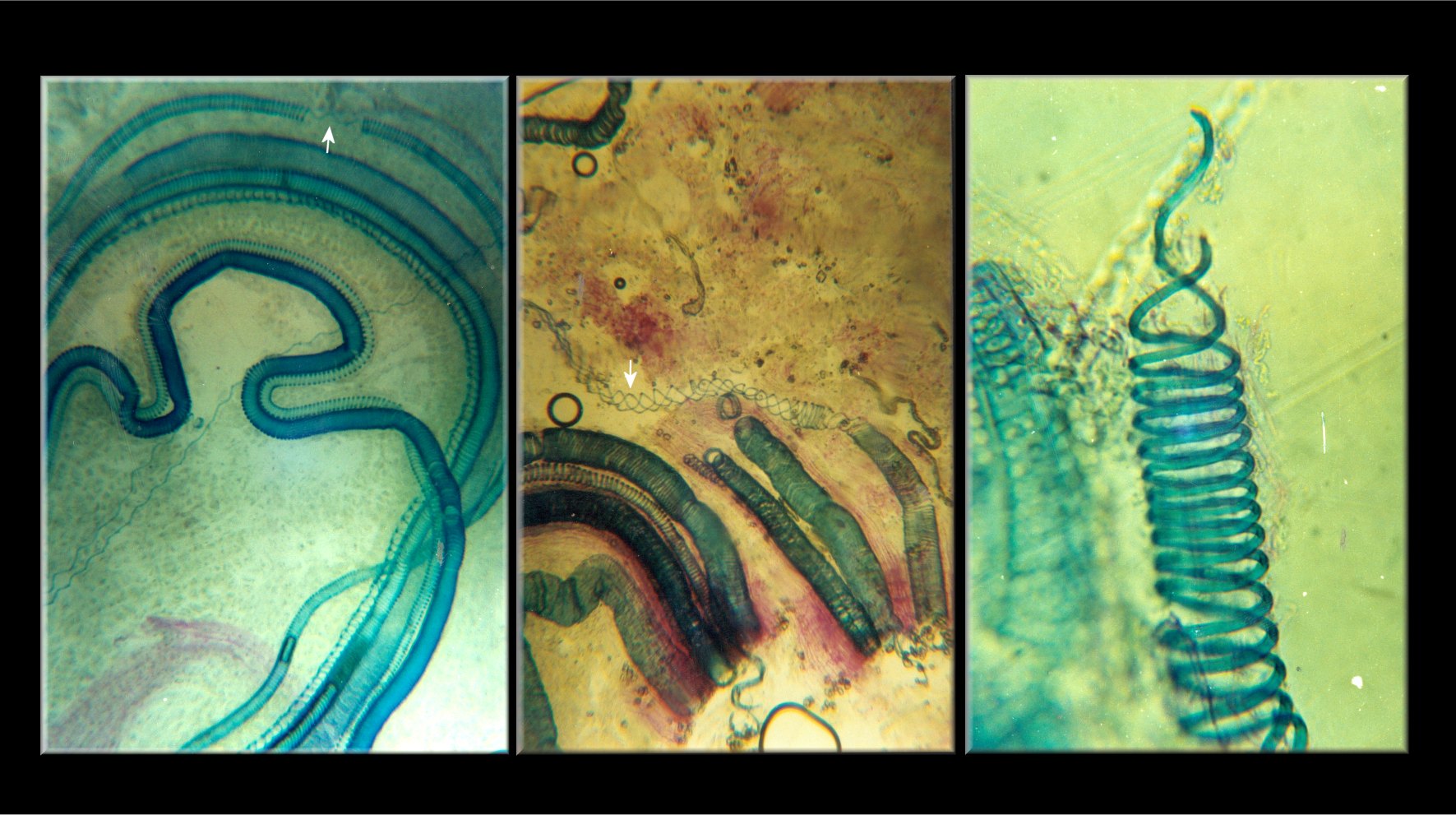
Gosslingia
''Gosslingia'' was a genus of Early Devonian land plant with branching axes. Fossils have been from the Lochkovian to the Pragian, . A cladogram published in 2004 by Crane et al. places ''Gosslingia'' in the core of a paraphyletic stem group of broadly defined "zosterophylls", basal to the lycopsids (living and extinct clubmosses and relatives). Hao and Xue in 2013 used the absence of terminal sporangia to place the genus in the family Gosslingiaceae in the paraphyletic order Gosslingiales, a group considered to have indeterminate growth, with fertile branches generally showing circinate vernation (initially curled up). Kenrick and Crane in 1997 also placed the genus in the family Gosslingiaceae, but they place this family in the order Sawdoniales The Sawdoniales are an order or plesion of extinct zosterophylls. The zosterophylls were among the first vascular plants in the fossil record, and share an ancestor with the living lycophytes. The group has been divided up in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sawdoniales
The Sawdoniales are an order or plesion of extinct zosterophylls. The zosterophylls were among the first vascular plants in the fossil record, and share an ancestor with the living lycophytes. The group has been divided up in various ways. In their major cladistic study of early land plants, Kenrick and Crane placed most of the zosterophylls in the Sawdoniales (which they treated as a plesion). Like other zosterophylls, members of the Sawdoniales bore lateral, reniform sporangia. They branched dichotomously, and grew at the ends by unrolling (circinate vernation). Some had smooth stems, others were covered in small spines; fungal bodies have been reported in some spines. Taxonomy In 1997, Kenrick and Crane placed most of the zosterophylls in the plesion Sawdoniales, characterizing the group as having "marked bilateral symmetry". Their summary cladogram did not resolve the taxa within the Sawdoniales, other than placing '' Zosterophyllum divaricatum'' within the zosterophylls bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crenaticaulis
''Crenaticaulis'' was an early genus of slender, dichotomously branching, leafless land plants, known from the Devonian period and first described in 1969. They were probably allied to the zosterophylls, and are assigned to subdivision Zosterophyllophytina, or class Zosterophyllopsida. They bore branches and scalariform tracheids. A cladogram published in 2004 by Crane et al. places ''Crenaticaulis'' in the core of a paraphyletic stem group of broadly defined "zosterophylls", basal to the lycopsids (living and extinct clubmosses and relatives). Hao and Xue in 2013 used the absence of terminal sporangia to place the genus in the family Gosslingiaceae in the paraphyletic order Gosslingiales, a group considered to have indeterminate growth, with fertile branches generally showing circinate vernation (initially curled up). Kenrick and Crane in 1997 placed the genus in the family Sawdoniaceae in the order Sawdoniales The Sawdoniales are an order or plesion of extinct zosterophyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oricilla
''Oricilla'' was a genus of Early Devonian land plant with branching axes. Fossils have been found from the Pragian to the Emsian (). A cladogram published in 2004 by Crane et al. places ''Oricilla'' in the core of a paraphyletic stem group of broadly defined "zosterophylls", basal to the lycopsids (living and extinct clubmosses and relatives). Hao and Xue in 2013 used the absence of terminal sporangia to place the genus in the paraphyletic order Gosslingiales, a group of zosterophylls considered to have indeterminate growth, with fertile branches generally showing circinate vernation (initially curled up). Kenrick and Crane in 1997 also placed the genus in the family Gosslingiaceae, but they place this family in the order Sawdoniales The Sawdoniales are an order or plesion of extinct zosterophylls. The zosterophylls were among the first vascular plants in the fossil record, and share an ancestor with the living lycophytes. The group has been divided up in various ways. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sawdonia
Sawdonia is an extinct genus of early vascular plants, known from the Upper Silurian to the Lower Carboniferous (). ''Sawdonia'' is best recognized by the large number of spikes (enations) covering the plant. These are vascular plants that do not have vascular systems in their enations. The first species of this genus (''Sawdonia ornata'') was described in 1859 by Sir J. William Dawson and, was originally attributed to the genus '' Psilophyton''. He named this plant ''Psilophyton princeps''. In 1971 Francis Hueber proposed a new genus for this species due to its "Divergent technical characters from the generic description for ''Psilophyton''." The holotype used for description is Dawson Collection Number 48, pro parte, Museum Specimen Number 3243. (See Dawson 1871, Plate IX, fig 101.) Sir J. William Dawson Collection, Peter Redpath Museum, McGill University, Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Morphology These plants are described by Hueber as having monopodially branched stems, that ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genera
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus '' Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should clearly demons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zosterophyll
The zosterophylls are a group of extinct land plants that first appeared in the Silurian period. The taxon was first established by Banks in 1968 as the subdivision Zosterophyllophytina; they have since also been treated as the division Zosterophyllophyta or Zosterophyta and the class or plesion Zosterophyllopsida or Zosteropsida. They were among the first vascular plants in the fossil record, and had a world-wide distribution. They were probably stem-group lycophytes, forming a sister group to the ancestors of the living lycophytes. By the late Silurian (late Ludlovian, about ) a diverse assemblage of species existed, examples of which have been found fossilised in what is now Bathurst Island in Arctic Canada. Morphology The stems of zosterophylls were either smooth or covered with small spines known as enations, branched dichotomously, and grew at the ends by unrolling, a process known as circinate vernation. The stems had a central vascular column in which the protoxylem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Plant
Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes () or collectively Tracheophyta (), form a large group of land plants ( accepted known species) that have lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They also have a specialized non-lignified tissue (the phloem) to conduct products of photosynthesis. Vascular plants include the clubmosses, horsetails, ferns, gymnosperms (including conifers), and angiosperms (flowering plants). Scientific names for the group include Tracheophyta, Tracheobionta and Equisetopsida ''sensu lato''. Some early land plants (the rhyniophytes) had less developed vascular tissue; the term eutracheophyte has been used for all other vascular plants, including all living ones. Historically, vascular plants were known as "higher plants", as it was believed that they were further evolved than other plants due to being more complex organisms. However, this is an antiquated remnant of the obsolete scala naturae, and the term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lycopodiopsida
Lycopodiopsida is a class of vascular plants known as lycopods, lycophytes or other terms including the component lyco-. Members of the class are also called clubmosses, firmosses, spikemosses and quillworts. They have dichotomously branching stems bearing simple leaves called microphylls and reproduce by means of spores borne in sporangia on the sides of the stems at the bases of the leaves. Although living species are small, during the Carboniferous, extinct tree-like forms formed huge forests that dominated the landscape and contributed to coal deposits. The nomenclature and classification of plants with microphylls varies substantially among authors. A consensus classification for extant (living) species was produced in 2016 by the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group (PPG I), which places them all in the class Lycopodiopsida, which includes the classes Isoetopsida and Selaginellopsida used in other systems. (See Table 2.) Alternative classification systems have used ranks fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |